lecture 3: Papillomaviridae Polyomaviridae
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
latency
Virus remains dormant in the host cell, not producing viral particles but can reactivate later (example: herpes cold sores)
episome
a genetic element that can replicate independently of the host chromosome or integrate into it
Episomal Latency
Viral genome stays as an episome (not integrated), circular / linear / lariat, transcriptionally silent (repressed)
NOT integrated, dormant DNA
Episomal Latency viruses
Used by papillomaviruses, polyomaviruses, herpesviruses
Proviral Latency
DNA integrates directly into the host cell genome (HIV)
Papillomavirus
infects mammals and birds, was discovered from filtered wart material and is transmitted by skin to skin
warts
benign epidermal tumors
HPV (Human Papilloma Virus)
Most common viral STI that causes warts and some strains cause cancer
HPV prevention
vaccine available that prevents infection and cancer
Common warts
hands, feet, elbows; cauliflower-like; non-cancerous
Plantar warts
soles; grow inward → painful; black dots = clotted vessels
Subungual
under fingernail; hard to treat
Periungual
under cuticle; hard to treat
Flat warts
face, arms; common in kids/teens; non-cancerous
Oral lesions & genital warts
caused by specific HPV strains
HPV virion structure
Non-enveloped, icosahedral capsid, circular dsDNA genome that carries NO viral proteins (VERY unusual).
No polymerase, no integrase—just DNA
HPV capsid
L1 protein alone will self-assemble into empty capsids of this form – this is the basis for the HPV vaccines
HPV genome
small, contains L1/L2 capsid proteins, E1/E2 for replication and transcription factors, and E6/E7 is oncogenic
oncogenic
can cause cancer by disrupting host cell regulation, leading to uncontrolled growth
HPV E6/E7
involved in immortalization & escape from cell cycle arrest & apoptosis….. CANCER
blocks p53 and blocks Rb
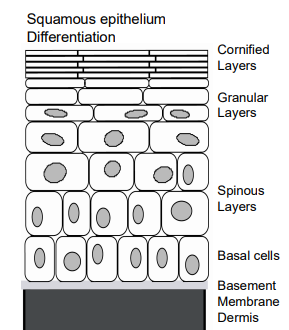
epidermis
consists of layers with cornified, granular, spinous, and then basal layer
HPV infects only
the cells of the basal cells by breaking through the skin to reach basal layer
HPV Life Cycle
Early genes: E1, E2, E6, E7 expressed first
Late genes: genome amplification + capsid proteins
Virions released when superficial layers shed
Integration of cancer
HPV DNA integrates and only E6 & E7 overexpressed; all other viral genes shut down.
p53 and Rb (retinoblastoma protein)
master gene regulators that prevent cancer transcription factors by controlling cell cycle, DNA repair, apoptosis, its essential for preventing uncontrolled growth
Cancer cells:
Dysregulation, uncontrolled division, abnormal nuclei, loss of boundaries, and loss of contact inhibition
How HPV Causes Cancer: E6
p53 stops cell cycle, repairs DNA or triggers apoptosis but this viral protein sends p53 proteasome degradation which allows cells with DNA damage to survive causing cancer
How HPV Causes Cancer E7
targets Rb for degradation causing uncontrolled proliferation and Rb blocks excessive cell cycle progression
Low Grade Lesions
Episomal HPV DNA and E6/E7 expression regulated
High Grade Lesions
Integrated DNA and high E6/E7 expression across layers
HPV Vaccines
prevents infection and cancer using L1 proteins self assembly
no antiviral drugs
antiviral treatment
none b/c only one viralenzyme
HPV types of cancers
Vaginal, anal, cervical, vulvar, penile, oropharyngeal cancers
pap smear used
Polyomaviruses: JC, BK
Not epidermal, life cycle is not linked to differentiation, cell tropism varies, and disease outcome varies
Polyomavirus Structure
small non-enveloped, icosahedral capsid, and circular dsDNA (supercoiled)
JC and BK spread on body (not immunodeficient)
1.Enter respiratory tract
2.Replicate
3.Primary viremia
4.Spread to kidney
5.Secondary viremia
6.Latency in kidney (if immunocompetent)
BK immunodeficient
urinary tract (kidney/bladder) → hemorrhagic cystitis
viruria, cystitis
JC immunodeficient
central nervous system → progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)
fatal; demyelinating disease
John Cunningham virus (JC)
human polyomavirus, effects 70-90% of people, and infected tonsils or tubular epithelium of kidneys
-crosses blood brain barrier
JC replication cycle
after viremia it crosses the BBB where it infects oligodendrocytes/astrocytes which causes PML, it enters via clathrin-mediated endocytosis and released by lysis (non-enveloped)
JC pathogenesis
latent in kidney/bone marrow, transported to brain inside B cells which causes demyelination, weakness, and poor coordination
BK virus
discovered in renal transplant patients, most infection occur in childhood, mild or asymptomatic, persist in kidney cells for life
BK replication
infects respiratory tract, then infects blood (viremia), hides in B cells/T cells/ monocytes, uses caveolin independent endocytosis and released by lysis (no integration)
BK disease
reactivation in immunocompromised patients, causes hemorrhagic cystitis, painful urination, incontinence, and a balance b/t immunosuppression is needed (too much is bad, too little is bad)
nephropathy
in transplant patients BK causes
Commensal viruses
are common, inapparent infections that do not usually cause symptoms or disease in the host
virobiota
the vast community of viruses (bacteriophages, eukaryotic viruses, retroviruses, giant viruses) living in and on the human body