Patho Exam 1
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
pathophysiology
study of the disease process
pathogenesis
sequence of cellular and tissue events that take place from the time of initial contact with an etiologic agent until the ultimate expression of a disease - describes how the disease process evolves
etiology
what sets the disease process in motion
risk factors
contributions that increase the chances that a certain disease will occur
types of risk factors
age - alcohol use - drug abuse - ethnicity - smoking - exposure - gender - genetics - isolation - poverty - poor hygiene - sexual practices - inadequate sleep - stress - poor nutrition
what do nurses do
education - motivate - facilitate
disease
interruption, cessation, or disorder of a body system or organ structure - abnormal functioning occurs
illness
the feelings that might come with having a disease - the subjective experience
subclinical/preclinical stage of disease
stage where the disease is present, but the patient is unaware
prodromal stage of disease
vague and non-specific symptoms
clinical stage of disease
disease is evident and identifiable - a diagnosis is clear
sign
objective, measurable
symptom
what the patient is feeling
prognosis
prediction about the outcome of a disease
sequelae
subsequent injuries related to the disease process
complications
new problems in addition to the original disease process
morbidity
number of illnesses per 100,000 people
mortality
number who died per 100,000
incidence
number of new cases
epidemic
rapid increase in incidence noted
passive transport
no energy - diffusion, osmosis, filtration, and facilitated diffusion
active transport
requires energy - includes transport by pumps and vesicles
diffusion
movement of particles from higher concentration to lower concentration
osmosis
diffusion of water down the concentration gradient through a selectively permeable membrane
autosomal dominant
abnormal gene is dominant - only one gene needed to express the trait - no carrier state - heterozygotes have less severe disease than homozygotes - most often signs and symptoms occur at delayed age
rules of inheritance - autosomal dominant
if the disease is present, most likely inherited from at least one parent - spontaneous mutation is rare - if one parent has the disease, 50% chance that each new pregnancy will result in diseased child - males and females equally affected
autosomal dominant inheritance
in a single gene disorder when the defective allele is dominant, it overrides the normally functioning allele and the disorder results - 50% chance of inheriting the defective gene and developing the disorder
marfan syndrom
autosomal dominant - connective tissue disorder with abnormalities in the skeletal, ocular, and cardiovascular systems
familial hypercholesterolemia
autosomal dominant - absent or dysfunctional LDL receptors, so cholesterol manufacture is not suppressed - fatty plaque buildup
autosomal recessive
offspring must inherit two copies of the defective allele before the disease manifests itself - carriers are children who inherit a single copy of the allele - child has a 25% chance of inheriting the defective allele from both parents and developing the disorder
PKU
autosomal recessive - defect in the gene that creates the enzyme PAH that converts phenylalanine to tyrosine, causing a lighter color of hair and skin - infants are routinely screened for PKU at birth
sickle cell disease
autosomal recessive - sickle hemoglobin can form stiff rods within the RBC changing it into a crescent shape - sickle cells are not flexible and can stick to vessel walls, causing blockage that slows or stops blood flow, when this happens, oxygen can't reach nearby tissues
sickle cell anemia
autosomal recessive - mutation causes structural fragility of the sickle cell anemia RBCs, where upon exposure to hypoxia or stress, the RBC contorts into a sickle shape
sickle cell vaso-occlusive crises
sickled RBCs become trapped, blocking blood flow and creating ischemia and consequent tissue hypoxia, which leads to organ damage and possible infarction
cystic fibrosis
autosomal recessive - chloride ions and water are blocked from moving in and out of cells, resulting in thick mucous secretions that block the lungs, pancreas, colon, and genitourinary tract
x-linked diseases
defect is carried on the X chromosome - 50% of males will have disease, 50% of women will be carriers - males cannot be carriers
hemophilia
x-linked - deficiencies of clotting factors cause a failure in producing clots - excessive bruising, hematomas, hemorrhage
multifactorial or polygenic dosorders
cannot predict outcome in offspring - environmental triggers are thought to be necessary for the trait to be expressed - patterns of inheritance are hard to predict, but strong familial tendencies are noted
cleft lip
multifactorial - during development, tissue and cells from each side grow toward the midline and join together - cleft lip occurs when the labial tissue does not join completely before birth, resulting in a cleft
cleft palate
multifactorial - occurs when the tissue that makes up the roof of the mouth does not join together
fetal alcohol syndrome
multifactorial - exposure to excess maternal alcohol consumption while in utero throughout entire pregnancy - retarded physical growth, intellectual disabilities, cardiac defects, and musculoskeletal abnormalities
apoptosis
programmed cell death
failure of apoptosis
can give rise to certain cancers, tumors, and detrimental hyperplasic cell changes
angiogenesis
ability for cancer cells to develop their own blood vessels
carcinogenesis
actual formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells
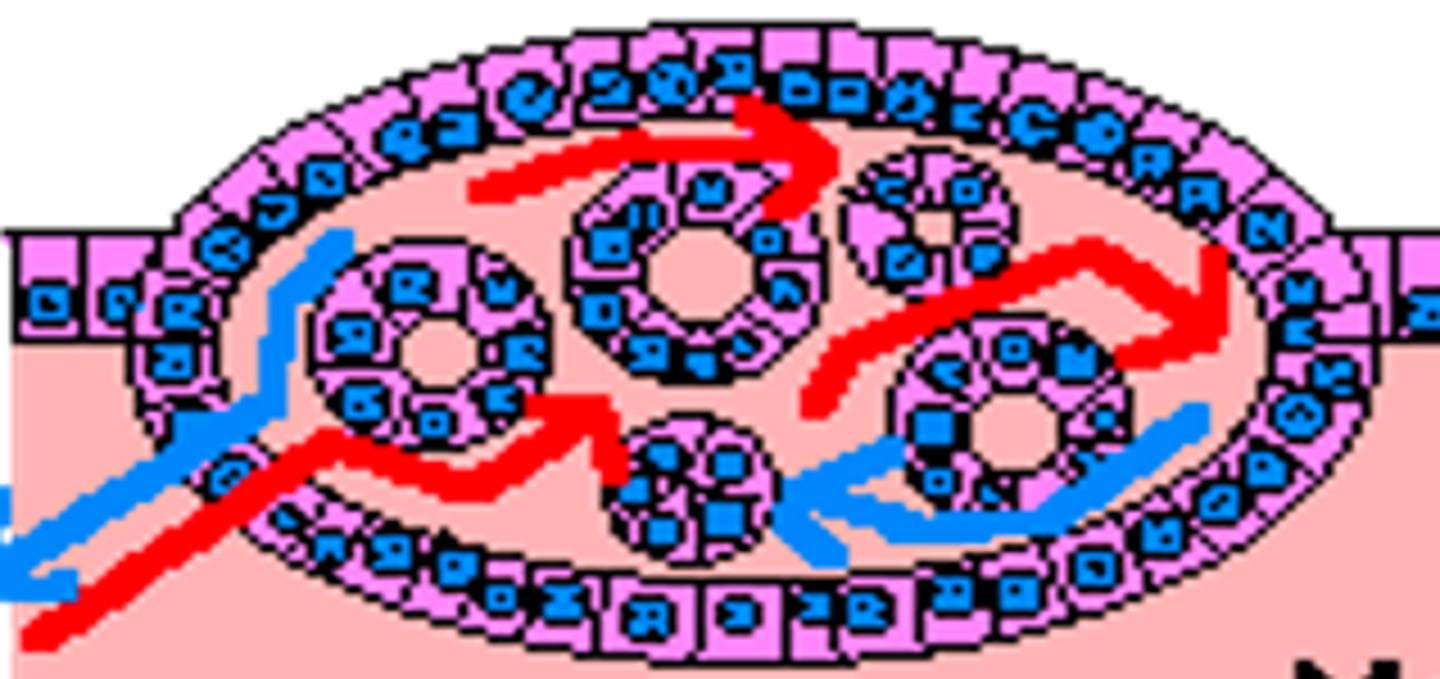
benign tumors
well-differentiated - remain localized - well demarcated from surrounding tissue - non invasive - do not break away or travel from the tumor cell mass
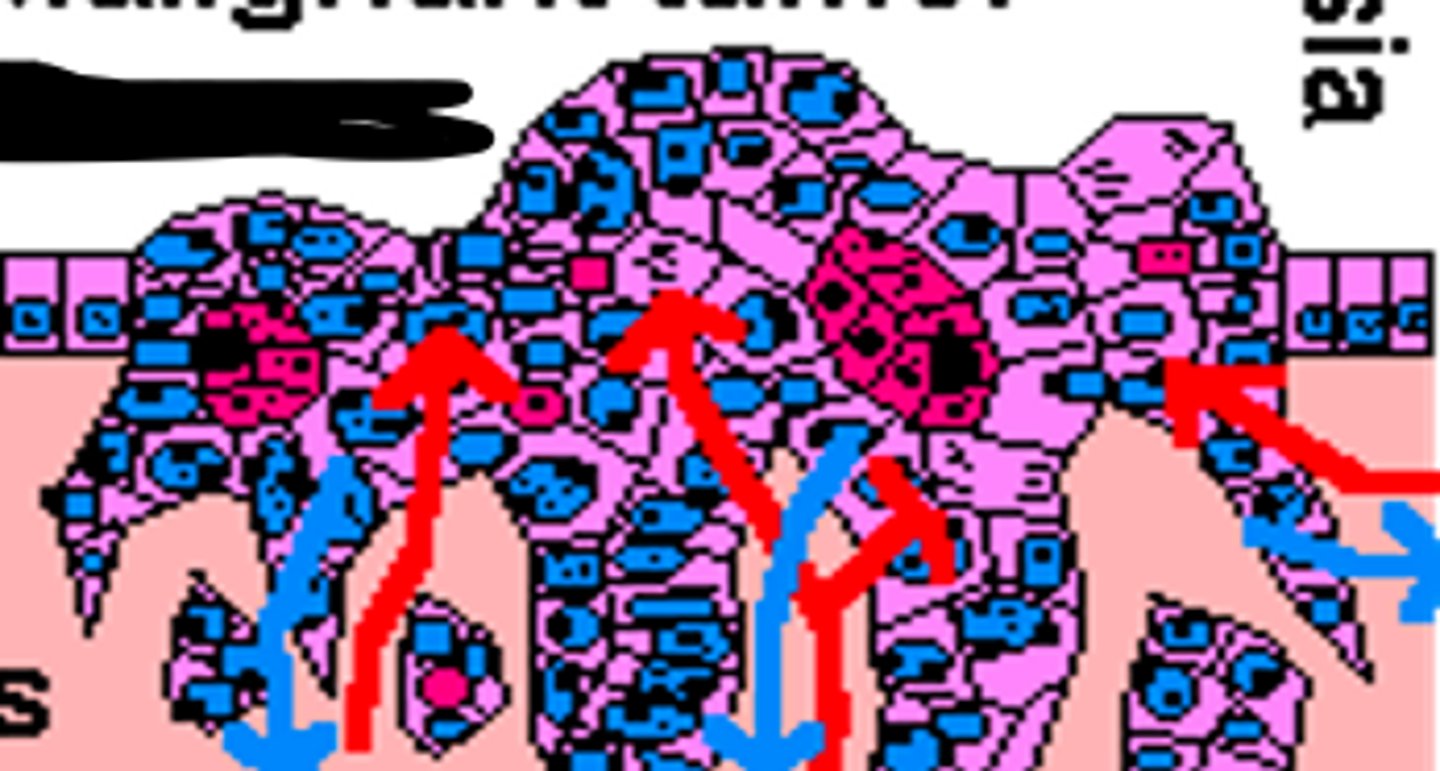
malignant tumors
range from well differentiated to poorly differentiated - invasive and destructive to surrounding tissue - lack adhesion to tumor mass and easily break free to travel to different sites
TNM scale
t is for tumor - n is for lymph node involvement - m is for metastasis to distant organs
atrophy
a decrease or shrinkage in size
hypertrophy
increase in cell size ex) lifting weights increases muscle size
hyperplasia
increase in the number of cells - ex) gingival hyperplasia common in pregnant women
metaplasia
reversible replacement of one type of cell with another type of cell in response to injury - ex) in esophagitis, the cells of the lower esophagus change into stomach cells
dyplasia
abnormal changes in size, shape, and organization of mature cells - may be irreversible - a precancerous condition
neoplasia
new growth - malignant or benign - lack normal cell function - divide uncontrollably - lack adhesiveness to other cells - break away and travel - invasive and destructive to other cells - abnormal structure and architecture - secrete inappropriate enzymes, hormones, clotting substance, tumor angiogenesis factor
anaplasia
poor cellular differentiation - reversion of cells to simpler and less differentiated form - not reversible, genetic damage has occurred to cells
hallmark of malignancy
anaplasia
differentiation
the extent that neoplastic cells resemble normal cells both structurally and functionally
lack of differentiation
anaplasia - total cellular disorganization - abnormal cell appearance - cell dysfunction
chemotherapy
cancer treatment used before surgery to shrink large tumors or after surgery to eradicate leftover cells - destroys all rapidly growing cells without differentiation
radiation
used to shrink solid tumors - localization may help reduce damage to surrounding tissues
reversible cell injury
cell experiences temporary damage that can be repaired and restored to normal function - disruption of function - common causes are edema, hypoxia, failure of Na/K pump
cell death
irreversible cessation of all cellular functions and processes
neurofibromatosis
autosomal dominant - genetic defect in tumor suppressing gene that regulates cell differentiation and growth - "elephant man" syndrome
tay sach's disease
autosomal recessive - infants appear normal until 6 months - generally fatal by 5 - characteristically a cherry red spot on the retina
OSHA
occupational health and safety administration - assure safe and healthful working conditions for working men and women by enforcing standards and providing training, outreach, education, and assistance
cyanosis
bluish coloration of the skin and mucous membranes caused by hypoxia
biopsy
a tissue sample removed for microscopic examination
proto-oncogene
genes that stimulate and regulate a cell's movement through the cell cycle, resulting in cellular growth and proliferation
oncogene
stimulate constant, unrelenting cellular proliferation and cell cycling
hypoxia
deficiency of oxygen
hypoxemia
deficiency of oxygen in blood
ischemia
local reduction of blood flow
infarction
an area of dead tissue to an organ caused by lack of blood flow to the area
necrosis
death of a small area of tissue or part of an organ that is surrounded by healthy tissue
gangrene
death of a large portion of tissue
eschar
blackened, thick layer of necrotic tissue often seen in burns and decubiti
viral induced cancer
mechanisms of action differ, but always involve the activation of growth-promoting pathways or inhibition of tumor suppressors in infected cells - ex) cervical cancer associated with HPV
cachexia of cancer
cancer patients who develop a progressive loss of body fat
tumor cell markers
products of cancer cells such as hormones, enzymes, genes, antigens, or antibodies that are found in blood, spinal fluid, or urine
manifestations of cancer
altered function - obstruction - effusion - hemorrhage - anemia - ulceration - necrosis - infection - vascular thrombosis - pain - cachexia - inappropriate production of hormones - hypercalcemia
early warning signs of cancer
change in bowel or bladder habits - a lesion that doesn't heal - unusual bleeding or discharge - thickening or lump noted - indigestion or difficulty swallowing - obvious changes in wart or mole - nagging cough or persistent hoarseness
dysplasia

healthy

benign tumor
malignant tumor - cancer