PART 2- Hussein Exam 1
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BASED OF SG I REPEAT BASED OFF SG
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Inflammation leads to a low grade fever which leads to…
increase phagocytosis
What’s the definition of epidemic?
a. an endemic that spreads throughout the world
b. present in high but constant level in an area/region
c. more cases than predicted within a certain community, used to describe disease outbreaks
d. total number of cases existing in a community at a given time
c
What’s the definition of endemic?
a. an epidemic that spreads throughout the world
b. present in low but constant level in an area/region
c. more cases than predicted within a certain community, used to describe disease outbreaks
d. total number of cases existing in a population at a given time
b
What’s the definition of pandemic?
a. an epidemic that spreads throughout the world
b. present in high but constant level in an area/region
c. less cases than predicted within a certain population, used to describe disease outbreaks
d. total number of cases existing in a population at a given time
a
What bacteria metabolizes glycogen to glucose to lactic acid. ALL to lower the pH and protect the vagina?
Lactobacillus
Virulence mechanisms basically describe how a bacteria survives inside the host and isn’t destroyed. For each of the following mechanisms, list the pathogen that uses that mechanism to survive phagocytosis:
Virulence Mechanism | Bacteria |
Prevention of Phagolysosome fusion | |
Escape into cytoplasm | |
Resistance | |
Inhibition of phagocytes oxidative pathway (no oxidative burst—> no killing) |
Virulence Mechanism | Bacteria |
Prevention of Phagolysosome fusion | Mycobacterium Tuberculosis |
Escape into cytoplasm | Shigella Dysenteriae |
Resistance | Leishmania |
Inhibition of phagocytes oxidative pathway (no oxidative burst—> no killing) | Legionella Pneumophila |
What type of organism is Leishmania?
parasitic, protozoan, unicellular flagellate
What are 2 antiphagocytic mechanisms that allow for intra-host survival of the bacteria? (aka what allows the bacteria to not be noticed by the phagocytes)
molecular mimicry
coat bacteria with sialic acid OR
O antigen blocks phagocytes access to bactera
How do bacteria evade defensins?
produce peptidase that break down the defensin (a peptide)
Which of the following is a virulence factor?
a. IgA
b. IgA-protease
c. IgG
d. IgG- protease
b.
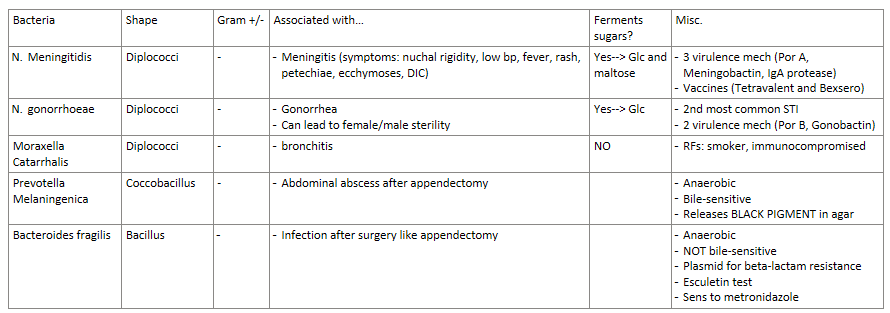
For each of the following exotoxins, list their AB domain:
Diphtheria
Cholera
Anthrax
Diphtheria- AB
Cholera- A+5B
Anthrax- 2A+B
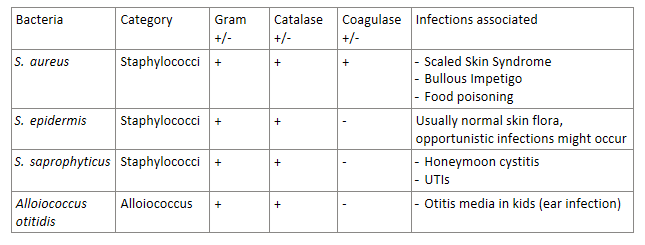
The 2 main types of GRAM + cocci bacteria are…
staphylococci and streptococci
THE MAJOR DIFFERENCE BETWEEN staphylococci and streptococci is whether it’s catalase + or -. Which is which?
staphylococci- CATALASE +
streptococci- CATALASE -
(FYI: catalase enzyme deals with whether it uses O2 or not)
Staphylococci and Streptococci can either be coagulase + or coagulase -
What strains of staphylococci and streptococci are each?
Coagulase + | |
Coagulase - |
Coagulase + | Staphylococcus aureus |
Coagulase - |
|
Simply just remember—> the ONLY coagulase + is Staphylococcus aureus
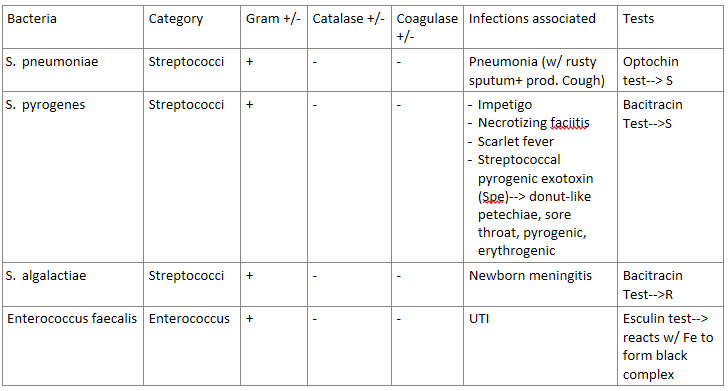
Strep hemolysis is used to classify Streptococci bacteria.
There are 3 types—> α/β/𝜸
How do each type present? (green, clear, or nothing?)
α hemolysis | Partial hemolysis—> APPEARS GREEN |
β hemolysis | Complete hemolysis—> CLEAR/WHITE |
𝜸 hemolysis | No hemolysis |
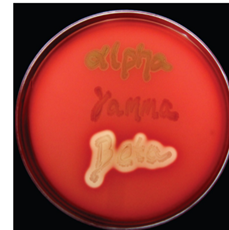
After a strep hemolysis is done, a Bacitracin test can be done to further classify Streptococci bacteria.
Does it further classify α, β, or 𝜸 hemolysis?
For the results—> which is sensitive (S)? which is resistant (R)?
β hemolysis
R (resistant)—> S. agalactiae
S (sensitive)—> S. pyogenes
After a strep hemolysis is done, an Optochin test can be done to further classify Streptococci bacteria.
Does it further classify α, β, or 𝜸 hemolysis?
For the results—> which is sensitive (S)? which is resistant (R)?
a hemolysis
R (resistant)—> Viridans Strep
S (sensitive)—> S. pneumoniae
The bacteria S. pneumoniae(a strep cocci bacteria) is associated with what infection? (hint: look at the name)
pneumonia—> with rusty sputum, and a productive cough
Answer the following about S. pyrogenes (a strep cocci bacteria):
Can enter through infected _____________
What infections can be caused by this bacteria?
What exotoxin is associated? What are the side effects of this exotoxin?
This bacteria has lipoteichoic acid that binds to…
can enter through infected mosquito bites
Infections—> Impetigo (skin infection), necrotizing fasciitis (flesh-eating infection), scarlet fever
Spe or Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin causes:
donut-like petechiae (red spots on roof of mouth)
sore throat
erythrogenic toxin (cause of red rash in scarlet fever) (FYI: this toxin causes another toxin if that makes sense)
pyrogenic (fever)
has lipoteichoic acid that binds to ECM protein fibronectin
Answer the following about Streptococcus agalactiae:
Gram + or -
hemolytic α/β/𝜸?
________- resistant
Lancefield group ___
what infection does this cause?
(disclaimer: a lot of this info was in the sg, but not his pp)
gram +
beta-hemolytic
bacitracin-resistant
Lancefield group B
cause of neonatal/newborn MENINGITIS
Answer the following about Enterococcus faecalis:
Gram + or -
____________ resistant
What test do we use to test for this bacteria? what indicates a + result?
causes what infection?
(disclaimer: this bacteria was in the study guide, but not his pp)
gram +
vancomycin resistant
Esculin test—> we react the bacteria with Fe, if it forms a black complex= positive result
causes UTI
The bacteria S. Saprophyticus (a staph cocci bacteria) is most associated with what infection? It is the second leading cause of this infection to what bacteria?
Honeymoon cystitis aka UTIs in sexually active young females
2nd leading cause of these UTIs, 1st leading cause is G- E.coli
Answer the following about S. aureus (a staph cocci bacteria):
coagulase + or -
What syndromes/conditions can be caused by this?
coagulase +
S. aureus can cause:
scaled skin syndrome (caused by EF)
bullous impetigo (caused by EF)
food poisoning (fast acting, associated with turkey stuffing)
MRSA stands for Methicillin resistant S. aureus and would cause resistance to what abx? What are some symptoms of MRSA?
resistance to BETA LACTAM ABX
symptoms: 101 degree fever, spider-bite-like sores with pus
Answer the following about S. epidermidis (a staph cocci bacteria):
Gram + or -
Catalase + or -
Coagulase + or -
is normally harmless on the skin flora, but can become _________.
G+
Catalase +
Coagulase -
is normally harmless on the skin flora, but can become opportunistic (aka lead to infection, especially if immunocompromised)
Answer the following about Alloiococcus otitidis (a cocci bacteria):
Gram + or -
Catalase + or -
Causes WHAT type of infection in children?
G+
Catalase+
causes OTITIS MEDIA (ear infection) in children
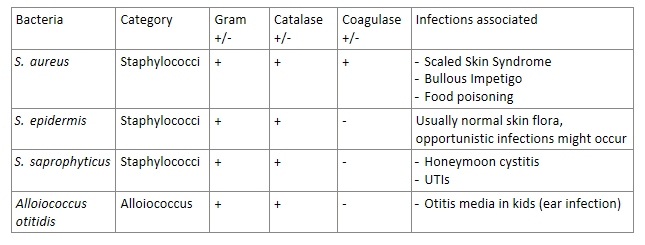
STAPH-COCCI BACTERIA REVIEW:
(grouped in Allo bc it’s similar)
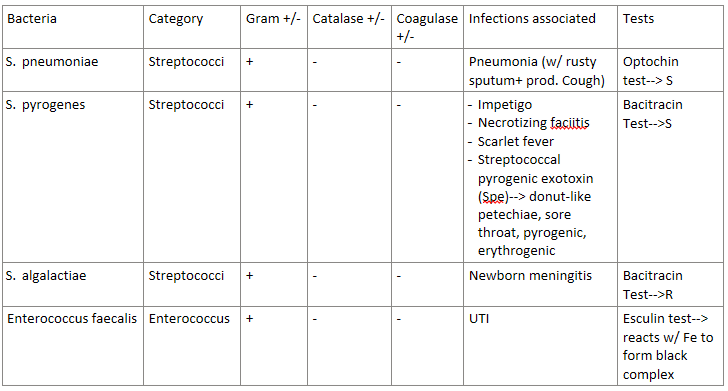
STREP-COCCI REVIEW:
(grouped in entero bc its similar)
A capsule is a common virulence factor in what bacterial strains?
meningitis strains of e.coli
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Haemophilus influenzae Type B
Neisseria meningitidis
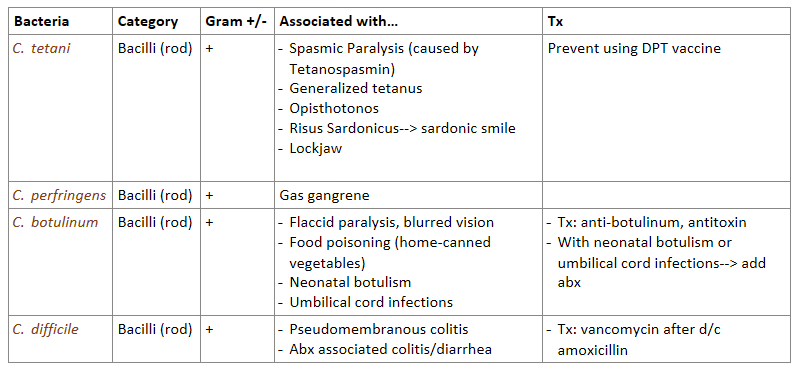
What are the 4 most important G+ bacilli species? Which are spore forming?
Clostridium tetani- spore forming
C. perfingens- spore forming
C. botulinum- spore forming
C. difficile
Answer the following about Clostridium tetani (G+ bacilli):
What can this bacteria cause? (adults?, kids?)
What vaccine is available to protect from this toxin?
Can cause:
spasmic paralysis- caused by tetanospasmin toxin
generalized tetanus
opisthotonos (severe back arching due to muscle spasms)
risus sardonicus in kids—> “sardonic smile” (face muscles contract and in kids you can’t breastfeed)
lockjaw
vaccine that contains tetanus toxoid—> DPT
Answer the following about Clostridium perfringens (G+ bacilli):
can cause what?
how is C. perfringens muscle destruction different from S. pyogenes flesh eating?
can cause GAS GANGRENE (muscle destruction, gas release)
differences:
C.perfringens—> targets muscle, a-toxin, G+ rod bacteria
S. pyogenes—> targets soft tissue, Spe toxin, G+ cocci bacteria
Answer the following about Clostridium botulinum (G+ bacilli):
can cause what symptoms/conditions?
treatment in general
additional tx for neonatal botulism and umbilical cord infections
can cause:
flaccid paralysis
blurred vision
food poisoning—> from home-canned vegetables (not an infection)
treatment: anti-botulinum, antitoxin
neonatal botulism AND umbilical cord infections MUST ALSO be treated with antibiotics
Answer the following about C.difficile:
This bacteria can cause severe inflammation of the colon with pseudomembranes called _________________.
Use of abx can lead to C.difficile associated _____________.
Treatment?
can cause pseudomembranous colitis
abx associated colitis/diarrhea (When using abx you kill good/bad bacteria, this allows C.difficile to overgrow and release toxins= colitis & diarrhea)
treatment with VANCOMYCIN after d/c amoxicillin
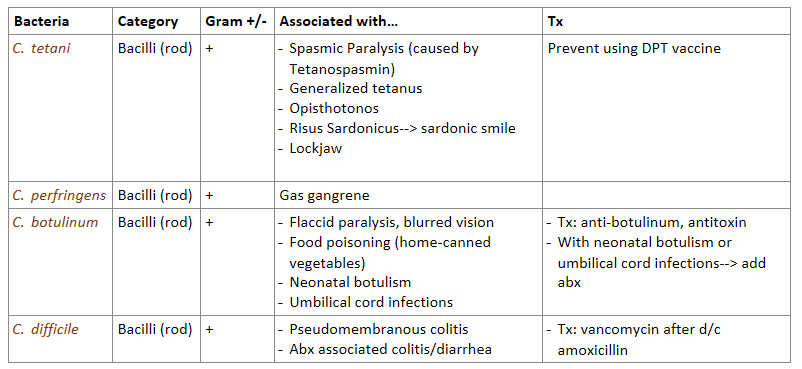
G+ BACILLI REVIEW:
Answer the following about Bacillus anthracis:
aerobe or anaerobe?
has ____________ that survive very long
has _________ plasmid that encodes what?
can cause what disease?
strict aerobe (needs O2 for growth)
has endospores that survive very long
has PXO1 plasmid that codes for EF (edema toxin/edema factor) which is an adenylate cyclase = leads to edema
can cause ANTHRAX MENINGITIS—> nickname “cardinal’s cap”
What would a positive Neisseria Oxidase test look like?
a. produces cytochrome c oxidase, turns TMPD blue
b. produces cytochrome c oxidase, turns colorless
c. does not produce cytochrome c oxidase, turns TMPD blue
d. does not produce cytochrome c oxidase, turns colorless
a
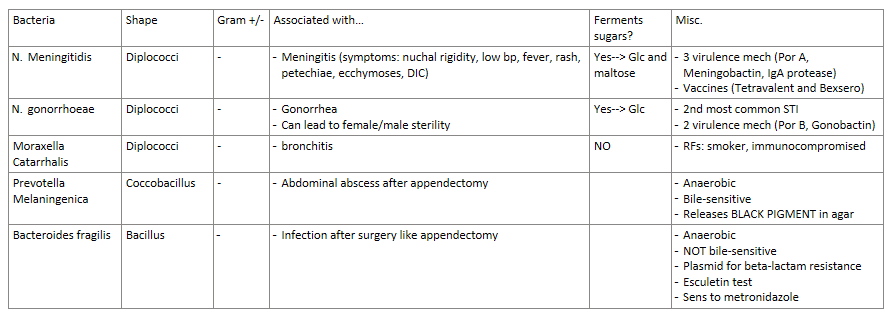
Answer the following about Neisseria meningitidis:
G + or - diplococci in CSF
Symptoms of meningitis
3 virulence mechanisms this bacteria uses
vaccines for meningitis
does it ferment sugars? if so which?
G- diplococci in CSF
symptoms:
nuchal rigidity (neck stiffness)
low bp (105/65)
fever
rash, petechiae, ecchymoses (bruising), and DIC (small blood clots in blood)
3 virulence mechanisms
Por A (resistance to serum killing)
Meningobactin (siderophore that allows bacteria to get IRON)
IgA protease
vaccines
Tetravalent for serogroup A, C, Y, W135
Bexsero for serogroup B
yes, ferments sugars—> Glc and maltose
Answer the following about Neisseria Gonorrhoeae:
what can this bacteria cause? if left untreated what occurs?
what can happen during pregnancy?
men?
2nd most common STI to what bacteria and STI?
2 virulence factors this bacteria uses?
does it ferment sugars? if so which?
causes:
gonorrhea
females: untreated= female sterility—> scarring of the fallopian tube, ectopic pregnancy
in pregnancy—> if mother is effected can cause Opthalmia neonatorum
male: male sterility—> infection spreads to prostate and epididymis
gonorrhea the 2nd most common STI in the world, 1st is Chlamydia
2 virulence factors
Por B (helps survive intracellular)
Gonobactin (siderophore that allows bacteria to get IRON)
yes, ferments sugars—> glucose
Answer the following about Moraxella catarrhalis:
G + or - diplococci
symptoms
risk factors
does it ferment sugars? if so which?
G - diplococci
symptoms- bronchitis
RFs- smoker, immunocompromised
NO sugar fermentation
Polymicrobic infection in an abscess is when multiple bacteria are in the same spot. What order do these bacteria grow in?
(hint: based on O2 needs)
strict aerobes
facultative anaerobes
strict anaerobe
Answer the following about Prevotella melaninogenica:
where is this bacteria most commonly seen/found?
G + or -
bile-sensitive?
aerobic or anaerobic?
unique characteristic of this bacteria is…
(disclaimer: this bacteria was in sg, not pp)
most common—> in abdominal abscess after appendectomy
G-
bile-sensitive
anaerobic
unique characteristic—> releases BLACK PIGMENT in agar (due to production of porphyrin)
Answer the following about Bacteroides fragilis:
where is this bacteria most commonly seen/found?
G + or -
bile-sensitive?
aerobic or anaerobic?
has a plasmid that encodes what kind of gene? results?
sensitive to what abx?
Results of Esculetin test?
(disclaimer: this bacteria was in sg, not pp)
most common—> infection after surgery like appendectomy
G-
NOT bile-sensitive, bile-resistant
anaerobic
plasmid that codes for beta-lactamase—> results in beta-lactam abx resistance
sensitive to metronidazole
Esculetin test—> reacts with iron to form black complex
GRAM - REVIEW!!!!!!