carbohydrates
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
"a-.."/a[#] is alpha, B or b-... / b/B[#]is beta; im too lazy to put in the real letter
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
empirical formula for carbohydrate
(CH2O)n, n = number of C atoms and ≥ 3
what are carbohydrates used for?
cell-cell signaling when attached to cell membranes
building blocks for larger molecules
energy source
monosaccharide (carbohydrate)
“simple sugars”
exist as straight chain
also exist as ring structure when there are 5+ carbons and dissolved in water
ring structures are usually more conducive to chemical reactions/interactions
carbohydrates are either [__] or [__] depending on which carbonyl group they have
carbohydrates are either aldehydes or ketones depending on which carbonyl group they have
how can carbohydrates be classified?
number of Carbon atoms & suffix “-ose”
eg. Hexoses have 6 Carbons
which 3 monosaccharides are isomers of each other?
glucose, fructose, galactose → different chemical & physical properties
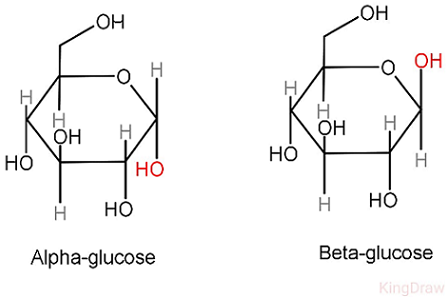
alpha-glucose (a-glucose)
isomer of glucose our body can use (hydroxyl group on carbon 1 sticks DOWN)
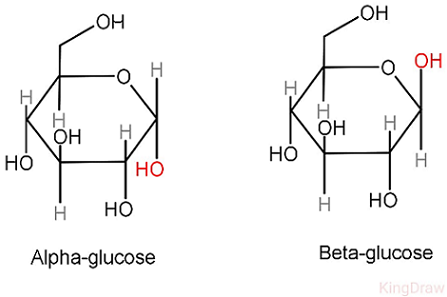
beta-glucose (B-glucose)
isomer of glucose our body doesn’t recognize
(hydroxyl group on carbon 1 sticks UP)
monosaccharides and diet (where it’s found (un)naturally, where you should consume carbs)
found naturally in foods like fruit, milk, milk products
occurs also in processed & refined sugars (candy, table sugar, syrup, soft drinks..)
carbohydrate intake should come from complex carbohydrates (starches) & naturally occurring sugars (NOT processed&refined)
about oligosaccharides
disaccharide, trisaccharide, or 2-10 monosaccharide units
formed in an anabolic reaction (dehydration synthesis)
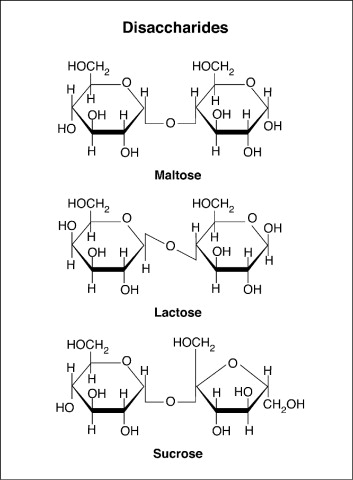
3 common oligosaccharides & their composition
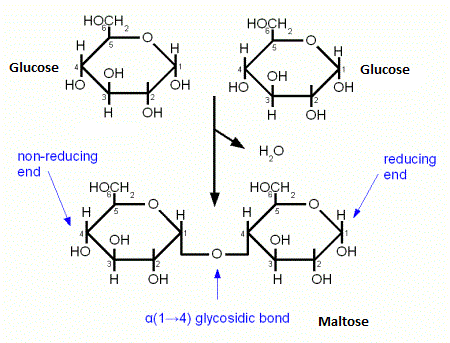
maltose — 2 a-glucose together (found in beer)
lactose — galactosr and 1 b-glucose (sugar found in milk) → 1 glucose and galactose
sucrose — 1 a-glucose and 1 fructose (found in table sugar)
what is a glycosidic linkage (we never defined this in notes)
a chemical bond in the form of a covalent connection that connects a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which might be another carbohydrate or not
glycosidic linkage bond between sugars in Maltose
a (alpha) 1-4 glycosidic linkage → occurs between Carbon 1 of the first a-glucose and Carbon 4 of the second a-glucose
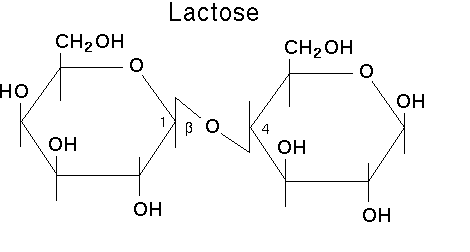
glycosidic linkage bond between sugars in Lactose
B 1-4 glycosidic linkage (between Carbon 1 of the glucose and carbon 4 of the galactose)
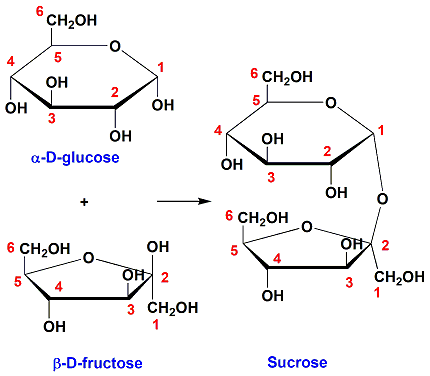
glycosidic linkage bond between sugars in Sucrose
a 1-2 glycosidic linkage (between carbon 1 of the glucose and carbon 2 of the fructose)
polysaccharides (what is it, structure)
hundreds-thousands of monosaccharides held together by glycosidic linkages
some straight chained, some are branched, others have side groups attached
use of polysaccharides
primarily used as carbohydrate storage, long-term energy source, some also used for structural support of the cell/organism
what is starch used for in plants?
primary carbohydrate storage unit of plants
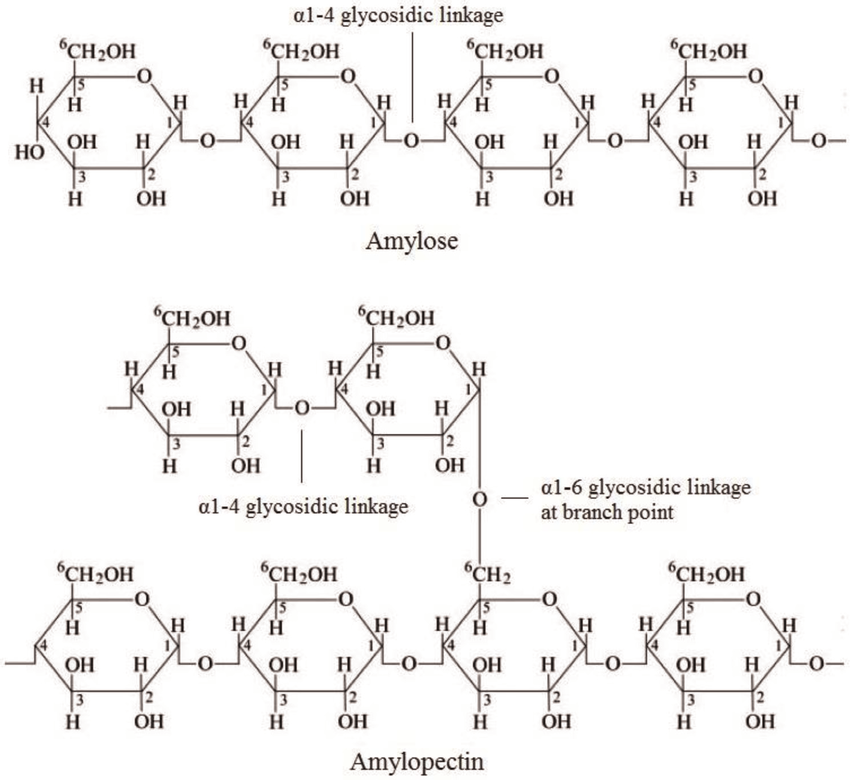
the 2 polysaccharides that starch is composed of
amylose: a straight chain of a-glucose molecules in an a1-4 glycosidic linkages
amylopectin: main chain of a-glucose in a1-4 linkages & branches of a-glucose off the main chain in a1-6 linkages at the branch points
why is starch insoluble & where is it stored
insoluble because of the angles of the glycosidic linkages, stored mainly in chloroplasts & some fruit of plants
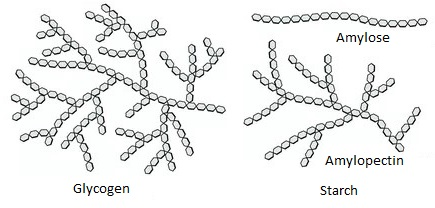
what is glycogen
long-term storage molecule in animals (similar to amylopectin but with more branching)
where does unused glucose go in the body?
glucose not use as energy gets stored in the liver & muscles as glycogen
where is cellulose found & what it’s used for
in plant cell walls, used for structural support
structure of cellulose
straight chain of B-glucose held together by B1-4 glycosidic linkages
every second glucose molecule is inverted
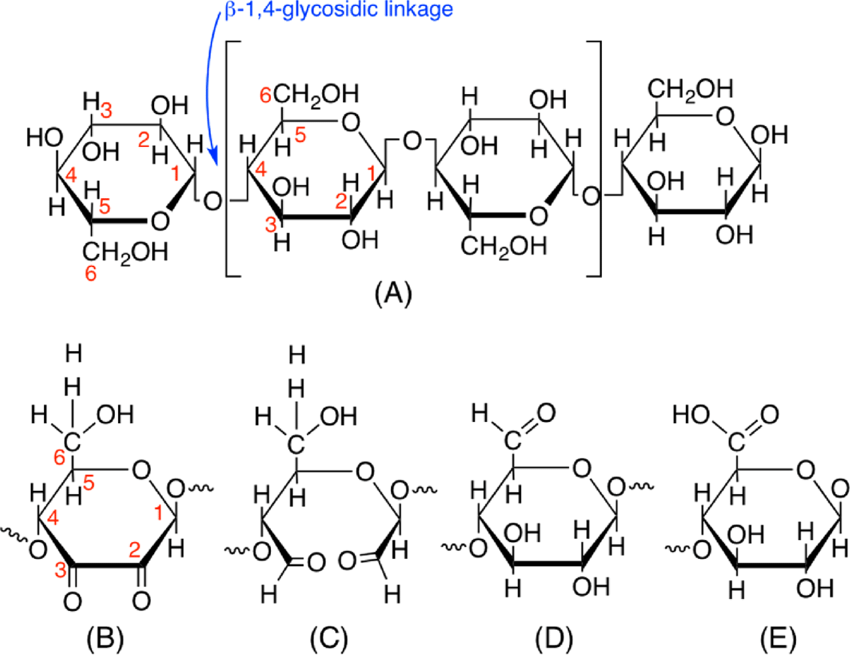
why do cellulose chains pack close together
H-bonds (which are strong) form between adjacent cellulose strands
cellulose in diet and digestion
cannot digest it due to enzymes being unable to hydrolyze B1-4 glycosidic linkages (upside down glucose molecules)
important part of the diet because it cleans out digestive tract (fiber)
chitin
material that makes of the exoskeletons of a lot of arthropods
its monomers are glucose w/ nitrogen group attached to the 2nd carbon
we can’t break it down because of B-glucose (B1-4 glycosidic linkage)
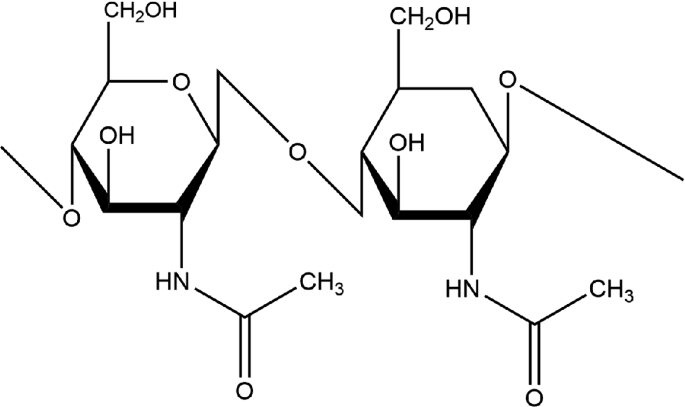
where is chitin used
contact lenses & biodegradable stitches
complex polysaccharides foods provide…
vitamins, minerals, fiber