SPONDYLODISCITIS, OSTEOMYELITIS, SEPTIC ARTHRITIS and TB
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is spondylodiscitis?
Infection in the spine involving the disc and vertebra.
What are the risk factors for spondylodiscitis?
Recent systemic infection (UTI, pneumonia, skin), spinal trauma, IV drug use, immunosuppression, long-term steroids, diabetes, cancer, urogenital tract instrumentation, vascular insufficiency, sickle cell anemia, peripheral neuropathy.
What are the clinical features of spondylodiscitis?
Fever in <20% of patients.
Severe back pain, worse with activity, wakes patient at night.
Radiculopathy/myelopathy in 10-20% if infection spreads to IVF or spinal canal.
Labs: WBC elevated in 50%, ESR and CRP elevated in 90%.
What are the imaging findings in spondylodiscitis?
X-ray: Disc space narrowing, ill-defined endplates (after 2-4 weeks).
MRI: Low signal on T1, high signal on T2/STIR, ill-defined endplates, high signal in disc, potential abscess formation.
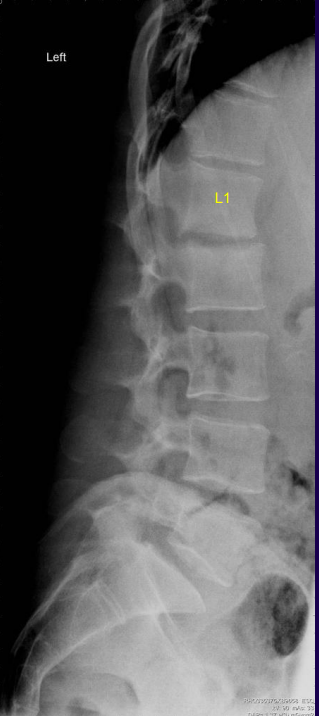
What findings and condition are present in this image?
30 yo IV drug user w intense back pain
Spondylodicitis
loss of height of L1/L2 joint space
• endplate sclerosis
• indistinct endplates
• These early changes may progress to destruction and fusion.
What is osteomyelitis?
Infection in a bone, which may spread to a joint. Most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
What are the clinical features of osteomyelitis?
Fever in only 1/3 of patients.
Swelling, redness, warmth.
Labs: Elevated WBC, ESR, CRP.
What are the 4 radiographic stages of osteomyelitis?
Latent Stage (1-10 days): No radiographic findings.
Early Stage (10-21 days): Decreased bone density + soft tissue swelling.
Middle Stage (weeks): Moth-eaten destruction + periosteal reaction.
Late Stage (months): Involucrum, sequestrum, cloaca.
What radiographic finding is present, and what condition is it related to?
Chronic Osteomyelitis-Brodie’s abscess formation
Reactive sclerosis Thick periosteal bone proliferation
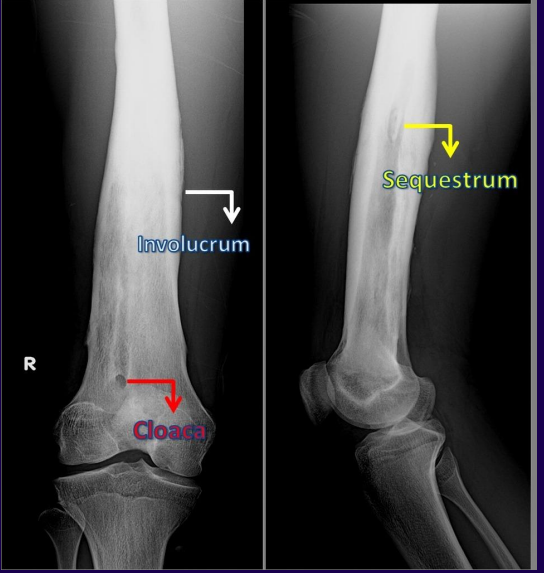
In this image of osteomyelitis, define the labels.
Sequestrum: Chalky, white area representing dead bone. ]=
• Involucrum: “Bony collar”- continuation of periosteal response. It will eventually represent the new periosteum.
• Cloaca: Draining sinus. More common with chronic disease. Chronic infection, stubborn to treat.
What is septic arthritis?
Infection of a joint, often caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Can result from hematogenous spread, direct extension, or penetrating injury.
What are the radiographic features of septic arthritis?
Joint effusion.
Juxtaarticular osteoporosis.
Erosions.
Joint space loss.
Periosteal reaction.
What is a key findings of septic arthritis of an xray?
Lytic destruction that crosses joint space
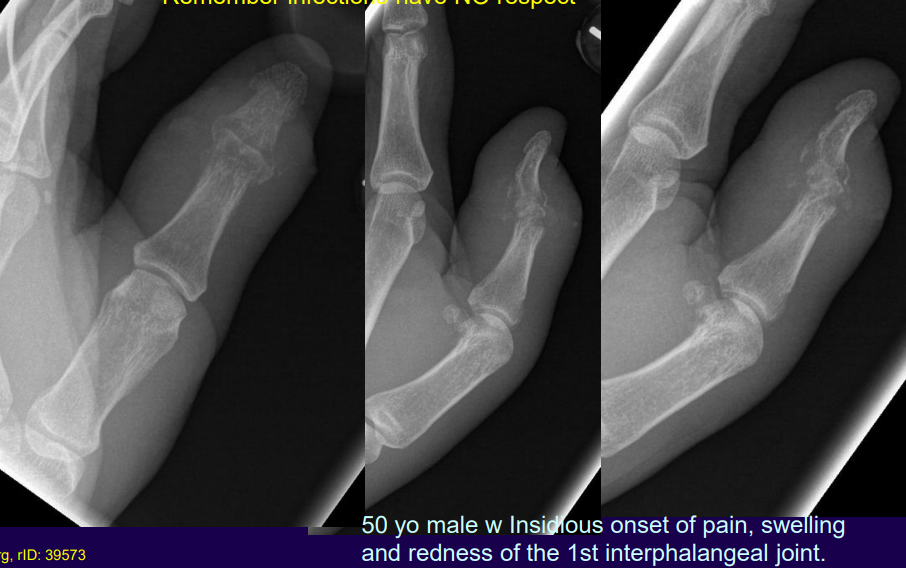
What condition is present in this image?
Septic arthritis
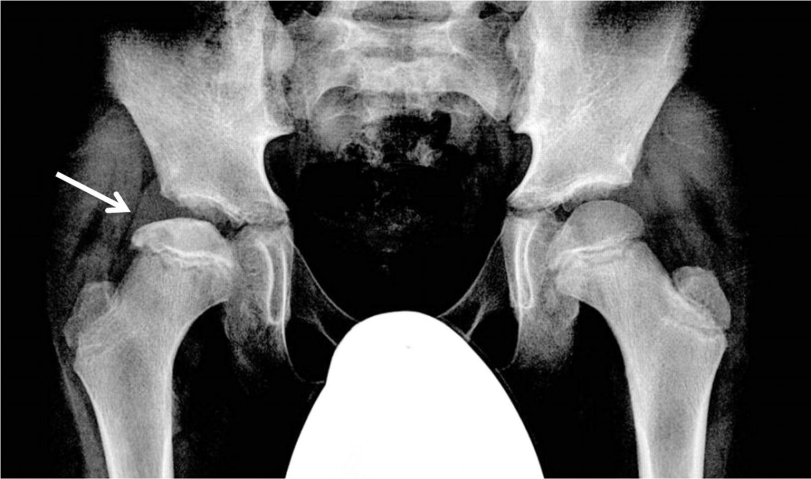
What findings is present?
Waldenstrom’s sign
Increase in distance between femoral head and Kohler’s teardrop. Not specific for septic arthritis, also seen with LCP, inflammatory and posttraumatic cases. In addition, elevated fat fold of gluteus medius is seen.
What are the key features of TB in the spine?
Spine is the most common skeletal location (50%), with L1 being the most common level.
Involves multiple levels with paraspinal cold abscesses.
Slower progression of joint destruction compared to suppurative infections.
What are the clinical features of TB?
Respiratory symptoms: productive cough, blood-tinged sputum, shortness of breath.
Weight loss, night sweats, vague joint/back pain.
Chest film shows granulomas in 50%, TB skin test positive in 90-100%.
What are the classic radiographic features of TB in the spine?
Similar to spondylodiscitis but with multiple levels involved.
Paraspinal (psoas) cold abscesses with calcification.
What are the features of chronic osteomyelitis?
Sequestrum (dead bone).
Involucrum (periosteal reaction forming a bony collar).
Cloaca (draining sinus).