WEEK 7 LECTURE- PLS-1-Root Systems and Soil Formation Overview
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Interactions with symbionts
The relationship roots have with other organisms that can benefit the plant.
Dicots roots
typically have taproots.
Monocot roots
typically have fibrous roots.
Primary roots
Roots formed from the radicle in the seed that give rise to secondary roots.
Seed coat
The protective outer layer surrounding the seed.
Cotyledon
The seed leaf within the seed.
Plumule
The beginning state of the shoot or stem.
Epicotyl
Part of the early stem within the seed.
Hypocotyl
The early part of the stem within the seed.
Hilum
The part that attaches the early seedling to the inside of the seed.
Micropyle
A small opening in the surface of the ovule.
Adventitious root
Roots that form from stems or leaves.
Adventitious prop root
A type of adventitious root that provides support.
Buttress Roots
Large above-ground roots that provide structural support.
Taproot
A single, thick primary root that grows downward, adapted for anchoring and storing nutrients.
Fibrous Root
Many small roots efficient for absorbing water and nutrients from soil.
Aerial Root
Roots that grow above ground or above water. This is a type of adventitious root, While they both grow from the stem, some adventitious roots may grow on the underground part of the stem, so this is a differentiating term between the two.
Storage Root
Roots modified to store nutrients and water. sweet potato and carrots are examples.
Haustorial Root
A parasitic root that burrows into a host plant to steal water and nutrients.
Root Hairs
Extensions of the epidermis of the root that absorb most of the water.
how to identify cross section of Dicot Root
Characterized by a star or x shape to the vascular bundle.
how to identify Monocot Root
Characterized by a ring shape of the vascular bundle.
Pericycle in roots location and function
Layer just inside the endodermis that controls secondary root growth in the root (controls secondary vascular growth in the stem)
Endodermis
The layer just outside the pericycle that regulates the flow of water and nutrients in and out of the vascular bundle.
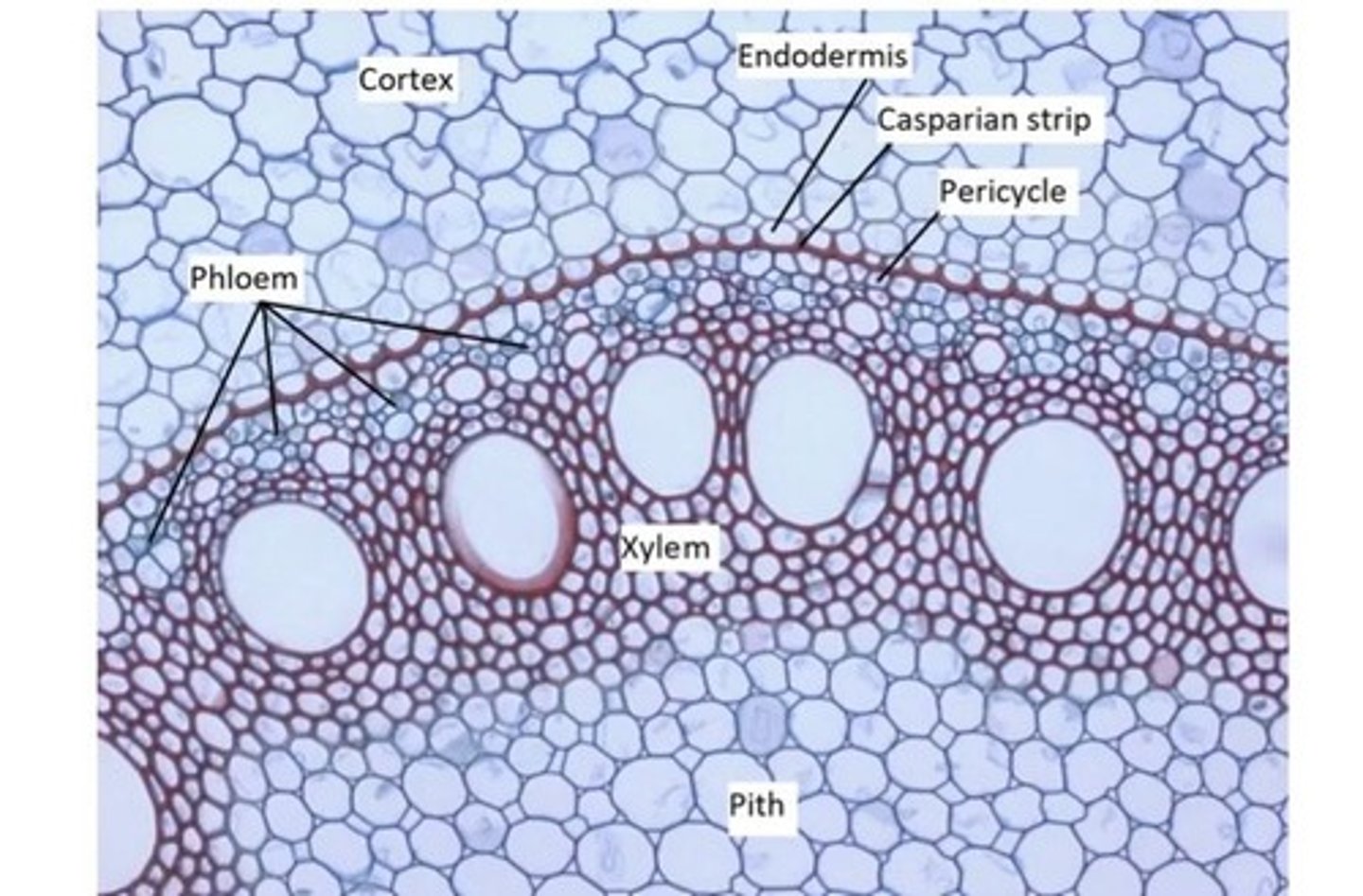
Suberin
A substance that coats the endodermis and controls water and nutrient entry. Stops
Epidermis
The outer-most layer of cells that protects the root and aids in water absorption.
Exodermis
The secondary layer beneath the epidermis that reduces water loss.
Cortex
Layer of parenchyma cells for storage and transport of nutrients.
Vascular Cylinder
Located at the center of the root containing xylem and phloem tissues.
Xylem
Transports water and dissolved minerals from roots to the rest of the plant.
Phloem
Transports sugars and other metabolic products downward from leaves.
Monocot Roots how to visually identify
Phloem cells are interspersed in a circle pattern between the xylem cells.
Pith definition, makeup and function
In monocot roots not dicot roots, it is the central part of the vascular system, made up of parenchyma cells, involved in storage.
Secondary growth occurs in monocots or dicots roots?
Dicots undergo secondary growth while monocots do not.
Water Uptake in Roots occurs through what process- describe the process
Water enters the roots through osmosis, because the water concentration outside the root is greater than that of the water concentration inside the root.
Osmotic Pressure Control- define
Roots can intake solutes like phosphorus to lower the water concentration inside the root, making uptake easier with lower water availability outside the root.
Water Cycle in Plants
Water goes from the soil, into the root, up the plant, and out into the atmosphere in a constant cycle.
Simplastic Flow
Water moves through the cells via chloroplast. this process is more selective, and slower.
Cortex Tissue
Water moves through cortex tissue, which are underground parenchyma cells, for short-distance transport and storage.
Casparian Strip
The Casparian Strip is located on the outside of the endoderm and stops symplastic movement of water into the vascular bundle.
Apoplast Pathway
Movement of water and solutes around the cells, via the extracellular spaces
Pros of Apoplast Pathway
Fast transport, bypasses membrane and transport barriers.
Cons of Apoplast Pathway
Blocked by Casparian strip in endodermis: less selective.
Symplast Pathway
Movement through the cells via the cytoplasm of cells interconnected by plasmodesmata.
Pros of Symplast Pathway
Selective: controlled by cellular processes.
Cons of Symplast Pathway
Slower due to crossing all membranes.
Root Nitrogen Fixation
Symbiosis of Rhizoids in the Fabaceae family contains nodules on roots and includes peas.
Rhizobia function
Nodules on roots that contain Rhizobia, which are bacteria that can break down N2 to ammonium, nitrite (N0), and nitrate (N0).
N2 in Soil usable or not usable to plants?
N2 is not usable by plants
N0 usable or not usable to plants?
A form of nitrogen usable by plants.
Rhizoids do what when present on roots?
When present on roots, can take N2 and convert it directly to N0 and give it to the plant.
Mycorrhizal relationships
Fungi form relationships with plants to exchange nutrients.
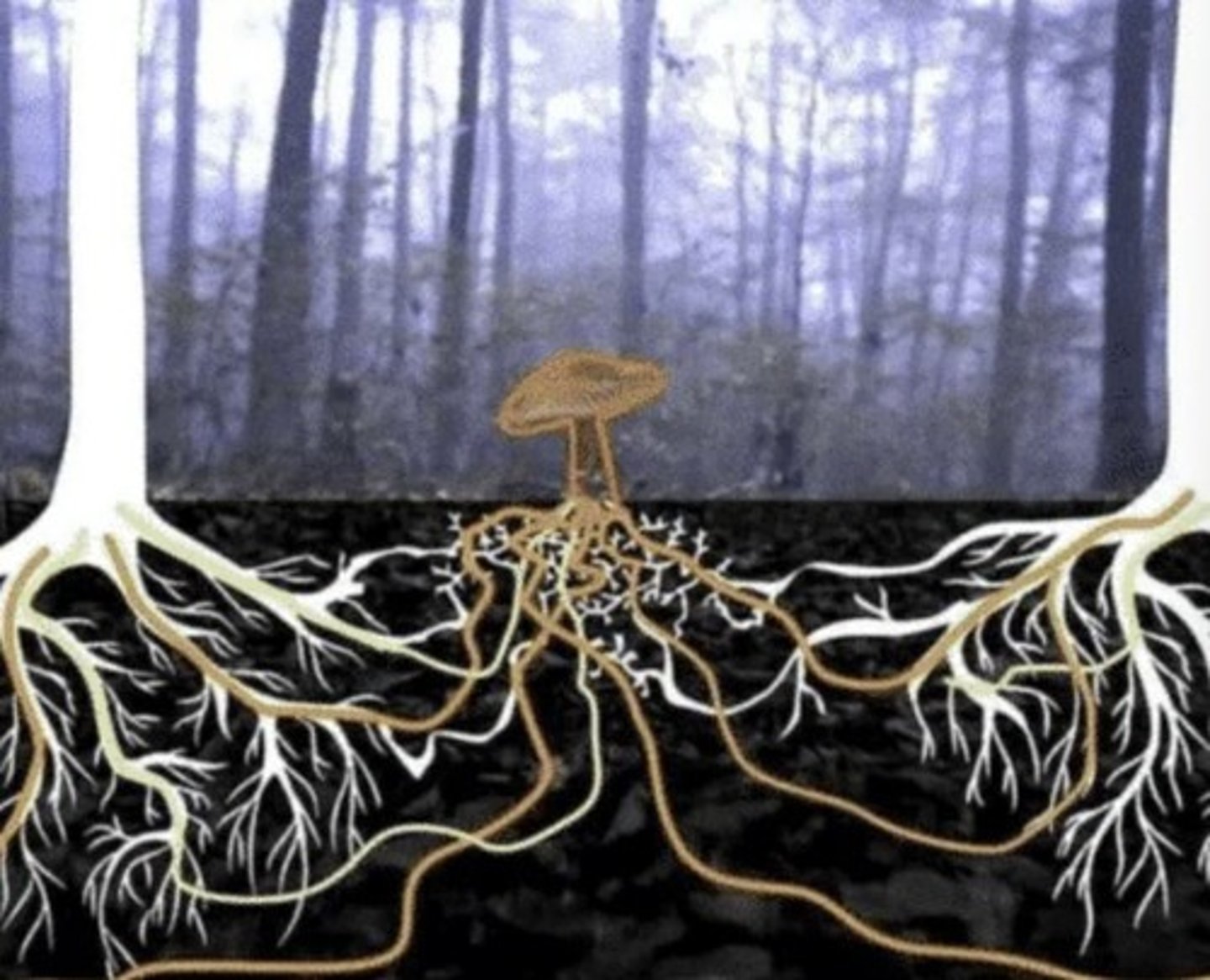

Mycorrhizal network
Contains mycelium beneath the soil.
Saprotrophic Nutrition
Fungi feed on non-living, dead or decaying organisms in the soil.
Enzyme expulsion by fungi- define this part of saprotrophic nutrition
Fungi expel enzymes into the soil and absorb nutrients after they are digested.
Heterotrophic
One organism relies on another for nutrients.
Fungi sugar acquisition
Fungi obtain sugars through a relationship with another plant like a tree.
Mycorrhizal net function
Surrounds a root, receives sugars from another plant, and provides minerals in return.
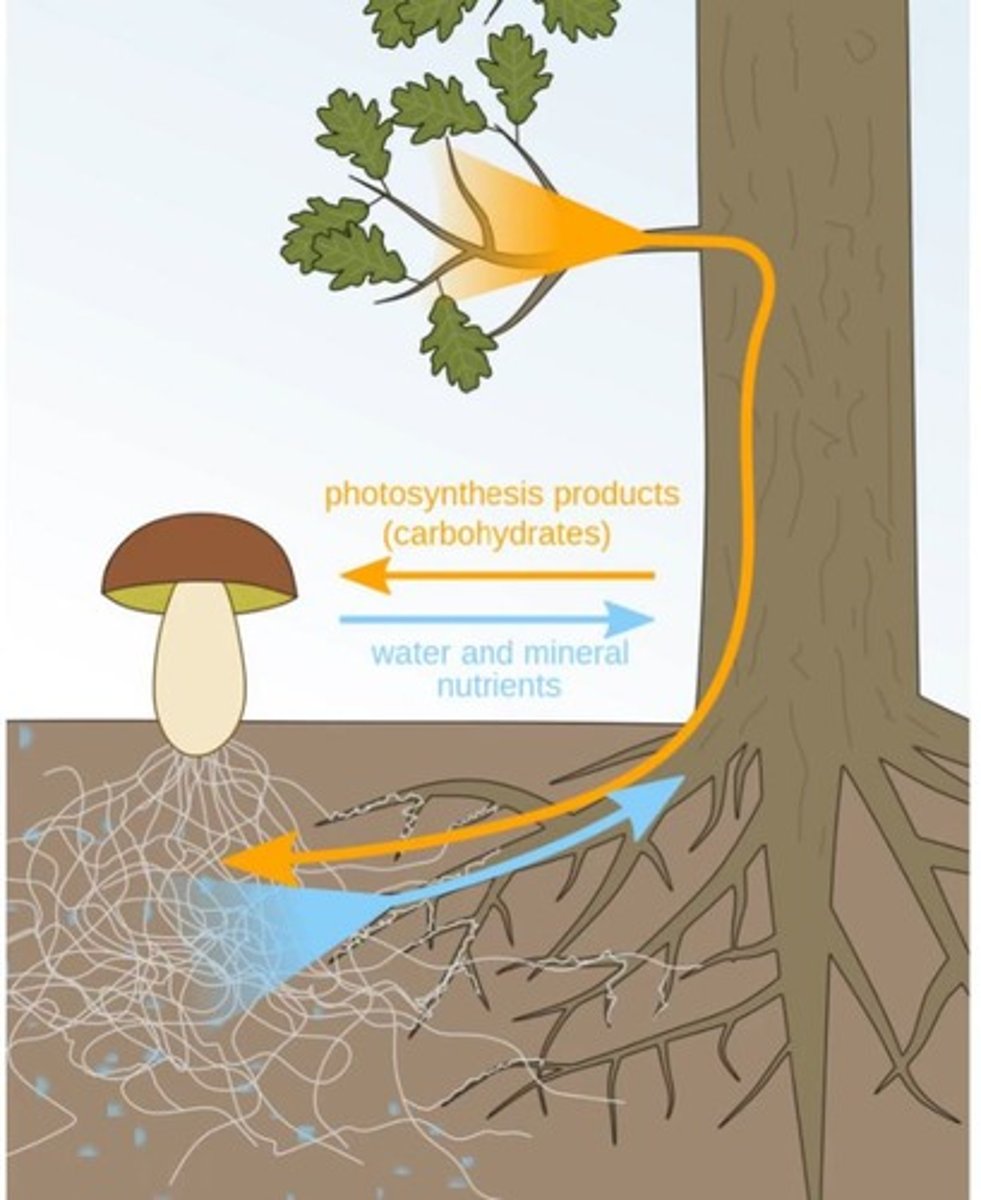
Mycorrhizal network communication
Connects plants and helps them communicate potential pest threats and run an ongoing nutrient sharing community.
Nutrient sharing
Mycorrhizal networks help share nutrients between plants.
what are Soil Horizons
Layers of soil with distinct characteristics.
O Horizon- define
Organic layer containing dead animals, dead plants, and decomposing materials.
A Horizon- define
Minerals and organic growth, good for plants; roots almost always reach here.
B Horizon
Rich in minerals, leached down, with not much organic material.
C Horizon
Parent material that develops into soil, consisting of broken down parent material.
R Horizon
Bedrock layer.
Soil Texture
Mixed percentages of sand, silt, or clay in the soil.
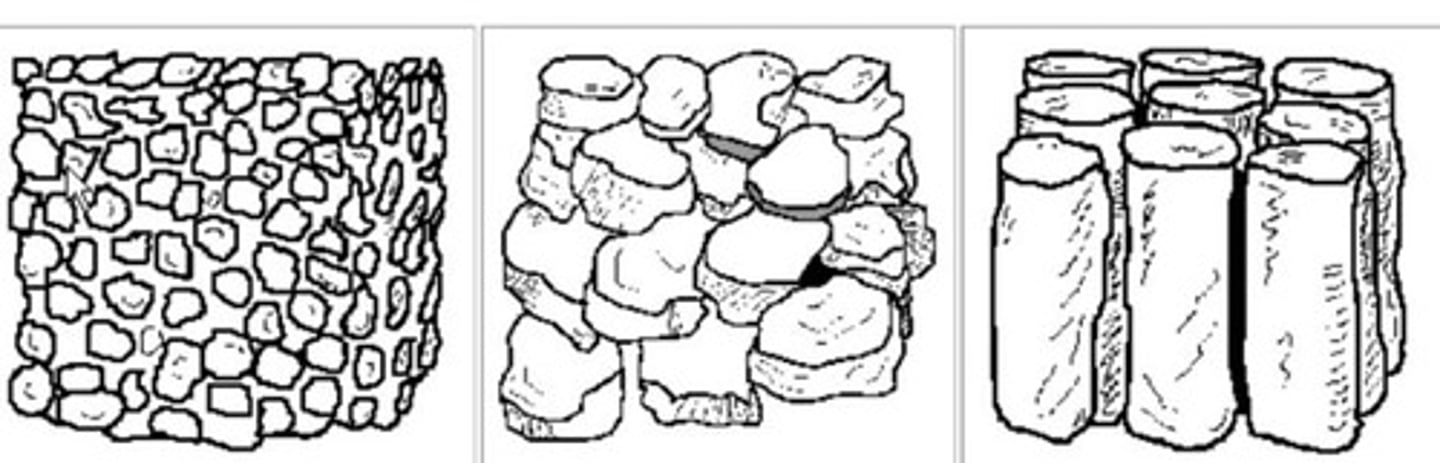
Sand
Large particles that allow water to fall through.
Silt
Particles measuring 0.05mm (small).
Clay
Particles measuring 0.02mm (super tiny) that hold water.
Water movement in soil define based on size
The size of particles dictates the ability of water to move through the soil. The larger the particle the more water loss.
Soil settling test
Mixing soil types in water to measure how quickly they settle.
Clay settling time
1-2 days.
Silt settling time
2 hours.
Sand settling time
1-2 minutes.
Mixed soil settles in what order
Clay on top, silt in between, sand on bottom.
Soil triangle test is used for what
Used to determine soil type based on percentages of clay, silt, and sand.
Water availability depends on?
Depends on soil type and impacts the water available to plants.
Clay water retention
Can “hold” lots of water, but due to tight compaction, making it less available to plants.
Loamyness- define
Increases water availability for plants by holding onto water and having less tightness in the space between particles due to multiple particle sizes.
Micronutrients
Essential elements only needed in small quantities.
Macro Nutrients
Nutrients required in larger quantities for plant growth.
Limiting Nutrients- define
Nutrients that if not available in sufficient amounts in the soil, will cause the plant's growth to suffer or be stunted.
Nitrogen (N)
A limiting nutrient obtained via the atmosphere.
Phosphorous (P)
A limiting nutrient obtained via the atmosphere.
Potassium (K)
A limiting nutrient obtained via the atmosphere.
Carbon
A nutrient obtained via the atmosphere.
Hydrogen
A nutrient obtained via the atmosphere.
Oxygen
A nutrient obtained via the atmosphere.
Calcium
A nutrient not classified as limiting.
Manganese
A nutrient not classified as limiting.
Sulfur
A nutrient not classified as limiting.
Soil pH, what is ideal?
6.2-7.3 is neutral to slight acidity preferred by most plants.
Nutrient availability dictates what about the soil?
Dictates the soil's pH level.
Toxins in soil what are they, what do they do to plants?
Substances in the soil that can negatively affect plant growth, including size and height of the plant, number of leaves, and size of leaves.
What are the 5 Soil formation factors?
Climate, living organisms, relief, parent material, and time.
Climate
Includes water (rain, rivers, streams, and snow) and temperature affecting soil formation.
Percolation- define
The process of water moving through soil, which can lead to leaching/ loosing of nutrients if excessive.
Leaching- define
Loss of nutrients from the soil due to excessive water.
Temperature effects soil in what ways?
High temperatures can cause rapid decomposition, while low temperatures may slow down decomposition.