Psychology unit 1
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This collection of flashcards are over the entirety of Prof. Gassin's Psych 101 class
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What 2 elements of understanding does science rely on?
logic and observation
descriptive approaches of observation
Naturalistic observation
Survey
Case study
What do you get from a correlational approach?
a basic process that gets data for you that helps with prediction
What can correlational approach NOT do?
determine cause and effect
What 2 pieces of information does the r in a correlational coefficient give us?
Direction of the relationship of the variables
How strong the relationship between the variables is
positive correlation
as values on one variable increase so does the other
negative correlation
as values on one variable increase, values on the other decrease
What does the experimental approach allow?
Allows for relatively reliable cause-and-effect claims
What is the downside of the experimental approach?
Have to heavily control and weed out many variables and creates very unrealistic contexts for testing cause-and-effect
Basic process of the experimental approach
Randomly assign participants to one of at least 2 groups
Implement intervention/experience with one of the groups
Measure effect of interest and compare group averages
What is the name of the group that gets an intervention/experience in an experimental approach?
experimental group
What is the name of the group that DOES NOT get an intervention/experience in an experimental approach?
control group
What are the six strategies for success in studying?
Retrieval practice
Interleaving
Spaced practice
Concrete examples
Elaboration
Dual coding
What is retrieval practice?
repeatedly bringing info into mind
What is interleaving as a study skill?
When you alternate between ideas when studying
Spaced practice as a study skill
when you break up study sessions over time
Concrete examples as a study skill
when you connect abstract ideas to examples, and find examples to real life
Elaboration as a study skill
when you flesh out ideas with details, get a different take on things, and ask why/how questions
Dual coding as a study skill
when you use both words and pictures
True or False: teaching to a specific study skill promotes better learning
False
What areas of study contribute to the study of psychology?
Philosophy
Biology
Physiology
Who is Wilhelm Wundt and what did he contribute to psychology?
Regarded as the father of psychology, Wilhelm Wundt founded the 1st psychology lab which marked the very beginning of psychology
Who is Mary Wilton Calkins and what did she contribute to psychology
Mary was the 1st woman president of the APA and emphasized the importance of memory and theories of the conscious self
Who is Francis Summer and what did he contribute to psychology?
He was the 1st African American to earn a PhD in psychology and worked in the development in mental well being for African Americans
Where does our understanding of the world come from?
Tradition
Intuition
Authority
Logic
Experience
Steps of the scientific method
develop question
develop hypothesis
design a study & collect data
analyze data
share findings
repeat
What is the descriptive approach to a study?
Allows the exploration of a question in a naturalistic way, this technique also utilizes surveys and case studies in a in-depth and multidimensional way
What is the correlational approach to a study?
Allows for numeric description of a relationship between the variables, this helps with prediction but still CANNOT determine cause and effect
Who is considered the father of modern psychology?
Wilhelm Wundt
If I am doing a research project where I am collecting many types of data (e.g., interviews, medical exam results, intelligence test results) about one person with a rare mental illness, what kind of study am I doing?
A case study
Consider two correlation coefficients, +.37 and -.52. If someone claims that the first is stronger than the second, are they correct?
No
Define the nervous system
A system in the body that coordinates sensory information and bodily action
What are 2 general types of cells?
Glial
Neuron
What are glial cells?
support for neurons, provide nutrients and clean waste products
What are neurons?
cells that allow very fast electrochemical communication over long distance
Neuron structure
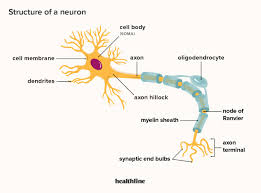
What is the chemical process between neurons?
the passing between chemicals/hormones between neurons
What is the electric process between neurons?
The change in voltage of a neuron when they pass neurotransmitters
What is resting potential in a neuron?
When at rest, the neuron has a negative charge inside
What is action potential in a neuron?
When the neuron has a positive charge that “skips” down the myelinated axon
What does the sympathetic system do?
The sympathetic system is part of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for 'fight or flight' responses, increasing heart rate, dilating pupils, and redirecting blood flow to muscles.
What does the parasympathetic system do?
Makes your body “rest and digest”
2 messaging neurotransmitters in psychology
Serotonin
Dopamine
What does serotonin do?
controls mood and appetite
what does dopamine do?
linked with sense of reward and motivation
What makes up the peripheral nervous system?
somatic nervous system
autonomic nervous system
sympathetic nervous system
parasympathetic nervous system
Does the autonomic nervous system control voluntary or involuntary movement?
Voluntary
What is the cortex of the brain and what is its function?
The wrinkled outer layer of the brain that deals with most advanced mental functions
What does the cortex do?
understanding language, thinking, learning, perception
What are the lobes of the brain?
Frontal lobe
Broca’s area
Parietal lobe
Temporal lobe
Occipital lobe
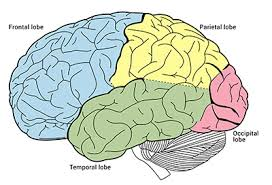
What happens when the Broca’s area is damaged?
Problems with speech, word choice, grammar
What does the frontal lobe do?
Touch, integrating with what we see and hear, overall sensory information, planning, thinking in advance,
What does the temporal lobe do?
processing auditory information, understanding language,
What does the occipital lobe do?
Visual processing
What is the limbic system?
The structures in the middle of the brain
What parts make up the limbic system?
Hippocampus
Amygdala
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
What does the limbic system do?
emotion, instincts, memory formation
What does the cerebellum do?
connecting and timing of movement, balance, timing
What does the brainstem do?
involved in basic life functions and arousal
Brain lateralization
The idea that left and right hemispheres of the brain have different functions
Left brain “versus” right brain
What allows the brain to act as a “whole”?
the corpus callosum, a fiber network that connects the 2 hemispheres
What is the connectome?
The other fiber networks that provide connections between brain regions
What is the endocrine system?
A system in the body that involves glands releasing hormones into the blood stream
What does the pineal gland produce?
melatonin
What do the adrenal glands produce?
adrenalin
How does the endocrine system compare to the nervous system?
the endocrine system is slower and has more widespread effects than the nervous system
Nature vs Nurture
What determines who we are and how do both contribute to our characteristics
Epigenetics
the study of how molecules around a gene influence the DNA and how its working
true or false: can epigenetics molecules be affected by the environment?
true they are affected by many environmental factors