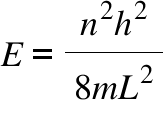Inorganic Chem Pre-Exam
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Screening/Shielding Effect
Electrons in inner shells of the atom cause the nucleus to have less pull on its valence electrons.
Coulomb Force
the force of attraction or repulsion between two charged particles
Nuclear Charge
Total charge of nucleus (atomic number Z)
Ionization Energy
Amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or molecule. Generally increases as you move towards top right corner.
Ionization Energy Exceptions
First ionization energies for elements in group 15 are higher than their counterparts in group 16 cause the p orbital is half-filled for group 15 (so more stable). For example, N has higher energy than O.
Nodal Planes
Place around an atom where likelihood of finding an electron is zero. n - l - 1. Principal Quantum number - azimuthal quantum number - 1.
VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion)
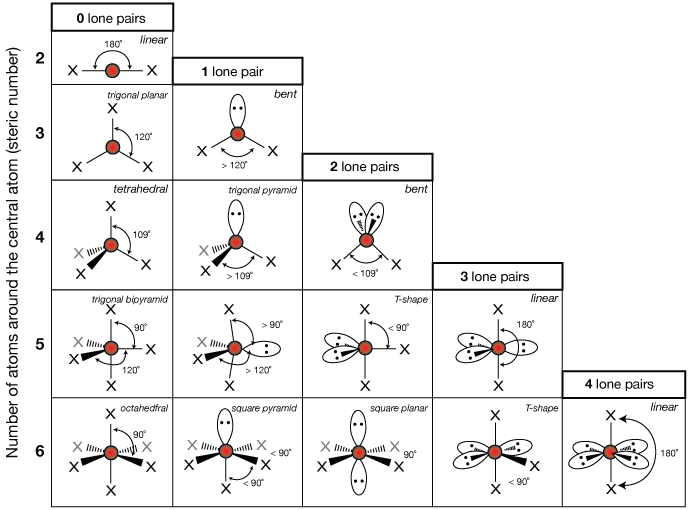
Bonding Orbitals
Molecular orbital in which two orbitals merge (constructive interference) and a bond is formed. Lower energy and more stable.
Antibonding Orbitals
Molecular orbital in which two orbitals cancel each other out (destructive interference). Nodal plane, so no electron density. Higher energy and less stable.
Particle-Wave Duality
Electrons and photons act both as particles and waves.
Einstein Photoelectric Effect
Electrons are emitted from a material when light hits it at a frequency higher than a certain threshold frequency. E = h*f.
Thomson Electron Diffraction
experiments that showed that electrons exhibit wave-like properties by showing they could be diffracted, similar to X-rays
Ruska Electron Microscope
uses a beam of high energy electrons to help magnify very small objects (organelles, viruses, etc)
Millikan’s Oil Drop Experiment
experiment that used charged oil droplets to determine the charge of an electron. found that all charges are multiples of that electron charge.
Ionic Character
difference in electronegativity between two bonded atoms. Greater value means more polarizable
Lewis Acid
Electron acceptor. ex: tranistion metals
Lewis Base
electron donor. ex: ammonia
Coordinate Bond
covalent bond in which both electrons come from one atom. ex: NH3 shares two electrons with H+ to become NH4.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
From low to high frequency/radiation: Radio, micro, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-ray, gamma. Rich Men In Vegas Use Xpensive Girls
Bohr’s Model
theory that electrons orbit a nucleus of an atom in shells. Higher/farther shells have higher energy.
Valence Bond Theory
unpaired valence electrons of two different atoms merge their atomic orbitals to form covalent bond.x
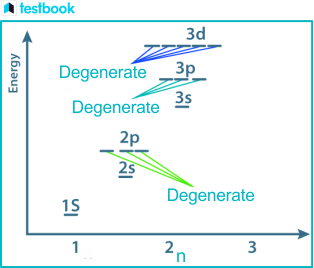
Degenerate orbitals
Orbitals that have the same energy level. ex: the electron pairs in a 2p6 are degenerate to each other. CH4 has triply degenerate orbitals, not four, because it’s tetrahedral.
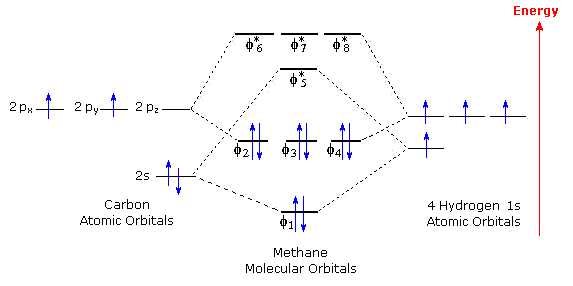
Molecular Orbital Theory
Atomic orbitals merge to form molecular orbitals. Bonding (low energy) orbitals fill first, then anti-bonding (high energy) orbitals.
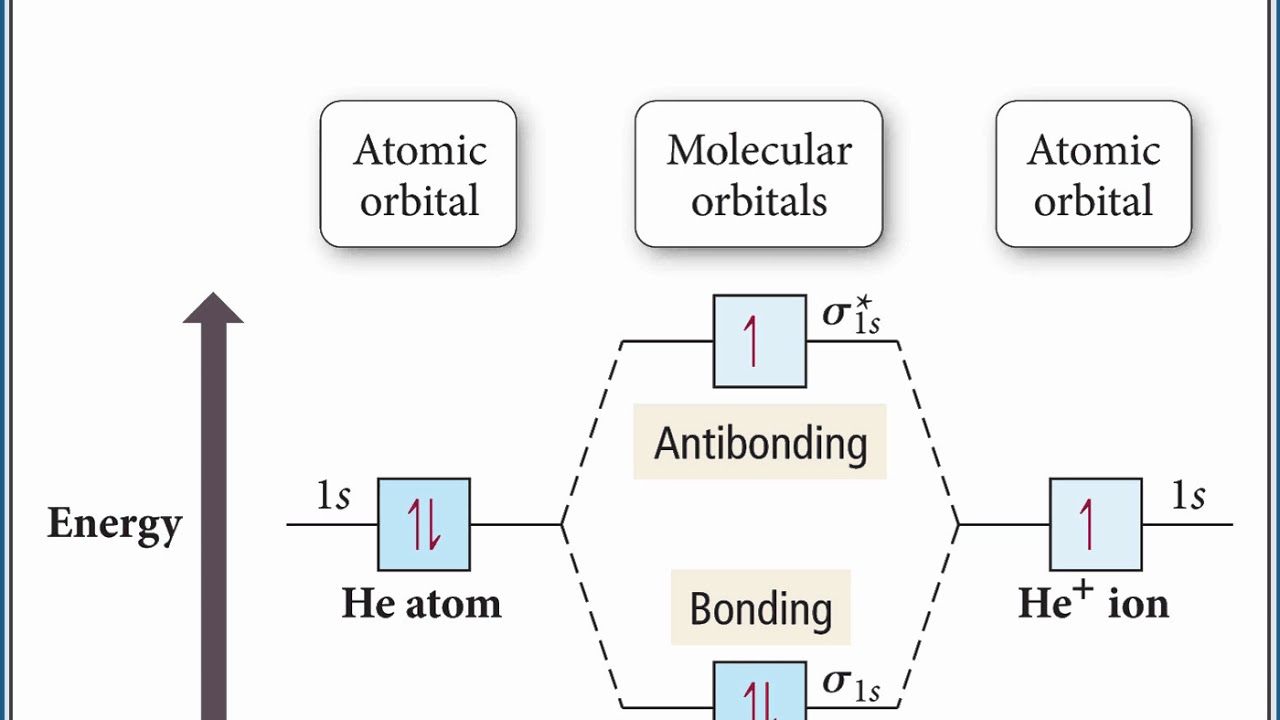
Effective Nuclear Charge
Atomic Number - Shielding Electrons (Z - S)
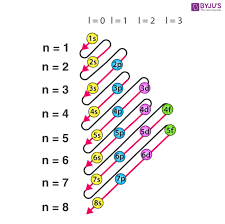
Electron configuration order
Octet Rule
General rule that atoms gain/lose the minimal amount of electrons to have 8 valence shell electrons
Geometric isomers
Stereoisomers with same chemical formula and connectivity but different spatial arrangement. Like cis-trans isomers.
Optical Isomers
Enantiomers. Same formula, connectivity, but non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
Dimeric structures
molecule formed from two identical chemical units
Gibbs Free Energy
Thermodynamic potential energy. Postive means non-spontaneous, negative means spontaneous. Equal to ΔH - TΔS
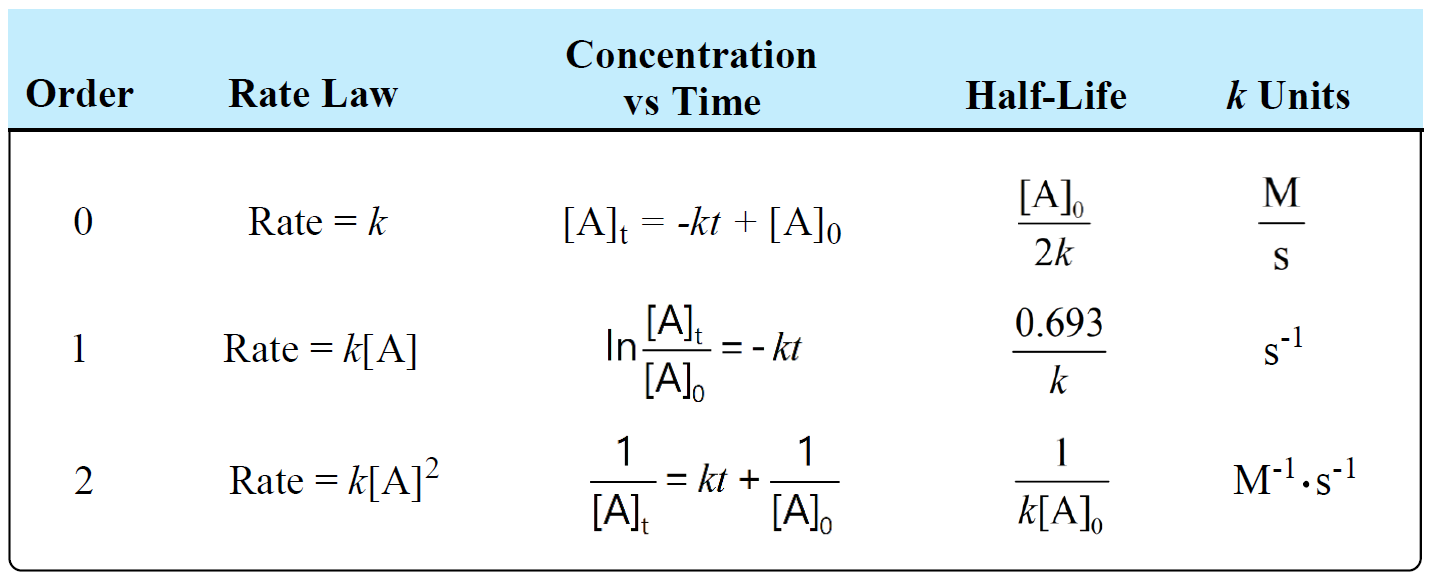
Rate laws
describes rate of a chemical reaction in relation to substrate concentrations.
Cis-trans isomers IR spectrum
cis isomers have much stronger signal than trans isomers
Why are there different frequencies for C=O stretches?
Carbonyls connected to EDGs, such as metals acting as Lewis bases, have lower IR frequencies
Particle in a box
A particle confined to a finite space can only have discrete, or quantized, energy levels.