Chemistry Chapter 4: Three Major Classes of Chemical Reactions
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
oh my god bruh
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What mixture is homogenous with a uniform composition and no visible boundaries among the components.
A solution
A solution consists of…
it consists of at least one solute and a solvent
What is the substance that dissolves in a solution?
The solute - it is usually the smaller quantity within the mixture.
What is the substance that dissolves the solute in a solution?
The solvent - it is usually the larger quantity within the mixture.
What is the solvent in an aqueous solution?
Water is the solvent in an aq
A particular solution has a specific…
it has a specific concentration - the quantity of solute dissolved in a given quantity of solution (or of solvent)
How is the concentration of a solution given?
It is given by the quantity of solute present in a given quantity of solution
Molarity (M) is often used to express concentration, what is the equation for molarity?
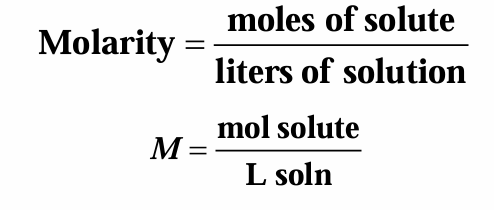
How is water such a good solvent?
It is a polar molecule, due to its uneven distribution of electron charge and its bent molecular shape.
It is great at pulling electrons and structures apart from solutes!
What form of reaction occurs when two soluble ionic compounds react to give an insoluble product?
It is a precipitation reaction - this insoluble product is called a precipitate
How does this precipitate form?
It forms through the net removal of ions from solution
Is it possible for more than one precipitate to form in precipitation reaction?
YES!!! It is possible for more than one precipitate to form
What do molecular equations show?
This equation reveals the least about the species that are actually in solution, because it shows all reactants and products as if they were intact, undissociated compounds
What equation shows all soluble ionic substances dissociated into ions?
Total ionic equations - this gives the most accurate information about species in solution
What are spectator ions?
They are ions that are not involved in the actual chemical change. They appear unchanged on both sides of the total ionic equation
What equation eliminates the spectator ions and shows only the actual chemical change?
Net ionic equations
How can you predict on whether a preciptate will form?
Note the ions present in the reactants.
Consider all possible cation-anion combinations.
Use the solubility rules to decide whether any of the ion combinations is insoluble. (Any insoluble combination identifies a precipitate that will form)
What substance produces H⁺ ions when dissolved in H2O?
This substance is an acid
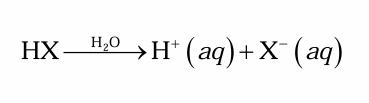
What substance produces OH− ions when dissolved in H2O
This substance is a base
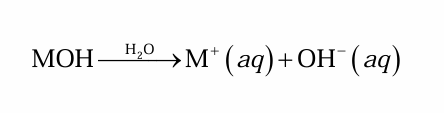
What is another name for an acid-base reaction
This reaction is also called a neutralization reaction.
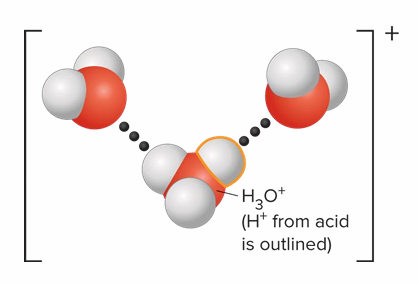
What compound is formed when H+ interacts with H2O
It forms H3O+, since H+ interacts strongly with H2O in an aqueous solution
What do strong acids and bases do in an aqueous solution?
They dissociate completely into ions in an aqueous solution
What type of acids and bases are strong electrolytes, and conduct well in a solution?
Strong acids and bases
What do weak acids and bases do in an aqueous solution?
These acids and bases dissociate very little into ions in aqueous solution
What type of acids and bases are weak electrolytes, and conduct poorly in a solution?
Weak acids and bases
What are strong electrolytes?
Ionic compounds
Strong Acids
Strong Bases
What are weak electrolytes
Weak acids
Weak bases
What are nonelectrolytes?
Covalent (molecular) compounds
What occurs in titration?
The concentration of one solution is used to determine the concentration of another
In an acid-base titration, a standard solution of base is usually added to a sample of acid of unknown molarity.
An acid-base indicator…
Has different colors in acid and base and is used to monitor the reaction progress.
What occurs at the equivalence point of titration?
The mol of H⁺ from the acid = the mol of OH− ion produced by the base at this point
What occurs at the end point of titration?
It occurs when there is a slight excess of base and the indicator changes color permanently.
Your solution is pink!!!
What is oxidation in reactions?
It is the is the loss of electrons
What is reduction in reactions?
It is the gain of electrons
What agent gains electrons and is reduced in a reaction?
It is the oxidizing agent in a reaction
What agent loses electrons and is oxidized in a reaction?
It is the reducing agent in a reaction
What type of reaction involves an electron transfer?
A redox reaction involves an ET
Does oxidation and reduction occur together?
YES!!!!! They occur together in a reaction
What are combination reactions in redox reactions?
This reaction occurs when two or more reactants combine to form a new compound:
X + Y → Z.
What are decomposition reactions in redox reactions?
This reaction occurs when a single compound decomposes to form two or more products:
• Z → X + Y.
What are the two types Displacement Reactions in redox reactions?
Double displacement:
AB + CD → AD + CB.
or
Single displacement:
X + YZ → XZ + Y
What is combustion in redox reactions?
It is the result from the process of combining with O2