Vibrio, Aeromonas, Campylobacter, Helicobacter
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Water Organisms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
these 4 genera cause diarrheal diseases and other infections
Vibrio, Aeromonas, Campylobacter, and Helicobacter (Campylobacter-like)
which genera is associated with large epidemics and pandemics?
Vibrio
which genera plays a role in GBS?
Campylobacter
which genera causes ulcers?
Helicobacter
GBS
Guillian-Barre Syndrome
Which genera relates to stool culture?
Aeromonas
Vibrio is the causative agent of what?
cholera (severe diarrhea)
where is Vibrio found?
fresh, brackish, and salt water
what are the 6 reasons there is a significant rise in isolation of Vibrio?
Increased:
ocean water temp
travel to cholera endemic places
raw seafood consumption
aquatic/recreational water exposure
immunocompromised people
awareness of microbes
Vibrio 4 risk factors
eating raw seafood
travel
gastroenteritis: rice-water stool
injury in nature water
Vibrio gram stain morphology
curved or comma-shaped G=
can be pleomorphic
nonsporeforming
flagella
Vibrio interaction with air
facultative anaerobe
Vibrio biochems
catalase
oxidase
nitrate
string test
glucose
urea
catalase (+)
oxidase (+)
nitrate (+)
string test (+)
glucose fermenter
urea (+)
Vibrio drug of choice
doxycycline or ciprofloxacin
Vibrio interaction with temperature, salt, and carbon metabolism
mesophilic, halophilic, chemoorganotrophic
how are Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio mimicus different from usual Vibrio?
they aren’t halphiic
how are Vibrio metschnikovii and Vibrio gazogenes different from regular Vibrio?
catalase (=)
oxidase (=)
Vibrio are [R/S] to O/129?
Susceptible
O/129
vibriostat disk containing 2,4-diamino-6,7-diisopropylpteridine
are Vibrio isolates [S/R] to Vibriostat disks
S
String test
tests bile solubility
emuslifies 2-3 colonies in sodium desoxycholate
how to differentiate Vibrio from Aeromonas?
O/129 susceptibility
Vibrio is S and Aeromonas is R
3 subgroups of Vibrio cholerae
Vibrio cholerae 01 (causative cholera agent)
Vibrio cholerae 0139 (epidemic cholera)
Vibrio cholerae non-O1
which antigens does Vibrio cholerae have?
H and O antigens
what are the 3 Vibrio cholerae O1 subtypes
Ogawa (A, B)
Inaba (A, C)
Hikojima (A, B, C)
what are the 2 Vibrio cholerae O1 biogroups
classic
El Tor
which Vibrio cholerae subgroup has a milder disease but doesn’t produce cholera toxin?
non-O1
which 2 Vibrio are non-halophilic?
Vibrio cholerae
Vibrio mimicus
where does much Vibrio cholerae epidmics happen?
developing countries: Bengal region of India and Bangladesh
Cholera
acute diarrheal disease spread through contaminated water and mishandled food
list 3 symptoms of Cholera
Diarrhea caused by toxin :(
rice-water stool (watery flecks of mucus)
water and electrolyte loss (pooping 10-30x per day)
dehydrated, hypovolemic shock, metabolic acidosis —> DEATH
what happens to cholera patient if left untreated?
DEATH
how does Vibrio cholerae enact virulence?
bacteria colonize small intestine and release toxin
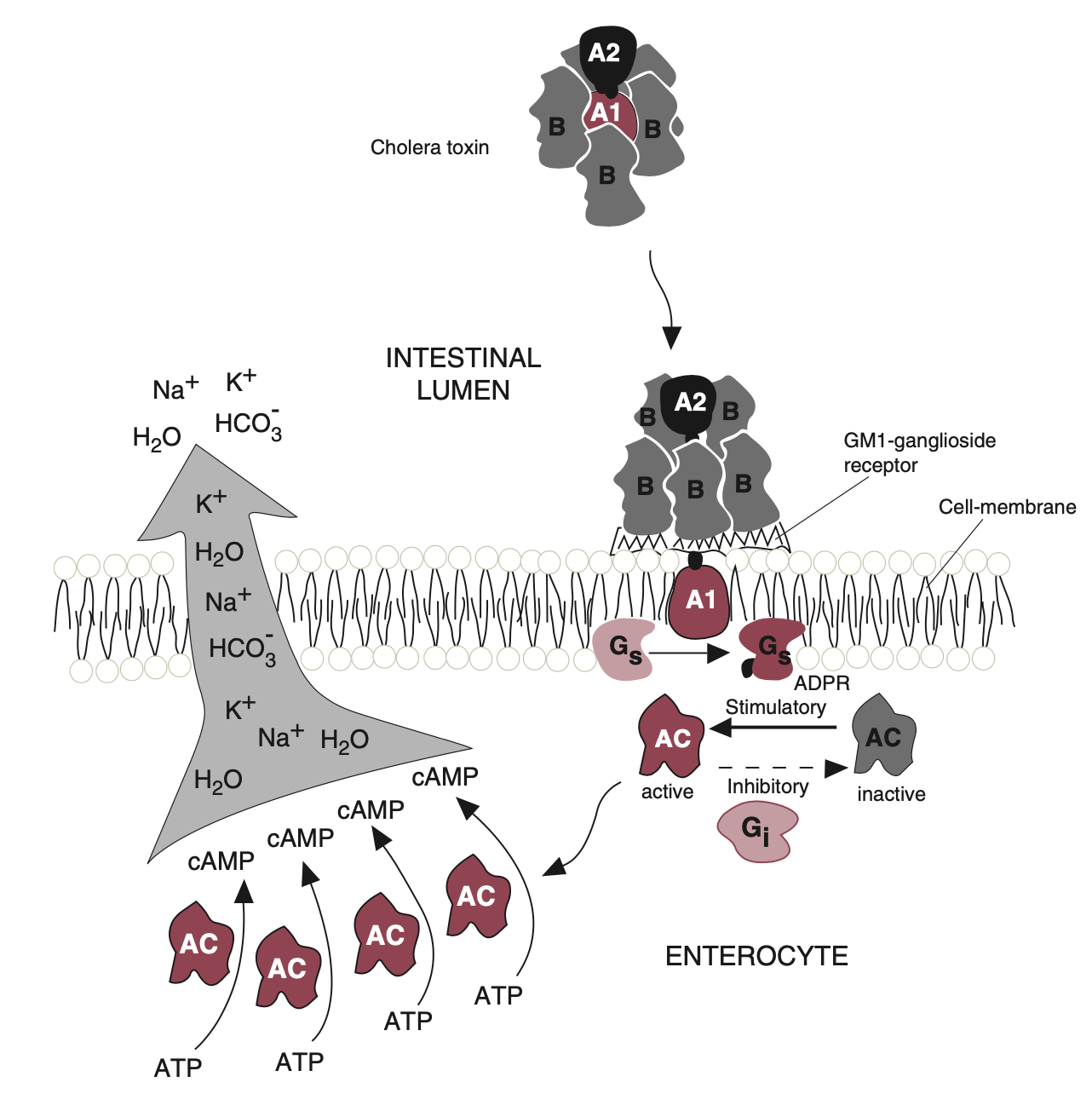
how does the cholera enterotoxin work (choleragen) in 3 steps?
B subunit binds to GM1 ganglioside receptor
A2 subunit allows A1 to enter
A1 subunit stimulates adenylate cyclase by inactivating a G protein, activating cAMP
Cholera treatment
Electrolytes: IV and oral fluids
how to differentiate between the 2 Vibrio cholerae 01 biogroups?
Classic: VP (=), nonhemolytic, grows with polymyxin B, does not agglutinate chicken RBC
El Tor: VP (+), hemolytic, inhibited by polymyxin B, agglutinates chicken RBC
Vibrio parahaemolyticus epidemiology
discovered in Japan (1950)
“summer diarrhea,” a large food poisoning outbreak
which Vibrio parahaemolyticus serotype emerged after 1996?
O3:K6
where does Vibrio parahaemolyticus like to grow?
1-8% NaCl, associated with seafood and raw oysters
Vibrio parahaemolyticus can be isolated from?
wound: eye, ear, pneumonia
Vibrio parahaemolyticus drug of choice
Tetracycline
Vibrio parahaemolyticus 3 symptoms and how long after ingestion do you experience them?
self-limiting watery diarrhea and cramping
sometimes vomiting
24-48 hrs after ingestion
Vibrio parahaemolyticus virulence factors
Kanagawa phenomenon: heat-stabile hemolysin can lyse human cells
what are the 1st and 2nd most common species in gastroenteritis
Vibrio cholerae
Vibrio parahemolyticus
Vibrio vulnificus epidemiology
atlantic, gulf, and pacific coasts
Vibrio vulnificus AKA
lactose-positive vibrio
what 2 symptoms does Vibrio vulnificus cause?
wound infections: traumatic aquatic wound
-can lead to-
septicemia: especially increased serum iron; 40-60% mortaility
Vibrio vulnificus wound infections (cellulitis) can progress to…
necrotizing faciitis or multiple organ system failure
Vibrio cholerae vs Vibrio vulnificus infection
cholerae: make you DIE
vulnificus: septic fluid; fatal within HOURS
which Vibrio is the least pathogenic?
Vibrio alginolyticus
Vibrio alginolyticus causes what types of infections?
extraintestinal: eye, ear, wound, burn
who is at risk with Vibrio alginolyticus infections?
fishermen or sailors
Vibrio plate morphology
SBA/CHOC: medium-large colonies
smooth, opaque, iridescent with greenish hue
Vibrio appearance on MAC plate
Lactose (=)
EXCEPT Vibrio vulnificus
what does TCBS agar do for Vibrio?
Thiosulfate Citrate Bile Sucrose
separates sucrose and nonsucrose-fermenters
other Vibrio: fermenter
Vibrio parahaemolyticus and vulnificus: nonfermenter
Vibrio specimen to collect; and HOW
body fluid, pus, tissue
Swab: Cary-Blair
stool: collected as EARLY as possible
which swab can you NOT use for Vibrio specimen?
buffered glycerol saline
Vibrio 3 non-culture ID methods
16S rRNA sequencing: not common, rarely isolated
Molecular: PFG or REP-PCR
Serological: polyvalent O1 antiserum
Aeromonas where and when is it found?
freshwater/marine
retail produce and animal meat
May-October (warmer months)
are Aeromonads enteric pathogens?
YES. it relates to the intestines
5 types of Aeromonas associated diarrhea
acute secretory diarrhea with vomiting
acute dysenteric form with blood and mucus
chronic diarrhea >10 days
cholera-like, watery-bloody
traveler’s diarrhea: nebulous syndrome
Aeromonas extraintestinal infections
wound, septicemia, and MANY more :(
Aeromonas hydrophilia wound infection caused by
leaches during plastic surgery to relieve congestion and swelling
Aeromonas veronii (sobria) septicemia is related with
traumatic injury, immunocompromised, liver disease
Aeromonas two groups
Mesophilic (37°C): Aeromonas hydrophila, bestiarum, salmonicida
Psychrophilic (22°C): Aeromonas salmonicida
which group of Aeromonas is motile?
Mesophilic
Aeromonas gram stain morphology
straight, coccobacillary-bacillary GNR
non-spore formers
Aeromonas growth on media?
grows readily, after 24 hr incubation
Aeromonas colony morphology?
large, round, raised, opaque
translucent and white, buff-colored
Aeromonas SBA and MAC growth
SBA: variable hemolysis
MAC: lactose fermenter
Aeromonas biochems
oxidase
indole
string test
O/129 disk
0% NaCl
inositol fermentation
oxidase (+)
indole (+)
string test (=)
Vibrostat disk (R)
0% NaCl (+)
inositol fermentation (=)
Aeromonas antibiotics resistant to
penicillin, ampicillin, carbenicillin
Aeromonas antibiotics susceptible to
SMZ, aminoglycosides, quinolones
Aeromonas hydrophilia unique extraintestinal infection
Keratitis: contact lens water
Aeromonas hydrophilia hemolysis
beta hemolysis
Aeromonas caviae vs. Aeromonas hydrophilia
Aeromonas caviae: H2S (=), VP (=)
Aeromonas hydrophilia: H2S (+), VP (+)
Aeromonas veronii vs Aeromonas hydrophilia
Aeromonas veronii: ODC+
Aeromonas hydrophilia: ODC=
where is Aeromonas veronii isolated from?
stool, wound, RT
where is Aeromonas caviae isolated from?
stool, surgical wound, liver abscess
Aeromonas and Plesiomonas vs Vibrio
Aeromonas and Plesiomonads:
string test (=)
NaCl 0%
Vibrio:
string test (+)
NaCl 6%
O/129 (S)
Aeromonas vs Plesiomonas
Aeromonas:
insitol (=)
O/129 (R)
Plesiomonas:
insitol (+)
O/129 (S)
Campylobacter members
Campylobacter jejuni ssp. Jejuni
Campylobacter fetus ssp. fetus
Campylobacter epidemiology
abortion in domestic animals (zoonotic organisms)
Campylobacter 5 methods of transmission
direct contact with animals
contaminated water/dairy
improper poultry cooking
person to person
STD
Campylobacter relation to air
microaerophilic: need 5% O2
Campylobacter gram stain
nonspore-forming GNR —over time—> coccobacilli
“seagull wing”
poor gram stain
Campylobacter biochem
oxidase
catalase
NaHipp
fermentation
incubation temp
Oxidase (+)
catalase (+)
NaHipp (+)
nonfermenter
42°C
Campylobacter motility
darting (seen on wet prep or phase contrast microscopy)
what is the most common diarrheal illness?
Campylobacter jejuni
Campylobacter jejuni symptoms
diarrhea with mild ab pain: fever, chills
self-limiting (2-6 days)
GBS
what specimen is Campylobacter fetus isolated from?
blood cultures
which Campylobacter causes abortions in cattle, sheep, and pigs?
Campylobacter fetus
who tends to get infected with Campylobacter fetus?
immunocompromised and old people
what 3 ways are Campylobacter specimen collected?
blood
stool
rectal swabs (less preferred)
if there is a delay in processing stool specimen for Campylobacter or Vibrio, what transport medium is used?
Cary-Blair
how to grow Campylobacter and Helicobacter isolates?
microaerophilic and capnophilic atmosphere
stool- 42°C
Campylobacter jejuni colony morphology
moist “runny looking” and spreading
nonhemolytic
raised and round/flat
Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus colony morphology
tan/pink/translucent
smooth, convex
Campylobacter gram stain UNIQUE
use carbol fuchsin as counterstain
if safranin is used: extend 2-3 min
what media can help cultivate Campylobacter?
Skirrow’s and Butzler