Muscle Pathology II
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
What is the most common cause of clostridial myositis in equines?
C. Septicum
What is the pathogenesis of Clostridal myositis in horses?
Clostridium gets into muscles via penetrated wounds and proliferates in anaerobic conditions
What are signs of all clostridial myositis?
Hemorrhagic mucles
Necrosis
Gas bubbles
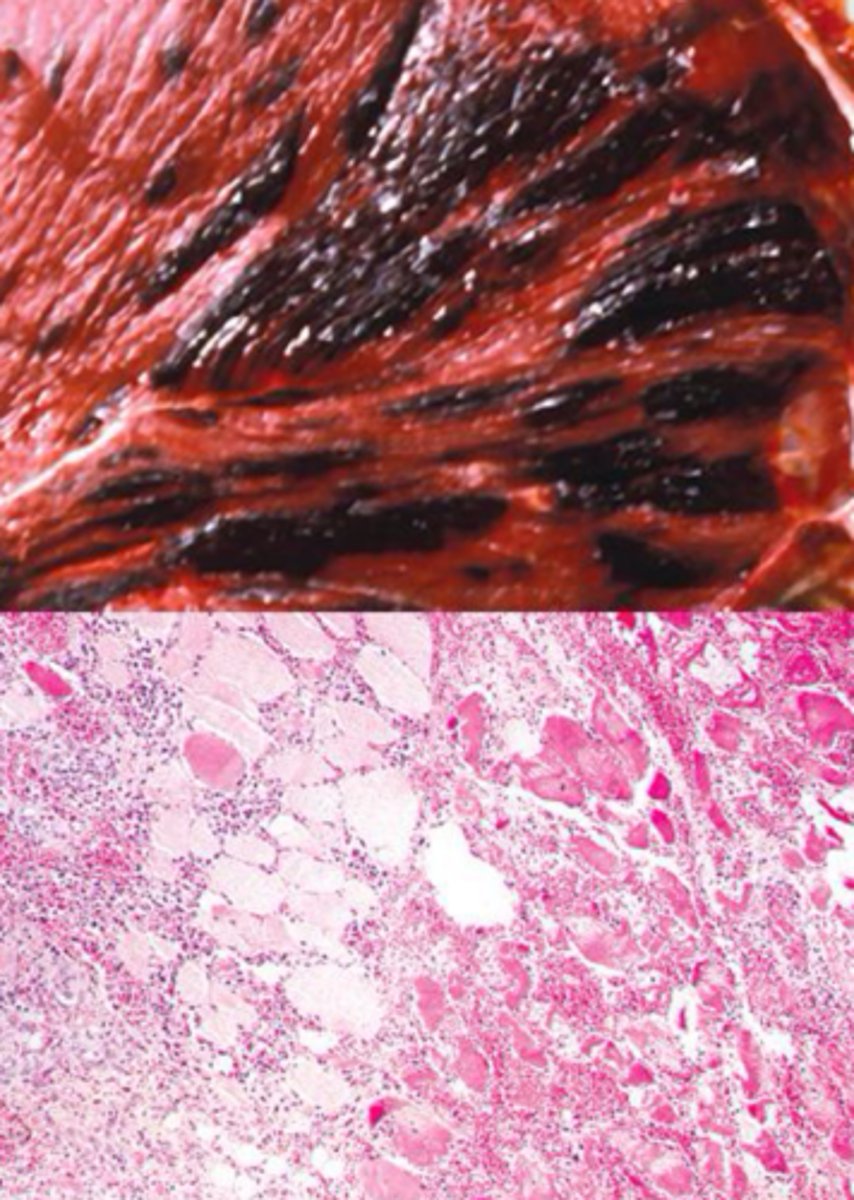
Identify the pathology?
Clostridial myostits - muscle necrosis
What will clostridium botulinum do?
Prevents release of ACh leading to a flaccid paralysis
What is used to dx Botulism?
Exclusion - toxin found in stomach contents/ food
-NO Findings on necropsy
What will cause pigeon fever?
Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis - gram + anaerobic bacteria
How does Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis cause dz?
Phospholipid D causes vascular damage - inhibits neutrophils
What are clinical signs of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis?
Intramuscular abscesses mostly in pectoral musculature
What is purpura hemorrhagica?
Type 3 hypersensitivity attacking vasculature
-IgA and strep M antigen cause infarction
What are clinical signs of purpura hemorrhagica?
Myoglobinuria
Elevated CK and AST
Cutaneous hemorrhage
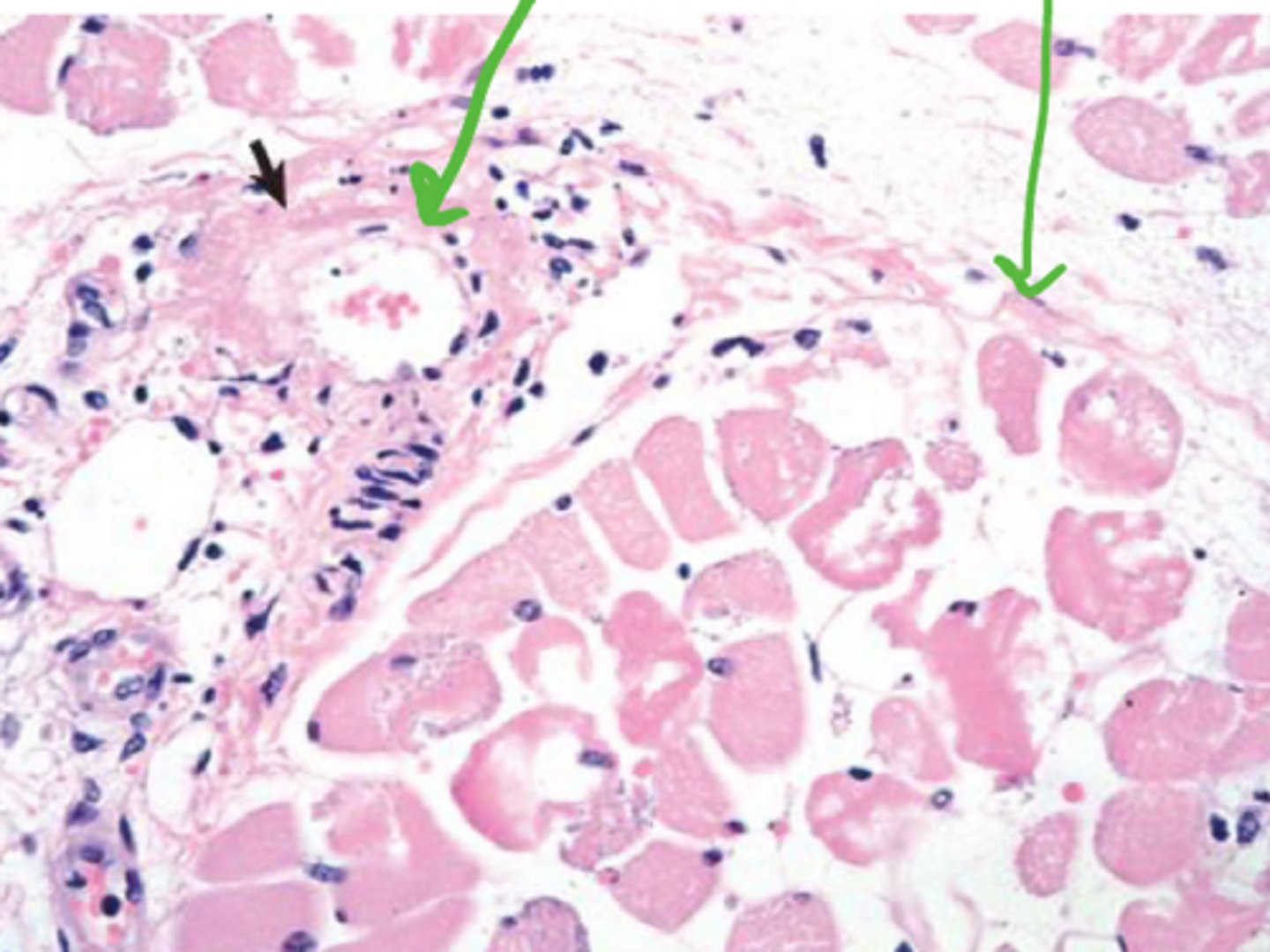
How is purpura hemorrhagica different from clostridial myositis?
No gas bubbles
What is streptococcal associated rhabdomyolysis and muscle atrophy?
An immune mediated damage due to cross reaction of muscle proteins and strep antigen - MHC will be increased on muscle membranes
What are classical signs of streptococcal associated rhabdomyolysis and muscle atrophy?
Muscle atrophy over the paraspinal and gluteal muscles
-high elevation of CK and AST (no purpura hemorrhagica signs)
What animals are most commonly affected by streptococcal associated rhabdomyolysis and muscle atrophy?
Young Quarter horses
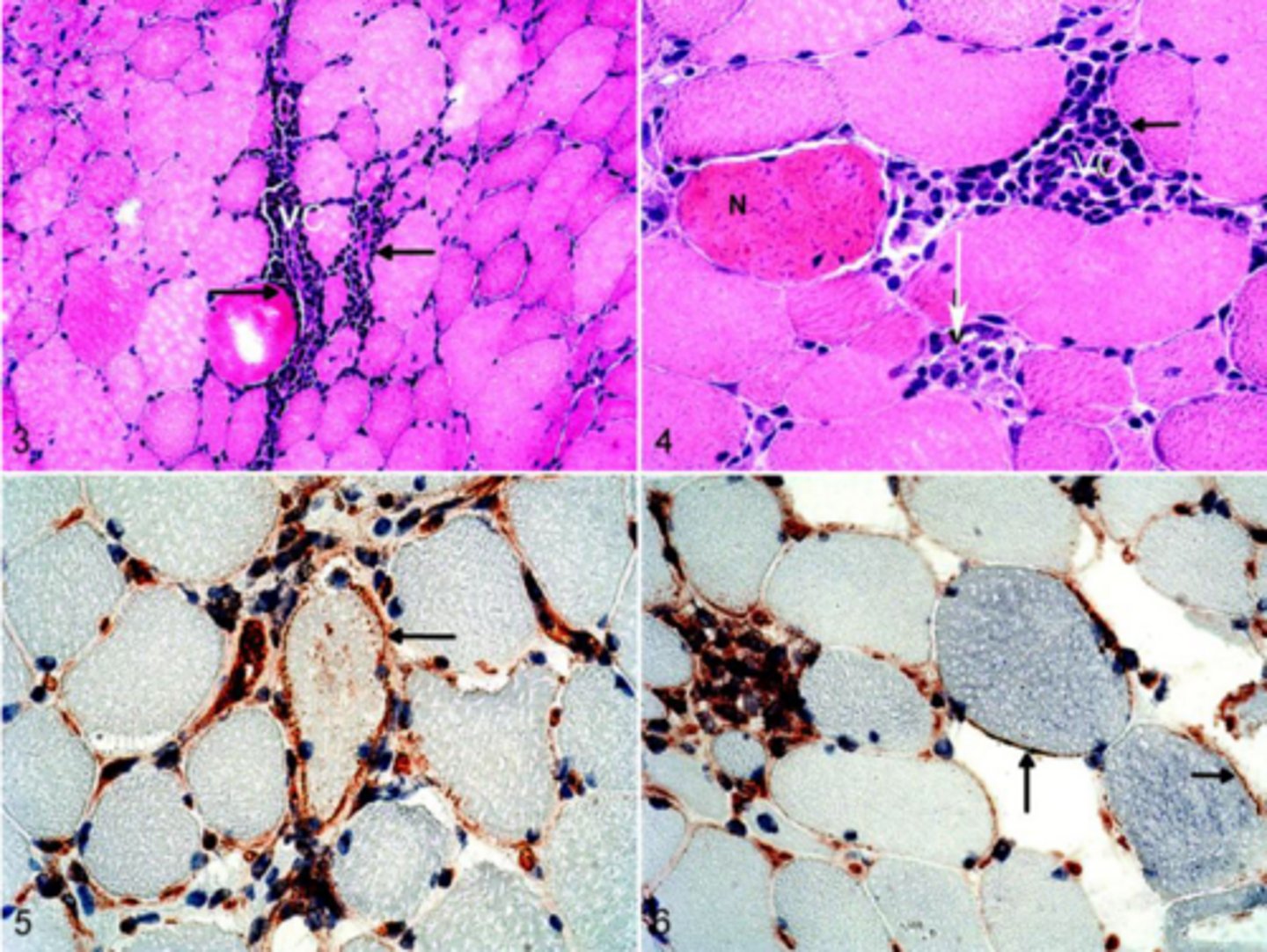
What stain is used to see streptococcal associated rhabdomyolysis and muscle atrophy
IHC -Lymphocytes between muscles and perivascular lymphocytic cuffing
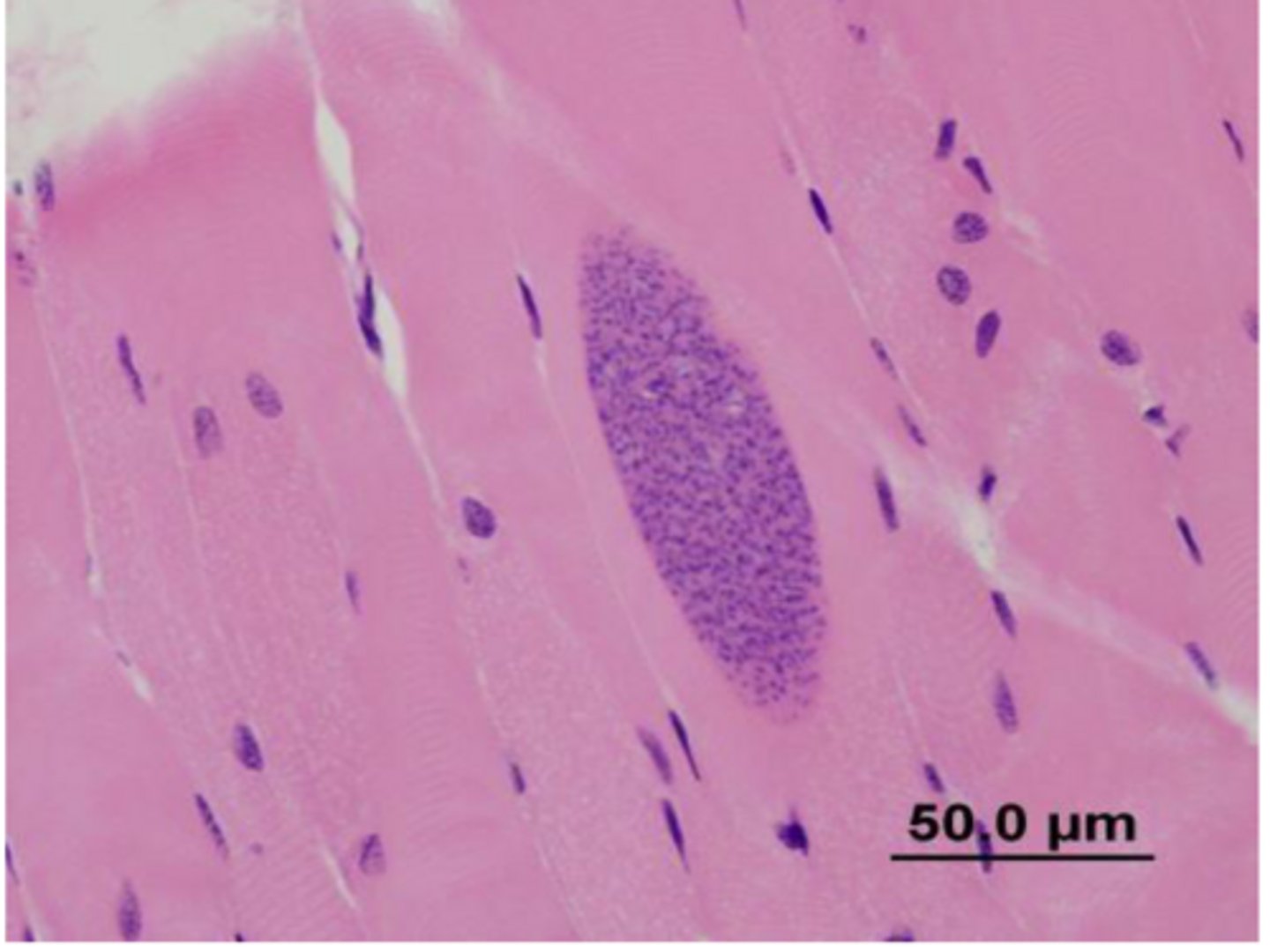
In most species Sarcocystis will be an ___ finding?
Insidental - protozoal
What does a lack of vitamin E and selenium do to the muscle?
Ehnance oxidative inj
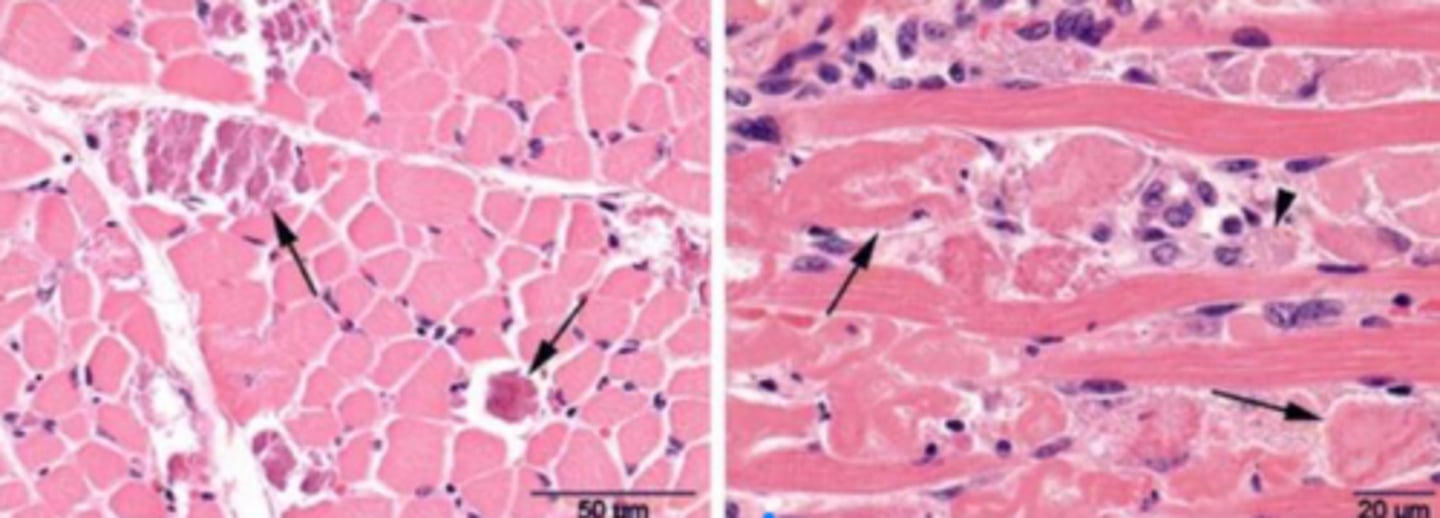
What horses are most susceptible to nutritional myopathy?
Foals to young adults problems swallowing/ atrophy of masticatory muscles
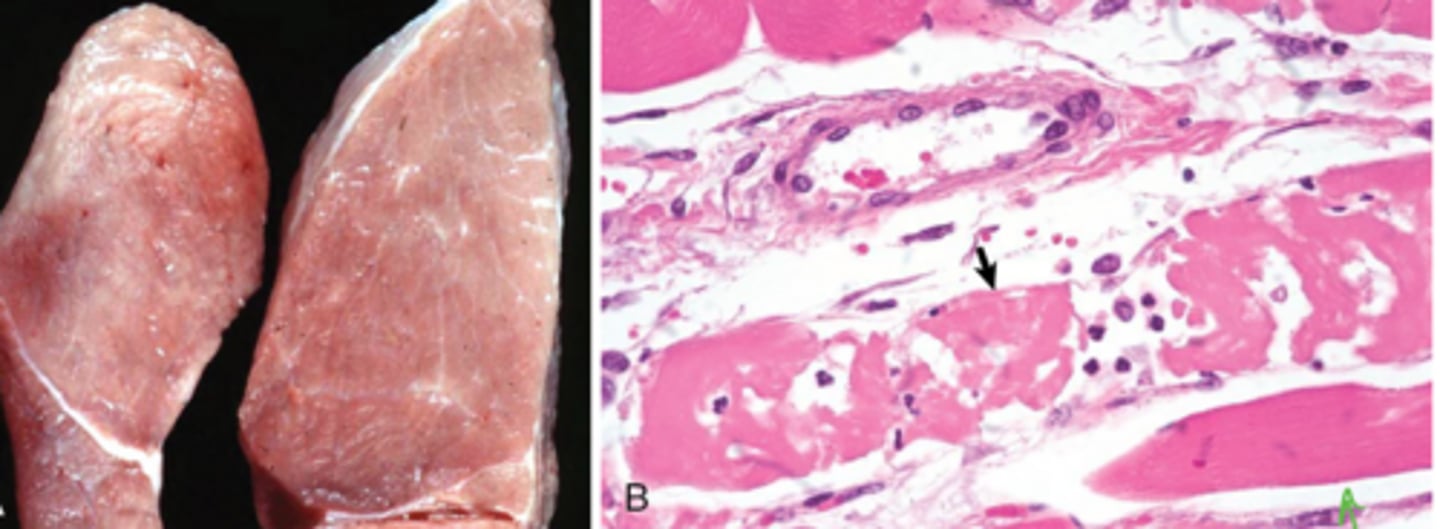
What animas are most susceptible to iodophore tox?
Horses - Ca2+ over load leading to sk and cardiac muscle necrosis
-replaced by fibrosis
What is going to cause equine polysaccharide storage myopathy (EPSSM)?
Autosomal dominant trait due to a mutation of Glycogen synthase 1 gene - Glycogen storage dz
What is the dx for EPSSM?
PAS - histology preferred
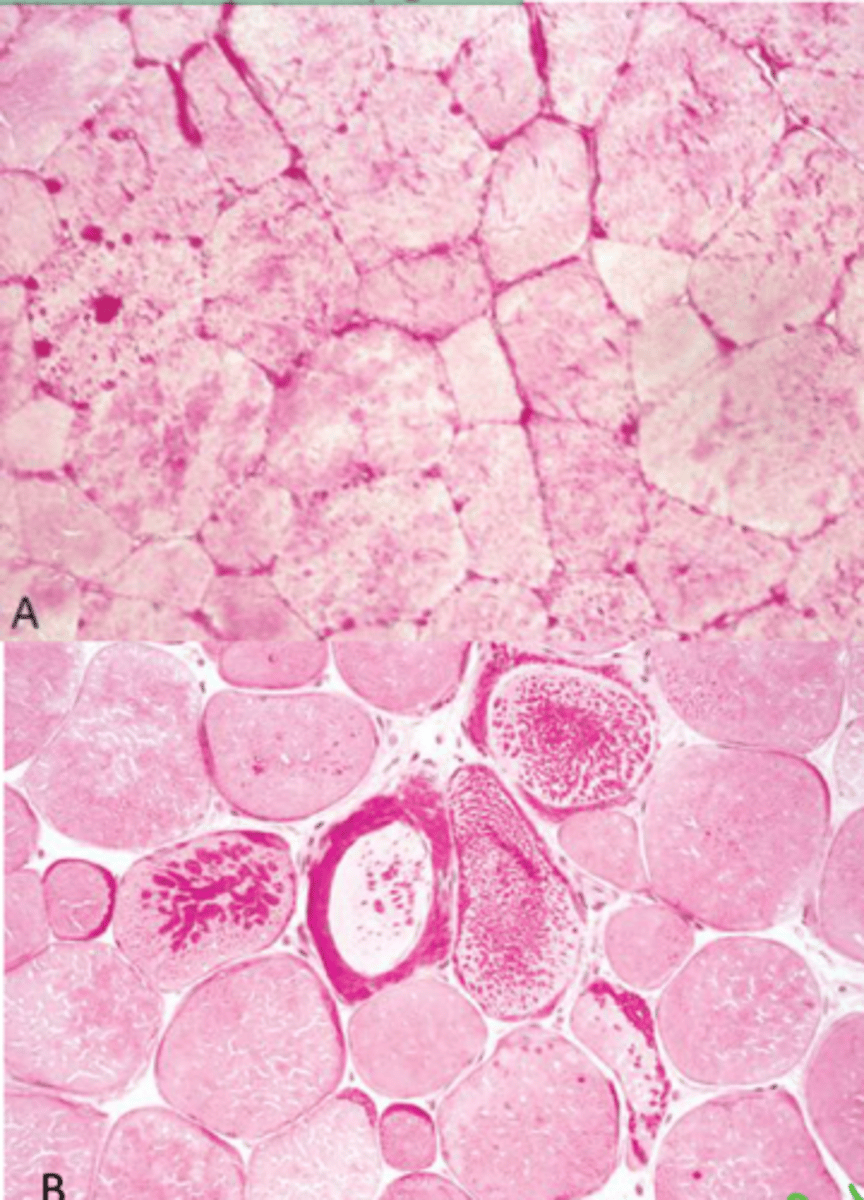
Identify the pathology?
EPSSM - Glycogen granules in muscle
What is going to cause Glycogen branching enzyme deficiency?
Autosomal recessive trait - deficiency of GBE type 4- no glycogen branching
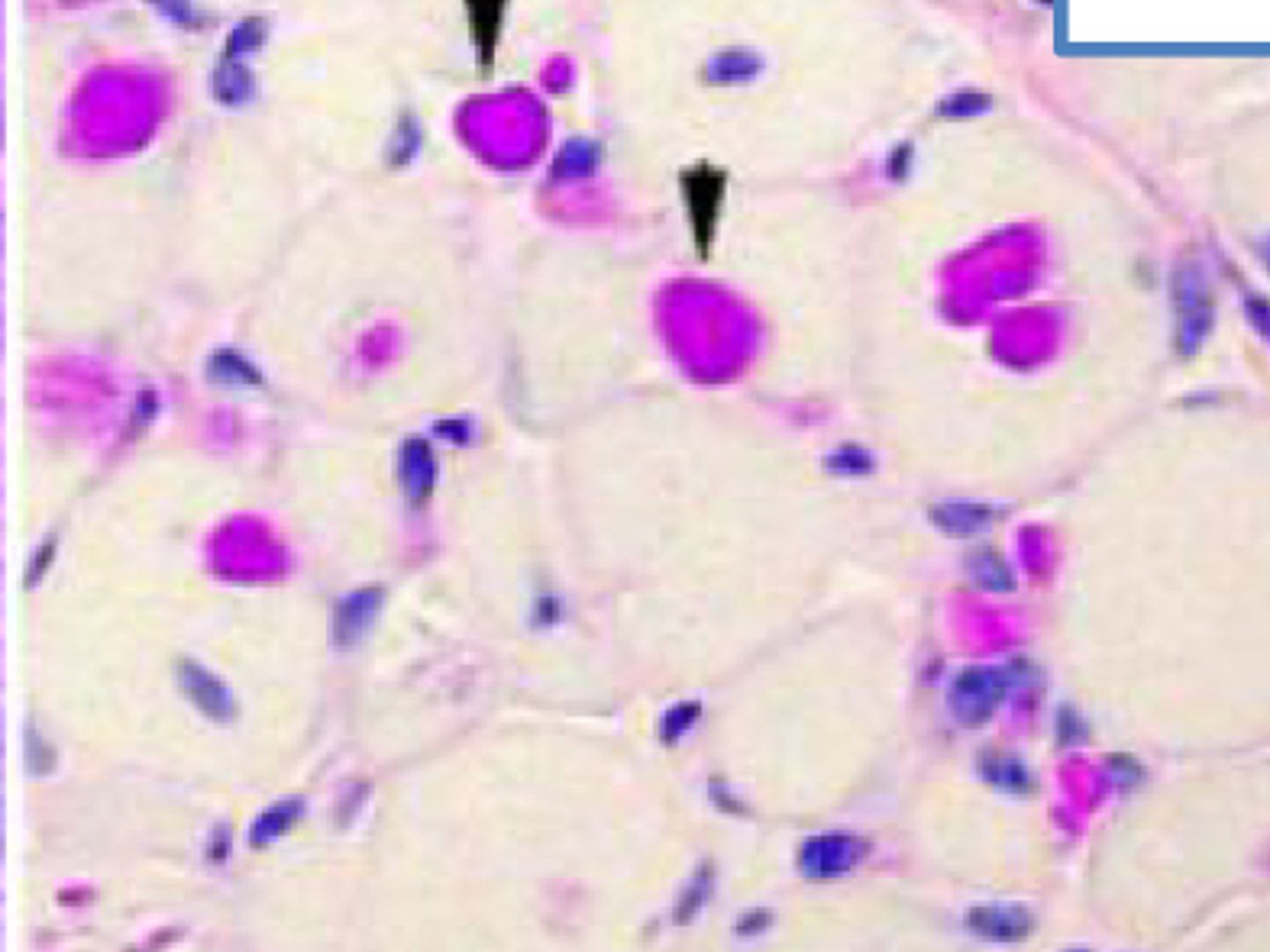
What stain is used to dx GBE deficiency?
PAS - Globs of glycogen
Most animals w/ GBE deficiency will be ___?
Still born/ aborted - not tx
What is equine exertion rhabdomyolysis?
Tying up - Stiff gait/ reluctancy to move w/ swelling and necrosis of muscles - during or after exercise
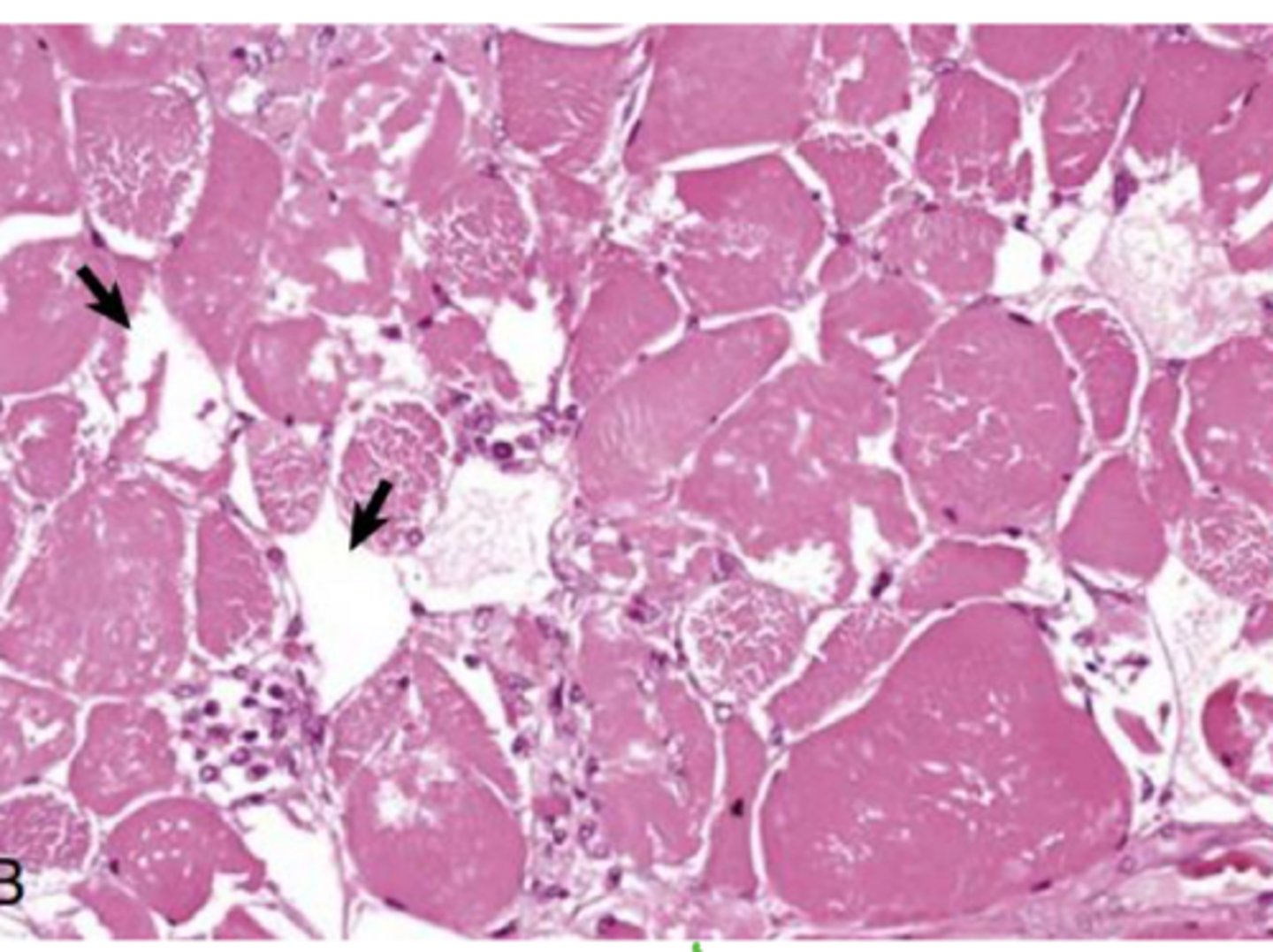
What will cells will equine exertion rhabdomyolysis target?
Type 2 myofibrils
What is ischemic myopathy?
Pressure vasculature due to recumbency causing infarct and necrosis of pectoral, abdominal and limb muscles
What endocrine disorder in horses can lead to muscle atrophy and type 2 atrophy with weakness?
PPID
What is Sweeney?
Unilateral scapular muscle atrophy - trauma to the supra scapular nerve -poorly fit harness
What is stringhalt in horses?
Exaggerated flexion of one or both hindlimb
What plant in Australia can cause stringhalt?
Hypochoeris radicatus
What will cause equine protozoal myeloencephalitis?
Sarcocystis neurona (rarely Neospora)
-denervation atrophy of facial and gluteal muscles
What causes Equine motor neuron dz?
Vit E deficiency - rapid muscle wasting -yellow to tan gelatinous texture of muscle
What is going to cause clostridial myositis black leg in cattle?
Clostridium chauvoei
What is the pathogenesis of clostridial myositis in cattle?
Ingestion of organism to the muscle then trauma all lead to anaerobic environment and toxin production - hemorrhage, edema, necrosis
What botulism toxins are Cattle most susceptible to?
C and D
how will a muscles be infected w/ Trueperella pyogenes and what will they look like?
Via contamination of wounds -> Yellow-green w/ foul-smelling
What causes wooden tongue?
Actinobacillus lignieresii - granulomatous/ fibrosing glossitis
What is going to cause Lumpy jaw?
Actinomyces bovis - osteomylitis - boney proliferation = lumpy
What is eosinophilic myositis?
A sarcocystis infection of cattle that leads to a hypersensitivity - green coloration of muscle
What will Neospora caninum do to cattle?
No clinical dz in adults
Abortion
What is the most common plant toxicity that causes degenerative myopathy in cattle?
Senna occidentalis
What is steatosis?
Muscle replacement w/ adipocytes
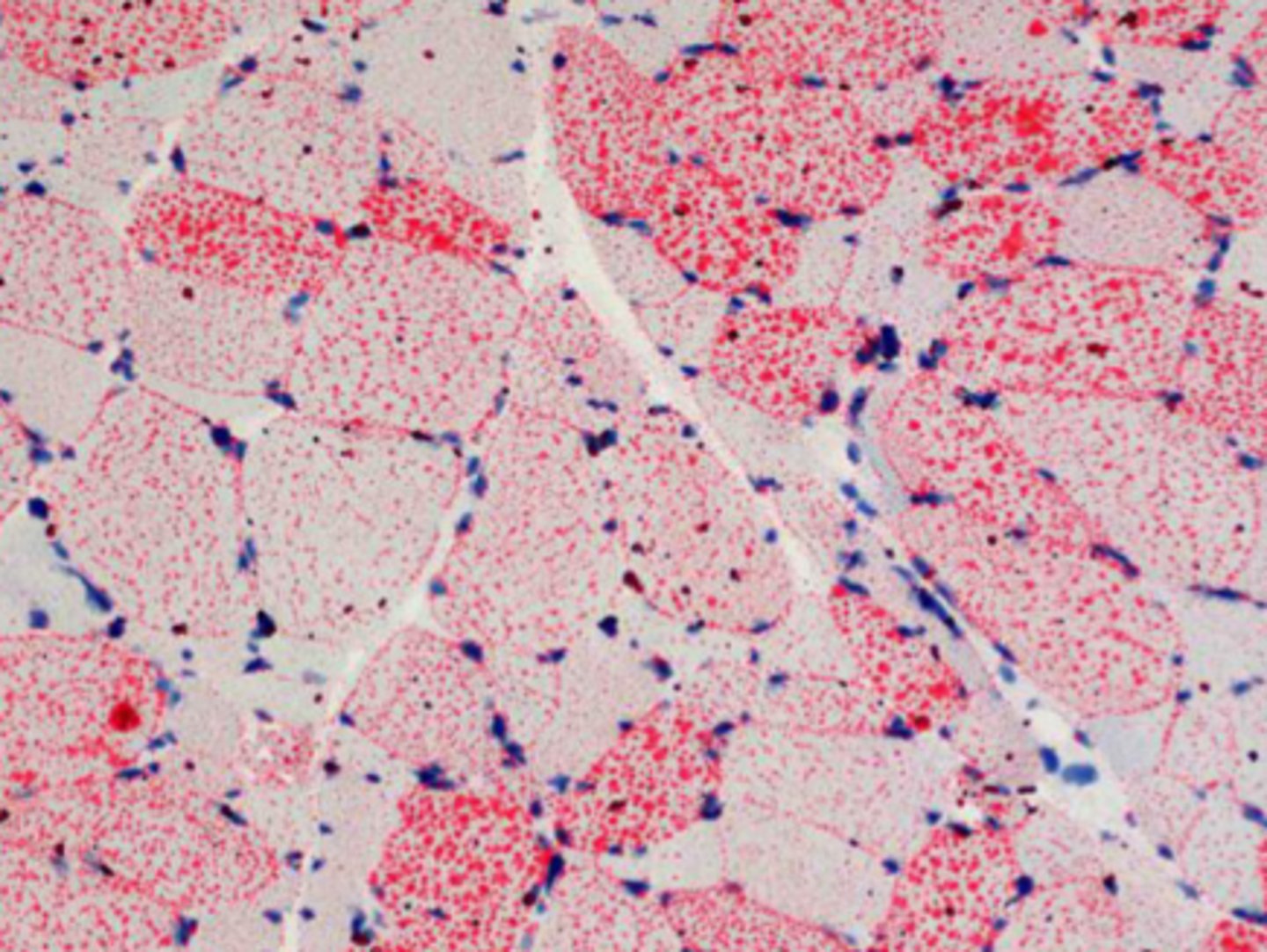
What stains can be used to see steatosis?
Oil-redO stain or Sudan black stain
What is the most common inherited myopathy of cattle?
Defect of myostatin gene - congenital muscular hyperplasia - double muscling
What does prosopis glandulosa cause in goats?
Degenerations of motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve -> masticatory muscles - emaciation from lack of eating
What is myotonia in goats?
Inherited autosomal dominant defect in skeletal muscle Cl channels
What are clinical signs of myotonia in goats?
Fainting goats - stiffness for 5-20s
What is going to cause clostridial myositis (Malignant edema) in pigs?
C. septicum
What are signs of clostridial myositis in pigs?
Swelling of neck and blue color
Gangrene
What is a parasitic myopathy that is in pigs?
Trichinella spiralis
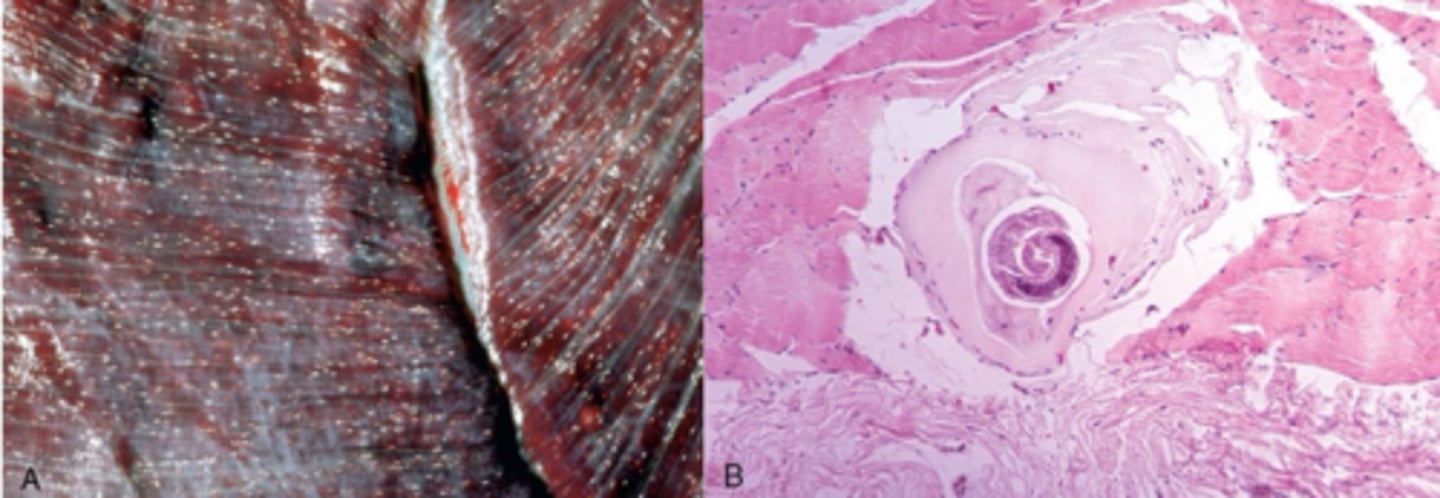
What is the pathology of parasitic myopathy in pigs?
Lives in SI moves to blood stream and encysts on myofibers in the diaphragm masticory and intercostal muscles
Senna/Cassia occidentali will affect the ___ and gossypol will affect the ___?
Diaphragm
Sk muscle/ cardia muscle
What is Myofibrillar hypoplasia/ splay leg?
Young piglets will abduct limbs progressively flattening the sternum
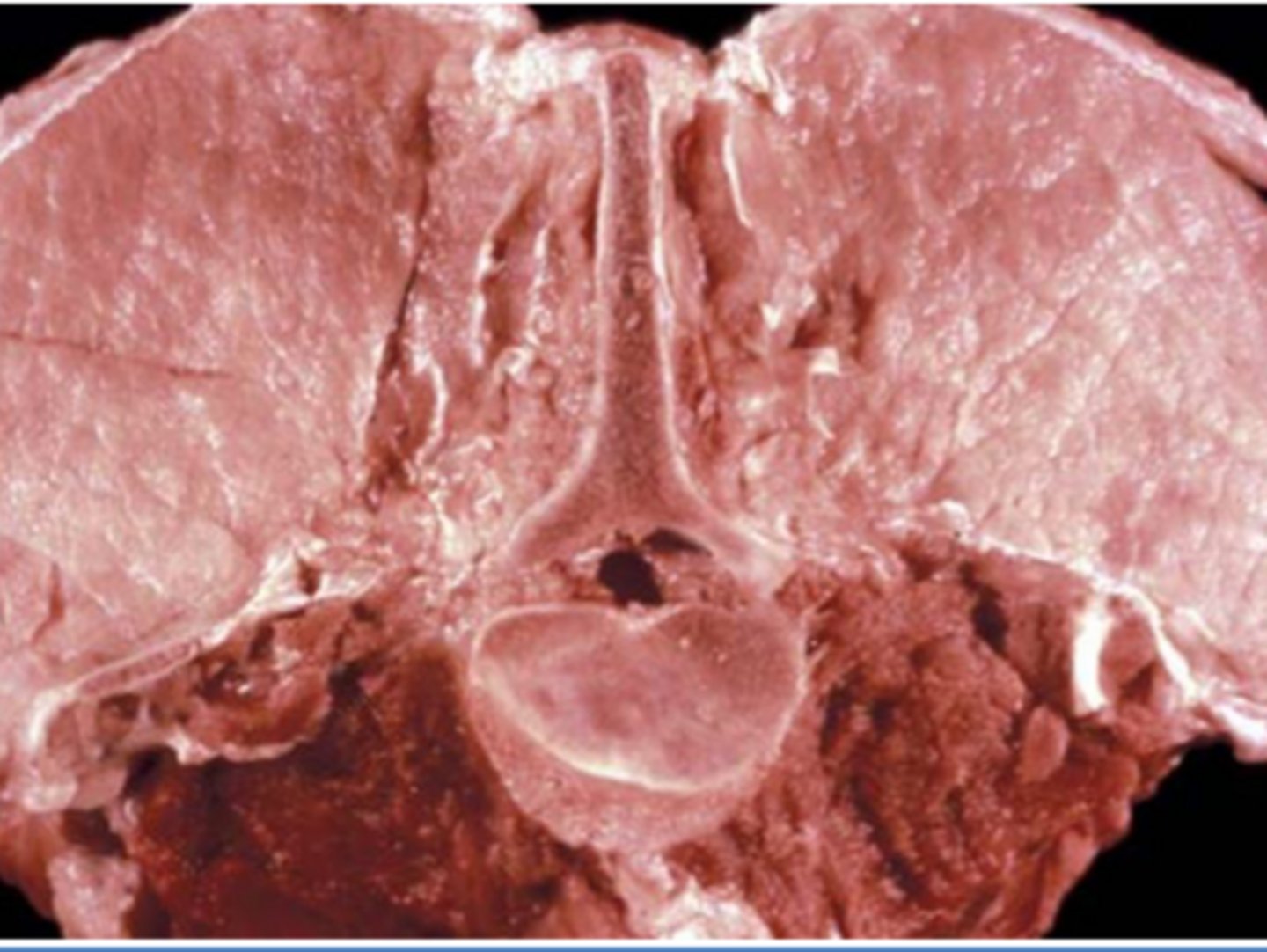
What is malignant hyperthermia?
Defect in ryanodine receptors - excessive contrations leads to increased heat production
- halothane anesthesia/ stress causes
What is going to cause protozoal myopathy in dogs?
Neospora caninum- affect ventral spinal roots causing denervation atrophy of muscles
What is going to cause X-linked muscular dystrophy in dogs?
Dystrophin gene defect
- leads to progressive weakness
- Resp failure related to sever diaphragmatic necrosis
-death
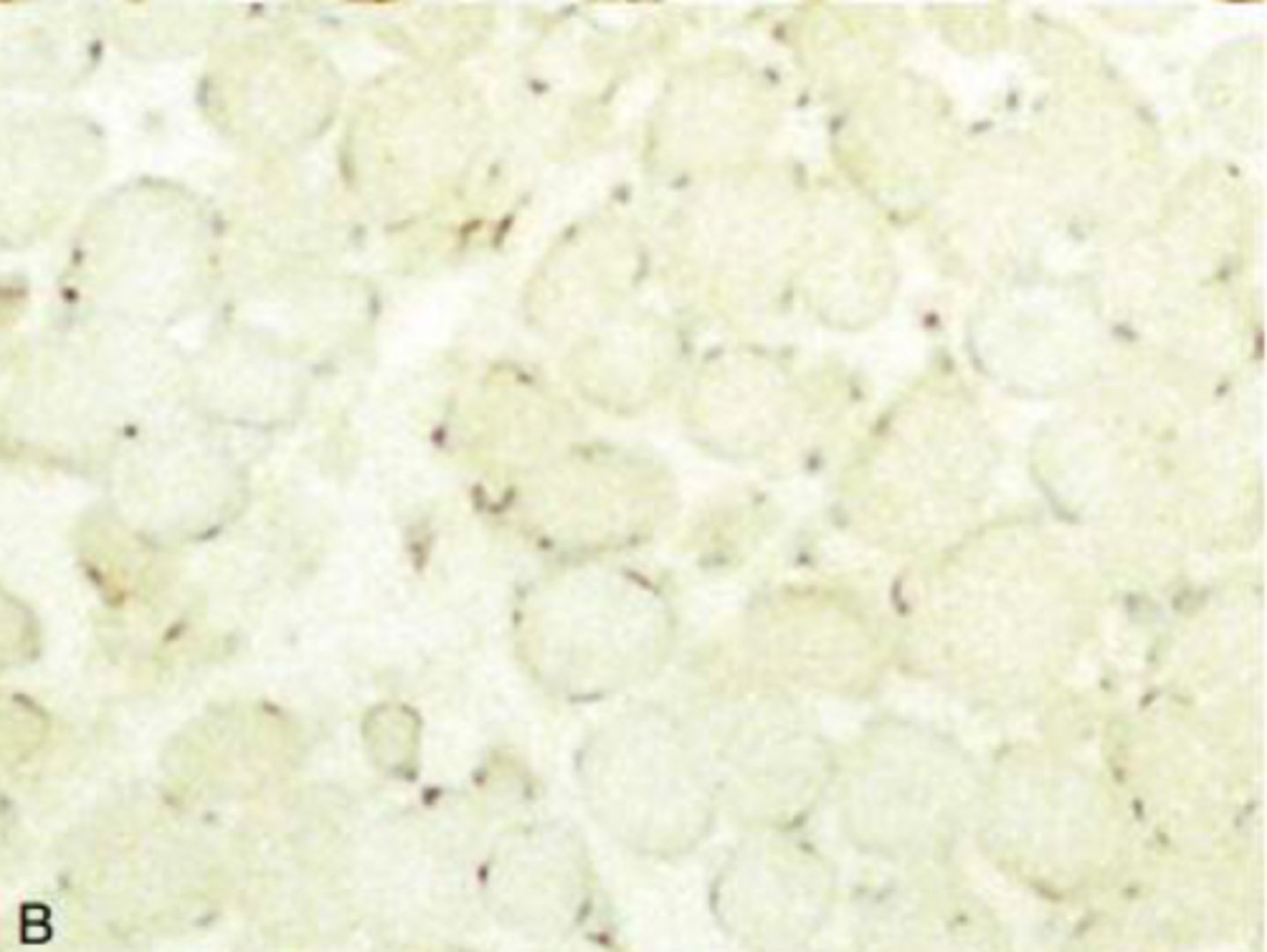
How is X-linked muscular dystrophy in dogs DX?
Muscle biopsy IHC - lack of brown means dystrophin is missing
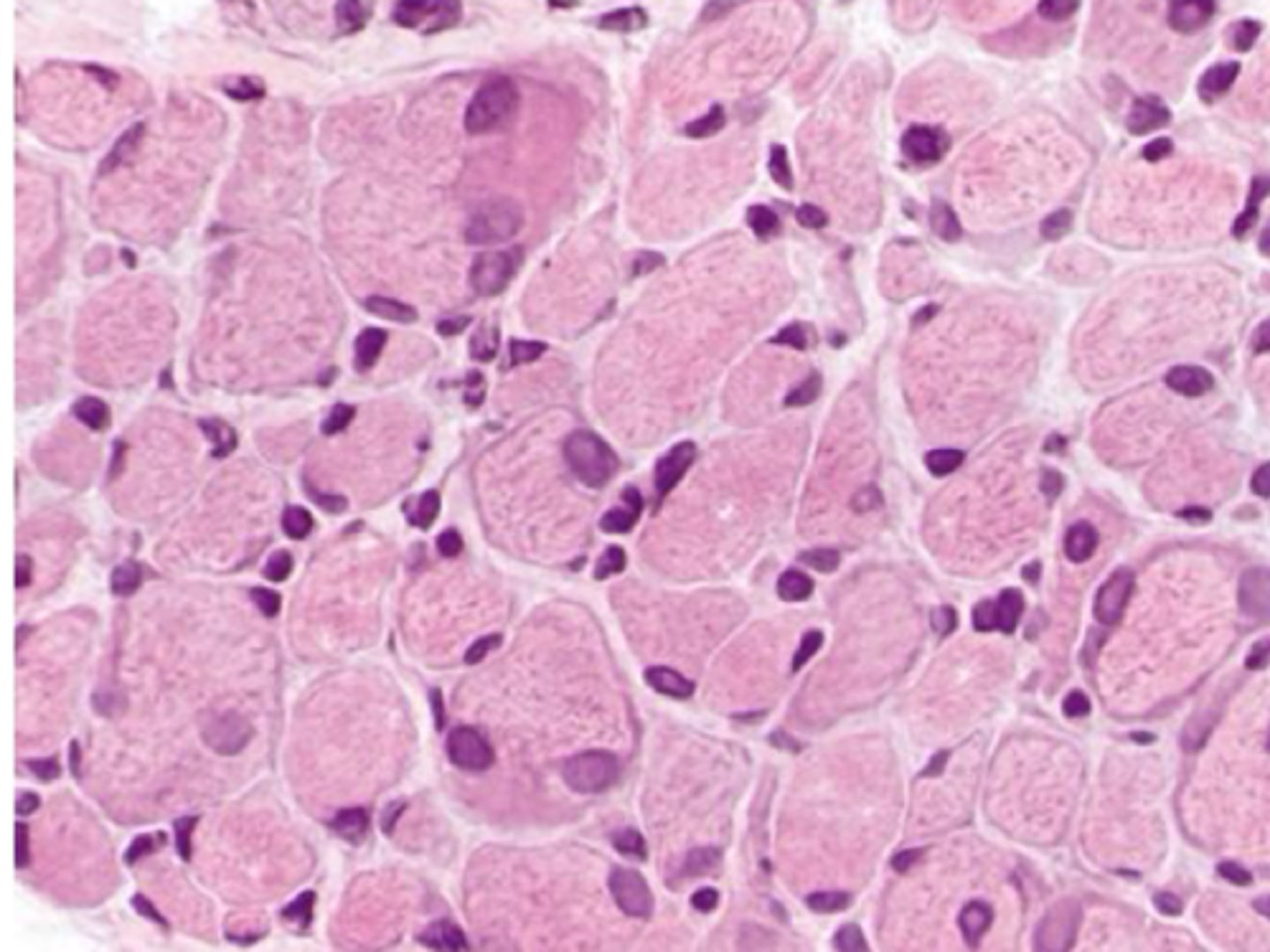
What are clinical signs of Labrador retriever Centronuclear myopathy?
Neuromuscular weakness due to recessive trait
Loss of patellar/triceps reflexes
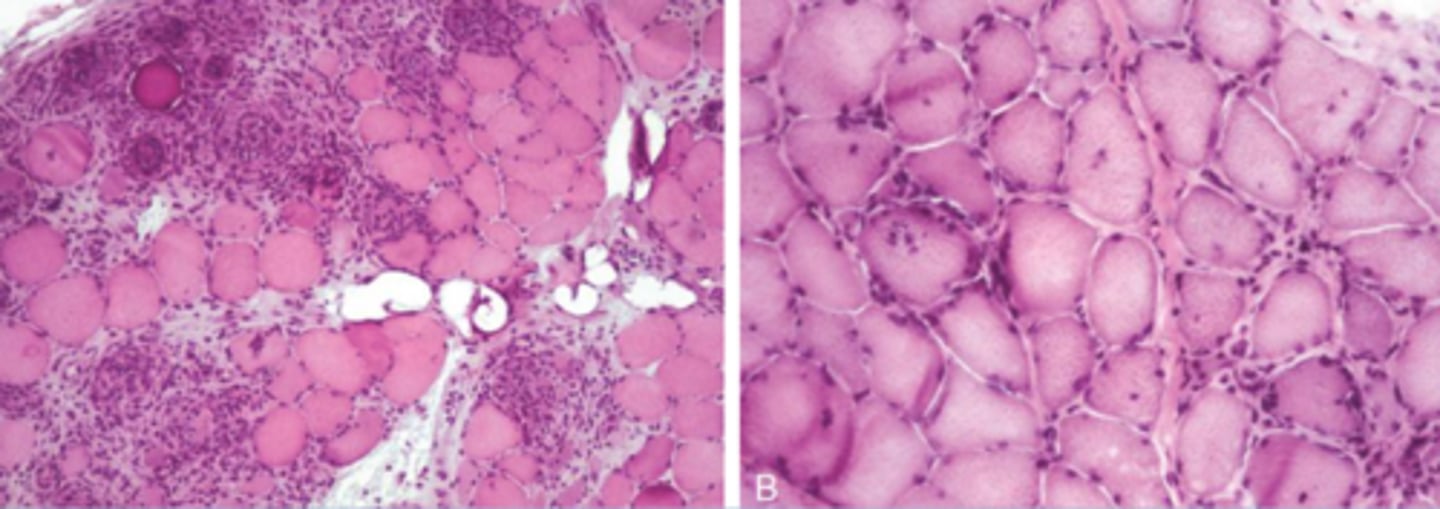
What is Polymyositis?
Antibodies against sk muscle - lymphocytic t-cell rich necrosis
-chronic can see Fibrosis
What is masticatory myositis?
Antibodies agains type 2M myosin - B-lymphocytes and eosinophils
What are clinical signs of acute masticatory myositis?
Bilateral symmetric swelling of temporals and master muscle - can't open mouth
How is masticatory myositis and polymyositis differentiated?
Serology testing for anti type 2M myosin antibodies
How is X-linked muscular dystrophy different in cats?
Hypertrophy of muscles
How does FIV cause myositiosi?
Lymphocytic inflammation w/ T cells
What metabolic condition will cause peripheral neuropathy/ denervation of atrophy?
Diabetes mellitus
What are clinical signs of chronic masticatory myositis?
bilaterally symmetric atrophy of temporalis and masseter muscles