TOPIC 1 - Types of forces and resultant forces
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
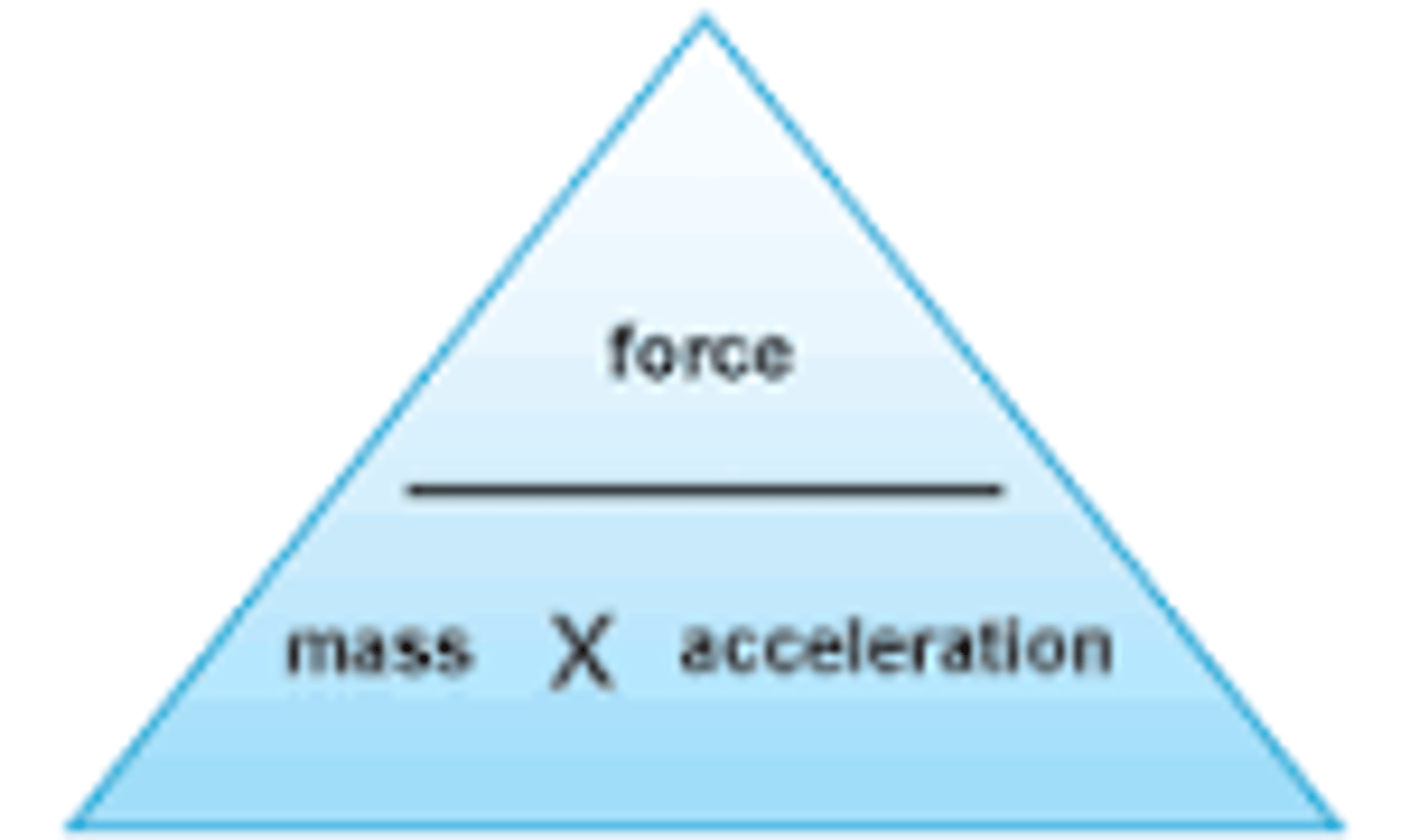
Equation linking force, mass and acceleration
Force = mass x acceleration
(F = ma)
Definition of a force
A force is a push or pull.
- There are 9 types of forces:
Gravity or weight
A force that acts straight downwards towards earth's center.

Reaction force
Acts perpendicular to a surface and away from it.

Electrostatic force
The force between two charged objects. The direction depends on the type of charge (like charges repel, opposite attract.)

Thrust
A reaction force (push or pull)

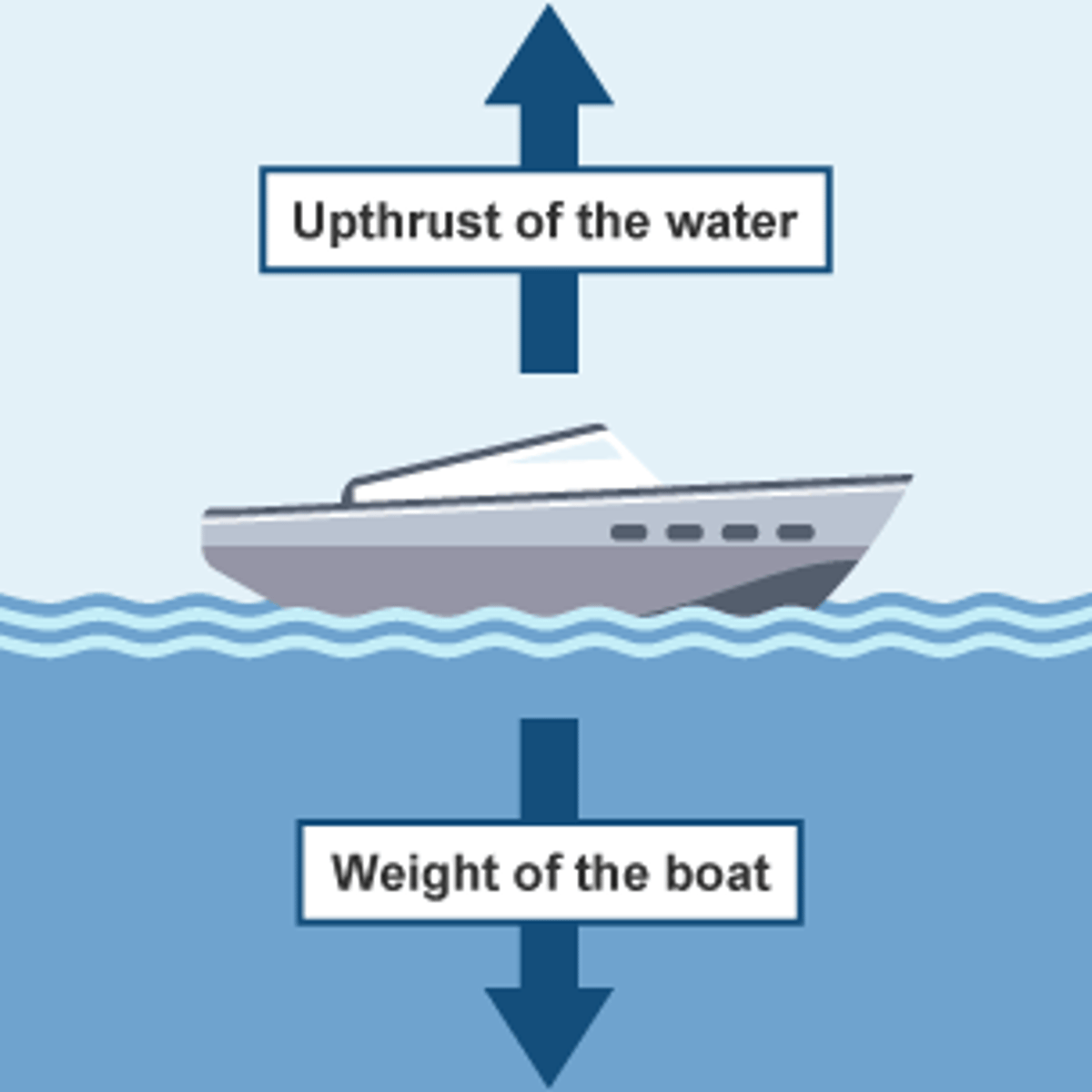
Upthrust
The upwards force of any object in fluid.
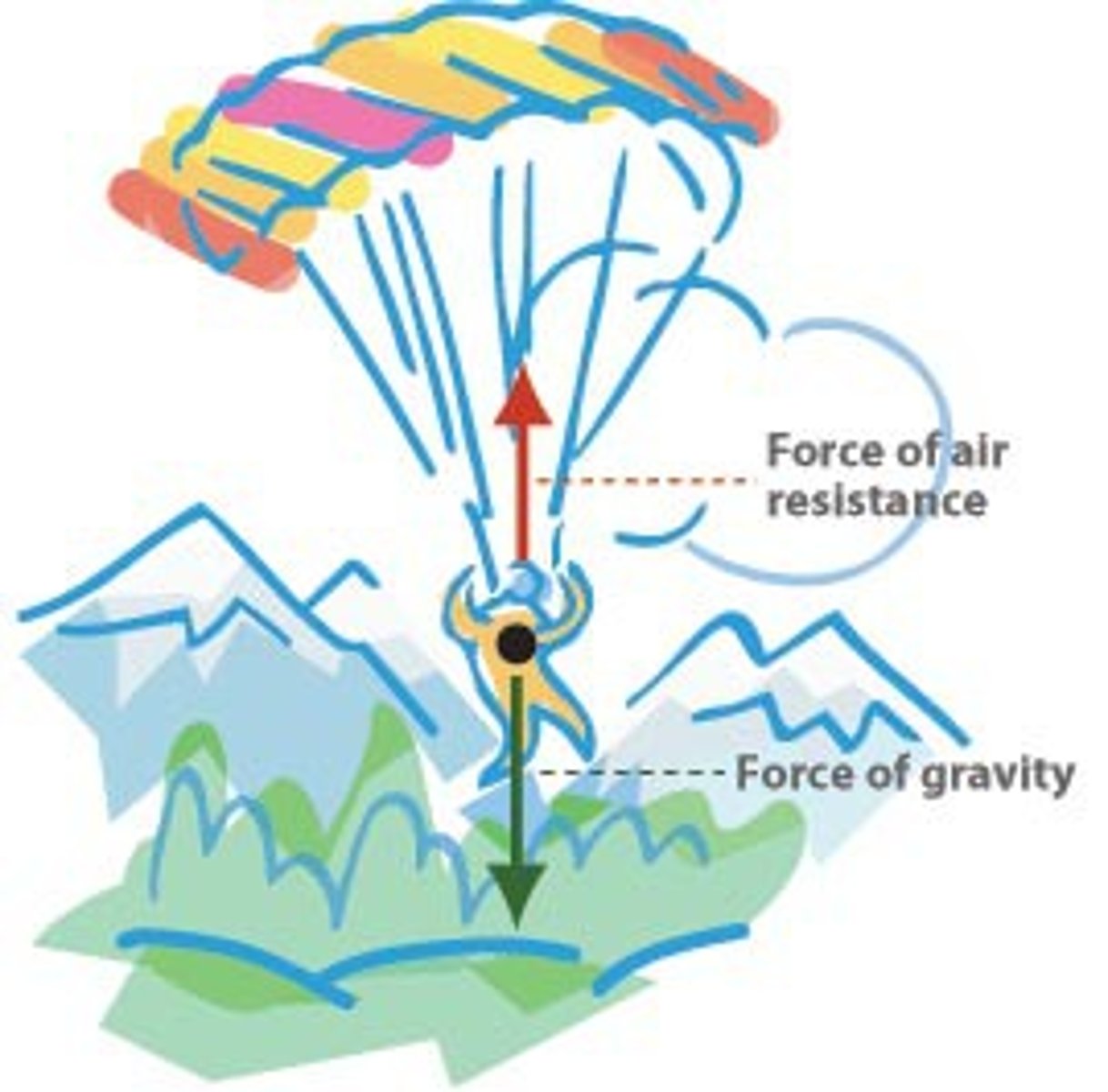
Drag, air resistance or friction
A force that slows down an object in motion.
Lift
A force that is perpendicular to the oncoming flow direction.
Tension
A force that stretches an object.
Compression
Forces that squeeze an object.

Why is force a vector quantity?
Force has both magnitude and direction.
Definition of friction
Friction is a force that opposes motion.
Describe the effects of forces between bodies (3)
- Changes in SPEED: forces can cause a body in motion to speed up or slow down.
- Changes in DIRECTION: forces can cause bodies to change their direction of travel.
- Changes in SHAPE: forces can cause bodies to stretch, compress, or deform.
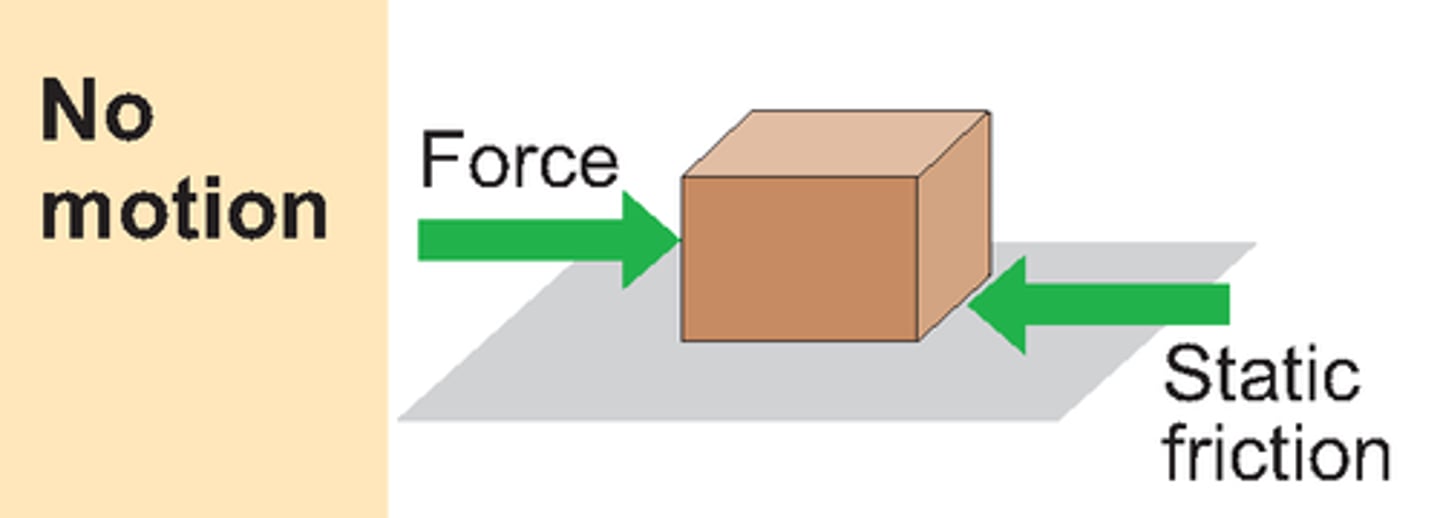
Friction: Static friction
Friction between solid surfaces which are gripping.
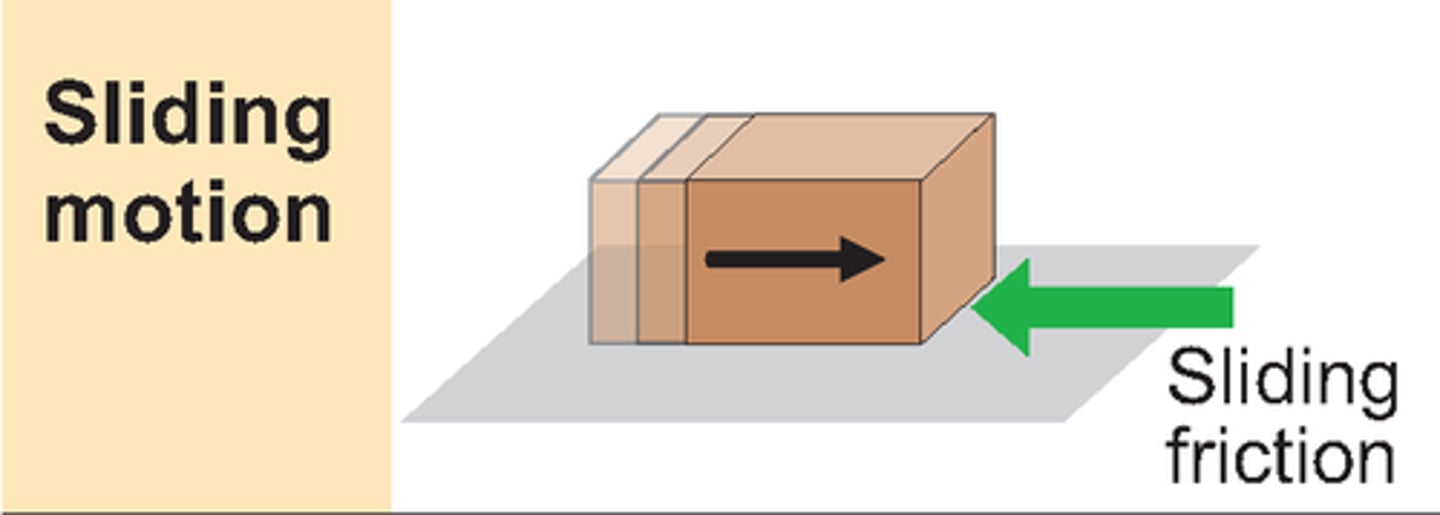
Friction: Sliding friction
Friction between solid surfaces which are sliding past each other.
Friction: Resistance or drag
Occurs in liquids and gases.

Balanced force
Equal forces acting on an object in opposite directions (eg. equal amount of weight and upthrust)
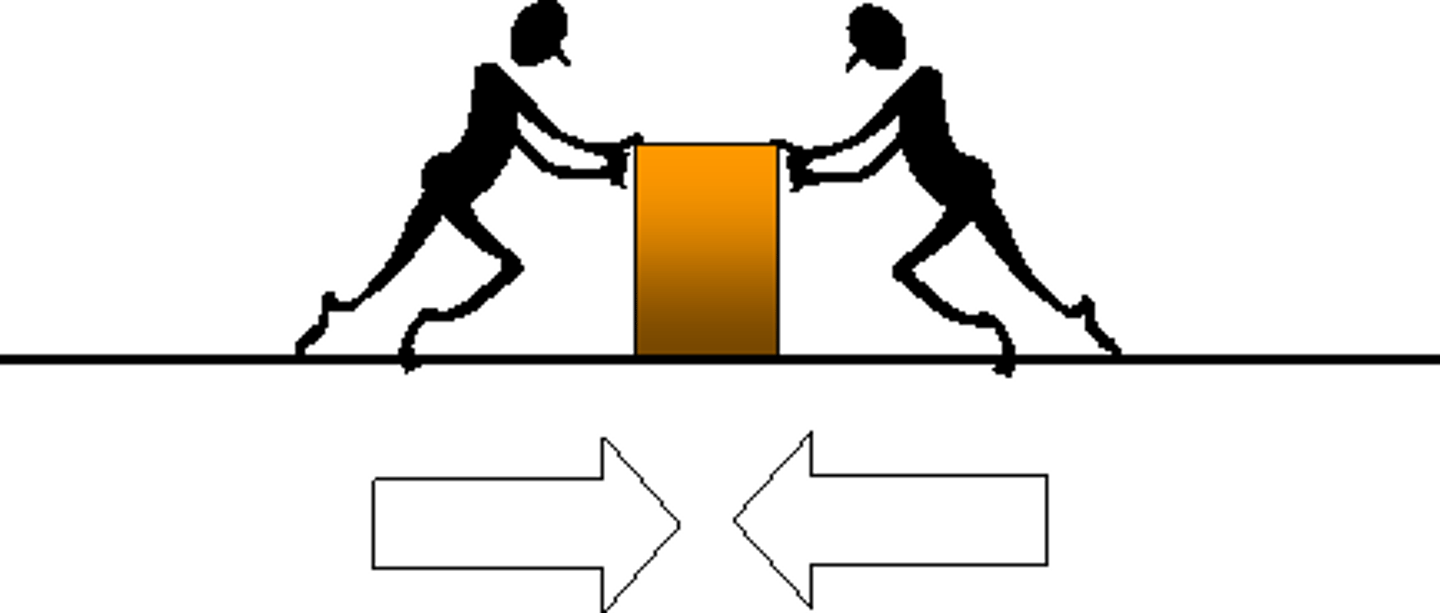
Unbalanced force
The force applied in one direction is greater than the force applied in the opposite direction.
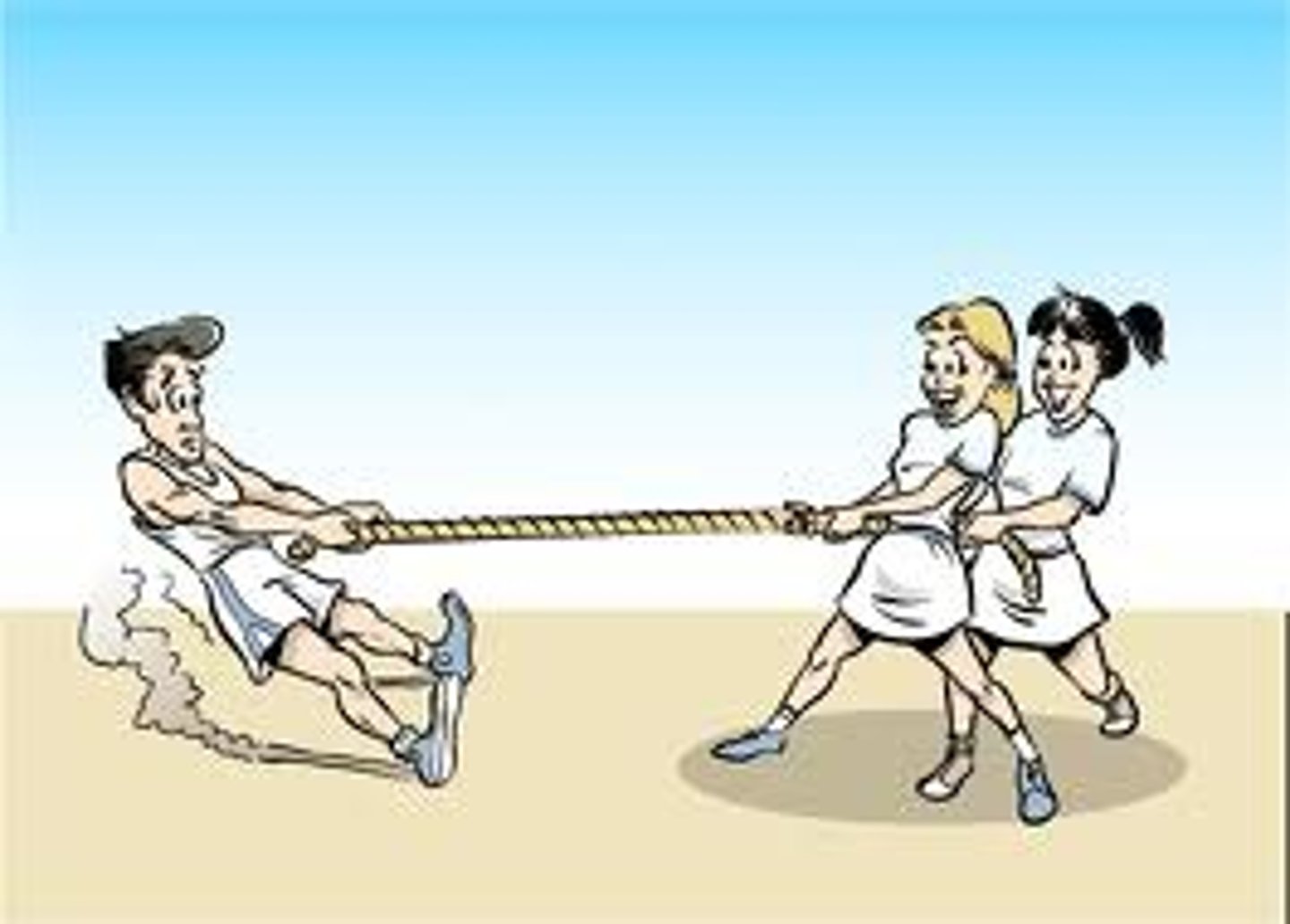
Definition of resultant force
A resultant force is the combined action of all the forces acting on an object.
Calculating resultant forces: Forces working in opposite directions
Subtracted from each other.
Calculating resultant forces: Forces working in the same direction
Added together.
Resultant force worked example: Calculated the magnitude and direction of the resultant force
Step 1: Add up all of the forces directed to the right
4 N + 8 N = 12 N
Step 2: Subtract the forces on the right from the forces on the left
14 N - 12 N = 2 N
Step 3: Evaluate the direction of the resultant force
The force to the left is greater than the force to the right therefore the resultant force is directed to the left
Step 4: State the magnitude and direction of the resultant force
The resultant force is 2 N to the left