Bio12AP: Cell Structure and Function
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(INCLUDES EXTRA AP VOCAB) mcq: cell diagram (identify structures/functions) frq: 2 multistep processes (endocytosis, intracellular digestion) , bilayer + embedded molecules , 2 word relationships (ex: hypotonic vs hypertonic, crenation vs lysis), relationship between ER and Golgi (how do products leave the cell?))
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
prokaryotes
single-celled organisms that lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Their genetic material is located in a region called the nucleoid, which is not enclosed by a membrane. Prokaryotic cells include bacteria and archaea.
Cell wall: In bacteria, this is composed of peptidoglycan, a mesh-like structure that provides rigidity and protection. (In archaea, the cell wall structure differs and lacks peptidoglycan.)
possess ribosomes
can a plant cell ever be damaged by a hypotonic solution?
usually, no: the cell wall provides mechanical support and prevents the cell from bursting under normal conditions
why does endocytosis involve atp?
a section of the cell membrane bends inward to surround the molecules being taken in
this rearranges the lipid bilayer, which involves energy
why does exocytosis involve atp?
atp is used to carry vesicles along microtubules to the plasma membrane
for the vesicle to fuse with the membrane, the lipid bilayers of both the vesicle and the plasma membraen must rearrange to become continuous, using ATP
what’s the distinction between how carrier proteins and channel proteins operate?
channel proteins stay in one place in the membrane and form a fixed pore/tunnel that doesn’t move
allow specific molecules/ions to pass based on size and charge
allows PASSIVE movement of molecules/ions
carrier proteins are also stationary, but their shape can undergo conformational (shape) change during the transport process
bind to the substance being transported, then change shape to shuttle it across the membrane
functions like a “revolving door” rather than a fixed gateway
may operatre via passive transport (facilitated diffusion) or active transport
why do cells size seek to optimize a high surface to volume ratio
cells with a large volume require more nutrients, oxygen, etc. and produce more waste
membranes are limitedf to moving material in or out of the cell at a max rate
more membrane = better activity to move materials in/out of the cell
how are lysosomes and vacuoles related
Lysosomes and vacuoles are both involved in cellular digestion and are produced by the Golgi apparatus. They can combine to break down larger molecules like food, forming a secondary lysosome. Lysosomes contain enzymes to digest waste and cellular debris, while vacuoles primarily store substances but also aid in digestion, particularly in plant cells.
why are plant cells so unique?
have a cell wall
large central water vacuole (used for turgidity)
possess chloroplasts and plastids
ALSO HAVE mitochondria
how do cilia and flagella differ in function?
Cilia: Move substances along the cell surface (e.g., mucus in respiratory tract) or enable movement for small organisms.
Flagella: Provide locomotion for cells, such as sperm in humans and many single-celled organisms.
phagocyte
refers to cells that engulf solid particles through phagocytosis
form large vesicles (phagosomes) around particles, bringing them into the cell
type of a white blood cell and part of the immune system
equipped with their own organelles, nucleus and other cellular structures
pinocyte
cells that engulg fluids and dissolved substances
form small vesicles around fluid droplets, bringing them into the cell
continuous process that helps cells take in nutrients and other essential substances
how do cilia and flagella differ in location?
Cilia: Common in multicellular organisms (e.g., respiratory tract cells).
Flagella: Common in single-celled organisms and some animal sperm cells.
how is the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus related
ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum) and Golgi Apparatus work together in protein and lipid synthesis. The ER produces proteins (rough ER) and lipids (smooth ER). They get sent to the Golgi that modifies, sorts, and packages them for transport inside or outside the cell.
how are ribosomes and the ER related
the rough ER provides a platform for ribosomes to synthesize proteins, and helps them process and transport these proteins. Ribosomes can also be free-floating in the cytoplasm, but those bound to the rough ER are specifically involved in making proteins for secretion or for use in membranes.
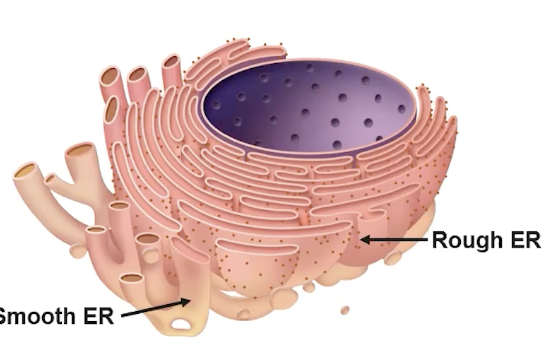
How are mitochondria and chloroplasts related?
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are both organelles involved in energy conversion. Mitochondria generate energy through cellular respiration, producing ATP from glucose and oxygen. Chloroplasts, found in plants and algae, carry out photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy (glucose that the mitochondria needs produce ATP)
Both organelles have their own DNA and are thought to have originated from endosymbiotic bacteria.
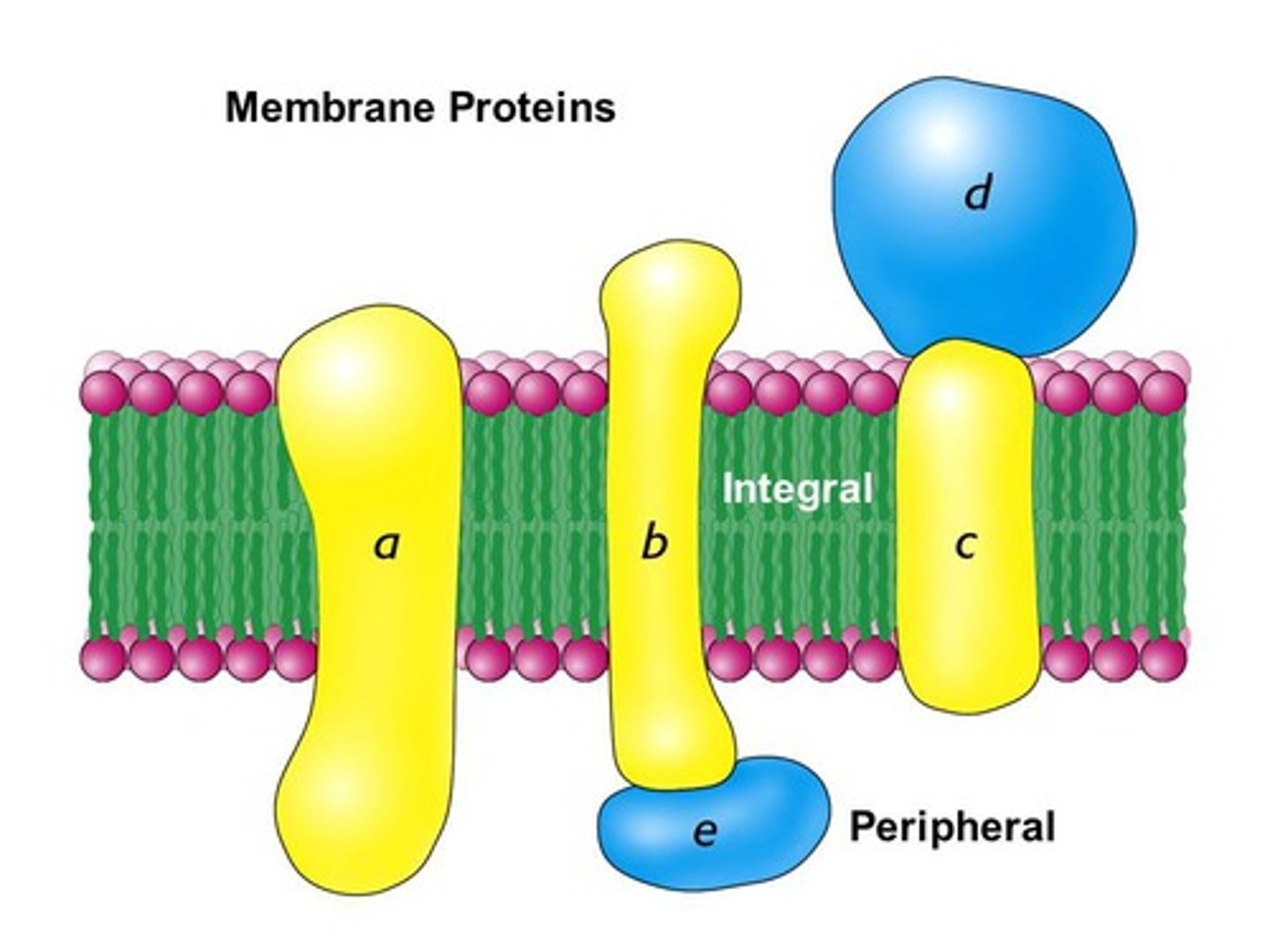
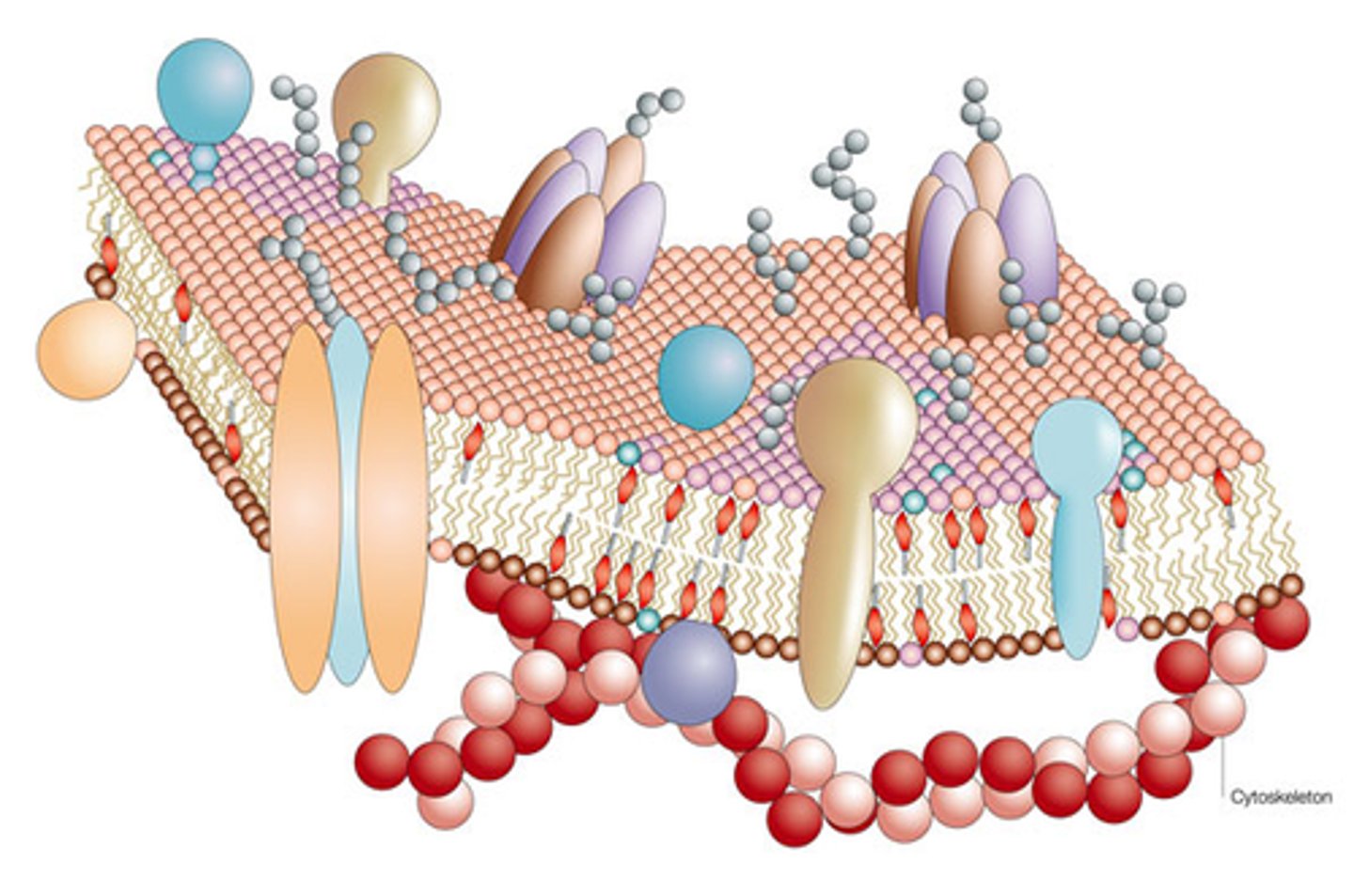
peripheral proteins
The proteins of a membrane that are not embedded in the lipid bilayer; they are appendages loosely bound to the surface of the membrane.
which organelle is found in the pituitary gland (produces hormones)?
golgi apparatus
which organelle is found in muscle cells?
mitochondria/rough er
crenation
shrivelling of a cell because of a hypertonic solution (the outside environment has more solutes, causing water to move by osmosis out of the cell)
what’s the difference between microtubules and microfilaments?
microtubules: structual support, intracellular transport, components of centrioles, basal bodies, flagella, cilia, key role in cell division
microfilaments: flexibility of the cell (cell contraction and expansion), organelle positioning, assisting endo/exocytosis
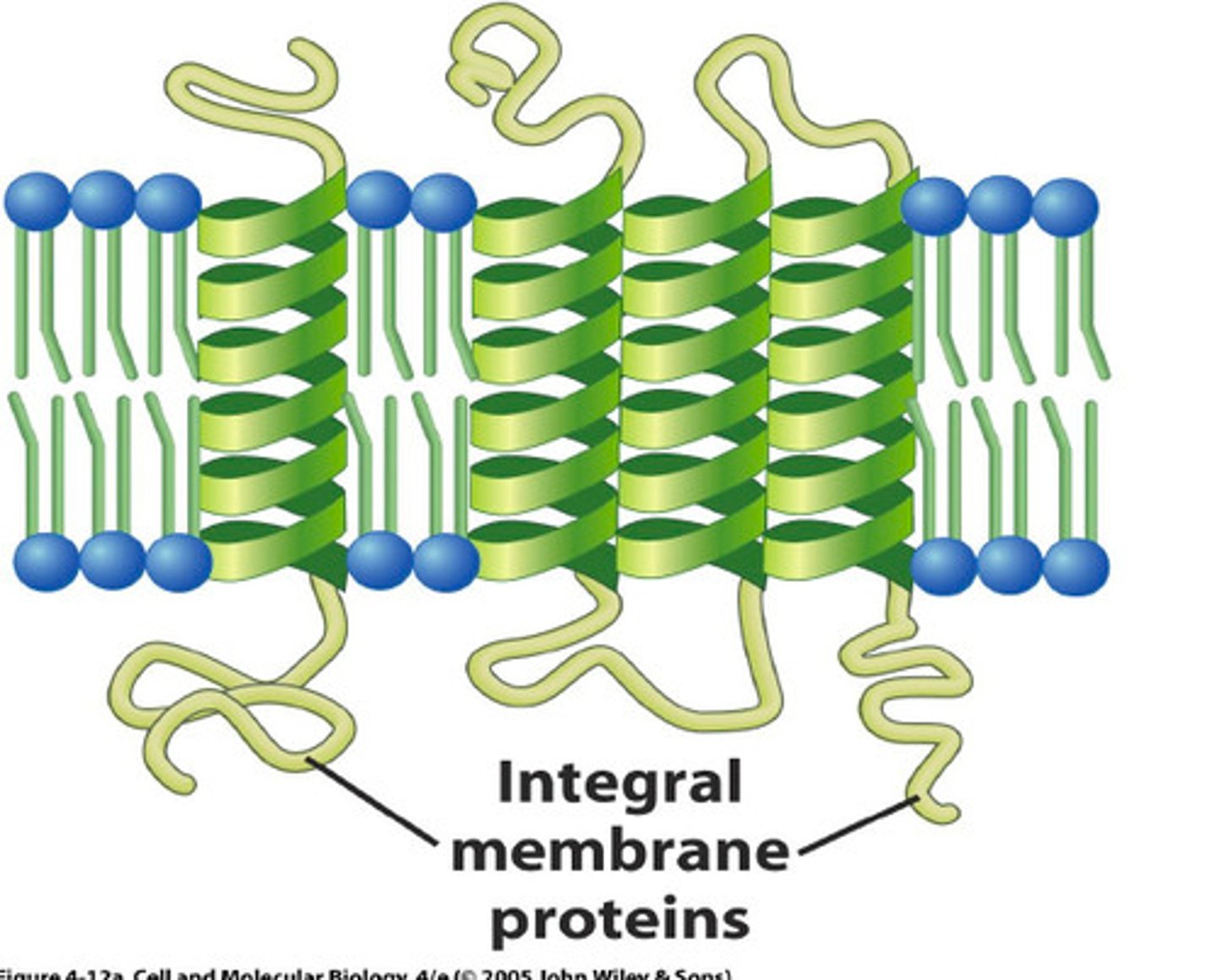
integral proteins
Proteins embedded within the cell membrane that span its entire width. They help transport molecules, send signals, or support cell structure.
glycoprotein
protein with sugar molecules attached to it, helps in cell signaling and recognition
transmembrane proteins
Transmembrane proteins are integral proteins that do not extend all the way through the membrane.
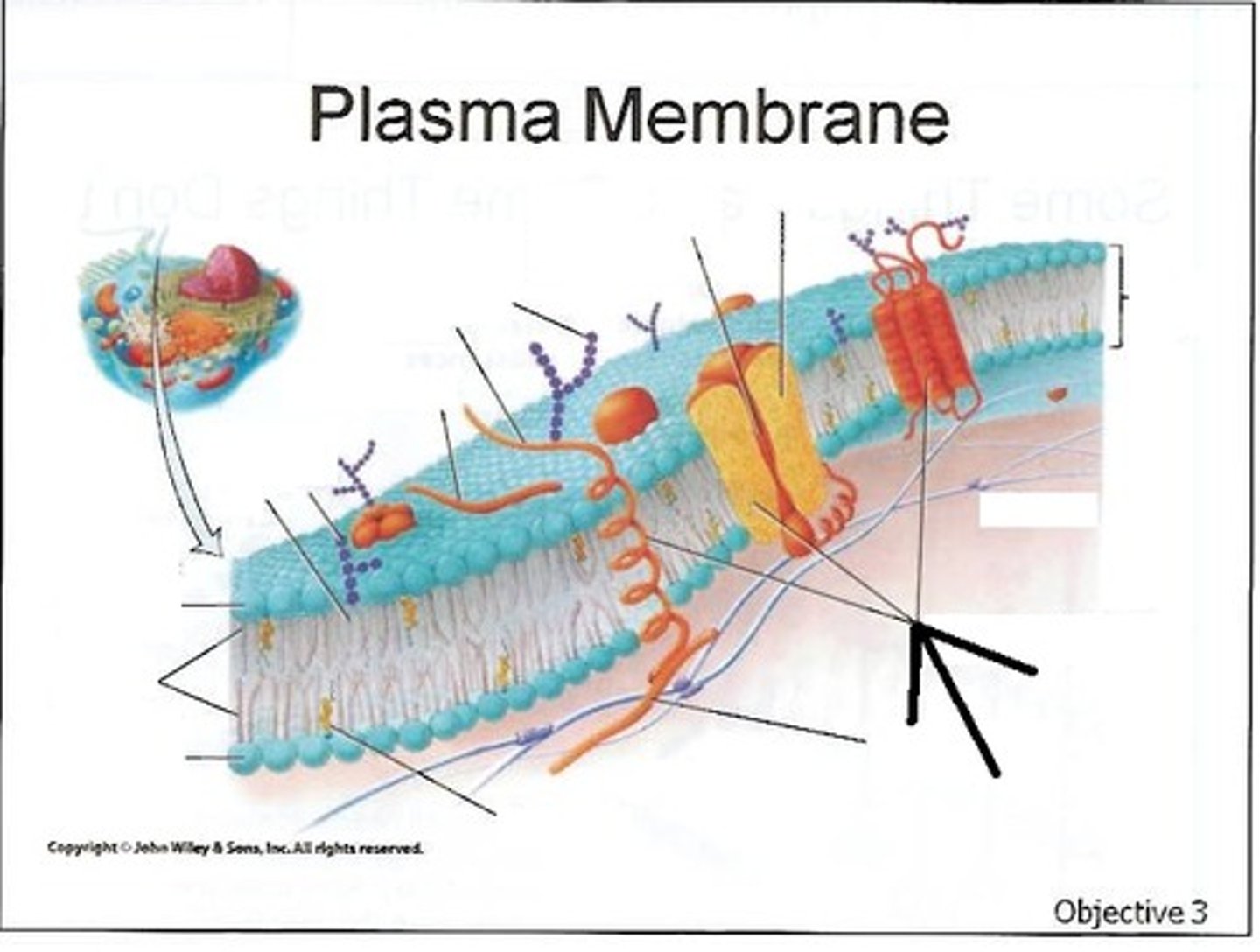
fluid-mosaic model
The currently accepted model of cell membrane structure, which envisions the membrane as a mosaic of individually inserted protein molecules drifting laterally in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids.
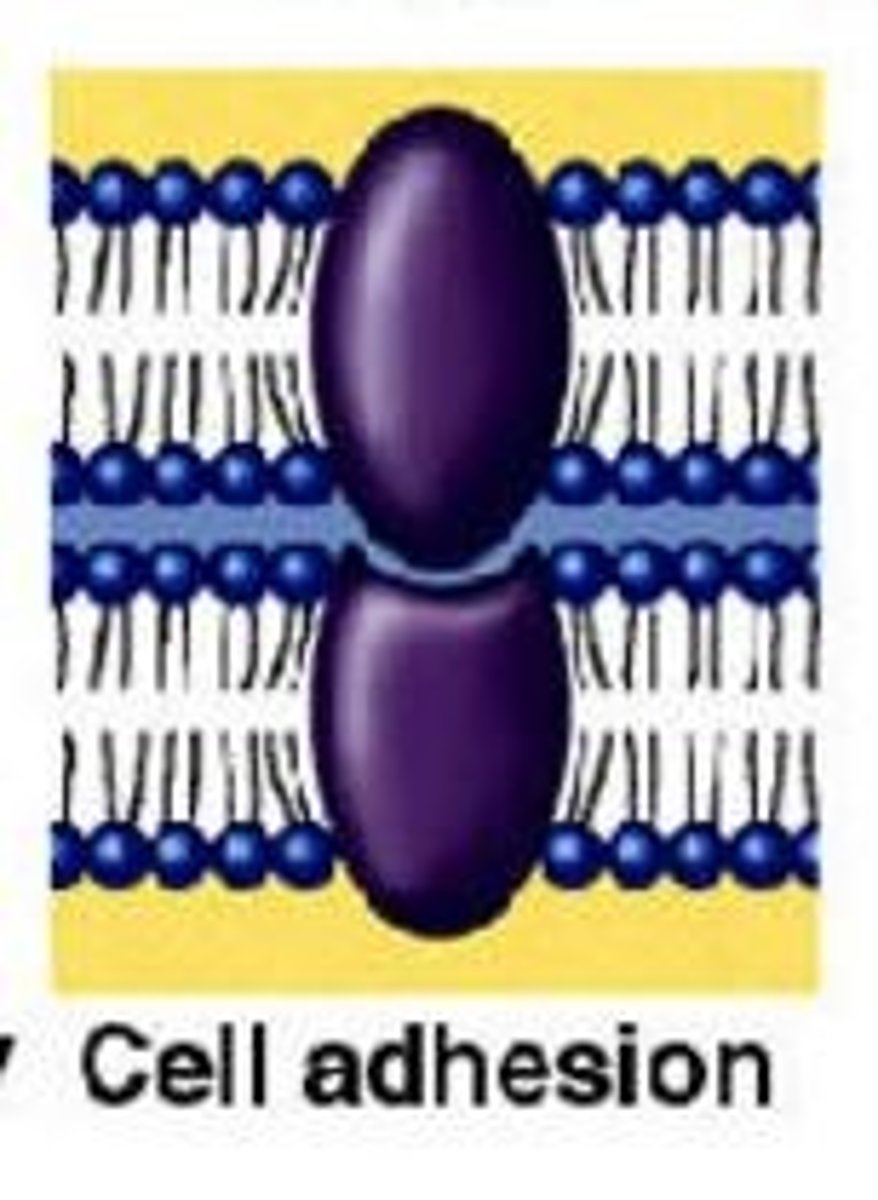
adhesion proteins
Adhesion proteins are membrane proteins that form junctions between adjacent cells.
What are the two main types of transmembrane proteins involved in transporting hydrophilic substances across the membrane, and how do they differ?
Protein Channels:
Form pores in the membrane to allow specific hydrophilic substances (e.g., ions or small polar molecules) to pass through.
Facilitate passive transport (no ATP required), moving substances down their concentration gradient.
Carrier Proteins (including Pumps):
Bind to substances and change shape to move them across the membrane.
Can facilitate passive transport or active transport (requiring ATP), as seen in pumps like the sodium-potassium pump.
channel proteins
: Channel proteins are integral membrane proteins that form pores in the cell membrane, allowing specific ions or molecules to pass through the membrane. They facilitate the passive transport of substances, enabling the movement of ions (such as sodium, potassium, calcium) and small polar molecules across the membrane, down their concentration gradients
nucleolus
A dense structure within the nucleus responsible for producing and assembling ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and combining it with proteins to form ribosome subunits.

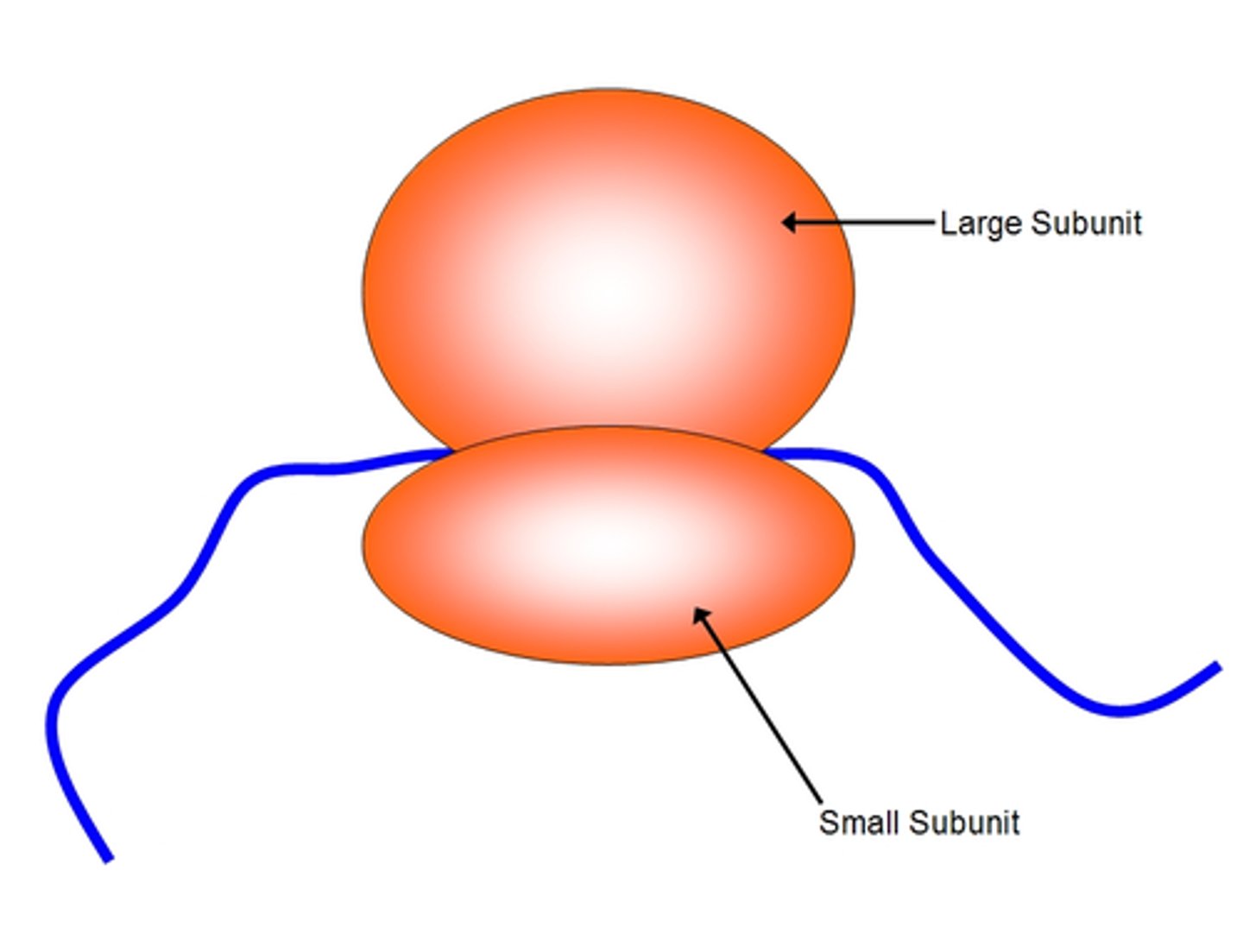
ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
- round structures of the large subunit. and the small subunit
- ribsomal RNA and proteins
-floating in the cell or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum
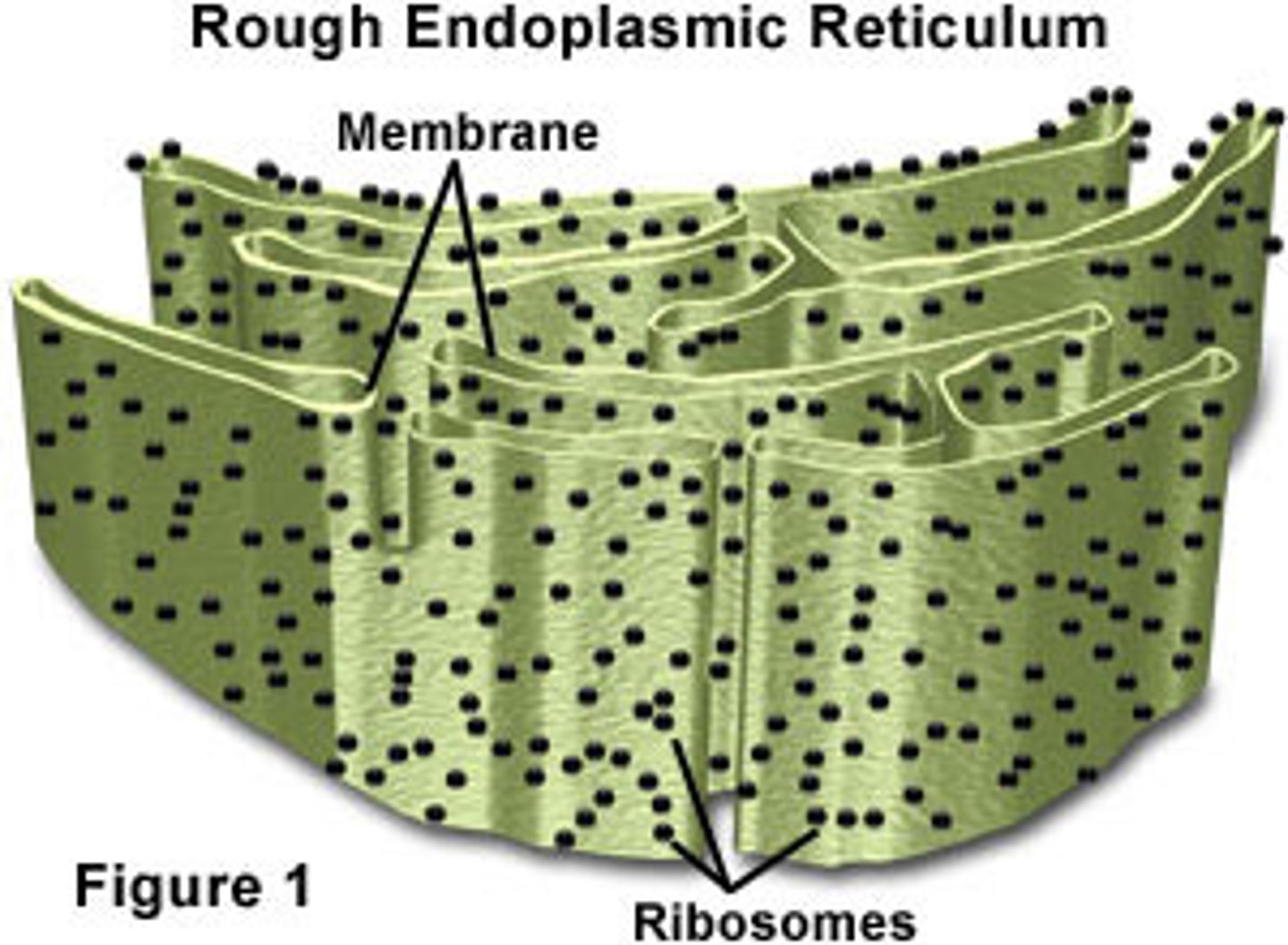
Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough)
A system of membranes that is found in a cell's cytoplasm and that assists in the production, processing, and transport of proteins (golgi bodies, lysosomes, the ER) and in the production of lipids.
- attached to nucleus, studded with proteins (compartmentalizes the cell)
golgi complex
a cell organelle (in eukaryotic cells) that helps make and package materials to be transported out of the cell
- packages them in vesciles, which gets carried to the plasma membrane
-involved in production of lysosomes
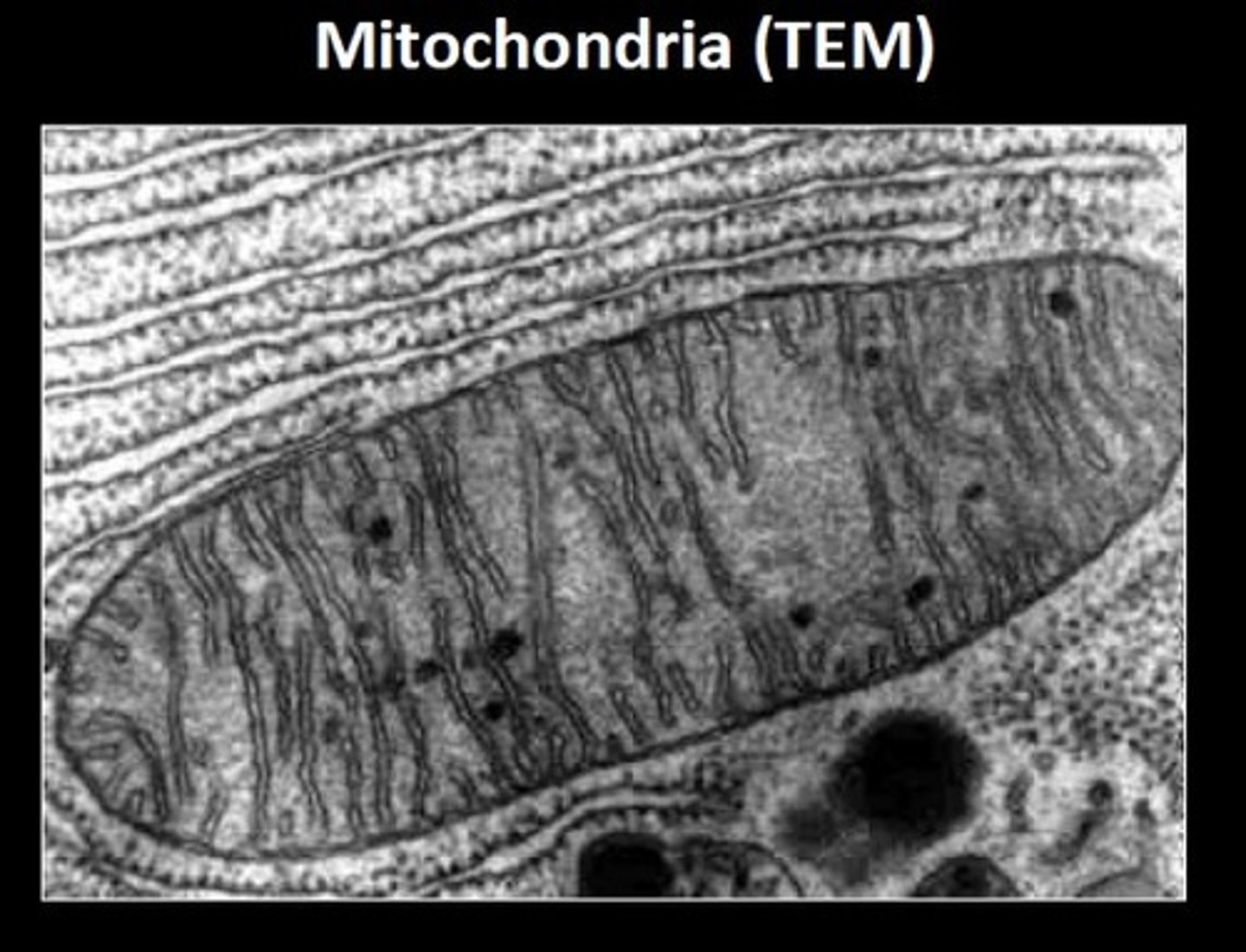
cristae
Infoldings of the inner membrane of a mitochondrion that houses the electon transport chain and the enzyme catalyzing the synthesis of ATP.
- seperates the matrix (innermost area) from the intermembrane space
- having folds increases surface area for making ATP
how do cilia and flagella differ in structure?
Cilia: Short, hair-like projections; typically numerous on a cell's surface
Flagella: Long, whip-like structures; usually only one or a few per cell
describe the internal structure of cilia and flagella
Cilia and flagella are membrane-bound organelles.
They have a 9+2 arrangement of microtubules (9 doublets around 2 central microtubules).
This structure allows them to perform functions like movement or signal reception.
how are basal bodies related to cilia? how is their internal structure different from that of cilia?
Basal bodies anchor cilia to the cell and help organize their formation. While cilia have a 9+2 arrangement of microtubules (nine doublets around two central microtubules), basal bodies have a 9+0 structure (nine triplets with no central microtubules)
structure of basal bodies and centrioles
Basal bodies are cytoskeletal structures found at the base of cilia and flagella.
They have a structure of 9 triplets of microtubules arranged in a circular pattern, with no microtubules in the center.
relationship between basal bodies and centrioles
basal bodies and centrioles are interconvertible (one can give rise to the other in certain situations)
centrioles can migrate to the plasma membrane and become basal bodies to anchor newly formed cilia/flagella
how are centrioles important for mitosis
responsible for organizing microtubules that form spindle fibers to separating the chromosomes during cell division
difference between “semi-permeable” and “selectively permeable”
semi-permeable: Allows some substances to pass through, often based on size (e.g., water, small molecules).
selectively permeable: Allows specific substances to pass through based on factors like size, charge, and polarity, often using transport proteins to regulate the movement.
centrioles
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in mostly animal cells
not present in prokaryotic cells
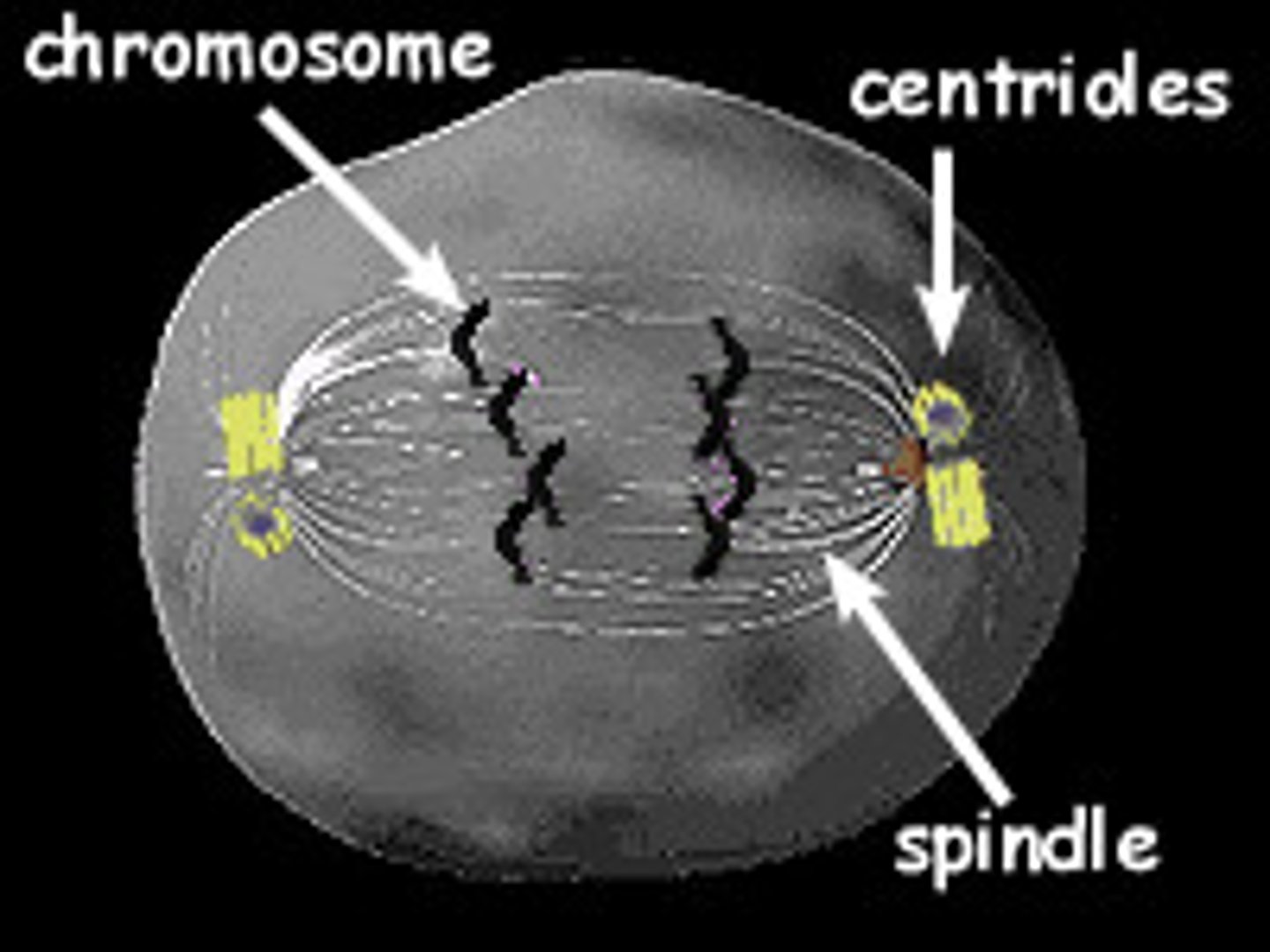
3 functions of microtubules and microfilaments
cellular movement
internal cytoskeleton
anchors/moves organelles
peroxisomes
Contain oxidase enzymes that detoxify alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and other harmful chemicals
- common in liver and kidney cells
cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
where do we find microtubules?
inside the structures of cilia/flagella
in the centrioles
cytoplasm/basal bodies
microtubules
made up of the protein tubulin
- cellular division and movement
Thick hollow tubes that make up the cilia, flagella, and spindle fibers. (centrioles)
provide structural support to the cell
microfilaments
composed of the protein actin
part of the cytoskeleton, and they play a key role in maintaining the cell's shape and structural integrity.
involved in cell movement, cytokinesis, and intracellular transport.
allow the cell to expand/contract by facilitating change in cell shape
eukaryotic ribosomes
80s, can be found attached to the endoplasmic reticulum
cell wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
- in fungi, it is made of chitin
aquaporins
A transport protein in the plasma membrane of a plant or animal cell that specifically facilitates the diffusion of water across the membrane
nucleus
enclosed by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. This structure contains pores that control the movement of molecules in and out of the nucleus, like RNA and ribosome subunits. Inside, the nucleus houses chromatin (DNA and associated proteins) and the nucleolus, where ribosome production begins. This organization allows the nucleus to perform its critical job of storing genetic information, regulating gene expression, and coordinating cell activities like growth and reproduction.
simple diffusion
passive movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration without the need for energy or carrier proteins.
It typically applies to small, hydrophobic molecules that can easily pass through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane.
facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels
plasmolysis
The process in which a plant cell's membrane pulls away from the cell wall due to water loss in a hypertonic solution, resulting in cell shrinkage.
What type of molecules pass through the cell membrane easily?
Hydrophobic molecules, such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and small nonpolar molecules, pass through the cell membrane easily because they can dissolve in the lipid bilayer and diffuse directly through it.
Why do hydrophilic molecules need assistance to pass through the cell membrane?
because the membrane’s lipid bilayer is hydrophobic, repelling water and polar substances. Transport proteins (like channels or carriers) help these molecules cross the barrier.
free ribosomes (in cytoplasm)
synthesize proteins that function within the cell's cytoplasm, such as enzymes involved in metabolism or proteins that work in the nucleus, mitochondria, or other organelles.
ribosomes on rough er’s function
synthesize proteins that are typically destined for secretion, incorporation into the cell membrane, or for use in lysosomes. These proteins are often processed in the ER and then sent to the Golgi apparatus for further modifications and transport.
polyribosomes
clusters of ribosomes attached to the same mRNA molecule, working together to produce multiple copies of a protein simultaneously.
what happens to the water potential when adding a solute to water
the water potential decreases because the solute lowers the number of free water molecules, making the solution more negative. This causes water to move toward areas with lower water potential.
sodium-potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell
- 3 sodium ions out, two potassium ions in
primary active transport
Active transport that relies directly on the hydrolysis of ATP to move molecules across the cell membrane against their concentration gradient
hydrolysis of ATP
Hydrolysis of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a chemical reaction where a water molecule breaks down ATP into ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and an inorganic phosphate (Pi).
Purpose: This reaction releases energy that cells use for various processes, such as muscle contraction, cell signaling
secondary active transport
use pre-existing gradient to drive transport of solute
resting membrane potential
the electrical charge difference across a cell membrane when the cell is not active
the inside of the cell is more negative than the outside
bc of unequal distribution of ions (more sodim outside, ore potassium inside)
the sodium-potassium pump helps maintain this balanace
typical value of -70mV, prepares the cell to send signals when needed
endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
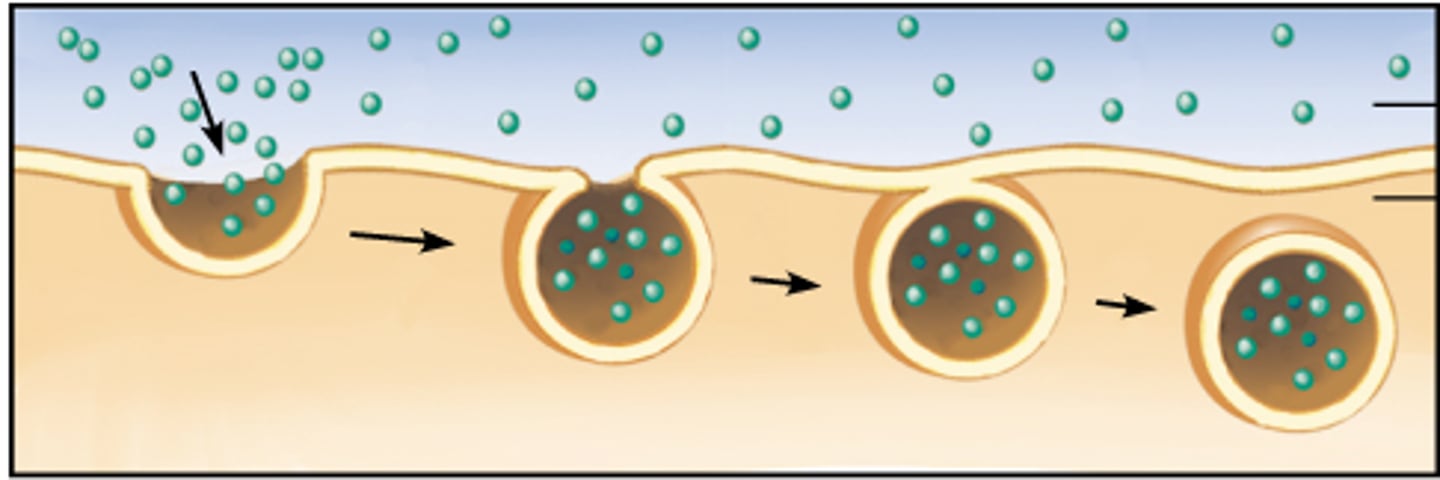
three types of endocytosis
phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor-mediated endocytosis
pinocytosis
often referred to as "cellular drinking”
cells engulf extracellular fluids and dissolved substances through endocytosis
the cell membrane folds inward, forming a vesicle to contain the ingested fluid
light microscopes
use light and glass lenses to magnify an image
- study stained or living cells
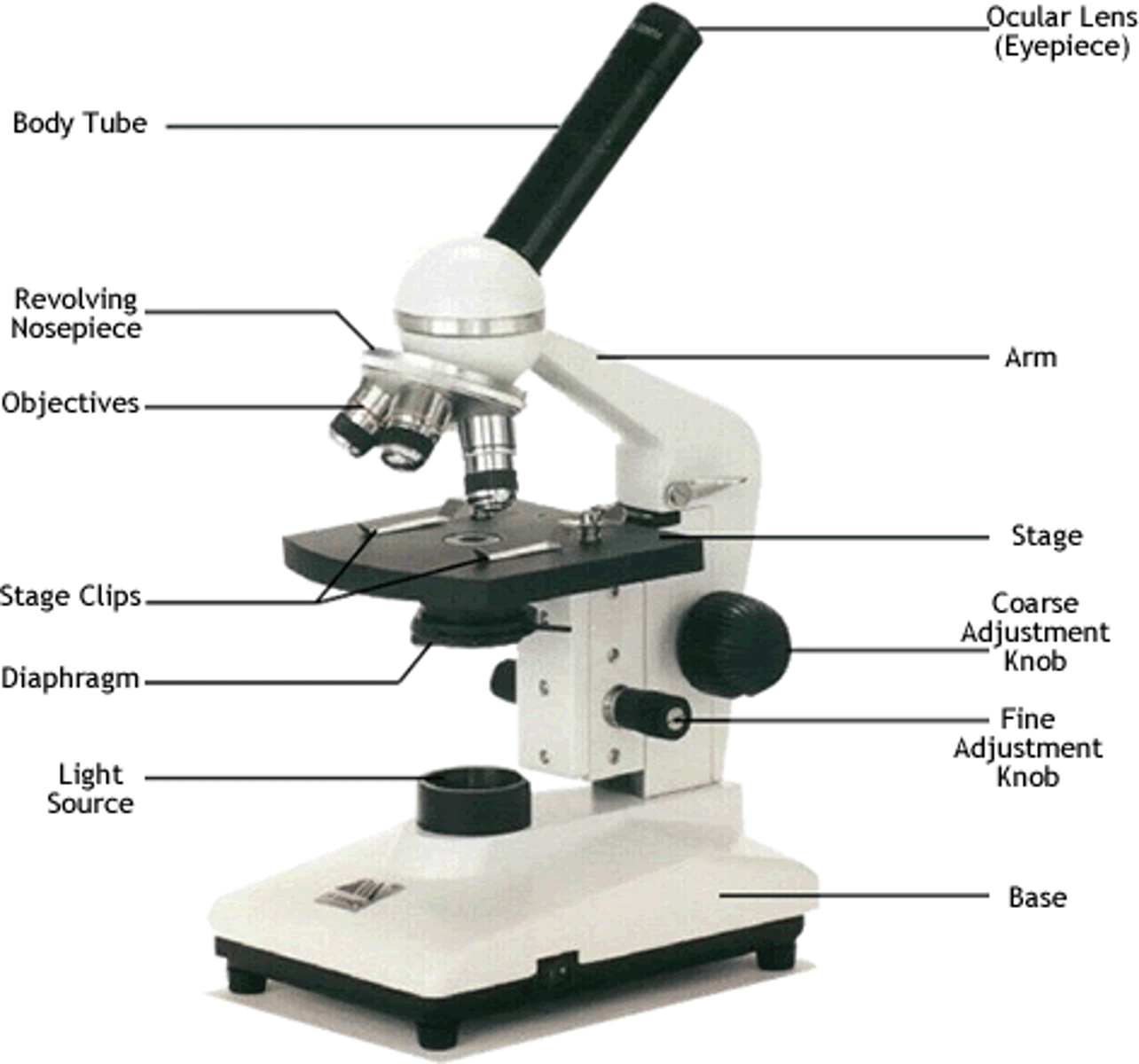
electron microscopes
use beams of electrons, rather than light, to produce images
- viruses, pores on nucleus
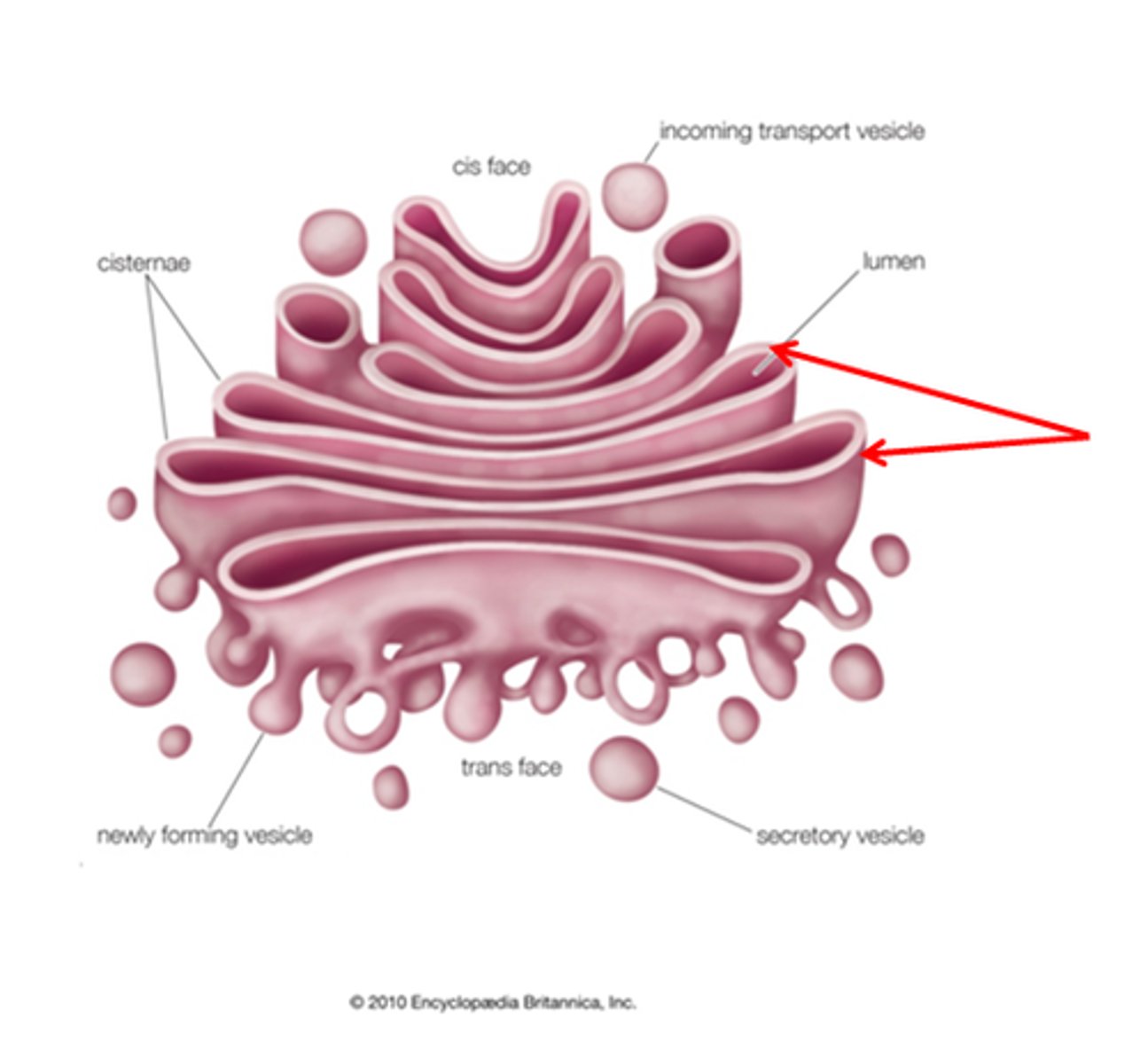
cisternae
Flattened, membrane-bound compartments that make up the Golgi apparatus.
- golgi stacks have around 3-20
- cis cisternae: close to RER
- medial: middle
- trans: farthest from the RER
-molecules can move between cisternae via vesicles
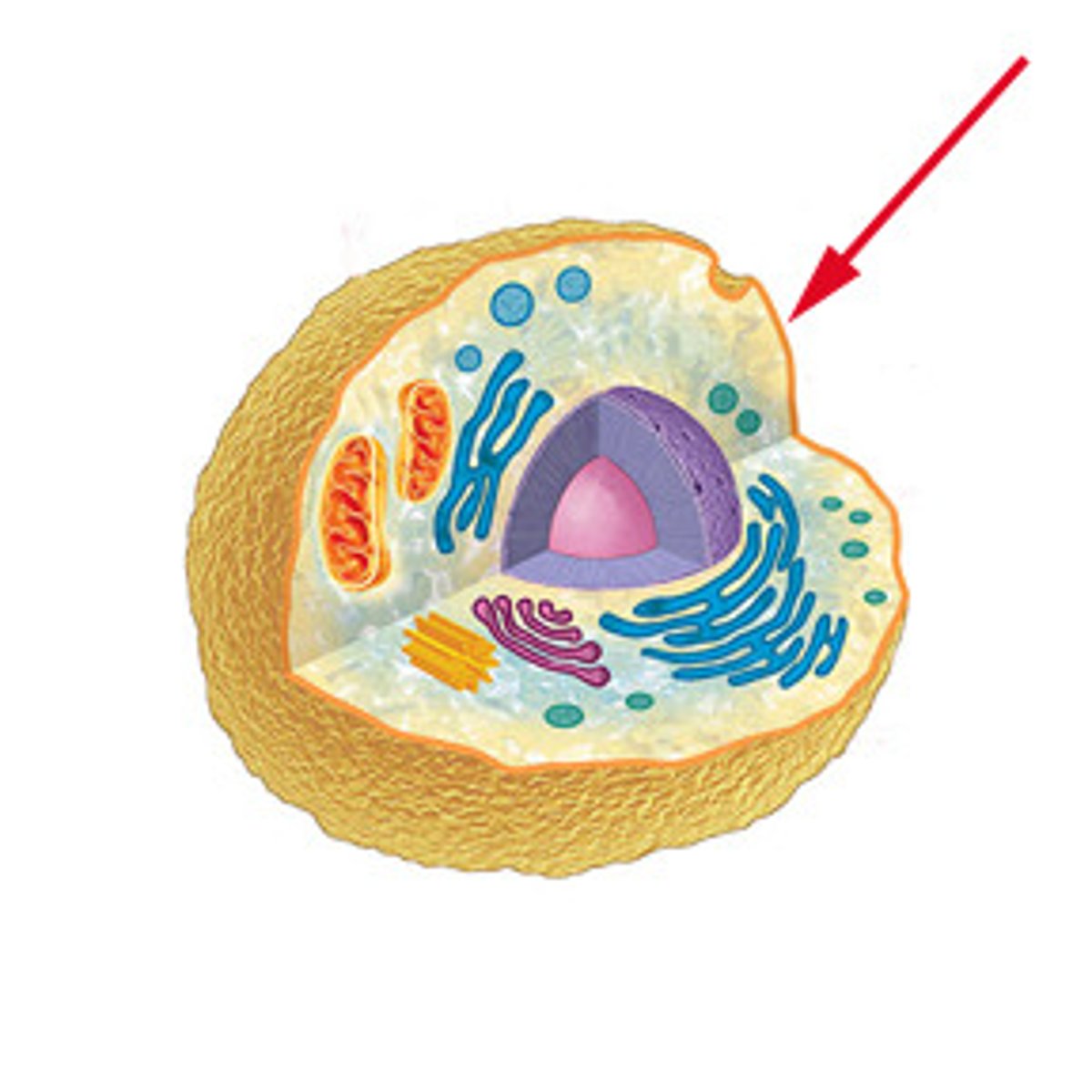
plasma membrane (cell membrane)
the “fully equipped” version of the phospholipid bilayer
it includes the phospholipid bilayer plus all the embedded proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrate chains that enable the cell to interact with its environment, transport materials, and communicate with other cells.
these additional components give the membrane its functionality and dynamic properties.
receptor proteins
Proteins that transmit information in and out of cells. They allow communication between cells.
- hormones
cell surface markers important for cell identification/recognition
glycoproteins and glycolipids
- a membrane protein that identifies the cell type
external glycogen chain
carbohydrate side chains
A carbohydrate side chain is attached to the surface of some proteins found only on the outer surface of the plasma membrane.
nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
function of cholesterol in the cell membrane
regulates how fast molecules are moving across the membrane
reduces membrane permeability
Smooth ER (SER)
type of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in cells that lacks ribosomes on its surface, giving it a smooth appearance. It is involved in various metabolic processes, including lipid synthesis, detoxification of drugs and poisons, and calcium ion storage. The SER also plays a role in carbohydrate metabolism and steroid hormone production.
mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
smooth outer membrane, inner membrane forms folds called cristae
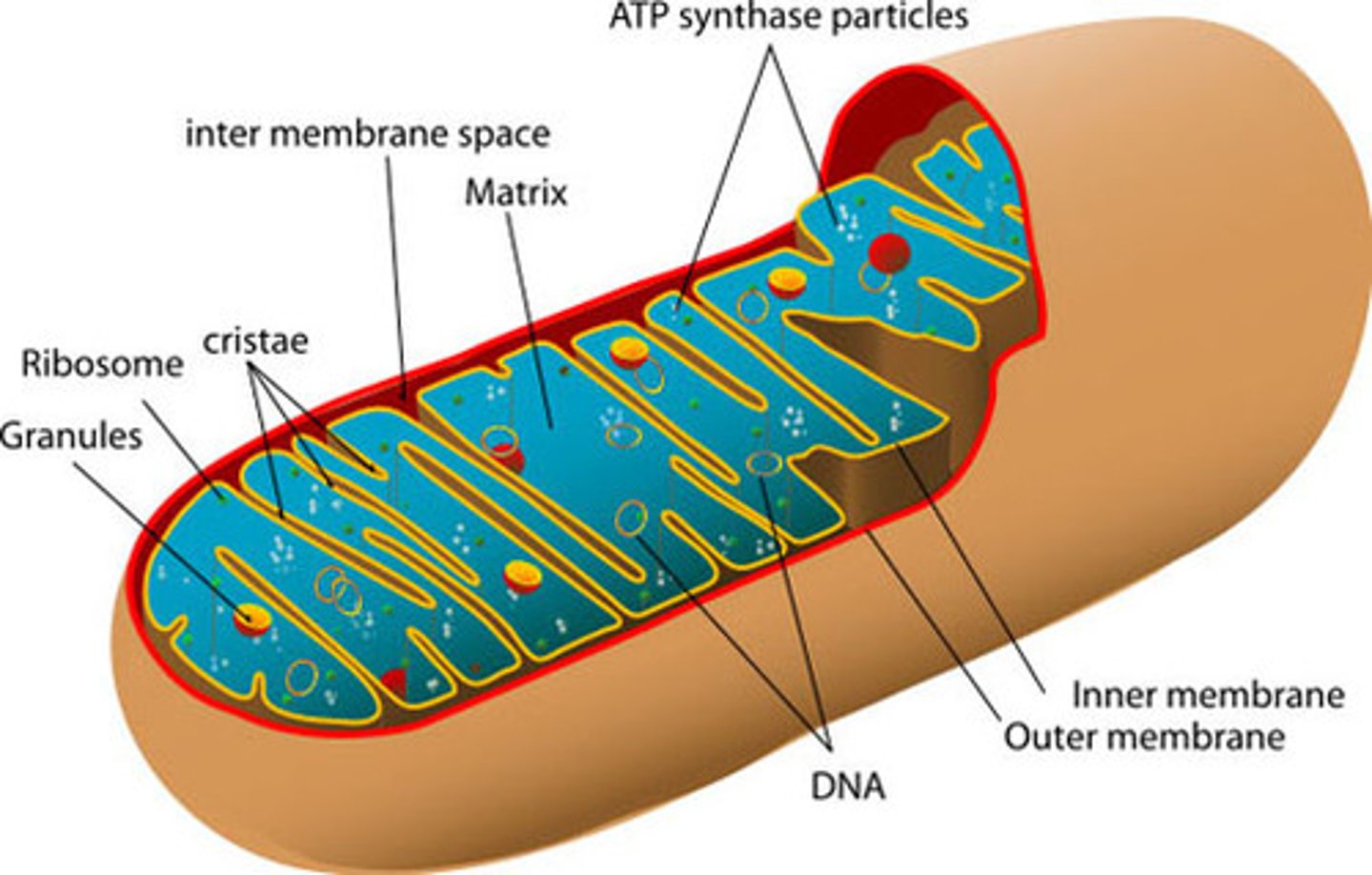
lysosomes
. They contain digestive enzymes that break down waste materials, cellular debris, and foreign invaders like bacteria. Lysosomes are often referred to as the cell's "waste disposal system" because they degrade and recycle macromolecules, playing a crucial role in cellular homeostasis and metabolism.
produced by the Golgi apparatus
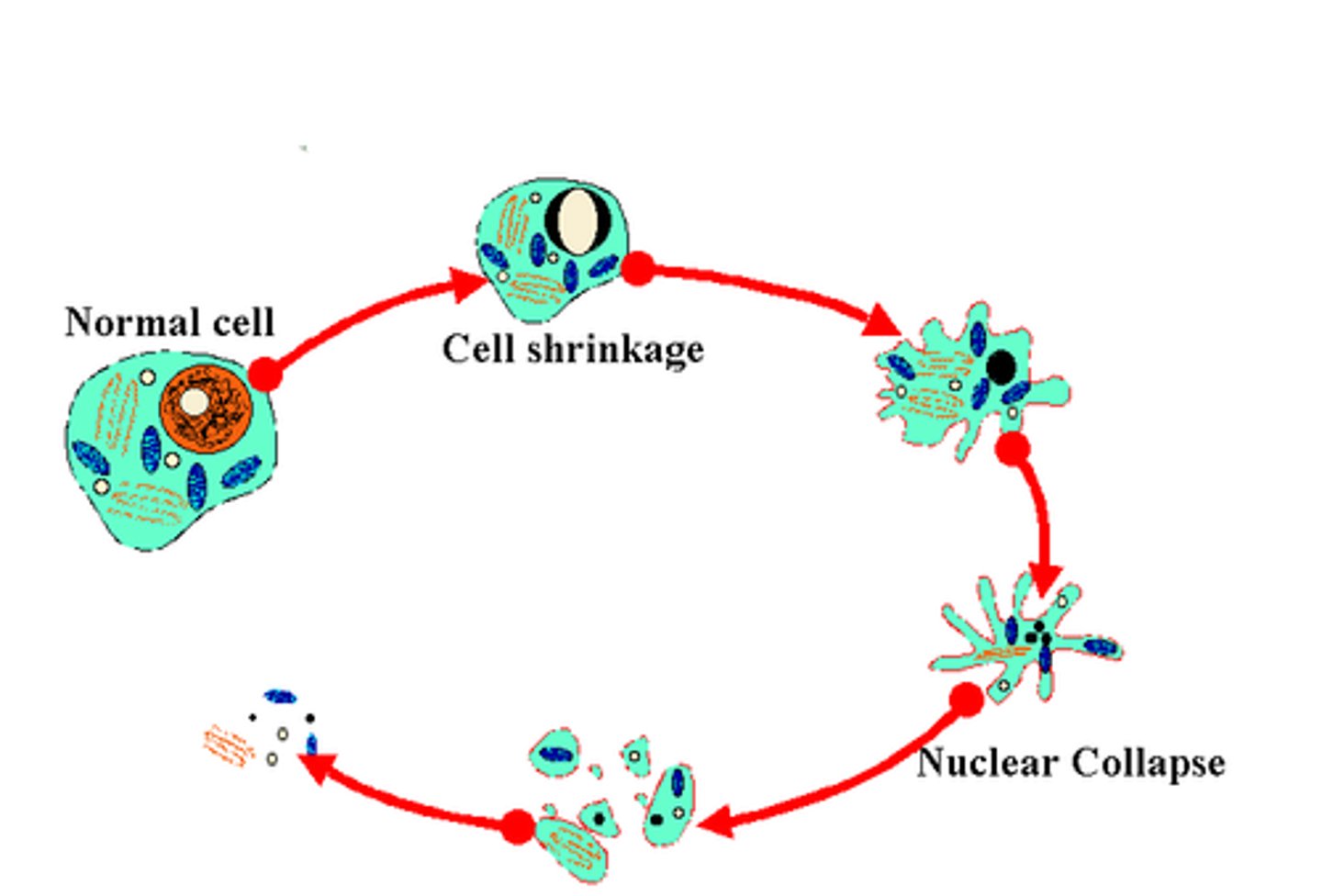
apoptosis
process of programmed cell death
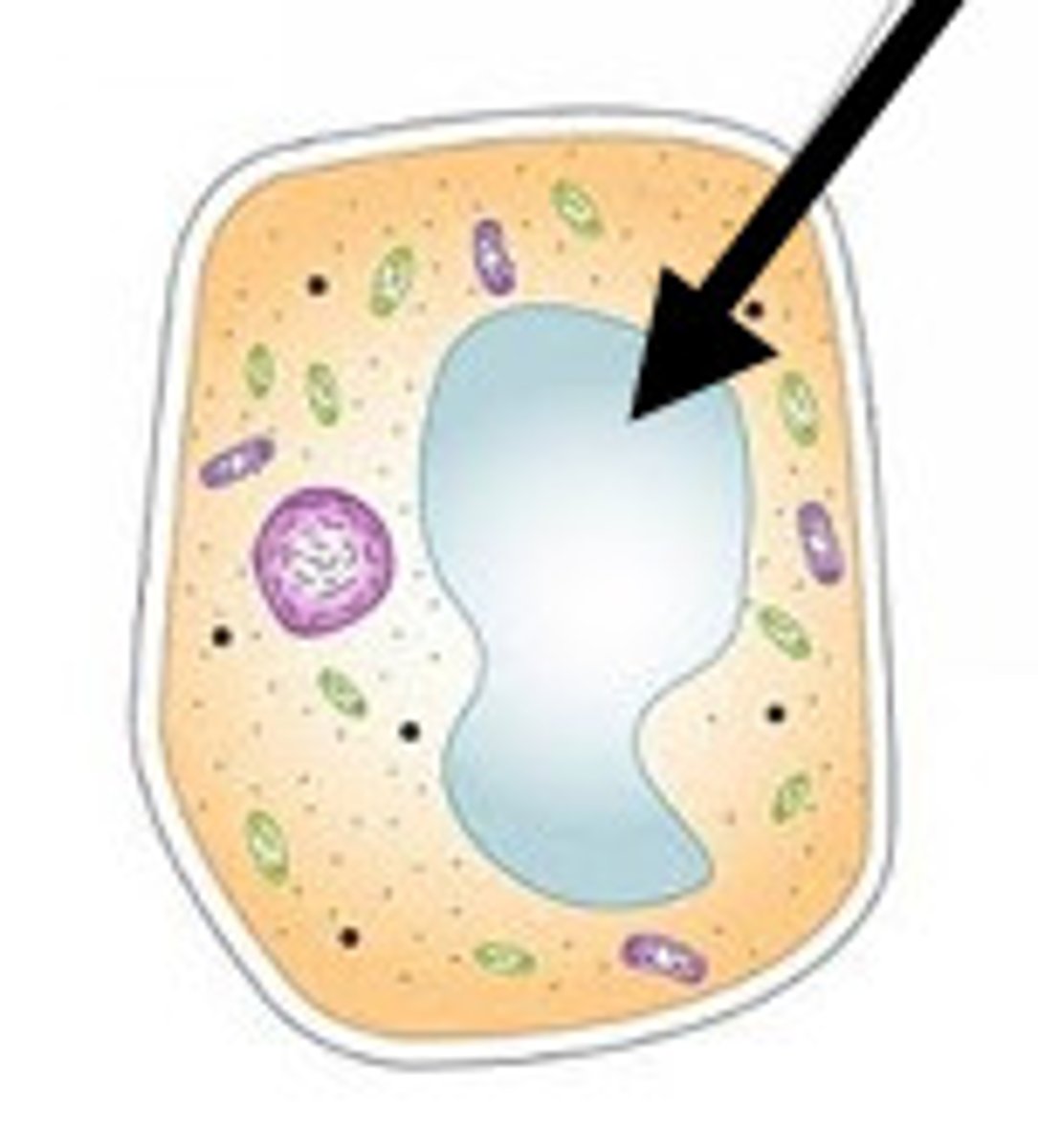
vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
cilia and flagella
hairlike structures that extend from the surface of the cell, where they assist in movement, signal reception, and organelle positioning (they are anchored by a basal body that interacts with the cell’s cytoskeleton)
prokaryotic ribosomes
(70s) smaller than eukaryotic ribosomes, found in the cytoplasm
chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
central vacuole in plants
stores excess water and provides extra support. The extra water in the vacuoles of plant cells keeps the plant from drying out.
what affects the ability of molecules to move across the cell membrane?
Size: Small molecules move through more easily than large ones.
Lipid Solubility: Hydrophobic (water-hating) molecules pass through easily, while hydrophilic (water-loving) ones need help
Transport Proteins: Large or hydrophilic molecules use proteins to cross.
Energy (ATP): Moving molecules against their concentration gradient needs ATP; moving with the gradient does not.
facilitated transport
Energy Requirement: Does not require energy (a type of passive transport).
Direction: Moves substances down their concentration gradient (from high to low concentration).
Mechanism: Utilizes carrier proteins or channel proteins embedded in the cell membrane to help specific molecules or ions cross the membrane.
diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
- movign down a concentration gradient
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
- water wants to move from high to low concentration
tonicity
The ability/strength of a solution surrounding a cell to cause that cell to gain or lose water.
concentration given. as a % of solution
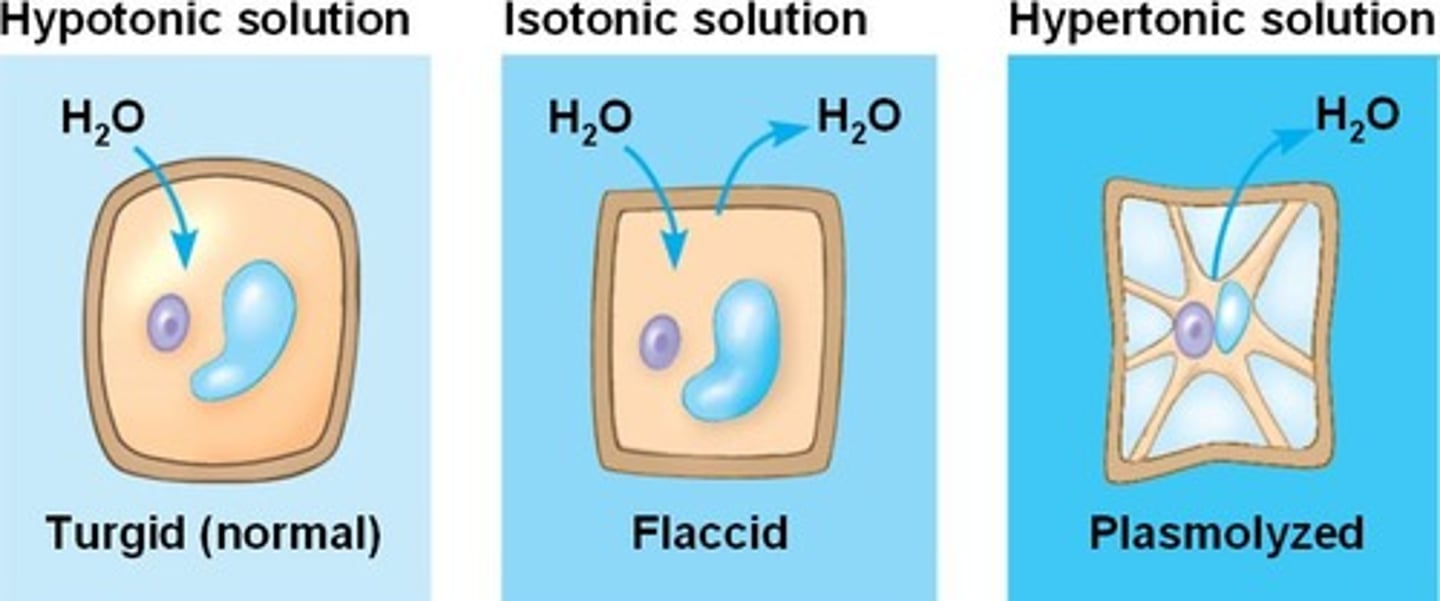
isotonic
- concentration of solute the same inside and outside
- cells in isotonic solutions won’t gain or lose H2O
-[outside cell] = [inside cell]
ex. 0.9% NaCl solution is ISOTONIC to red blood cells
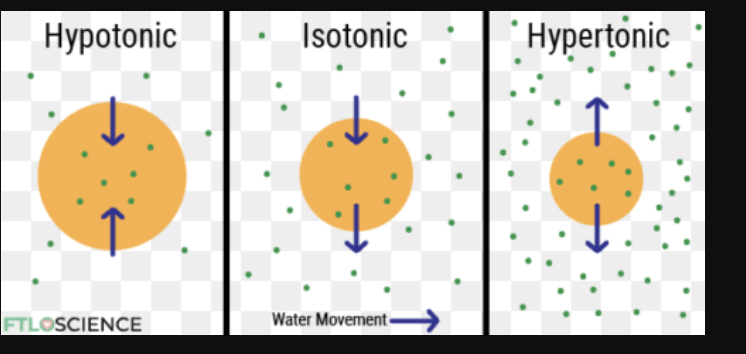
hypertonic
A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solute compared to another solution, typically the cytoplasm of a cell. This causes water to move out of the cell to balance the solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane. As a result, the cell experiences dehydration and begins to lose water, leading to a shriveled appearance, known as crenation.
cell contains 0.1% glucose; solution outside contains 0.5% glucose
hypotonic
A solution with a lower concentration of solute compared to another solution, leading to water moving into the cell
In animal cells, this can result in cell lysis (bursting), while plant cells are generally protected by their cell wall, but can still become very turgid.
hyperosmotic
A solution with a higher concentration of solute compared to another solution, resulting in water moving into the hyperosmotic solution due to osmosis.
hyposomotic
What it means: A solution is hypoosmotic when it has a lower total concentration of solutes (like salt, sugar, etc.) compared to another solution.
When is it used?: It’s used to compare two solutions, not in relation to cells, just comparing their overall solute concentrations.
Example: If Solution A has fewer solutes than Solution B, Solution A is hypoosmotic to Solution B.
water potential
The physical property predicting the direction in which water will flow, governed by solute concentration and applied pressure.
what happens when a red blood cell is added to water
will explode, because water will move into the cell
water is hypotonic compared to the blod cell, as it has fewer solutes than the inside of the cell
water moves into the blood cell because the water potential inside the cell is lower
since the cell has no cell wall (like plant cells do), it can’t withstand the pressure, and it bursts (lysis)
active transport
Energy (ATP) and carrier protein requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
active transport cells high in mitochondria
phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis “cell eating” in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells by extending its membrane AROUND the particle to form a pocket that eventually pinches off, creating an internal vesicle called a phagosome.
the produced vesicle merges with a lysosome, to break down the engulfed material

receptor-mediated endocytosis
The movement of specific molecules into a cell by the inward budding of membranous vesicles containing proteins with receptor sites specific to the molecules being taken in (lined with the protein clathrin) ; enables a cell to acquire bulk quantities of specific substances.