Case 3 + 4: Alexandria Vardalos + Ms. LW
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Hb: Types
HbA
HbA2
HbF
HbS
HbA
Adult Hb
Subunits: α2β2
2 alpha chains
2 beta chains
Contain heme groups
O2 Binding Affinity: High
4 O2 molecules
Major HbA variant
96-98% of total Hb
HbA2
Adult Hb2
Subunits: α2δ2
2 alpha chains
2 delta chains
O2 Binding Affinity: Higher than HbA
Minor HbA variant (2-3%)
HbF
Fetal Hb
Subunits: α2γ2
2 alpha chains
2 gamma chains
O2 Binding Affinity: Higher than HbA
HbS
Sickle Hb
Cause sickle cell disease
Subunits: αA2βS2
2 normal alpha chains
2 abnormal beta subunits
O2 Binding Affinity: Lower than HbA
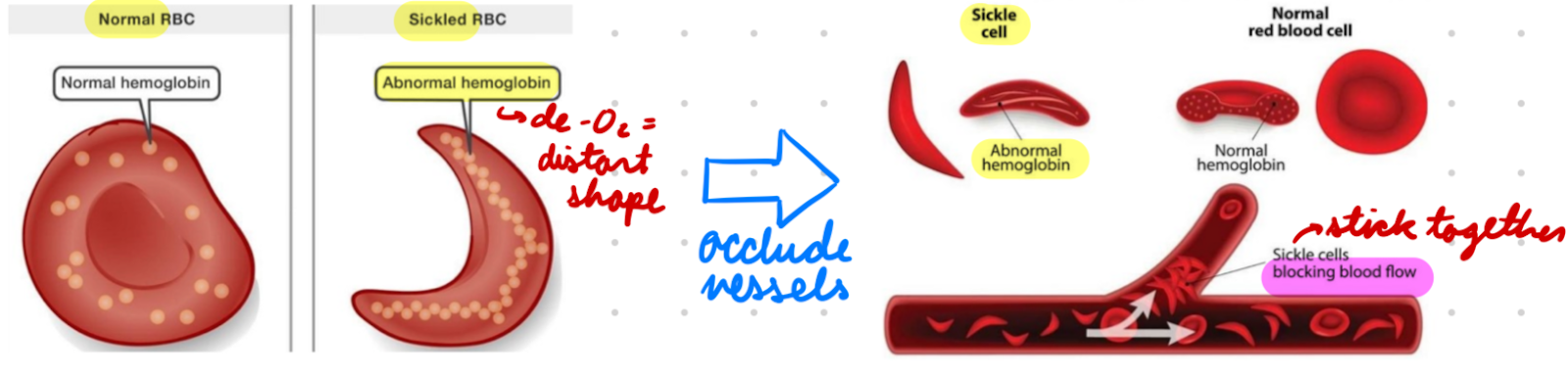
De-O2 form = Sickled rod shape = RBC distortion = RBC stick together
Occlude blood vessels
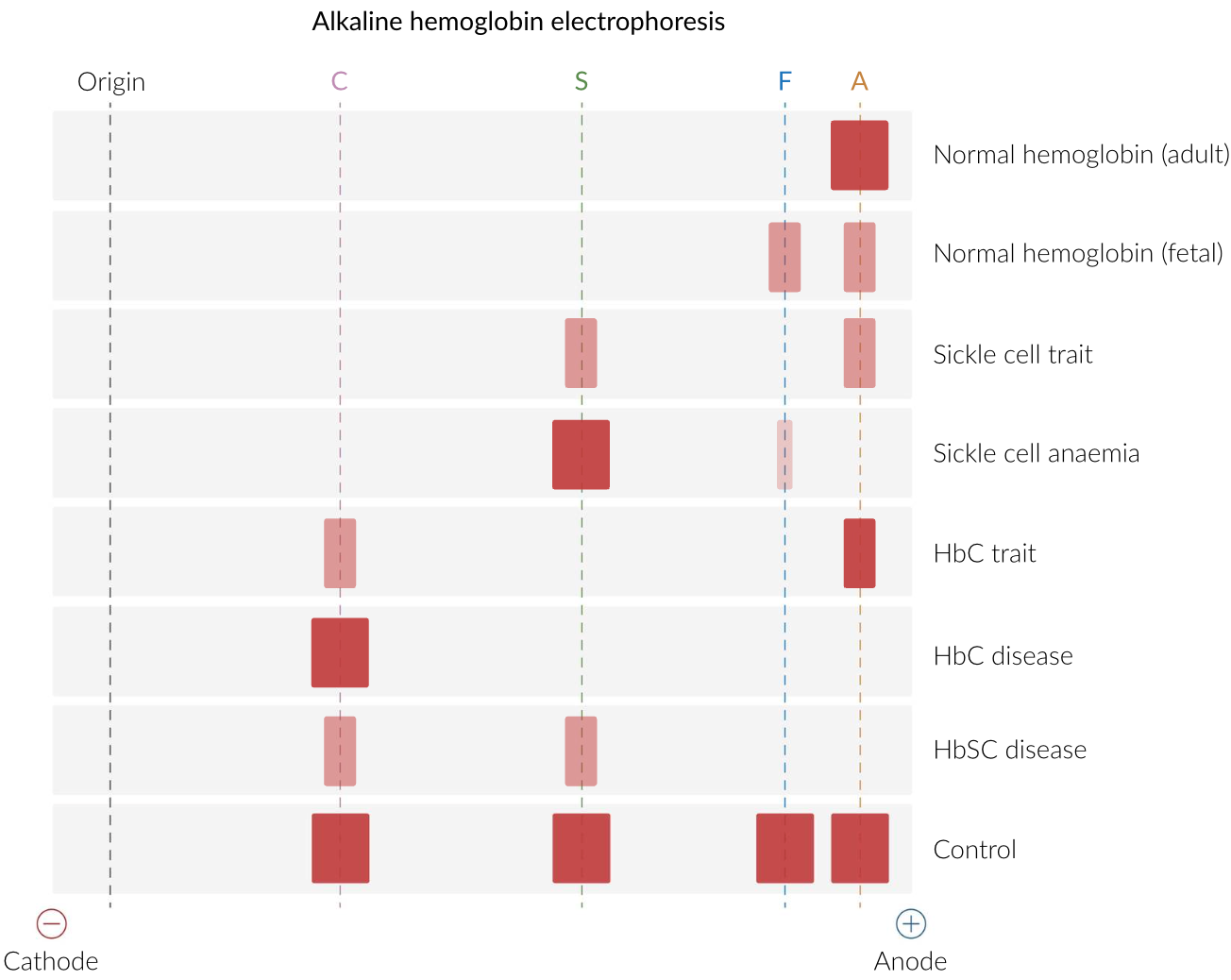
Hb Electrophoresis
Quantify Hb types in blood using electrical current to separate (by charge)
Diagnose sickle cell anemia and thalassemia
Hb Electrophoresis: Procedure
Hemolyze blood sample
Add sample to gel electrophoresis buffer + apply electric field
Hb types separate by charge
Neg Hb → Anode
Stain gel to visualize
Greatest → Least Migration: HbA > HbF > HbS > HbA2 and Hb C
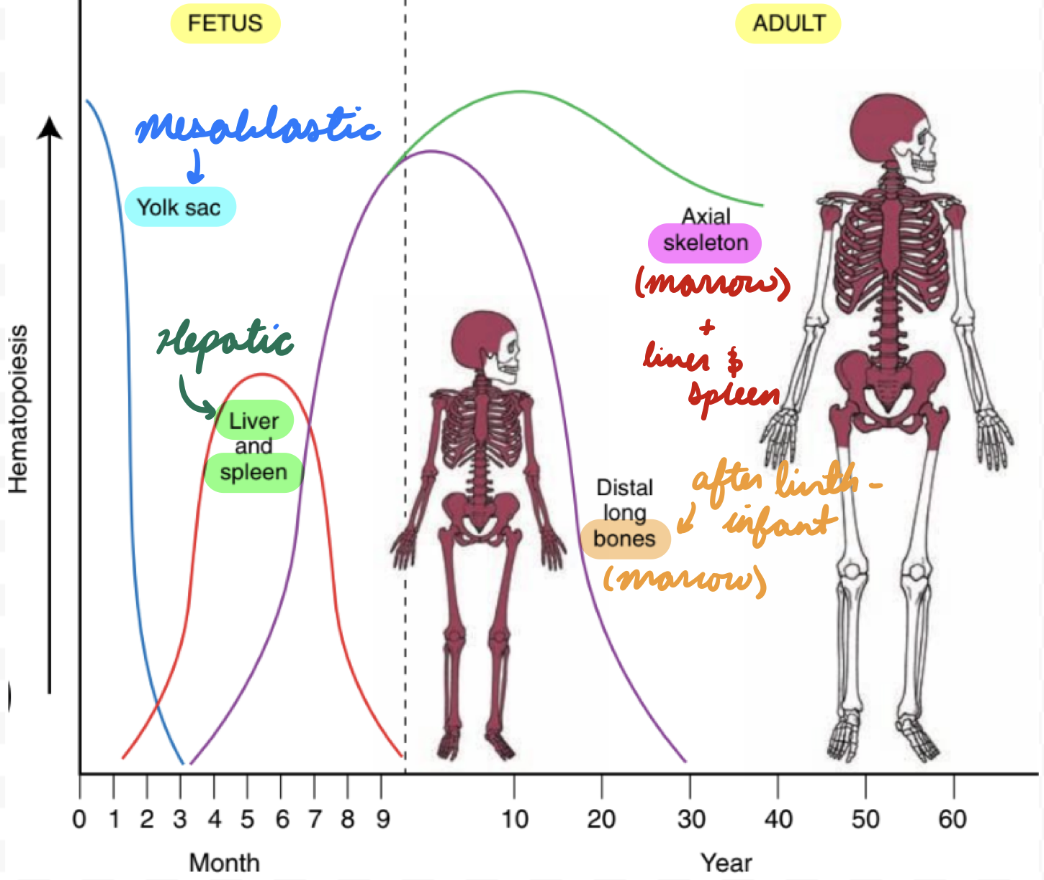
Erythropoiesis: Fetus
Mesoblastic Period: 2 weeks - 2 months
Yolk Sac: Produce embryonic Hb
No survival into adult life
No O2 delivery
Hepatic Period: 2-7 months
Liver: Produce HbF and RBC
Spleen, Thymus, Lymph Nodes: Produce RBC and lymphocytes
Before Birth: 7-9 months
Bone Marrow: Produce RBC, HbF, HbA
Erythropoiesis: Adult
After Birth: < 6 months
Bone Marrow:
Decrease HbF production (decrease gamma chains)
Increase HbA production (increase beta chains)
Infant: 6+ months
Bone Marrow: HbA > HbA2 > HbF
Adult:
Intramedullary Hematopoiesis: Bone marrow (most)
Extramedullary Hematopoiesis: Outside bone marrow
Liver and spleen = Hepatosplenomegaly
When needed: Bone marrow infiltration, tumour
Hb Destruction
RBC circulate for 120 days
Biochemical and structural changes = Mark for clearance
RBCs phagocytosed by macrophages
In Cells: Liver, spleen, bone marrow
In Spleen: Filtration (older RBC undergo hemolysis, healthy RBC survive)
Hb degraded in macrophages
Breakdown globin chains → Amino acids
Breakdown heme moiety → Fe, biliverdin, CO
Fe bind transferrin → Transport to…
Bone Marrow: Produce new RBCs
Liver: Storage as ferritin
Biliverdin converted to bilirubin (yellow pigment)
Converted to bile in liver → Excreted into intestines → Colour stool brown
CO exhaled from lungs
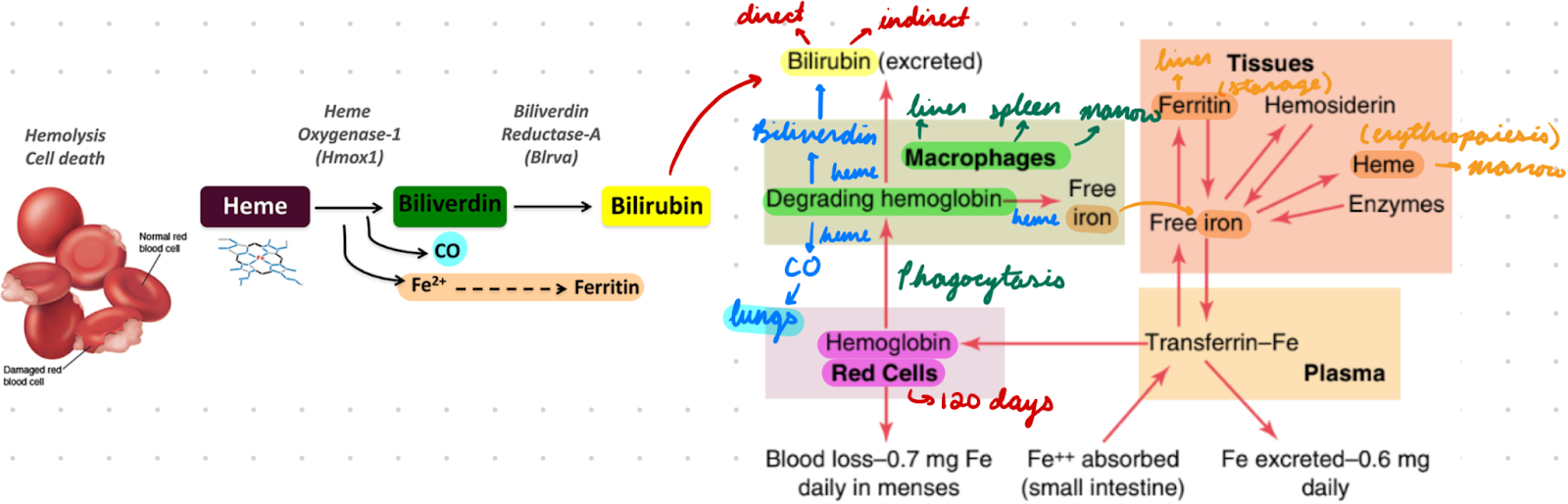
Bilirubin: Types
Direct: Measured conjugated bilirubin
Water-soluble
Increased = Hepatic dysfunction
Indirect: Unmeasured unconjugated bilirubin
Lipid-soluble
Increased = RBC breakdown/improper degradation
Calculated from total bilirubin
Total: Measured
Direct + indirect bilirubin
Jaundice: High bilirubin in blood
O2-Hb Dissociation Curve
O2 binding to Hb as function of PO2
Sigmoidal Shape: Positive cooperativity
O2 binding increases affinity of heme to bind additional O2
P50: PO2 of 50% Hb saturation
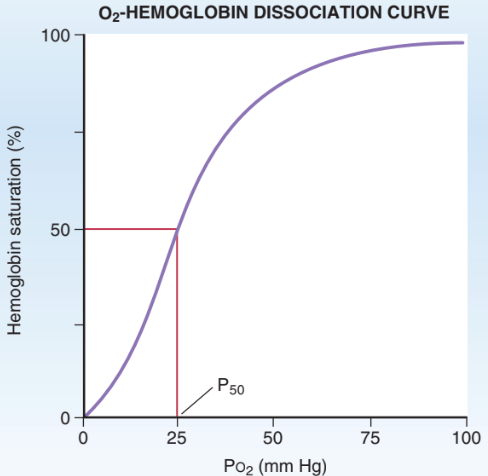
O2-Hb Dissociation Curve: In Lungs
PaO2 = 100 mmHg
100% saturation
High Hb affinity for O2
Tight binding to maximize O2 loading
Can tolerate O2 drops until 60 mmHg
O2-Hb Dissociation Curve: In Tissues
PVO2 = 40 mmHg
75 % saturation
Decreased Hb affinity for O2
Loose binding to increase O2 unloading
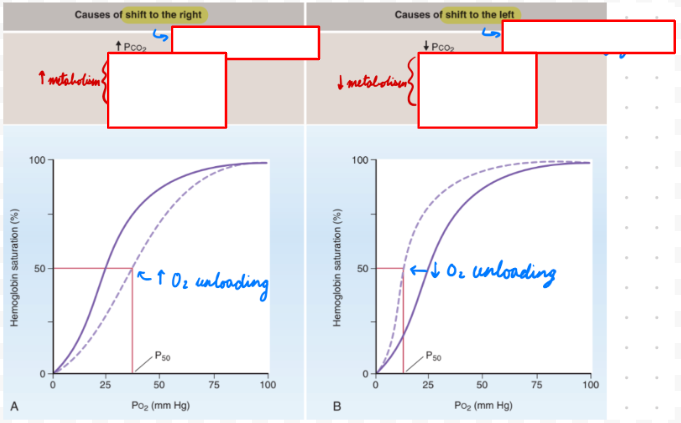
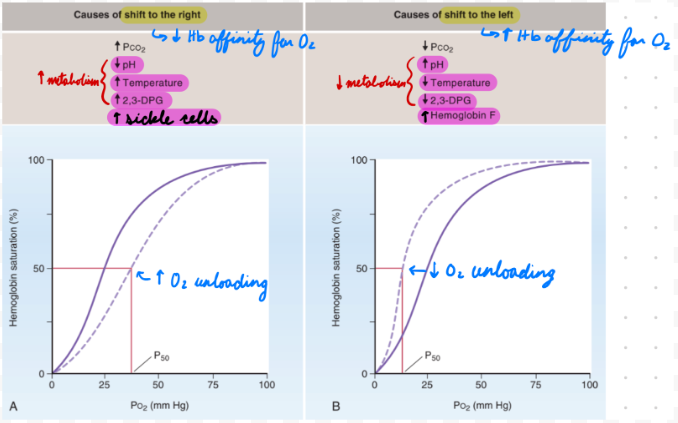
O2-Hb Dissociation Curve: Right Shift
Decreased Hb affinity for O2 = Increased unloading
Decrease pH
Increase temp
Increase 2,3-biphosphoglycerate (BPG)
Sickle cell anemia
Right Shift: Decrease pH
Increase metabolic activity = Increase CO2 = Decrease pH
Increase O2 unloading to tissues = Match O2 demand
Right Shift: Increase Temp
Increase metabolic activity = Increase heat
Increase O2 unloading to tissues = Match O2 demand
Right Shift: Increase 2,3-BPG
RBC glycolysis byproduct
Increase during hypoxemia
Bind beta chains = Decrease affinity for O2
Right Shift: Sickle Cell Anemia
Increased 2,3-BPG binding + Sickled Hb chains = Decrease affinity for O2
O2-Hb Dissociation Curve: Left Shift
Increased Hb affinity for O2 = Decreased unloading
Increase pH
Decrease temp
Decrease 2,3-BPG
HbF
Left Shift: Increase pH
Decrease metabolic activity = Decrease CO2 = Increase pH
Low O2 demand = Decrease O2 unloading to tissues
Left Shift: Decrease Temp
Decrease metabolic activity = Decrease heat
Low O2 demand = Decrease O2 unloading to tissues
Left Shift: HbF
Decreased 2,3-BPG binding to gamma chains = Increase affinity for O2
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
Require 2 copies of nonsex alleles to express phenotype
Usually more severe than autosomal dominant conditions
Autosomal Recessive Pedigree
1 Homozygous Parent: 0% expressed, 100% carriers
1 Heterozygous + 1 Homozygous Parent: 50% expressed, 50% carriers
Heterozygous Parents: 25% expressed, 50% carriers, 25% unaffected
Thalassemia: Description
Hereditary Hb disorder from:
Alpha: Alpha-chain mutations
Beta: Beta-chain mutations
Thalassemia: Epidemiology
Alpha: Common in Asia and Africa
Beta: Common in Mediterranean descent
Partial resistance to malaria
Thalassemia: Etiology
Autosomal recessive gene mutations
Alpha Thalassemia: Etiology
Deletion of alleles in alpha-globin gene on chromosome 16
Severity depend on number of defective alleles
Silent Carrier: 1 defective allele
Alpha-Thalassemia Trait: 2 defective alleles
Hb H Disease: 3 defective alleles
Increase HbH production (unstable beta chain = Aggregate in RBC)
Hb Bart’s Disease: 4 defective alleles
Increase Hb Bart production (4 gamma chains)
Beta Thalassemia: Etiology
Point mutation in beta-globin locus on chromosome 11
Minor: 1 defective allele
Major (Cooley Anemia): 2 defective alleles
Thalassemia: Pathophysiology
Anemia from:
Decreased erythropoiesis
Increased hemolysis
Thalassemia Pathophysiology: Decreased Erythropoiesis
Beta:
Decreased beta chain synthesis = Increase gamma/delta chains = Increase HbF (infant) → HbA2 (adult)
Low HbA and high HbA2 = Decreased erythropoiesis
Alpha:
Decreased alpha chain synthesis = Low alpha chain pairing with beta/gamma chains = Increase free beta/gamma chains = Increase HbH and Hb Bart
Low HbA = Decreased erythropoiesis
Thalassemia Pathophysiology: Increased Hemolysis
Low alpha/beta chains = Compensatory overproduction of other chains = Precipitation form inclusions in RBCs = Hemolysis
Alpha Thalassemia: Clinical Presentation
Silent Carrier: No anemia
Alpha-Thalassemia Trait: No/mild anemia
Hb H Disease:
Jaundice
Anemia (chronic hemolytic)
Hepatosplenomegaly
Hb Bart’s Disease: Incompatible with life
Intrauterine ascites
Edema
Hepatosplenomegaly
Cardiac + skeletal anomalies
Beta Thalassemia: Clinical Presentation
Minor: No/mild anemia
Intermedia:
Variable anemia
Jaundice
Major:
Severe hemolytic anemia
Hepatosplenomegaly
Growth retardation
Skeletal deformities
Thalassemia: Investigations
CBC
Hemolysis evaluation
PBS
Hb electrophoresis
*Genetic studies
Thalassemia: CBC
Microcytic hypochromic anemia
**Normal RDW
*High RBC
Mentzer Index: MCV/RBC ratio
Thalassemia: < 13
IDA: > 13
Thalassemia: Hemolysis Evaluation
Low haptoglobin
Plasma glycoprotein binding free Hb for clearance
High lactate dehydrogenase
High reticulocytes
Hyperbilirubinemia
Normal Fe studies
Thalassemia: PBS
*Target cells
Dacrocytes (teardrop cells)
*Anisocytosis (diff/abnormal RBC sizes) and poikilocytosis (diff/abnormal RBC shapes)
**Inclusion bodies
**Erythroblasts
Thalassemia: Hb Electrophoresis
Beta:
Increased HbA2 and HbF
Less HbA
Alpha:
Normal
HbH/Hb Bart’s
Thalassemia: Genetic Studies
Determine diagnosis and mutations
Thalassemia: Treatment/Management
General:
Patient education
Genetic counseling
Screening for relatives
Minor:
No treatment
*Folic acid supplements
Major/Intermedia:
Transfusion
Hb < 7 g/dL
Target: Hb > 9-10 g/dL
***Splenectomy
Allogenic HSC transplant
Stem cells from genetically similar donor
Gene therapy
Thalassemia: Complications
Fe overload
Hypercoagulopathy
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD): Description
Genetic disorders causing HbS production
HbS polymerization
Vasoocclusion
Hemolytic anemia
SCD: Epidemiology
Most common in African and Eastern Mediterranean descent
SCD: Etiology
Autosomal recessive point mutations in beta-globin gene on chromosome 11
Glutamic Acid → Valine: HbS
Heterozygotes (HbAS): 1 normal allele + 1 sickle allele → Sickle cell trait (carrier)
Homozygotes (HbSS): 2 sickle alleles → Sickle cell anemia
Glutamic Acid → Lysine: HbC
Heterozygotes
HbSC: 1 HbS allele + 1 HbC allele → HbSC disease
More severe than sickle cell trait
Less severe than SCD
HbAC: 1 normal allele + 1 HbC allele → HbC trait (carrier)
Homozygotes (HbCC): 2 HbC alleles → HbC disease
SCD: Pathophysiology
Deoxygenated HbS = Polymerization = Sickled RBCs
Deoxygenation from low O2 tension:
Infections
Dehydration
Acidosis
Stress
Sickle cells = Low elasticity + Adhere to vascular endothelium = Occlude blood vessels = Tissue infarction
Increased RBC hemolysis = Anemia
Increase HbF production to compensate
SCD: Clinical Presentation
Sickle cell trait
Asymptomatic
Hematuria (papillary necrosis)
Nocturia
Renal medullary carcinoma
SCD: Start after 3-6 months from decreasing HbF and increasing HbS
Vascular occlusion
Dactylitis (fingers/toes inflammation)
Severe pain
Increased infections
Acute hemolytic crisis
Splenic sequestration: Splenic vasoocclusion (blood trapping) cause pain and hypotension
Aplastic crisis: Mass hemolytic anemia
Chronic hemolytic anemia
Pigmented kidney stones
SCD: Investigations
Neonatal screening
Confirmatory studies: < 2 months
Hb electrophoresis
High performance liquid chromatography
Capillary electrophoresis
CBC
PBS
SCD: Neonatal Screening
Positive and inconclusive results → Confirmatory studies
SCD: Hb Electrophoresis
HbS and HbC findings
SCD: High Performance Liquid Chromatography
Low HbA
High HbS
High HbF
SCD: CBC
Anemia with reticulocytes
Increased neutrophils and platelets
SCD: PBS
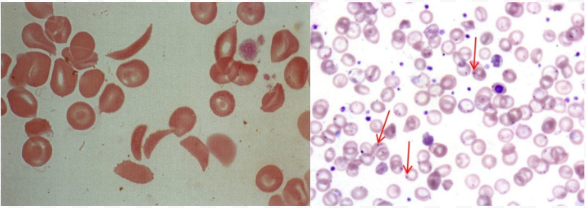
Crescent-shaped sickle RBCs
Howel-Jolly Bodies: Basophilic DNA remnants in immature RBCs
Indicate splenic dysfunction
SCD: Treatment/Management
Vaccines
Prophylactic penicillin
Hydroxyurea therapy
RBC transfusion
Allogenic HSC transplant
SCD Management: Vaccines
Prevent infections
SCD Management: Prophylactic Penicillin
Children < 5 years
Prevent pneumococcal infection
SCD Management: Hydroxyurea Therapy
Antineoplastic drug prevent cell proliferation
Increase erythropoiesis + HbF levels = Decrease HbS and sickle cell crises
SCD Management: RBC Transfusion
Simple Transfusion: Dilute patient blood with donor erythrocytes
Preferred to manage acute anemia
Exchange Transfusion: Remove patient blood and replace with donor erythrocytes
Preferred to prevent vasoocclusive events
Indications: Acute complications
Risks:
Simple:
Increase Hct levels = Increase viscosity = Increase vasoosclusive event risk
Fe overload
Exchange: Increase alloimmunization (immune response against foreign antigens) risk
SCD Management: Allogenic HSC Transplant
Indications:
Sickle cell anemia (HBSS)
Increased complications
SCD: Complications
Recurring vascular occlusion = Infarction = Organ damage + function loss
Homozygotes: High morbidity and mortality
Heterozygotes: Rare
*Hematuria from papillary necrosis
Stroke
**Decreased phagocytosis in spleen = Infection risk