Chem Lab Final
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Simple Distillation
Used for separation of two or more liquids with different boiling points
Distillation set up
Water flows IN from bottom part and OUT from top part. Use a regulator between power socket and heating mantle (to control amount of heat). Never have a closed distillation system
Liquid Liquid Extraction
Used for separation of solutes with different solubility in given solvents
Separatory funnel
Apparatus used for liquid-liquid extractions, make sure to vent the funnel when originally mixing liquids. Make sure the stopcock is closed. The top layer is the less dense (organic) layer and the bottom layer is the more dense (aqueous) layer. if using DCM it will be on the bottom
CaCl2
Common dry agent because its fast, has a high capacity, reacts with some organic compounds and good for drying tubes
Gravity filtration
A technique that utilizes gravity to separate solids from liquids by passing the mixture through a filter paper.
Percent recovery
final/initial x 100%
recrystallization
A purification technique used to separate and purify solid compounds by dissolving them in a suitable solvent and allowing them to crystallize. (mainly using heat and boiling and dissolving a substance to remove impurities, followed by cooling to form pure crystals.
Melting point
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid, indicating the phase transition of a substance.
Melting point range
The first point at which you see a miniscus start to form and then the last point is when the sample is completely liquid
Liquification point
the temperature at which a sample starts to melt
TLC:Stationary phase
solid absorbent sometimes can be silica gel
TLC: mobile phase
Liquid solvent
TLC (thin layer chromatography)
can be used to:
identify unknown substances and unknown compounds of mixtures
to determine the best solvent for column chromatography
to determine whether a substance is purified by recrystallization or another method still contains appreciable amounts of impurities
TLC: Solvent front
Distance that the mobile phase travels on the stationary phase. Always mark solvent front
TLC Visualization
Observe the TLC plate under ultraviolet light
RF calculation
RF = distance traveled by spot / distance traveled by solvent
Stereochemistry: Plane polarized light
Light that is passed through a polarimeter
Observed rotation
The angle by which a sample of an optically active substnace rotatied the plane of that beam
Polarimetry
movement of the angles of the observed rotation
Stereochemistry equations
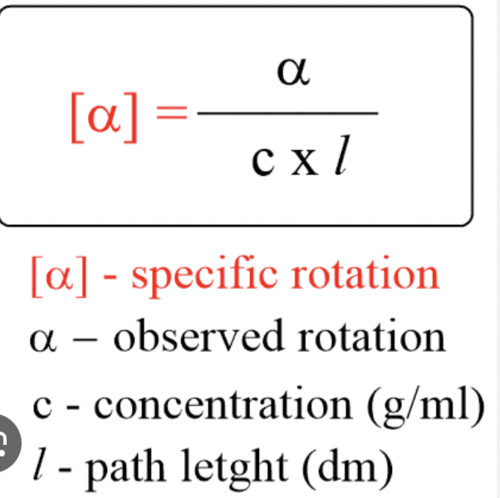
Enantiomeric excess
EE = observed rotation / observed rotation of pure enantiomer X 100%
Extinction point
when light is blocked out so its intensity is at a minimum
Free Radical Bromination: Statistical Factor
Determined by the number of hydrogen atoms whose replacement will give a specific constitutional isomer
Free radical bromination: energy factor
related to the strength of the type of C-H bond being broken and is called the relative reactivity
Aliphatic
Hydrogen bound to sp3 hybridized carbons. can be primary, secondary, or tertiary depending on the number of other carbon atoms attached to the reference carbon atom
Allylic/Benzylic
When a hydrogen is attached to a sp3 hybridized carbon that is bound to a vinylic or aromatic carbon
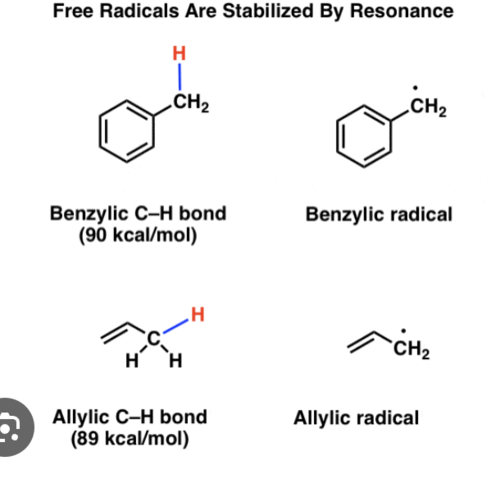
Vinylic/aromatic
hydrogens attached to sp2 hybridized carbons
Acetylenic
hydrogens bonded to an sp hybridized carbon atom
Free radical bromination mechanism
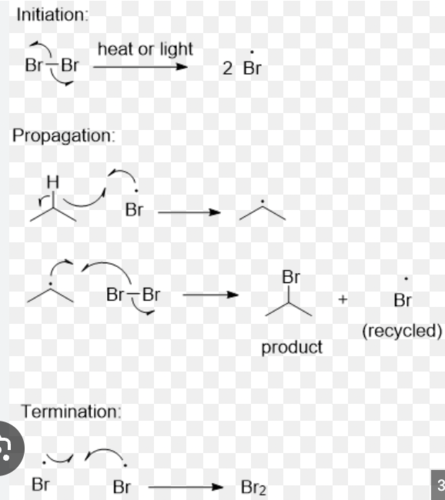
Free radical bromination results
the compounds that had structures that contained only aliphatic hydrogens did not experience bromine discoloration during the allotted observation time, whereas the ones with benzylic or benzylic and aliphatic hydrogens did react during the allotted observation time
Alkylation of saccharin: reaction
a reaction involving oxygen as the nucleophile should occur faster than one involving nitrogen as the nucleophile becuase oxygen is more electornegative than nitrogen
Alkylation of saccharin:DMF
DMF should be used for this experiment because:
it does not solvate the nucleophile strongly, leaving it free to attack the substrate
solvation reduces the strength of a nucleophile and its rate
Alkylation of saccharin: How to get grams from mmol
10mmol x 1 mol / 1000 mmol x 205g / 1mol = 2.05 g sodium saccharin
percent yield
actual yield / theoretical yield x 100
Markovnikov
the H atom will always bond to the C with more H
Zaitsev product
the more higly substituted alkene that results from an elimination reaction
Dehydration of alcohols: mmol to g
150mmol x 1mol / 1000ml x 114.2g/1mol = 17.13g
Dehydration of alcohols: g to ml
Use density : 17.13 g x 1ml/0.93g = 18.6 ml
Dehydration of alcohols: Chromatogram
first high peak = initial boiling point
second high peak = final boiling point
Dehydration of alcohols: percentage of each product
calculate area for each peak corresponding to each of the two products
sum up the areas
the percentage of given product will equal the area of the peak corresponding to given product divided by the sum of both the areas
multiply by 100 to get a percent
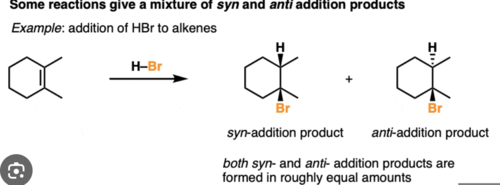
Anti addition
addition form opposite sides of the double bond
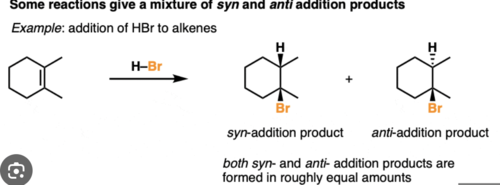
syn addition
addition from the same side of a double bond
bromine and acetone
DO not mix them, will create tear gas/bromoacetone
Bromination of Cinnamic acid: ml to mmol
10ml x 3.12g/1ml x 1mol/159.8g x 1000mmol/1mol = 195.2 mmol of bromine.