Chapter 3: Electric Forces and Fields
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
It deals with electric charges and fields associated with it.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
1
New cards
Electric Charge
1. In an isolated system, the charge is always conserved.
2. Protons and electrons have a quality called electric charge.
3. The charge is invariant in nature.
4. The charge is quantized.
* ***(Q = n e)***
* e = 1.6 \* 10^-19 C
* n = no. of electrons
* Q = charge
2
New cards
Ionisation
It involves addition or removal of electrons.
3
New cards
Coulomb’s Law
The electric force between two particles with charges q1 and q2 separated by distance r has a magnitude by the equation:
***F = Kq1q2/r^2***
* F = force
* K = coulomb’s constant
* q1 and q2 = charges
* r = distance between the charges
***F = Kq1q2/r^2***
* F = force
* K = coulomb’s constant
* q1 and q2 = charges
* r = distance between the charges
4
New cards
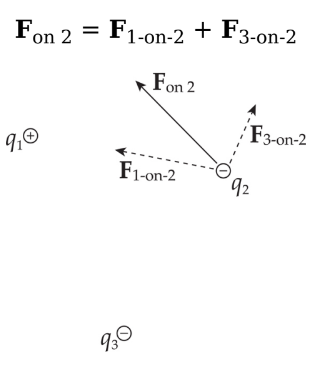
Addition of forces
Consider three point charges: q1, q2, and q3. The total electric force acting on, say, is simply the sum of F1-on-2, the electric force on q2 due to q1, and F3-on-2, the electric force on q2 due to q3:
5
New cards
Electric Field
The space is surrounded by a charge in which another charged particle experiences the force.
***E = F on q/ q***
It describes the electric field vector from the force vector on a positive charge.
***E = F on q/ q***
It describes the electric field vector from the force vector on a positive charge.
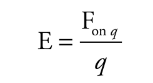
6
New cards
Electric field due to a point charge
The electric field surrounding the point charge is:
***E = 1/4πε0 * Q/r^2***
* E = electric field
* Q = charge
* r = distance between charges
* ε0 = permittivity of free space
***E = 1/4πε0 * Q/r^2***
* E = electric field
* Q = charge
* r = distance between charges
* ε0 = permittivity of free space
7
New cards
Three types of electric field
* Radial field
* It is generated by a collection of point charges.
* An infinite sheet of charge.
* It is generated by a collection of point charges.
* An infinite sheet of charge.
8
New cards
electric field lines
* The electric fields follow the same addition properties as the electric force.
* The electric field lines never cross.
* The electric field lines never cross.
9
New cards
The uniform electric field
* A lot of problems deal with the uniform electric field.
* The field may be taken as uniform at least in the middle.
* The uniform field just signifies the constant force.
* The field may be taken as uniform at least in the middle.
* The uniform field just signifies the constant force.
10
New cards
Conductors
Materials which allow the flow of excess charge without resisting it.
11
New cards
Insulators
Materials that resist the flow of electrons.
12
New cards
Charging by friction
It involves rubbing the insulator against another material, thereby stripping electrons from one to another material.
13
New cards
Charging through conduction
When we connect two conductors charge flows from one to another until the potential of both the conductors becomes the same.
14
New cards
Charging through induction
The process of charging by induction may be used to redistribute charges among a pair of neutrally charged spheres.
15
New cards
If the sphere is an insulator made up of glass
* There aren’t any free electrons.
* The atoms make up the sphere will become polarised.
* The atoms make up the sphere will become polarised.
16
New cards
charge of proton
positive
17
New cards
charge of electron
negative
18
New cards
law of charges
the directions of the electric forces on the charges of mutual interaction; like charges repel, opposite charges attract.
19
New cards
net charge
an object with an excess of positive or negative charges
20
New cards
electrostatic charging
accomplished by Friction, Contact, Induction, or Polarization
21
New cards
Charging by Polarization
Charging by Polarization
22
New cards
How do objects become charged?
By gaining/losing electrons
23
New cards
Electric charge is always _______.
Conserved
24
New cards
What is the numerical value of one charge?
1 e = 1.6 x 10^-19 Coulombs
25
New cards
The SI unit of a charge is in ______.
coulombs
26
New cards
What happens when an insulator is charged?
Only the small spot which was directly contacted with a charge remains charged.
27
New cards
What is the name of materials that contain properties somewhere between conductors and insulators?
semiconductors
28
New cards
A dipole consists of:
two equal and opposite charged
29
New cards
In what direction to field lines go?
From positive to negative charges ALWAYS
30
New cards
What indicated field strength?
The density of field lines
31
New cards
What do few field lines between charges indicate?
a weak field
32
New cards
Which one of the following rules, laws, or principles describes how the net electric charge of an isolated system undergoing any process remains constant?
law of conservation of electric charge