Histamine/Antihistamines
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
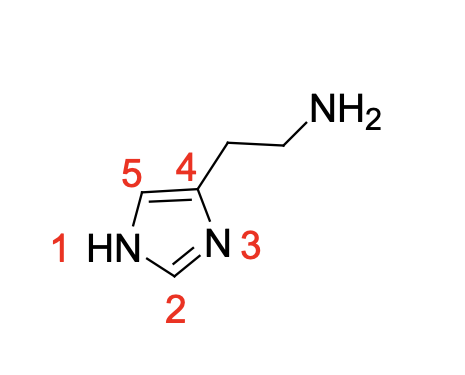
Correct Numbering and structure of histamine
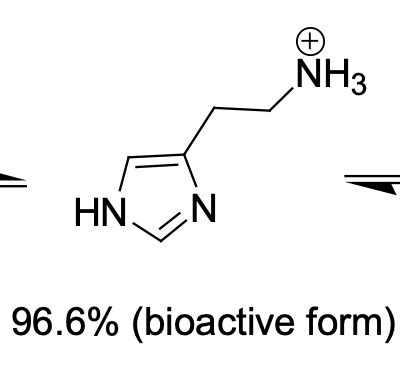
Bioactive form of histamine
N distal (80%)
The ______ histamine tautomer is the major tautomer
small vascular vessel dialtion
vascular permeability
bronchi CONSTRICTION
Intestine contraction
Gastric acid secretion
Stimulate nerve ending (pain and itching)
Wakefulness, cognition, food consumption
Biological effects of histamine
H1 receptor (smooth muscle, endothelial cells - allergy effects) AND H2 receptors (Gastric parietal cells - gastric acid secretion)
Biological targets of histamine
methyl (CH3)
When you add a _____ group to histamine’s structure, it changes potency from H1 receptor from 100 to 0.2 (uneven receptor potencies! 40 to 0.2!!)
Histidine decarboxylase
Histidine is transformed into HISTAMINE by _____ (takes away the COOH)
Histamine synthesis inhibitors
Histamine release inhibitors
Histamine receptor antagonists
Three class types of antihistamines
Inhibiting histidine decarboxylase; alpha-methylhistidine + Brocresine
Inhibitors of histamine synthesis work by ____, and examples of them are____
Preventing bronchial asthma
Prevent exercise-induced bronchospasm
Prevent seasonal allergic rhinitis
Examples: Cromolyn sodium, Khellin, Nedocromil sodium
Inhibitors of histamine release work by preventing the release of histamine (like from mast cells) and have indications for ____
Binding reversibly to histamine binding site (competitive antagonist) and examples are H1 receptor antagonists and H2 receptor antagonists
Histamine receptor antagonists work by _____
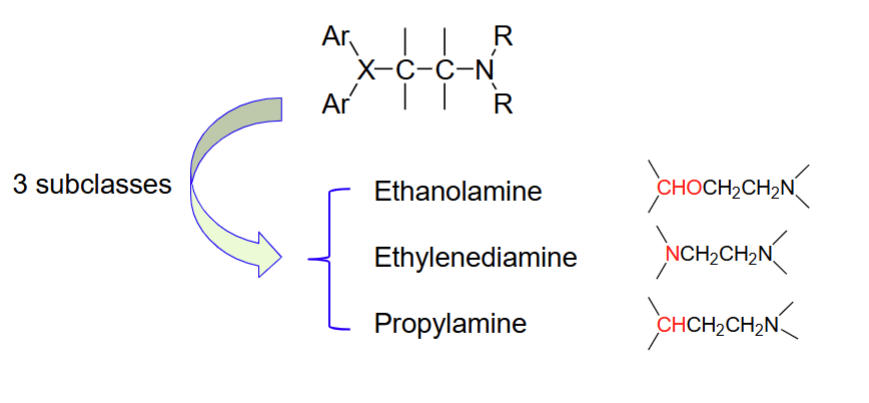
3 subclasses of the H1 receptor antagonists
Aryl group domain
Spacer domain
Alkyl amine domain
The 3 sections/domains of a H1 antagonist structure (SAR)
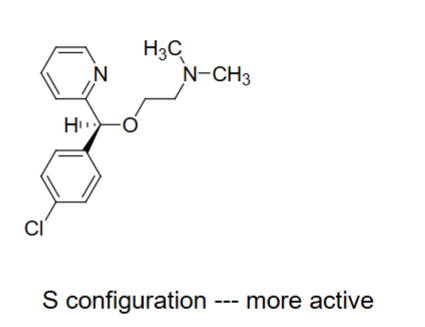
S configuration (think left handed gun)
The ____ configuration is more active for the aryl group domain in H1 receptor antagonists
decreased; branching
For the spacer domain, the more carbons in the middle, the activity is _____ , and the same effect happens with ____ as well. Most agents have 4 to 5 carbons between aryl and N group
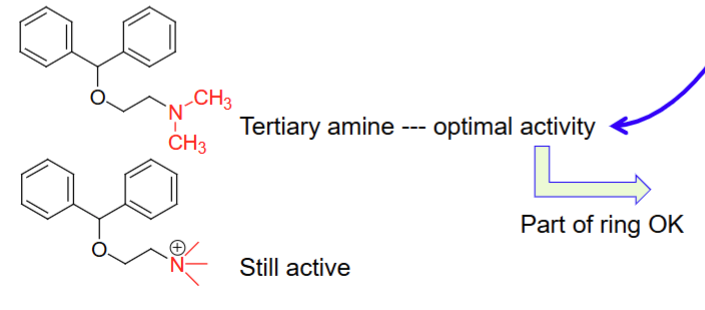
tertiary amine; quaternary charged amine
For the Alkyl amine domain for Histamine H1 antagonists, the ____ amine has optimal activity, while the ____ amine is also still active but not optimal
Increased anticholinergic effects - dry mouth, blurred vision, urinary retention ,etc.
The quaternary amine in the amine domain of H1 antagonists is still active but NOT preferred because
Ethanolamines; S enantiomer
The _____ subclass of H1 receptor antagonists are typically used for allergic reactions (benadryl and daramamine are examples), and the ___ enantiomer is the most potent
antihistamines; SSRI’s
Ethanolamines can also become _____ or _______
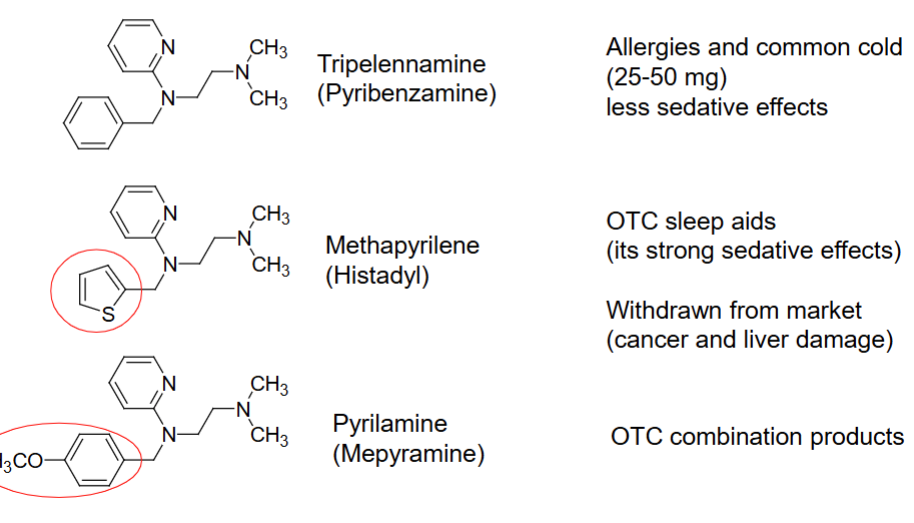
two nitrogen’s connected by CH2-CH2
Ethylenediamines have these two key structures
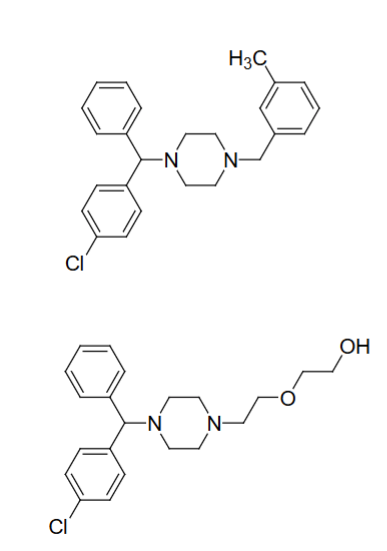
Meclizine(top); Hydroxyzine (bottom)
____ and ____ are examples of H1 antagonist ethylenediamines
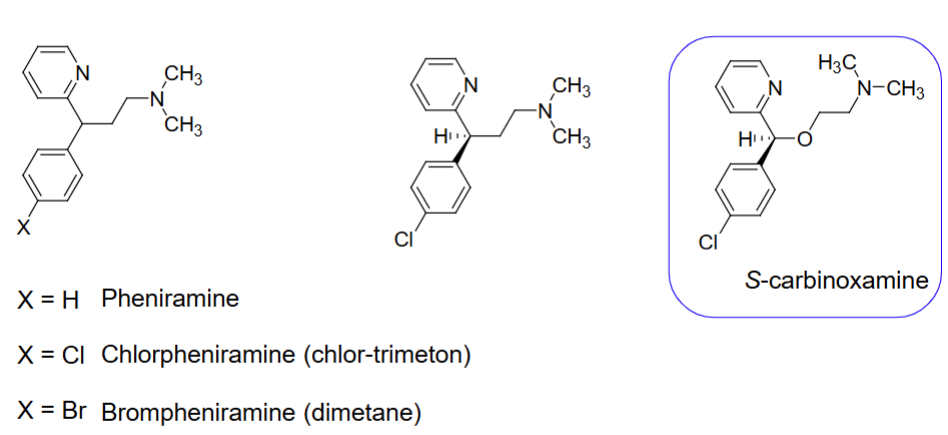
Structure of H1 antagonist subclass - propylamines
S isomer (d-isomer)
The____ isomer of H1 antagonists subclass propylamines is the most potent
Fenethazine, promethazine, and chlorpromazine
Three examples of tricyclic compounds that resemble H1 antagonist antihistamines
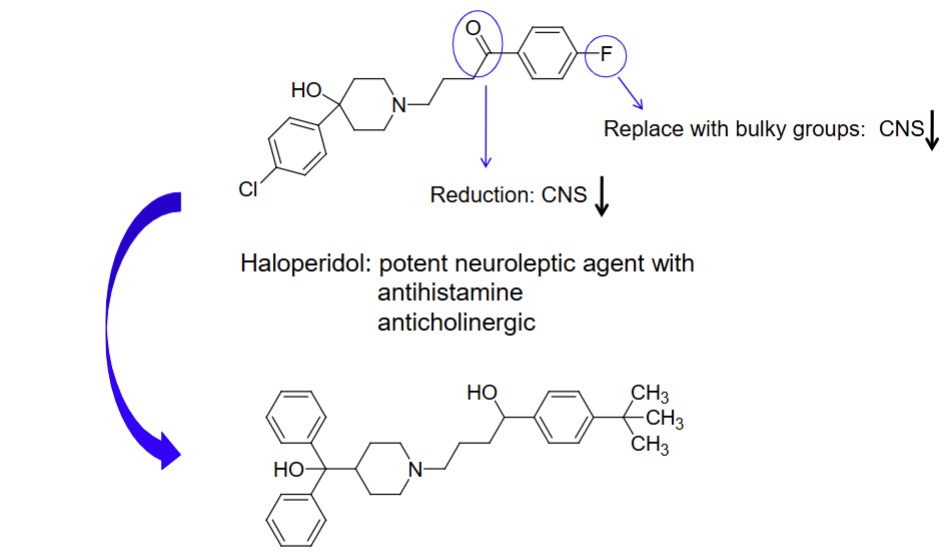
substituting ketone and halogen group with reduction (ketone) and bulky group (halogen)
For second gen non-sedating antihistamines, they are made by _________
Ventricular arrhythmias
Regular second gen antihistamines can have these effects
CYP450
To have 2nd gen antihistamines without arrhythmia side effects, the 2nd gens were metabolized into new drugs by ______
96% protein bound
20 hr half life
DOA: up to several weeks
CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIA!!!
Characteristics of Astemizole (withdrawn in 1999)
Loratidine; Cetirizine
_____ and ____ have no cardiac arrhythmias (2nd gens)
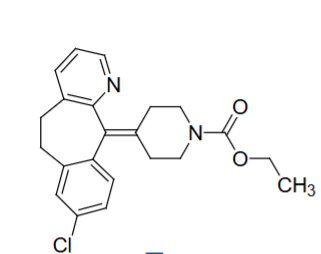
Structure of Loratidine
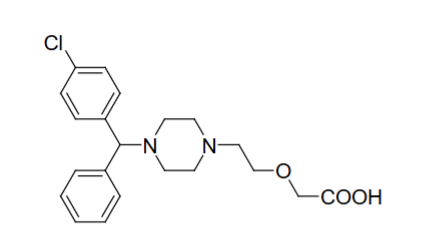
Structure of Cetirizine
Hydroxyzine
____ can become cetirizine by oxidizing the terminal alcohol
They might form zwitterionic species which have limited BBB penetration, thus less sedationa ctivity
Why do 2nd gen antihistamines become “non-sedating”?
Azelastine; active metabolite
____ is a dual H1-receptor antagonist and mast cell stabilizer (2nd gen) and was made a nasal spray/ophthalmic due to an _____ in the oral version
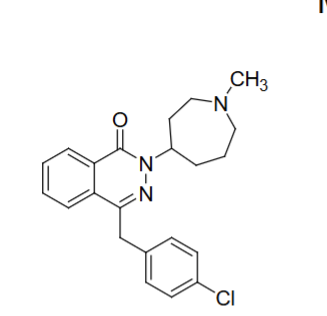
Azelastine structure
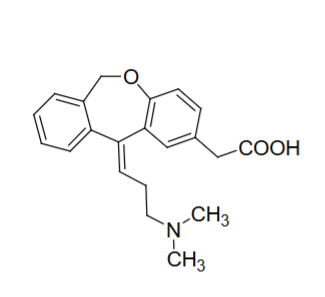
Olopatadine structure

Cimetidine
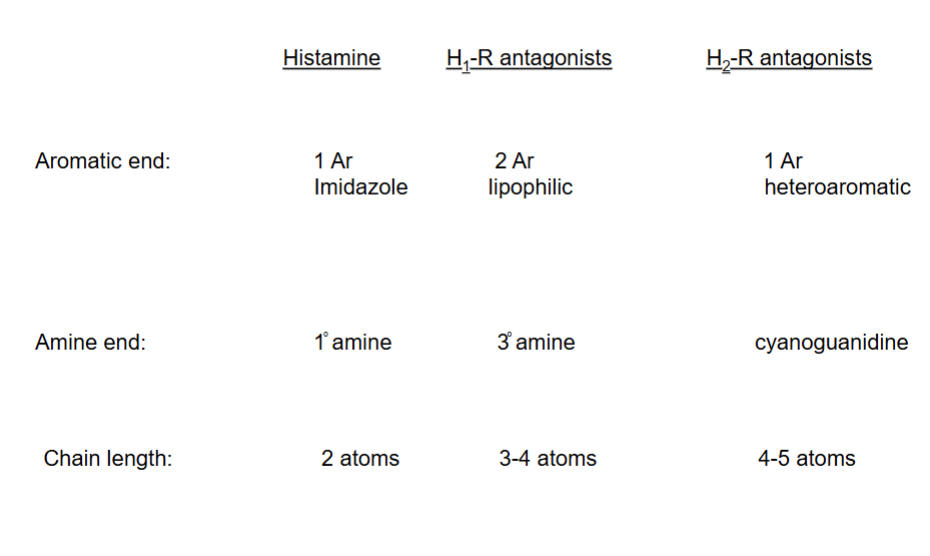
Summary of SAR of antihistamines