iGCSE Edexcel Chemistry Inorganic Part 1
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
why are alkali metals stored under oil?
to prevent reactions with oxygen or water
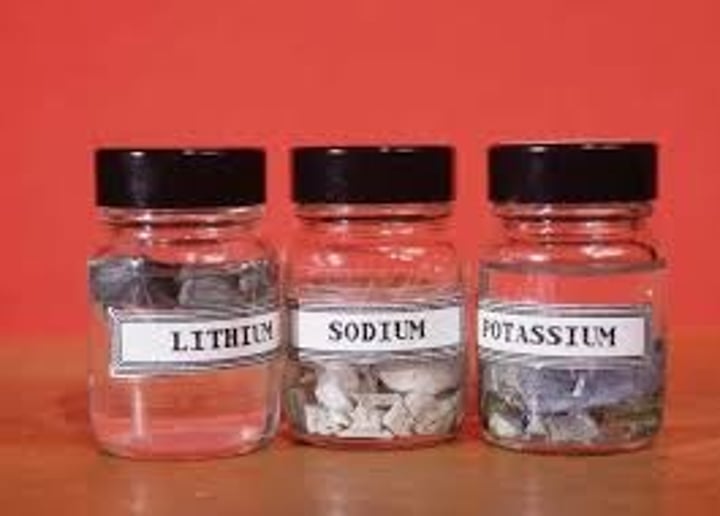

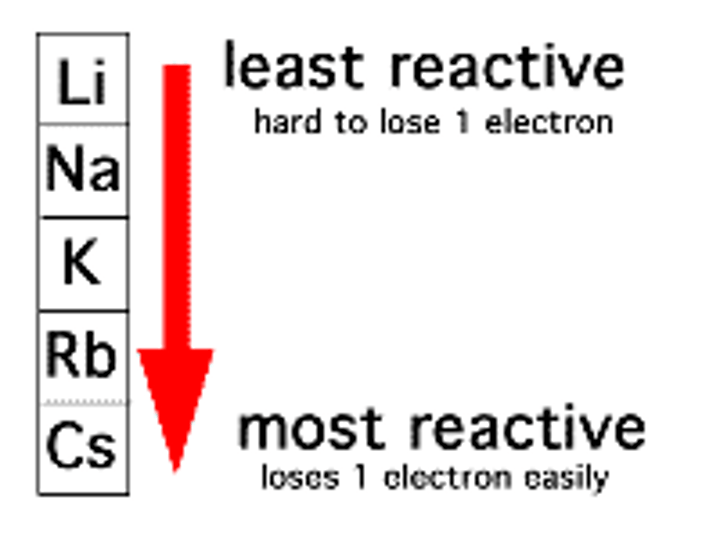
how does reactivity change moving down group 1? why?
it increases as the atoms get larger and the distance between the nucleus and the outer electrons increases and thus the attraction from the nucleus decreases, allowing them to more easily lose electrons
what happens when group 1 metals react with water?
group 1 metal + water ➡️ metal hydroxide + hydrogen
2M(s) + 2H₂O(l) ➡️ 2MOH (aq) + H₂
describe how potassium reacts with water
-reacts more violently than Na
-enough heat released so if burns with a lilac coloured flame
-melts into a shiny ball that dashes around the surface
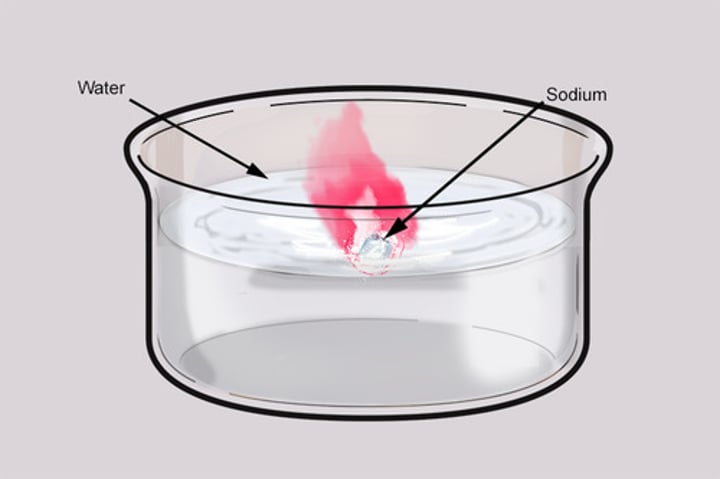
describe how sodium reacts with water
-large amounts of heat released cause the Na to melt
-hydrogen released catches fire and causes the ball of sodium to dash across the surfaces
describe how lithium reacts with water
-relatively slow reaction
-lithium doesn't melt
-fizzling can be seen and heard as the lithium reacts
how do you test to see if a solution is alkaline?
if the UI turns purpke
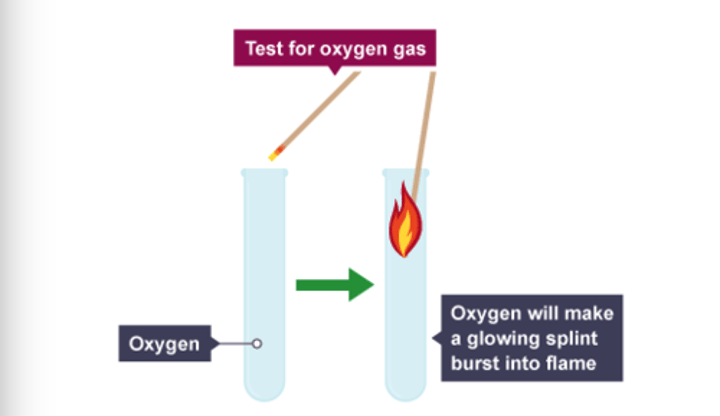
how do you test for the presence of oxygen?
glowing splint relights
how do you test for the presence of hydrogen?
squeaky pop test

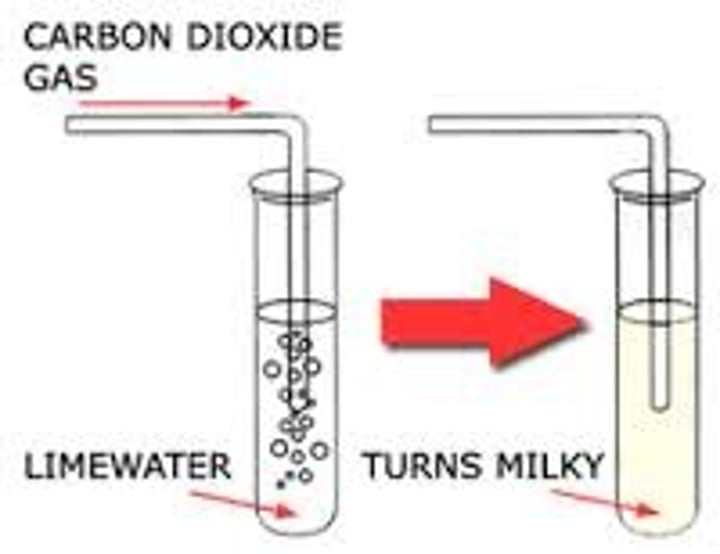
how do you test for the presence of carbon dioxide?
limewater
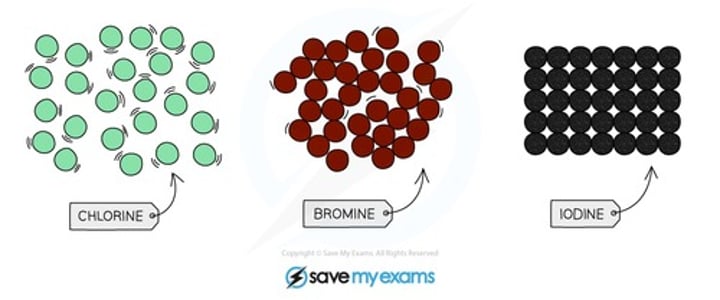
how does reactivity change moving down group 7? why?
reactivity decreases as the number of shells increase so there is less ability to attract electrons
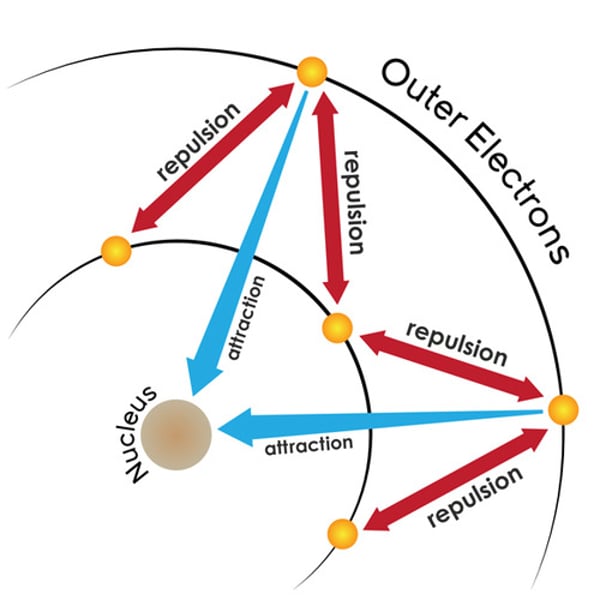
what is shielding?
when electrons in inner shells weaken the attraction between electrons in the outer shell
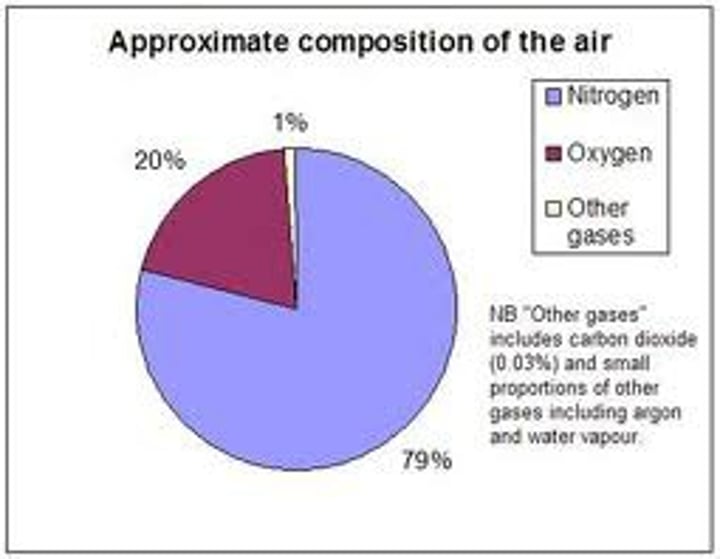
what is the composition of air?
78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% other
what is thermal decomposition?
the breaking down of a substance due to the action of heat
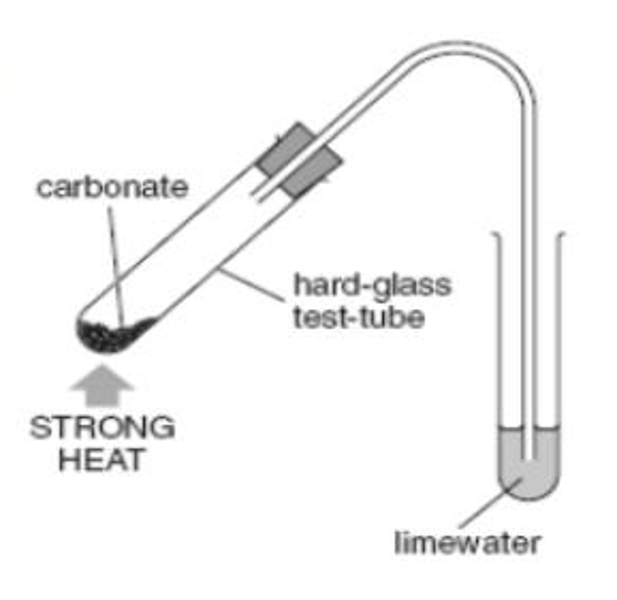
state the formula of thermal decomposition of a metal carbonate
metal carbonate ➡️ metal oxide + carbon dioxide
what is the chemical formula for rusting of iron?
iron + water + oxygen ➡️ hydrated (III) oxide
what is galvanisation?
a process where the iron is to be protected is coated with a layer of zinc
state methods to prevent rusting
painting, lubrication, galvanisation
what is oxidation in terms of oxygen?
addition of oxygen
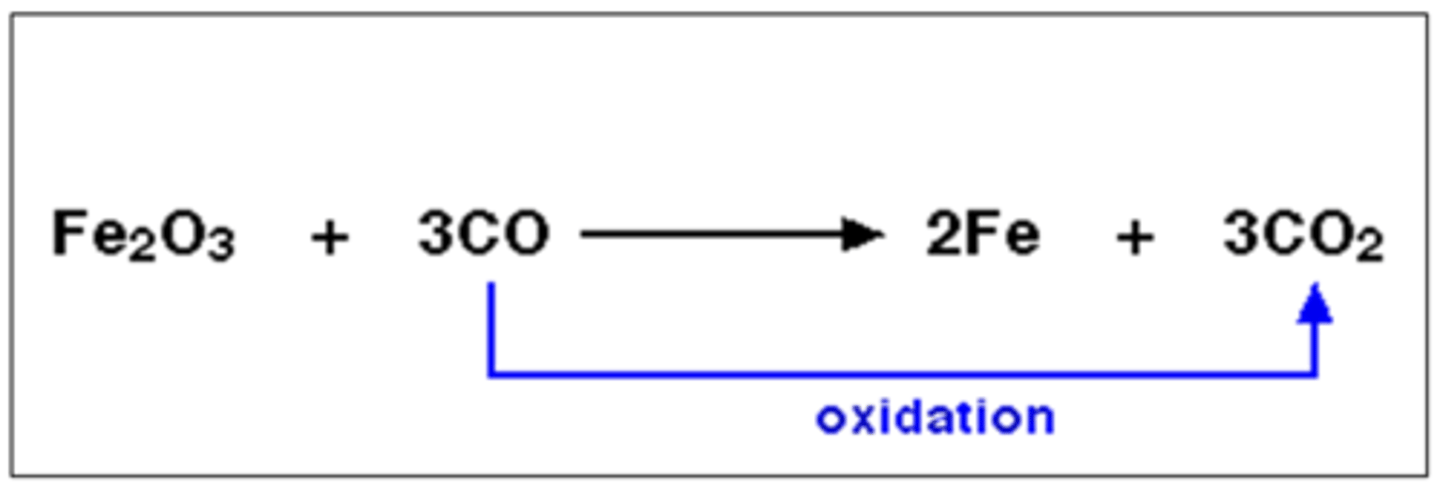
what is reduction in terms of oxygen?
substance loses oxygen
what is a reducing agent?
substance which removes oxygen
what is an oxidising agent?
substance which supplies oxygen
state the chemical formula for the reaction of lithium and water
lithium + water ➡️ lithium hydroxide + hydrogen
state the chemical formula for the reaction of sodium and water
sodium + water ➡️ sodium hydroxide + hydrogen
state the chemical formula for the reaction of potassium and water
potassium + water ➡️ potassium hydroxide + hydrogen
state the formula for the reaction of the alkali metals with oxygen
metal + oxygen ➡️ metal oxide
properties of group 1 metals
-soft (they can be cut with a knife)
-low density + mp (first three less dense than water)
-very reactive (only need to lose 1 electron)
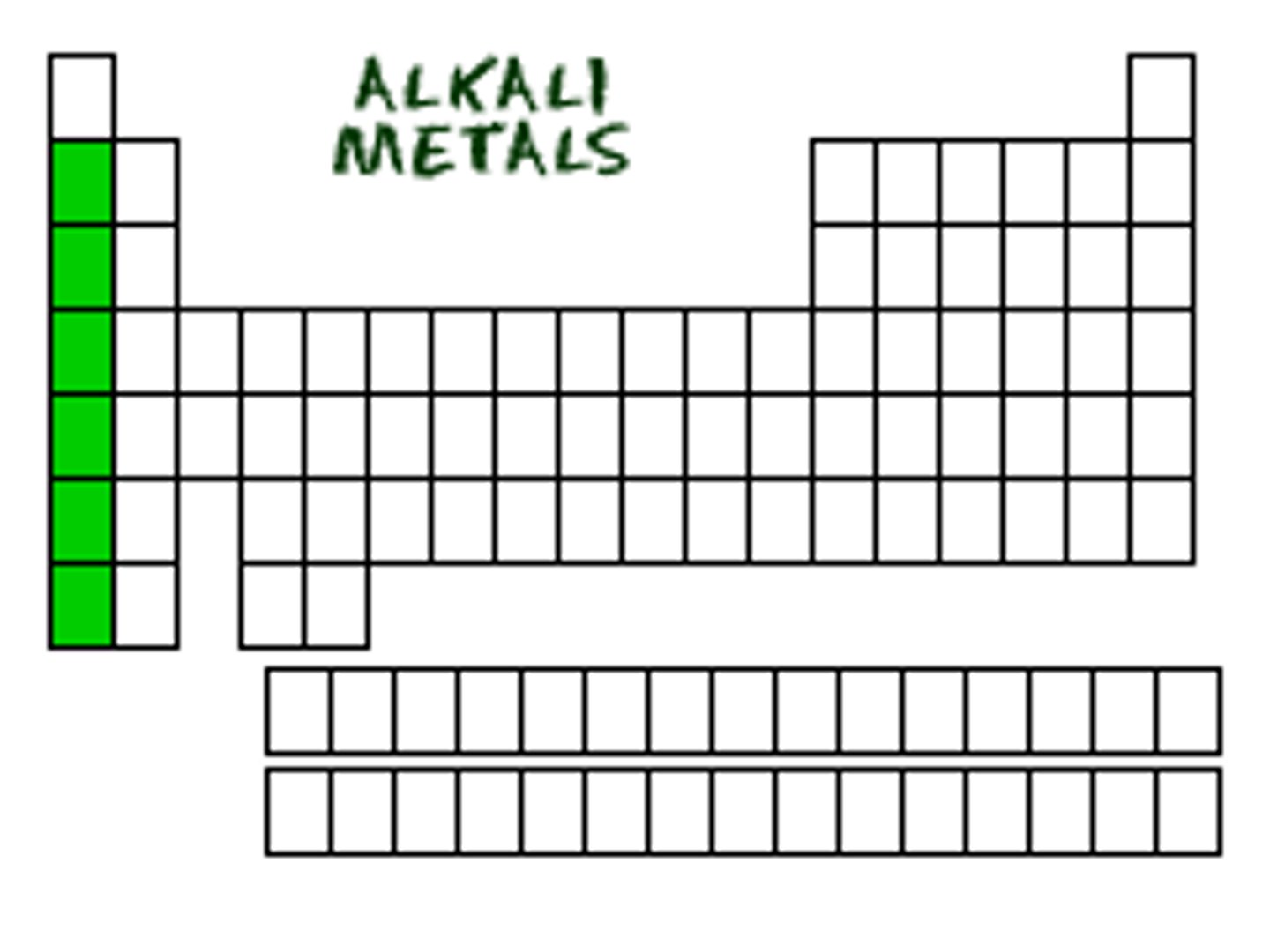
what are group 1 atoms known as?
alkali metals
what are group 7 atoms known as?
halogens
metal halides
halogens react with some metals to form ionic compounds
non-metal halides
halogens react with non-metals to form simple molecular structures e.g. hydrogen chloride
when does a halogen displacement reaction occur?
when a more reactive halogen displaces a less reactive halogen from an aqueous solution of its halide
what colour is iodine in a displacement reaction?
brown
what colour is bromine in a displacement reaction?
yellow-orange
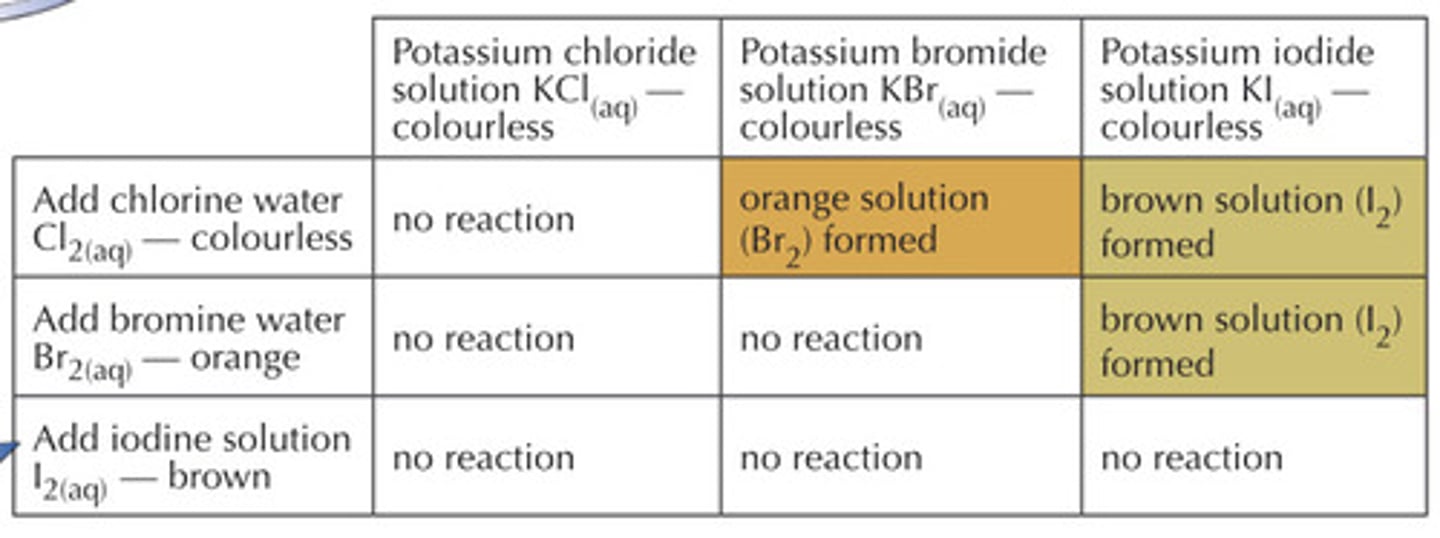
what colour is shown in a displacement reaction?
colour of displaced ion
what happens when a halogen is mixed with a halide of a more reactive metal?
no reaction occurs
what are the uses of carbon dioxide?
essential for keeping the planet warm
what is an exothermic reaction?
chemical reactions in which energy is released or produced such as in combustion

what is the chemical name for rust?
iron oxide

state two observations that would be seen when magnesium burns in oxygen
-intense white flame
-white powder (MgO) os produced
state an observation that would be seen when sulfur burns in oxygen
blue flame
what is combustion?
a chemical change in which oxygen reacts with elements or compounds to produce oxides

state the chemical formula for the decomposition of copper carbonate
copper(II) carbonate ➡️ copper (II) oxide + carbon dioxide
CuCO3 ➡️ CuO + CO2
what are sources of carbon dioxide?
combustion of wood and fossil fuels, respiration of plants and animals, thermal decomposition of carbonate rocks and the effect of acids on carbonates
state the reactivity series
1. potassium
2. sodium
3. lithium
4. calcium
5. magnesium
6. aluminium
7. carbon
8. zinc
9. iron
10. hydrogen
11. copper
12. silver
13. gold

how do colour of the halogens change as you descend the group?
they become darker
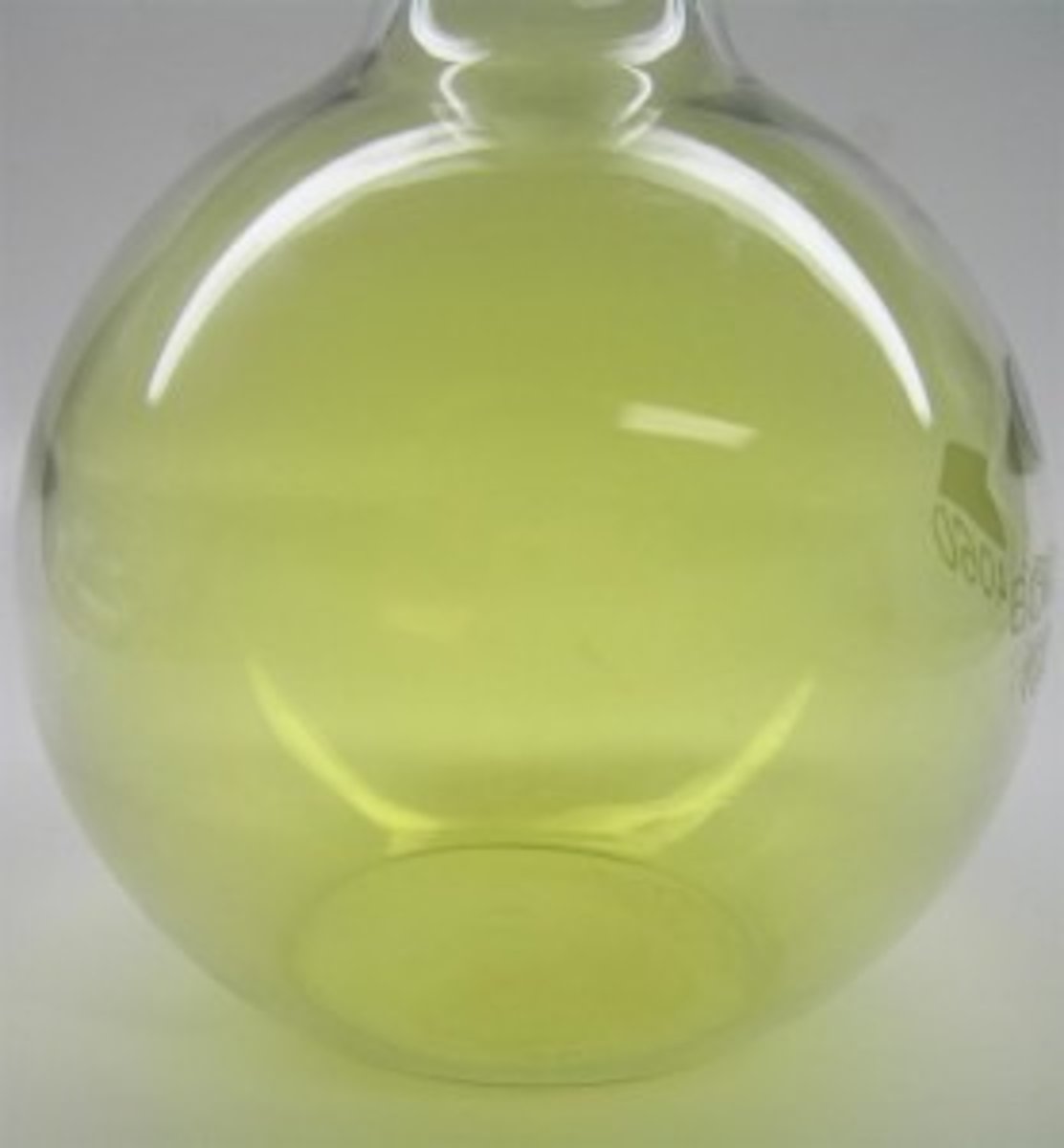
what is the colour and state of fluorine at room temperature?
yellow gas
what is the colour and state of chlorine at room temperature?
pale yellow-green gas

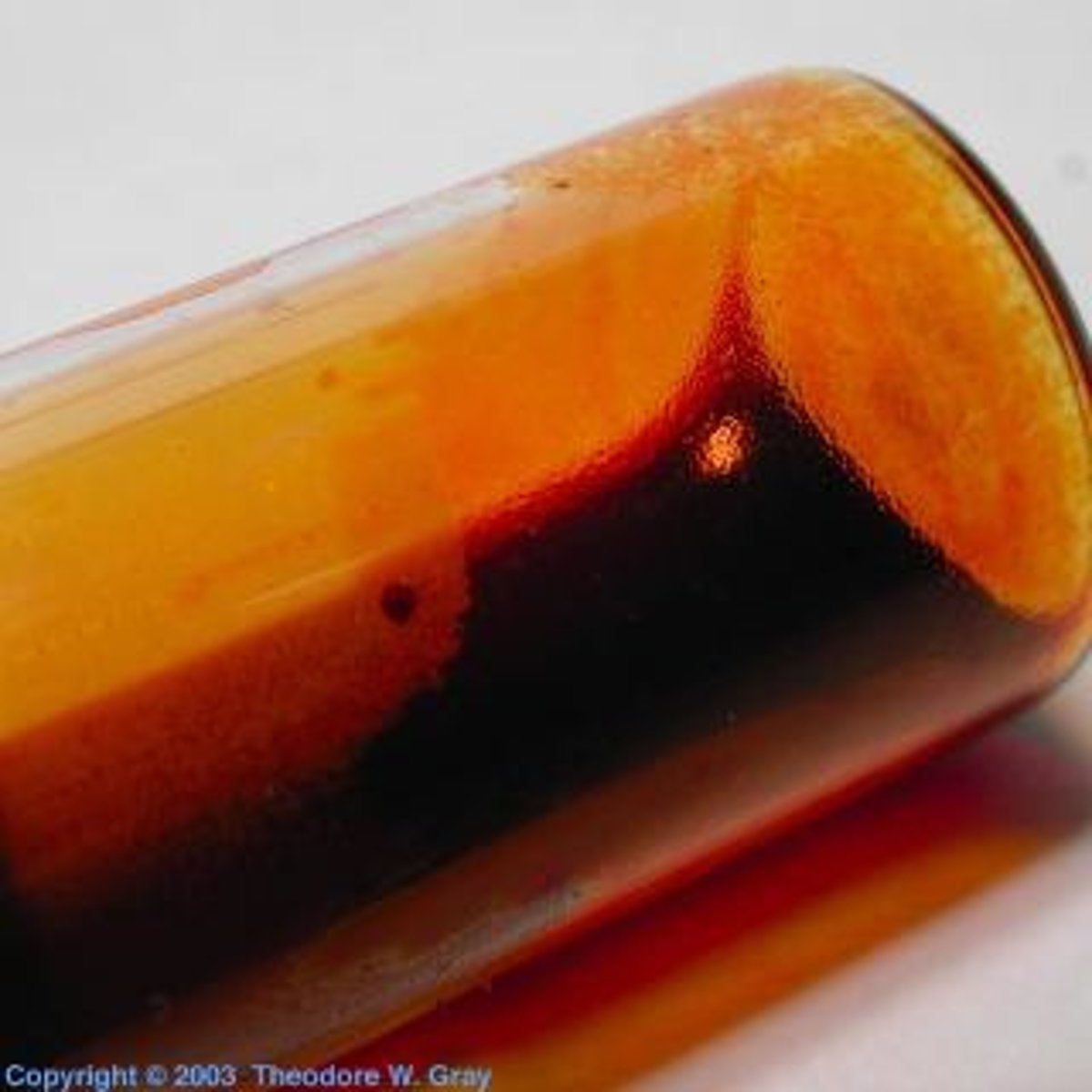
what is the colour and state of bromine at room temperature?
red-brown liquid

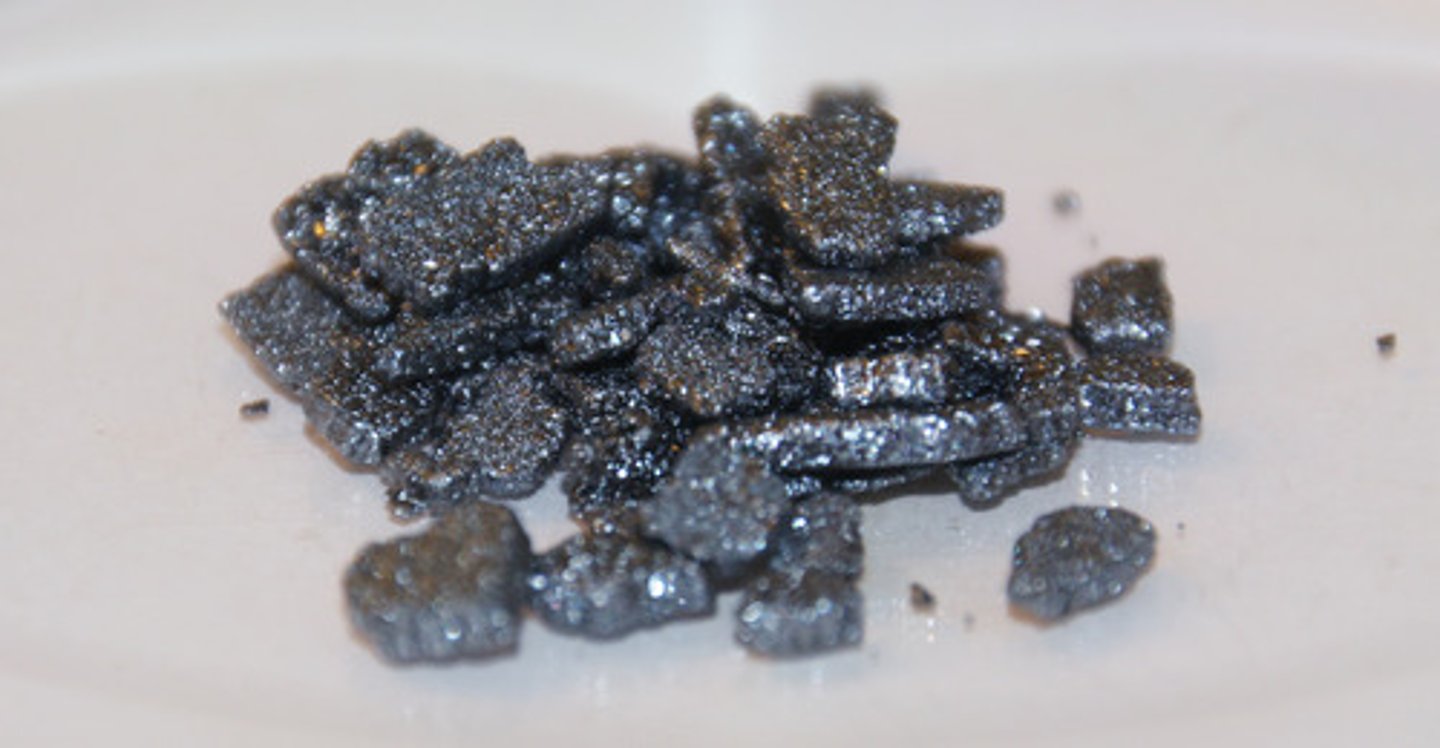
what is the colour and state of iodine at room temperature?
purple-black solid

what is an alloy?
mixtures of metals, where the metals are mixed together physically but are not chemically combined
what are uses of aluminium and why?
-aeroplane bodies - high strength-to-weight ratio
-saucepans - good conductorof hear
-foodcans - non-toxic
-window frames - resitant to corrosion

what are uses of copper?
-electrical wiring - good conductor of electricity and malleable
-water pipes - easy to work with and bend, non-toxic and nonreactive (does not react with water)

what is the difference between corrosion and rusting?
rusting is specific to iron

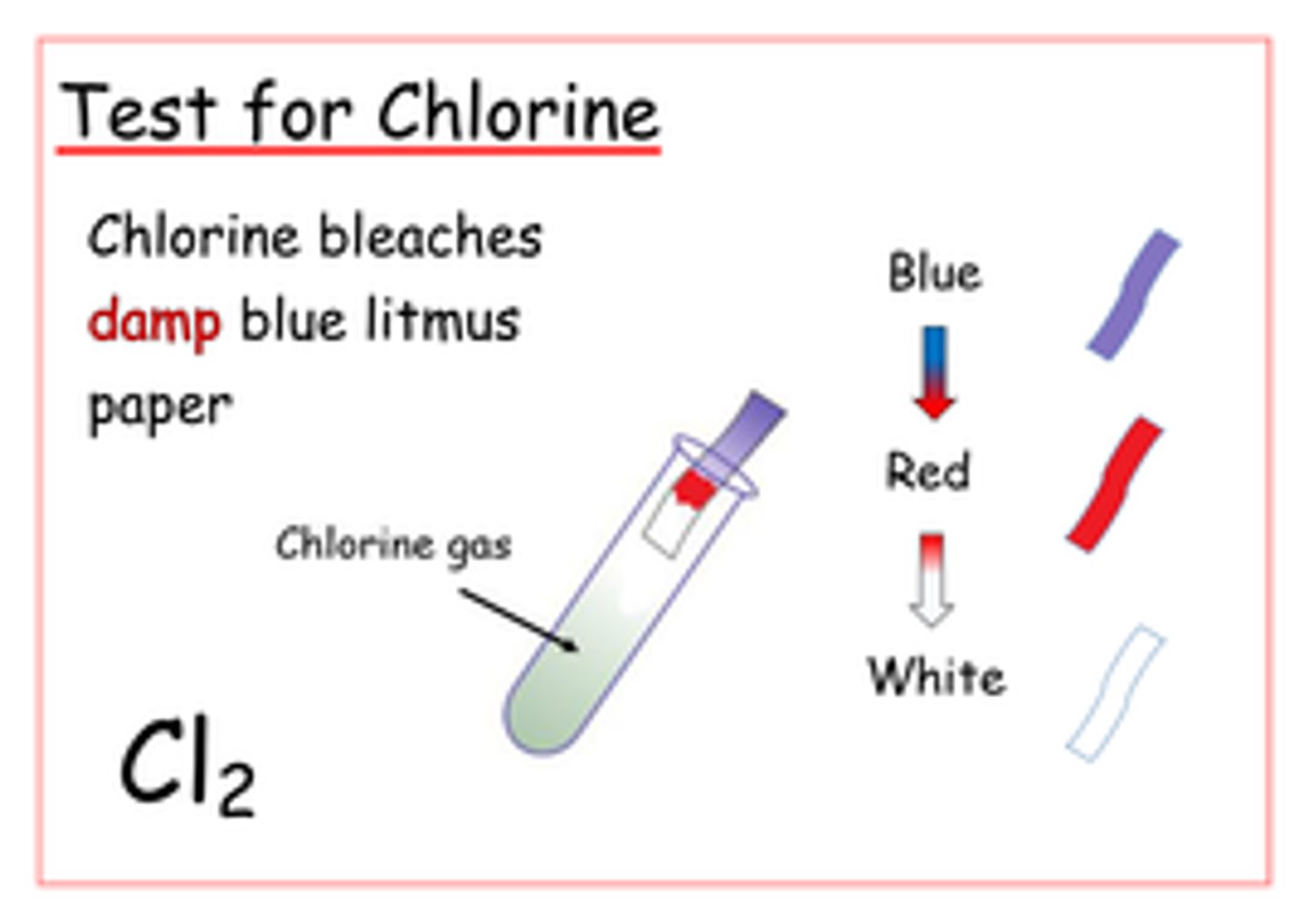
how do you test for chlorine?
it bleaches damp litmus paper, turning it white
state why aluminium cannot be extracted from its oxide by reduction with carbon?
aluminium is more reactive than carbon
what is the anode?
positive electrode
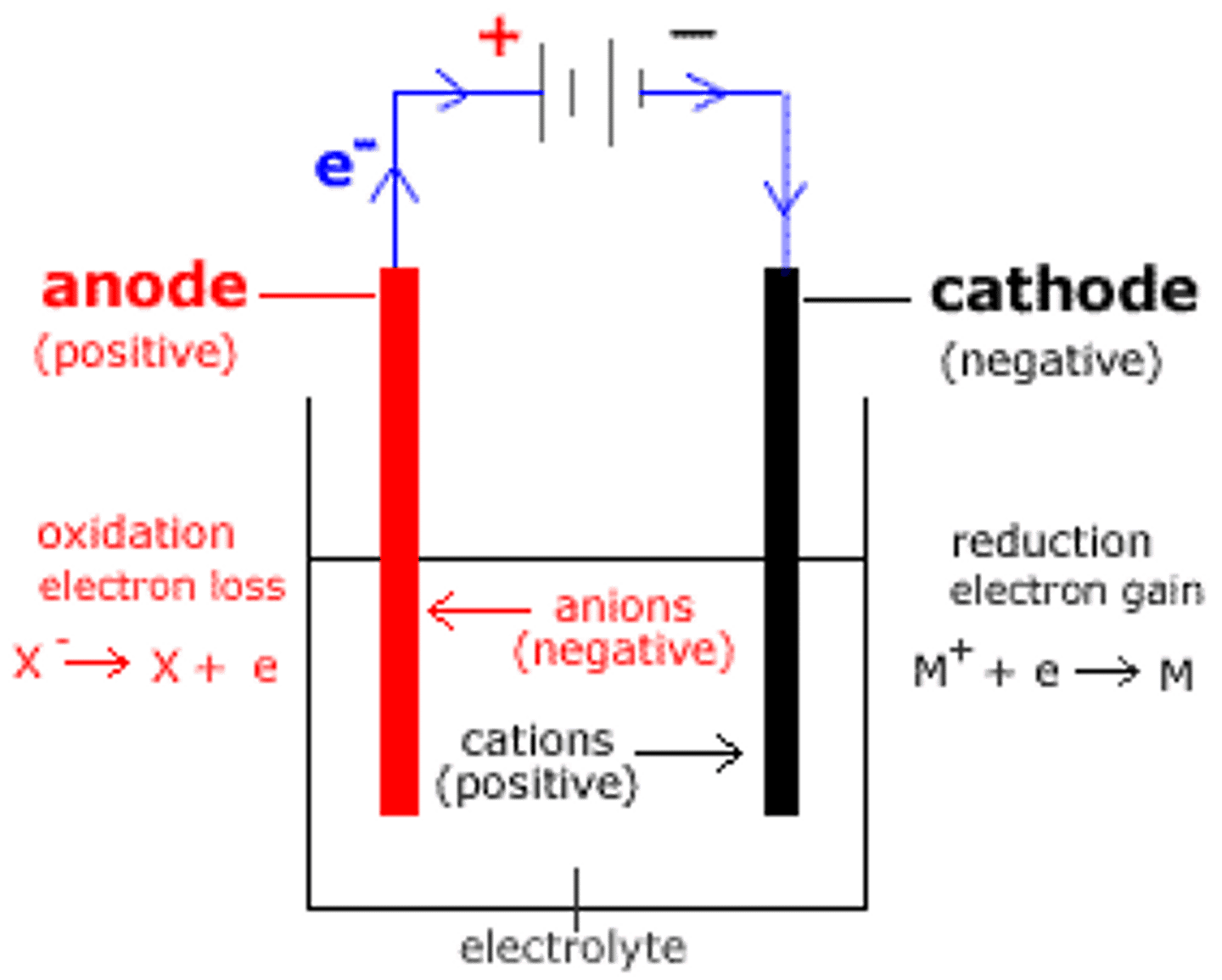
what is the cathode?
negative electrode
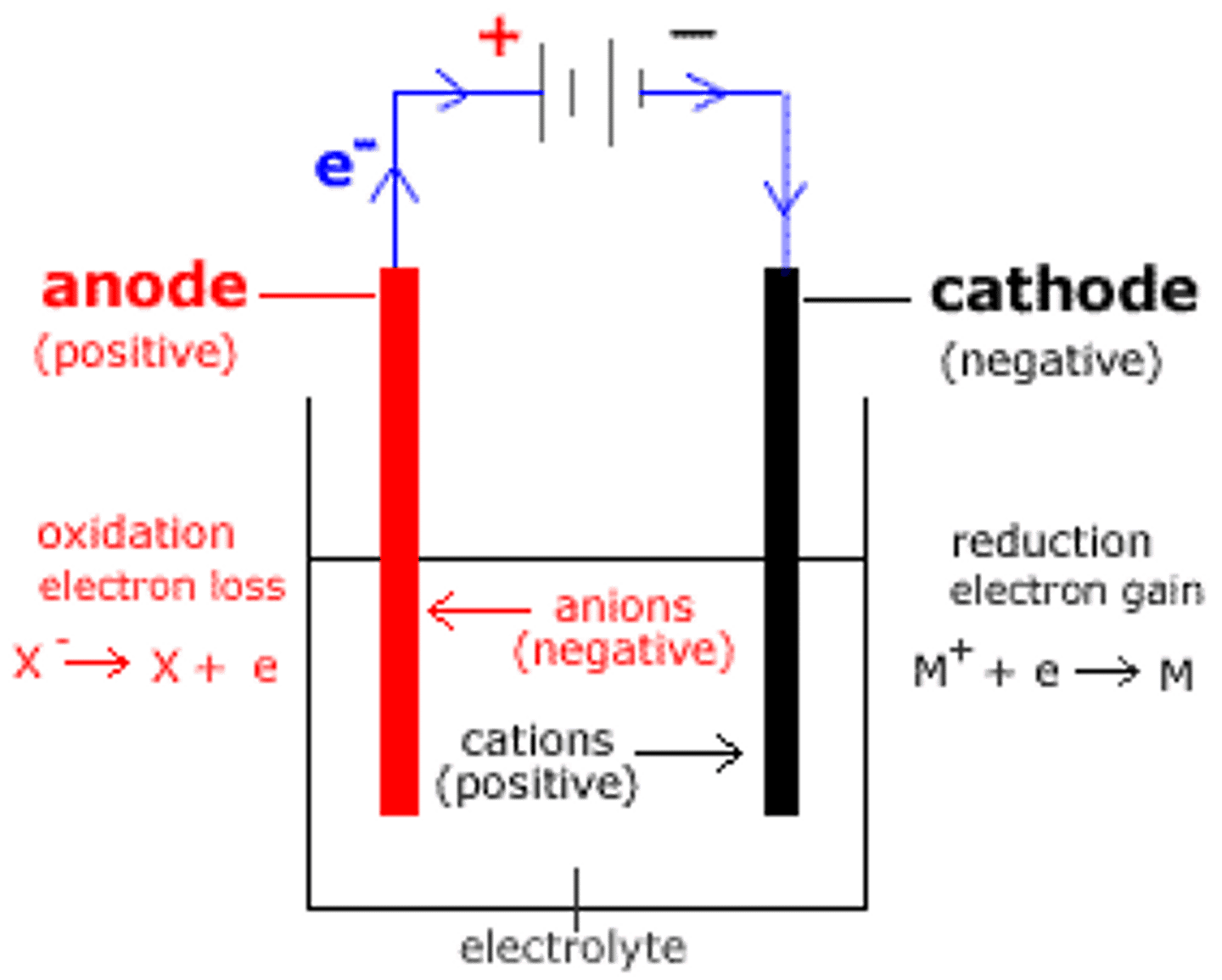
what are the anions?
negatively charged ions
what are the cations?
positively charged ions

why is cryolite used in the electrolysis of aluminium oxide?
to lower the melting point of aluminium

give two reasons why the extraction of aluminium is expensive
-carbon is frequently replaced
-large amounts of electricity needed
write the half equation at the anode in the electrolysis of aluminium oxide
2O2- ➡️ O2 + 4e-
write the half equation at the cathode in the electrolysis of aluminium oxide
Al3+ + 3e- ➡️ Al
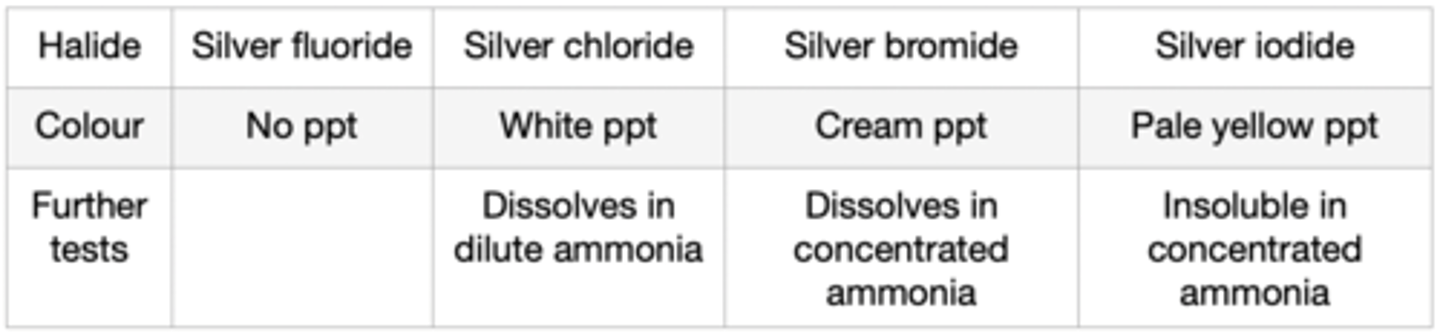
state the result shown when silver nitrate solution and dilute nitric acid reacts with chlorine halide ion
white precipitate is formed
state the result shown when silver nitrate solution and dilute nitric acid reacts with bromine halide ion
cream precipitate is formed
state the result shown when silver nitrate solution and dilute nitric acid reacts with iodine halide ion
yellow precipitate is formed
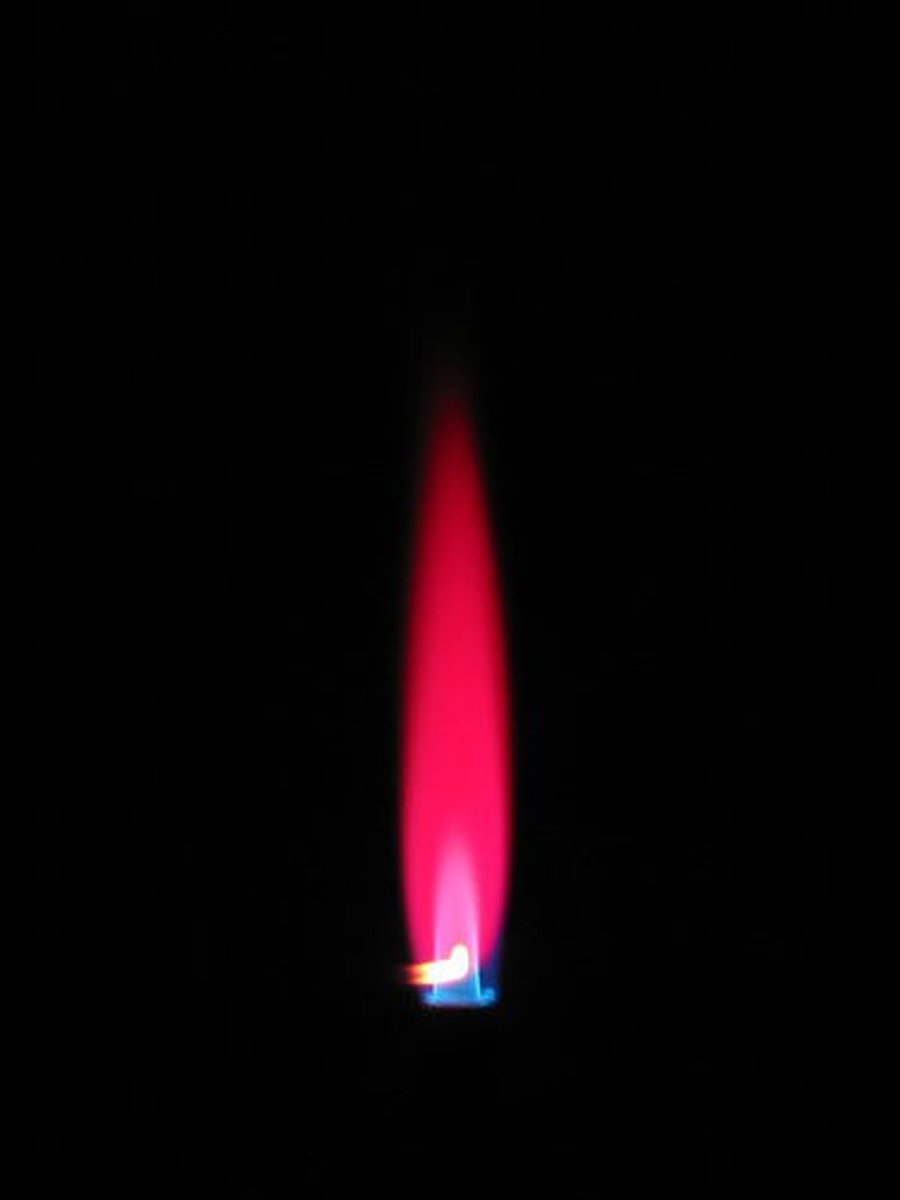
what is the colour of flame of lithium?
red

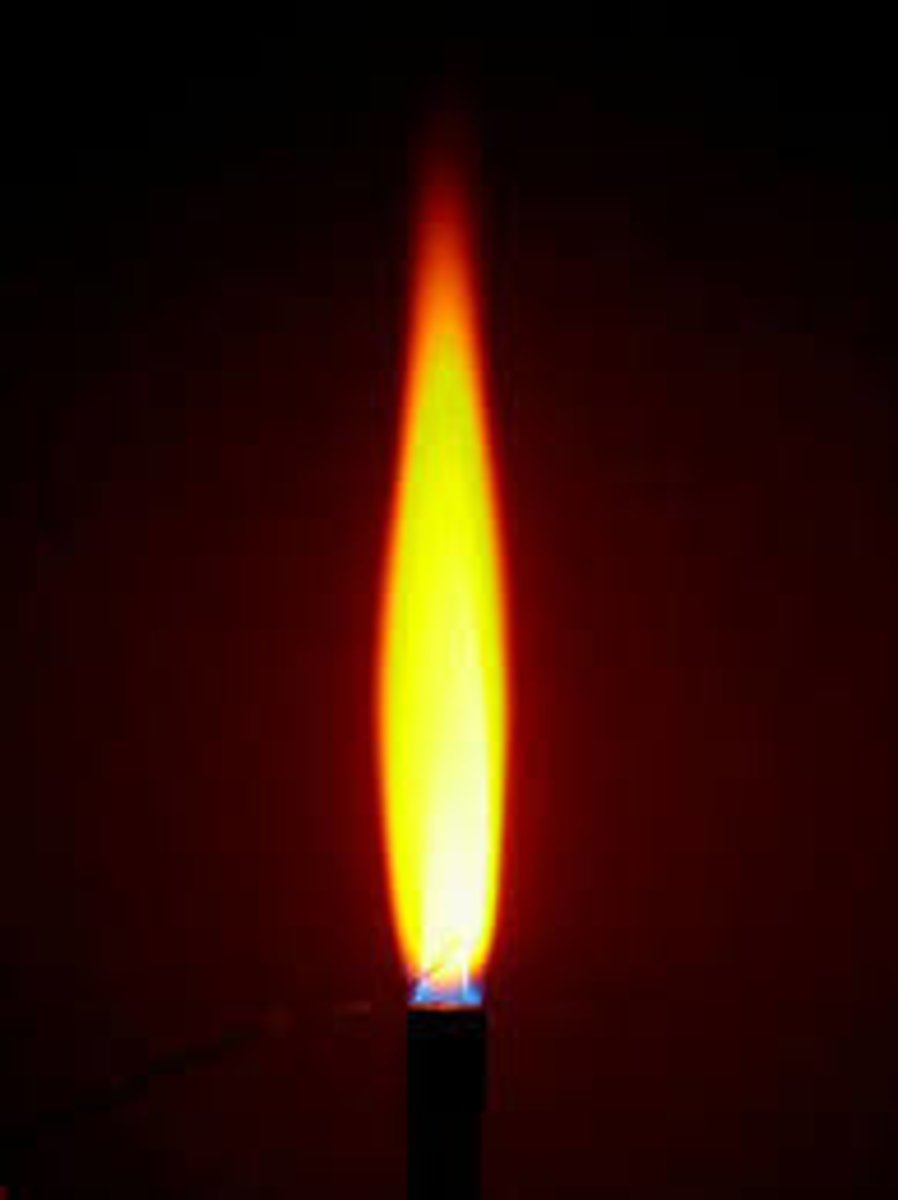
what is the colour of flame of sodium?
yellow

what is the colour of flame of potassium?
lilac
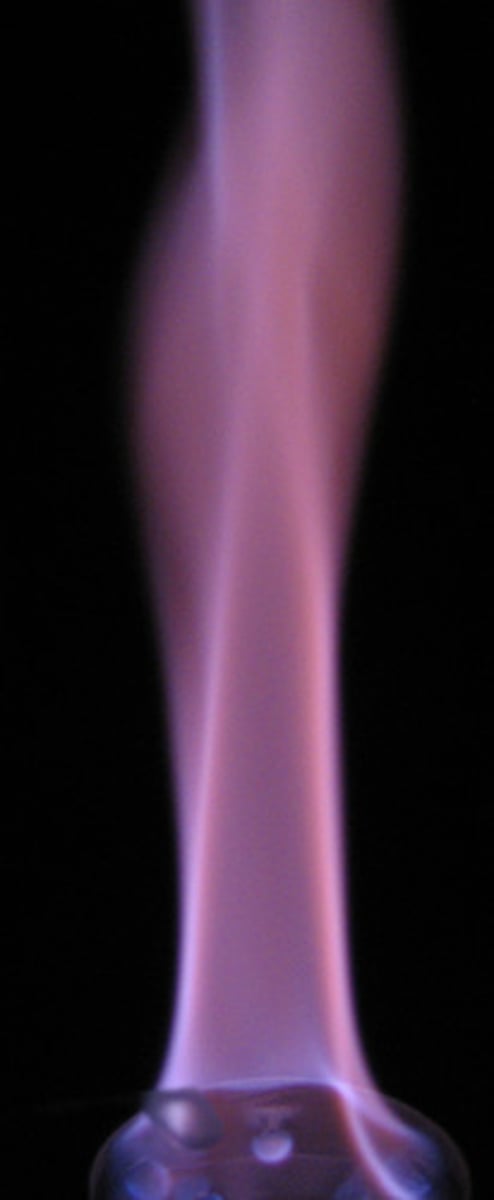

what is the colour of flame of Ca2+?
orange-red
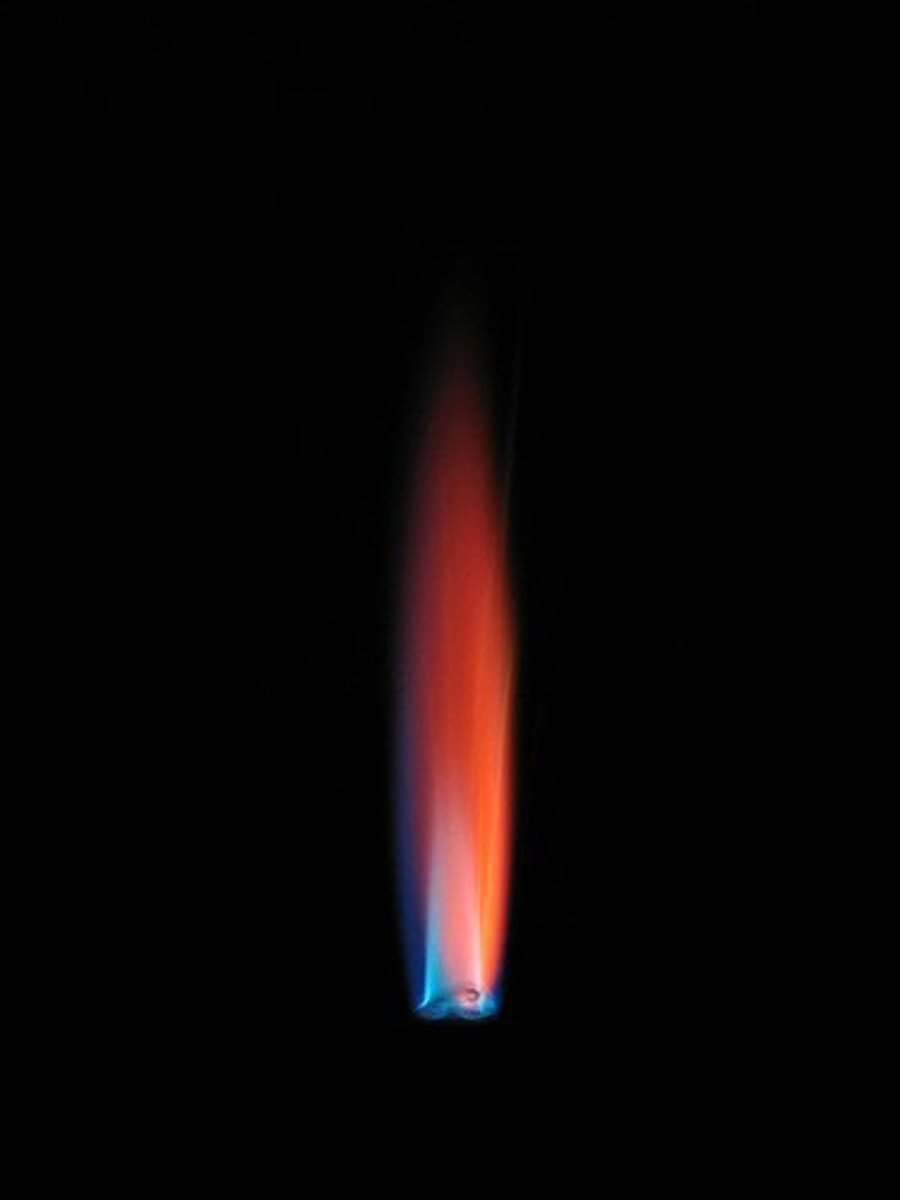

what is the colour of flame of Cu2+?
blue-green
