Biochemicals Study Guide
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
what is a polymer?
a large molecule made of multiple repeating units
what is a monomer?
one individual unit
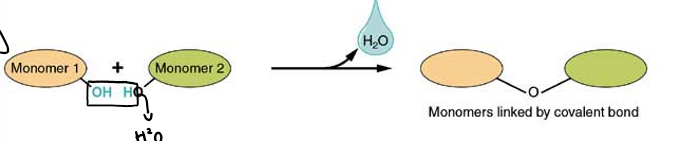
how are polymers formed?
via dehydration synthesis
what is dehydration synthesis?
monomers are joined by removed OH from one monomer and removed H from the other
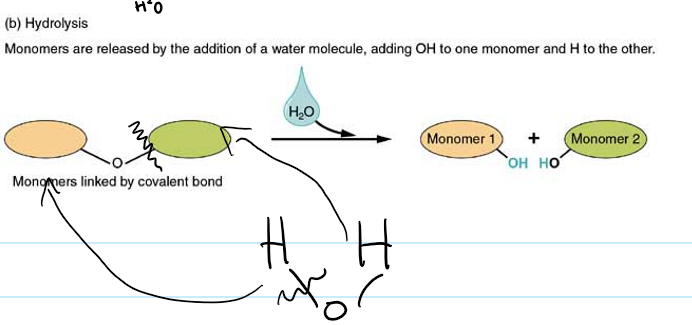
how are polymers broken down by?
hydrolysis
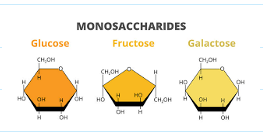
what are the four major macromolecules?
carbohydrates, lipids, protiens, and nucleic acids
what is a carbohydrate monomer called?
monosaccharide
what do carbohydrates do?
give quick energy
what foods are high in carbohydrates?
starches, sweets, bread, fiber
if a molecule ends in “ose”, what does it mean?
it’s a sugar
what are some exceptions to the “ose” = “sugar” rule?
amylopectin, chitin
what are carbohydrates made of?
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
what are monosaccharides?
one sugar
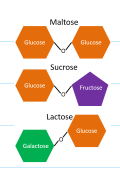
what are disaccharides?
two sugar
what are polysaccharides?
many sugar
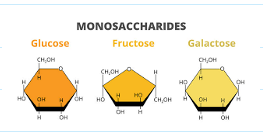
what are some examples for monosaccharides?
glucose, fructose, galactose
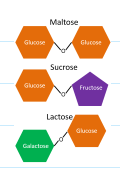
what are some examples for disaccharides?
maltose, sucrose, lactose
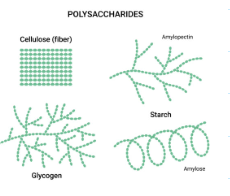
what are some examples for polysaccharides?
starch, cellulose, and lactose
how do plants store energy?
starch
how do animals store energy?
glycogen
how do plants maintain structures?
cellulose
how to fungi and arthropods maintain structure?
chitin
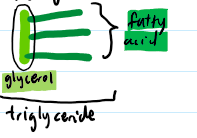
what are lipid subunits called?
triglyceride
what’s the use for lipids?
long term energy storage, insulation, and making cell membranes
what elements make up lipids?
carbon, hydrogen, and very little oxygen
what foods have a lot of lipids?
oils, butter, animal fat, and lard
what are some lipid molecule examples?
hormones, phospholipids, steroids, vitamin a, d, and k
what are the three types of fats?
saturated, unsaturated, and trans fats
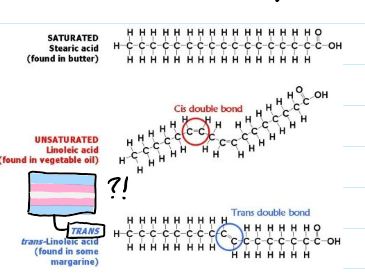
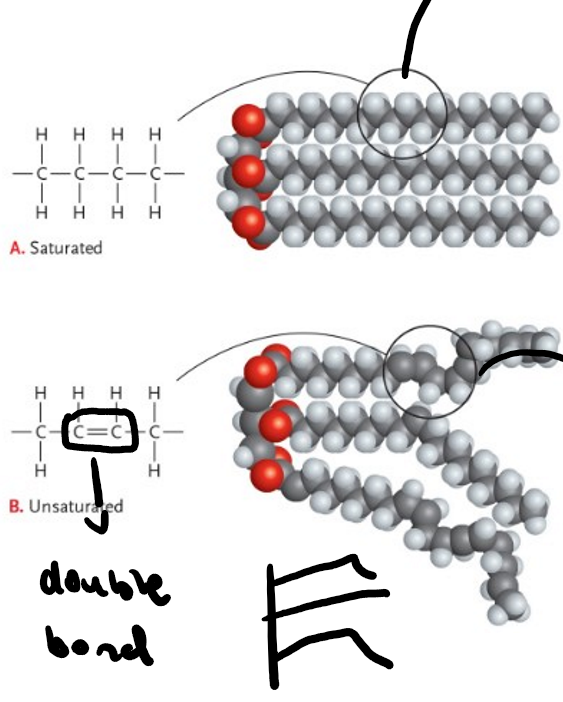
what are the differences between saturated and unsaturated fats?
saturated is tightly packed and animal based, unsaturated are loosely packed and plant based
how to polar and non-polar substances react with one another?
each type will mix with their own, but they will not mix with the opposite type
what are protein monomers called?
amino acids
what elements make up proteins?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur
what do proteins do?
helps create muscle tissue, hair, nails, and skin cells
what foods are high in protein?
meats, peanut butter, beans, egg whites, tofu, dairy
what are some protein molecule examples?
collagen, insulin, actin or myosin, hemoglobin, enzymes, amylose
what are the different groups of an amino acid structure?
amino group, side chain, and carboxyl group
how do proteins work?
they have to have the correct shape
what are the different structures of proteins? name all of them.
primary structure, secondary alpha/helix, secondary pleat/sheet structure, tertiary structure, quaternary structure
what do actin and myosin do?
actin is basically useless while myosin is responsible for contracting and relaxing muscles
what are nucleic acid monomers called?
nucleotides
what elements are nucleic acids made of?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus
what does nucleic acids do?
provide instructions for building proteins, stores genetic information
what foods are high in nucleic acid?
all living things
what are some nucleic acid molecule examples
RNA and DNA
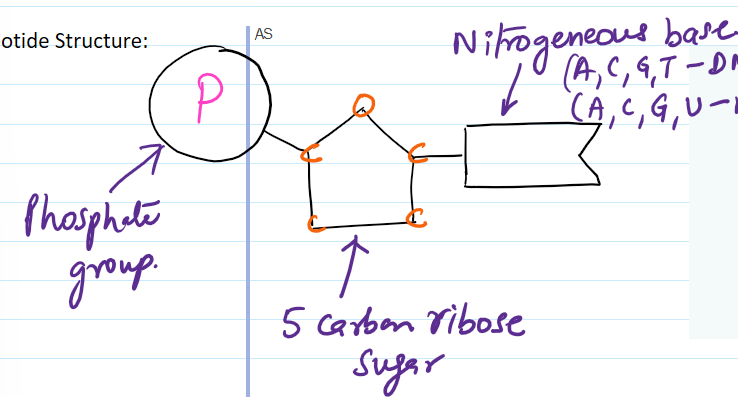
name all the different parts that make up a nucleotide
phosphate group, 5 carbon ribose sugar, and nitrogenous base
what are the different chemicals that make up DNA?
A, C, G, T
what are the different chemicals that make up RNA?
A, C, G, U
what’s the chemical formula for monosaccharides?
C6H12O6

which disaccharide is this?
sucrose

which disaccharide is this?
maltose
why can’t dna leave the nucleus but rna can?
rna has a weaker h-bond compared to dna
what are enzymes?
proteins that speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy
what do amylase, lactase, and sucrase do?
breaks down carbohydrates
what do protease and peptidase do?
breaks down proteins
what does lipase do?
breaks down fats
what do DNA and RNA polymerase do?
put together to create nucleic acid
how do digestive enzymes work?
via hydrolysis
how do synthesis enzymes work?
via dehydration synthesis
what is metabolism?
all chemical reactions in an organism’s body
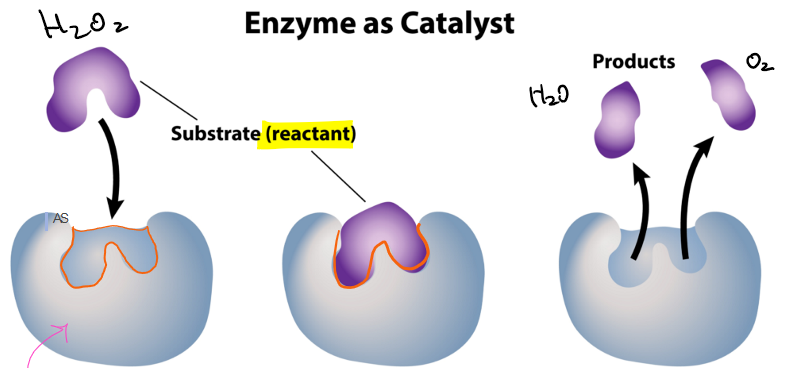
what is the orange part of the diagram called?
active site
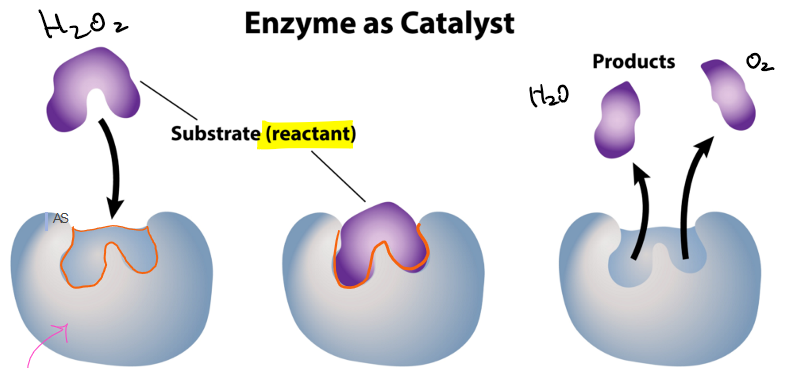
what is the purple part of the diagram called?
the substrate or reactant
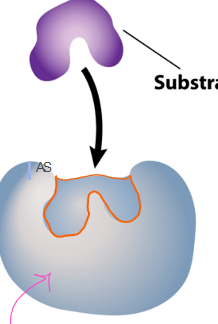
which stage of the enzyme as catalyst is this?
enzyme: substrate enters the active site of the enzyme
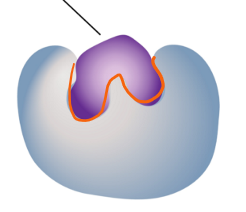
what stage of the enzyme as catalyst is this?
enzyme-substrate complex: chemical reaction is triggered by enzyme
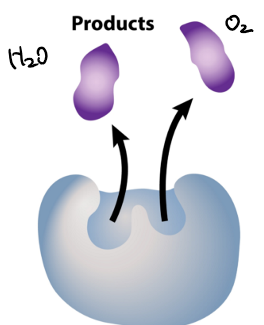
what stage of the enzyme as catalyst is this?
enzyme and product: enzyme releases product
enzymes are both —- and —-
reusable, specific
what is a catabolic reaction?
cutting or breaking the bond
what are anabolic reactions?
merges or creates the bond
what is an inhibitor?
controls enzymes from catalyzing reactions
what are the two types of inhibitors?
competitive: blocks the active site, non-competitive: changes the shape of the active site
what is needed for enzymes to catalyze reactions?
cofactors: helpers of enzymes
what’s the difference between facts that REGULATE and AFFECT enzymes?
regulate is only temporary, while affect is permanent
what does “denature” mean?
changing the shape of the enzyme by unfolding, making it useless
what are the four factors that can affect enzymes?
temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, and substrate concentration
in — temperatures, enzymes begin to slow down and completely denature.
high
in — temperatures, enzymes slow down but do not denature
low
changing the number of neutrons gives you an…
isotope
changing the number of electrons gives you a…
negative charge
what type of bond is this? electrons are transferred.
ionic
what type of bond is this? electrons are shared equally
covalent
what type of bond is this? electrons are shared unequally
ionic
what type of bond is this? weak attractions between molecules
covalent
what is the difference between an atom and a molecule?
an atom is the smallest unit of matter, while molecules are a chain of atoms
explain how you can find the number of valence electrons an element has.
The electron in the last shell/circle are valence electrons. These take part informing a bond.
what types of bonds gives water its special properties?
cohesion and adhesion
what is cohesion, and why is it important to life?
cohesion is when water molecules stick to other water molecules. it’s important since it’s why water’s boiling point is high and helps us regulate our body temperature
what is adhesion and why is it important to life?
adhesion is when water sticks to other polar substances, it’s important because it’s useful for fluid transport.
what is high specific heat and why is it important to life?
it’s when it takes a long time for water to heat up, it’s important because it useful for regulating body temperature
what is evaporative cooling, and why is it important to life?
it’s when water evaporates from a surface, causing it to cool down. it’s useful for maintaining homeostasis, such as sweating.