BNT 2025 Reviewer
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
POTS refers specifically to the traditional analog telephone service that operates over copper wires, facilitating basic voice communication.
Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS)
PSTN is the broader global network of interconnected telephone systems, which includes both analog (POTS) and digital technologies like fiber optics and Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN).
Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)
_______: Voice
_______: Voice and Data
Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS): Voice
Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN): Voice and Data
is a system of communications employing an apparatus that transforms a sound wave into an electrical wave, transmits the electrical wave over a suitable medium, and then transforms the electrical wave back into a sound wave at the receiver
-focuses on voice communications
-traditionally wire communications
-may be wire or wireless
Telephony
telephony block diagram
subscriber (old telephone) ---subscriber loop---central office
telephony according to sir matias is all about ________
switching
what is a central office?
switching ng calls
used standard voltage for telephone exchanges (central offices) to avoid corrosion (using a negative voltage reduces electrochemical corrosion in copper wires, prolonging their lifespan.)
-48V DC
key stages in a traditional telephone call setup
1. offhook
2. dial tone
3. addressing (tone dialing)
4. line status evaluation
5. call established
6. onhook
Voice Channel
Europe:
North America:
Nominal Voice Channel BW:
Voice Channel
Europe: 300Hz-3400Hz
North America: 200Hz-3300Hz
Nominal Voice Channel BW: 4 kHz
key stages in a traditional telephone call setup
1. _______
-When you lift the handset, the telephone switch detects a change in loop current (caused by completing the circuit in a -48V DC loop).
-This signals to the exchange that you want to initiate a call.
-nakaangat yung plunger ng telephone
OFFHOOK
key stages in a traditional telephone call setup
2.___________
-The central office (CO) or PBX sends a continuous tone (350Hz + 440Hz in North America) to indicate the system is ready to accept input.
-If no input is received within a timeout period, the call attempt is canceled.
DIAL TONE
key stages in a traditional telephone call setup
3.____________
-You dial the number using either:
DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency) - modern phones send tones for each digit.
Pulse Dialing - older rotary phones break the loop circuit in a specific pattern.
-The exchange interprets the digits and determines the route to the destination.
ADDRESSING (TONE DIALING)
key stages in a traditional telephone call setup
4. _____________
The exchange checks whether the called number is busy or idle
A. if busy
_________
B. if idle
________
LINE STATUS EVALUATION
A. if busy
(440Hz + 480 Hz)
B. if idle
(480Hz + 620 Hz)
key stages in a traditional telephone call setup
5.___________
-When the recipient answers (also goes Off-Hook), the exchange connects both lines.
-Two-way voice communication is established.
-The exchange maintains supervision, monitoring the line for disconnect events.
CALL ESTABLISHED
key stages in a traditional telephone call setup
6. _________
-When either party hangs up, their phone breaks the DC loop (no more current flow).
-The exchange detects this and disconnects the call.
-If only one party hangs up, the other hears a reorder tone (fast busy) until they also go On-Hook.
-nakababa yung plunger ng telephone
ONHOOK
SIGNAL IMPAIRMENTS (AND)
ATTENUATION
NOISE
DISTORTION
ONHOOK means
OFF HOOK means
ONHOOK means NO DC CURRENT FLOW
OFF HOOK means DC CURRENT FLOWS
WHEN DIALING
DC:
AC:
WHEN DIALING
DC: (dial tone) ->busy signal
AC: ringing signal and ringback signal
Tone dialing ->
Tone dialing -> Dual tone multi-frequency
minimum sampling rate must be satisfied to avoid _________
aliasing
fs(min)=2fa
if there is no fa or BW given consider ____. standard fs(min) is ______
4KHz
8KHz
telephone service as as an __________
waveguide act as _______
low pass frequency
high pass frequency
parallel to onhook/offhook circuit, equalizer circuit and hybrid yung ___________
ringer circuit
components of basic telephone set
- hook switch (cradle switch)
- dial assembly
- ringer assembly
- handset (containing Tx and Rx)
ringer assembly
green
red
yellow
white or black
green -> tip -> transmit
red -> ring -> receive
yellow -> slave phones (extensions) party line configurations or setups where multiple phones shared a single ring generator
white or black -> ground
subscriber loop design\resistance design:
RDC=0.1095/d^2
RDC -> ohms/miles
d -> inches/mils (finals ans)
subscriber loop requirements
-enough current/power to "activate" switches, telephone, transmitter/receiver, etc.
-minimum loss, minimum echo, distortion, crosstalk, etc.
-there must be an adjustable gain/loss
three types of subscriber loop design
1. normal loop
2. long line
3. special service
________-> least line
_________ -> common. no additional device to extend distance limitation - uses long coil to extend distance but: line cannot be used for internet because it operates at high freq. , loading coil only uses low pass freq. (voice)
special service
normal loop
- used for existing copper line/wire for high speed data transmission
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
is a broadband architecture where fiber optic cables run to a nearby street cabinet, and then existing copper wires (usually telephone lines) or coaxial cables complete the connection to homes and businesses.
FTTS (Fiber to the Street)
reference freq. in ph
800 Hz
Broadcast frequency
50 Hz - 15 KHz
subscriber loop length limits
1. attenuation limit
2. signaling limit
-refers to loop AC-loss at refrence frequency measured in dB or Np
-ref. freq. : 1000 Hz (North Am), 800 Hz (Eu, and other countries)
ATTENUATION LIMIT (TRANSMISSION DESIGN CRITERIA)
as a telephone is extended in length, _____________________________
as a telephone is extended in length, its loss at reference frequency increases
as loop extended in length while the battery (supply) voltage is kept constant, the effectiveness of signaling is ultimately lost
SIGNALING LIMIT (RESISTANCE DESIGN CRITERIA)
ATTENUATION LIMIT:
SIGNALING LIMIT:
ATTENUATION LIMIT: FREQUENCY
SIGNALING LIMIT: RESISTANCE
both ______ and ______ are to be considered in determining maximum subscriber loop length/design
resistance and frequency
- in a communication network refers to the aggregate of all user requests being serviced by the network
- traffic engineering alone who is responsible for Grades of Service na ipoprovide
Telephone Traffic
______
-large group of servers are more efficient for it to avoid callers having to wait but is more costlier.
- the rate at which calls arrive is seldom uniform
- alternate route to the destination increase the robustness of the network
principles that govern network design
fundamentals of traffic engineering
1. system
2. magbibigay ng service
3. maghahandle ng load
GRADE OF SERVICE
QUANTITY OF SERVER/TRUNK
TRAFFIC LOAD
is any effort on the part of a traffic source (subscriber, line, selector, etc.) to seize a circuit, switch or other traffic channel, whether or not the attempt is successful)
ATTEMPT
is any actual engagement or seizure of a circuit, switch or other traffic channel.
CALL
is the number of calls per unit of time. In practice, the time unit generally used is the busy hour. Calling rates frequently also designate the sources as, for example busy hour calls per main stations.
CALLING RATE
is the continous 60 minute period of the day during which the highest usage occurs. It does not necessarily coincide with a clock hour such as 9-10 a.m., etc. but may be offset as, for example, 9:15-10:15 a.m
BUSY HOUR
is the ratio of busy hour to total day calls. This is sometimes expressed as LENGTH OF DAY and when so expressed is the reciprocal of the above ratio. Thus, if the call concentration is, say, 0.125, the length of day is 1.00/0.125, or 8 hours.
CALL CONCENTRATION
is the length of time during which a call engages a traffic path or channel. In practice, the holding time will usually differ for each call, and there is no uniform holding time. For engineering purposes the average holding time for a large number of calls, obtained on a sampling basis, is usually employed.
HOLDING TIME
is the total occupied time of circuit, switches, or other traffic paths. It is obtained as the product of calls and the average holding time or those calls. The units in which the holding times are expressed determine the resultant units in which traffic is expressed.
TRAFFIC
NOTE: ■ In some of the literature on traffic, one hour of circuit occupation is designated as a __________. The name "_____" has now been adopted officially (International Standard Unit), to avoid confusion with "Traffic Unit"
"Traffic Unit" (TU)
Erlang
Is the traffic per time unit. In practical traffic calculations, the units usually employed are the CCS and the busy hour, so that traffic density is usually stated in terms of CCS per busy hour, abbreviated BH CCS., For mathematical calculations and development of formulae, it is customary to express traffic in terms of busy hour Erlang (BH ERL), since the use of the Erlang unit simplifies calculations,
TRAFFIC INTENSITY
is the busy hour traffic density per traffic source (subscriber line, selector, etc.) note that there is a difference between calling rate, which is calls per traffic source, and traffic rate, which is density (BH CCS, BH ERL, etc.) per traffic source.
TRAFFIC RATE
is a measure of the probability, that during a specified period of peak traffic a call offered to a group of trunks or circuits will fail to find on Idle circuit at the first attempt. Usually applied to the busy hour of traffic.
GRADE OF SERVICE
Traffic flow formula
A = C (calling rate per hour) x T (the average holding time per call)
The preferred unit of traffic is the Erlang named after the Danish Mathematician, _________. The Erlang is a dimensionless unit.
A.K. Erlang
another unit for traffic unit (TU)
1 ERL = 1 TU = 1 SERVER
other traffic unit that are not dimensionless are as follows:
Call hour (Ch)
Call second (Cs)
is the quantity represents by one 100s call or by aggregate of 100 Cs of traffic.
"Cent" Call-second (CCS)
is the average intensity in one or more traffic paths occupied in the busy hour by 1-2 minutes call or for an aggregate duration of 2 minutes
Equated Busy Hour Call (EBHC)
traffic units can be related as follows:
__ Erlang = __ EHBC = __ CCS = ___ Cmin
1 Erlang = 30 EHBC = 36 CCS = 60 Cmin
1 Erlang is how many servers?
1 server = 1 erlang
___- di ka makaconnect / nasa queue
___- nakakaconnect ka/ naoccupy yung channel
Holding Time
Traffic
- probability that a call will be blocked at first attempt and at busy hours
Grade of Service (GoS)
to convert minutes into erlang you should just ___________
to convert erlang into CCS you should just _______
divide it into 60 mins
multiply it to 36 CCS
typical GOS range: ____________
P01 - P05
Possible way to increase Traffic caused by a group of circuit:
o Queueing (waiting)
o Alternate Routing
Blockage Theories
■ Block Calls Cleared or BCC (Loss probability equation or GOS)
■ Block Calls Delayed (Delay probability equation)
■ Block Calls Held (Loss probability equation)
when blockage is encountered calls overflow and then completed
Block Calls Cleared or BCC (Loss probability equation or GOS)
calls are held in Queue until a server is available and then call is completed
Block Calls Delayed (Delay probability equation)
merely given a fast busy signal or Teoder signal and must redial later
Block Calls Held (Loss probability equation)
formula for Erlang B (BCC)
P = (A^n/n!)/summation of (A^x/x!) from x=0 to n
formula for Erlang C (BCD)
P = (A^n/n!) (n/n-A)/summation of (A^x/x!) + (A^n/n!) (n/n-A) from x=0 to n
formula for Poisson (BCH)
P= (e^-A)(summation of (A^x/x!)
max. frequency: ~1 MHz
max. data rate: Voice only
CATEGORY OF UTP CABLE
Category 1 (Cat 1)
max. frequency: ~4 MHz
max. data rate: 4 Mbps
CATEGORY OF UTP CABLE
Category 2 (Cat 2)
max. frequency: 16 MHz
max. data rate: 10 Mbps (Ethernet)
CATEGORY OF UTP CABLE
Category 3 (Cat 3)
max. frequency: 20 MHz
max. data rate: 16 Mbps
CATEGORY OF UTP CABLE
Category 4 (Cat 4)
max. frequency: 100 MHz
max. data rate: 100 Mbps
CATEGORY OF UTP CABLE
Category 5 (Cat 5)
max. frequency: 100 MHz
max. data rate: 1 Gbps
CATEGORY OF UTP CABLE
Category 5e (Cat 5e)
max. frequency: 250 MHz
max. data rate: 1-10 Gbps (up to 55 m)
CATEGORY OF UTP CABLE
Category 6
max. frequency: 500 MHz
max. data rate: 10 Gbps (up to 100 m)
CATEGORY OF UTP CABLE
Category 6a
max. frequency: 2000 MHz
max. data rate: 25-40 Gbps (short range)
CATEGORY OF UTP CABLE
Category 8
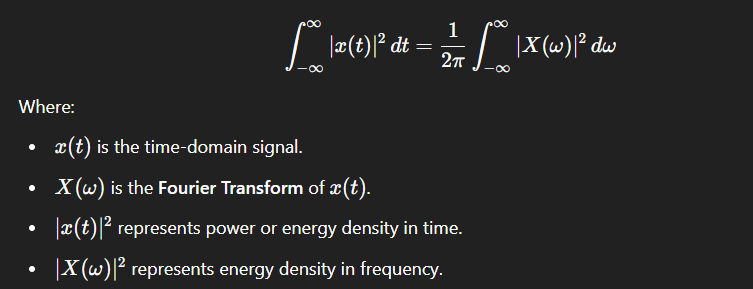
The total energy of a signal in the time domain is equal to the total energy in the frequency domain.
Parseval's Theorem (Energy Theorem)
is like STP, but with an extra outer braided or foil shield similar to coaxial cable as shown in figure 4, which offers still improved protection from interference
from external sources.
S/STP
SCREENED SHIELDED TWISTED PAIR WIRE
parts of coax
A:outer plastic sheath, B:copper screen, C:inner dielectric insulator, D:copper core
RG ___ used in thinnet
RG-58
especially constructed
hollow metallic pipes. they are used at microwave freq.
Waveguides
______ is the power loss of a radio signal as it travels from the transmitter to the receiver.
free space loss
The first artificial satellite, launched by Russia (then known as the
Soviet Union) in the late 1950s, was about the size of a basketball. It did nothing but transmit a simple______ signal over and over.
Morse code
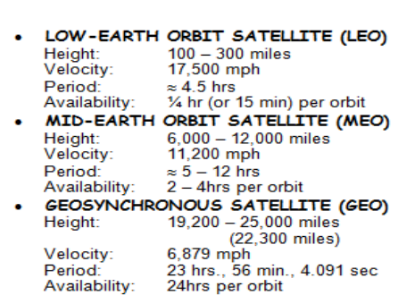
frequency bands used in satellite and radar

Satellites can be
classified according to orbits, in terms of altitude, such as:
the___________can transmit data to many destinations at the same time. The broadcast radio covers the range of frequency
from 3 to 300 Hz. From 30MHz to 1GHz, this range is most effective for broadcast radio to transmit data.
broadcast radio
________ is achieved using transceivers (see figure 9) that modulates non-coherent infrared light. Transceivers must be line of sight to each other, either directly or by reflection from light-colored surface such as the ceiling of the room.
Infrared communication
The infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum covers the range from roughly 300 GHz (1 mm) to 400 THz (750 nm). It can be divided into three parts:
• Far-infrared
• Mid-infrared
• Near-infrared
_______ is the combination or hybrid of different bounded media of the same type in order to increase the capacity (such as bandwidth and distance) of the
line carrying the information. It provides the capability for handling low speed data communication, high-speed local area network communication, and sometimes
also video signal distribution.
Cabling system
-is a thin, flat electrical conductor separated from a ground plane by a layer of insulation or an air gap
-used in printed
circuit designs
microstrip
-is a conductor sandwiched by dielectric between a pair of ground planes
-like microstrip but sandwiched between two ground planes and respective insulating layers
stripline
is a measure of how far electrical conduction takes place in a conductor, and is a function of frequency.
skin depth
is a graphical calculator. it allows us to see at a glance
what the effects of altering the transmission line (feed)
geometry will be. If used regularly, it gives the practitioner a
really good feel for the behavior of transmission lines and the
wide range of impedance that a transmitter may see for
situations of moderately high mismatch (VSWR).
Smith Chart