Microbiology Exam I
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
List the types of Microorganisms
1. Bacteria
2. Archaea
3. Fungi
4.Protozoa
5.Algae
6. Viruses
Rules for nomenclature
1- Italicized or Underlined
2. The genus is capitalized, and the specific epithet is Lowercase.
What did Edward Jenner discover?
Inoculated a person with cowpox
virus, who was then protected from smallpox
vaccination
What are Antibiotics?
Who discovered the first antibiotic?
Antibiotics: are chemicals produced by bacteria and fungi that inhibit or kill other microbes
Alexander Fleming
In a ------------ microscope, the image from the objective lens is magnified again by the ocular lens
compound microscope
Staining the background instead of the cell is
called ------
Negative staining
------- is the ability of the lens to distinguish two points
Resolution
Special Stain is used to
Used to distinguish parts of microorganisms
What are the types of differential stains? And
the use of each.
A. Gram Stain: Classifies bacteria into gram positive or gram-negative
B. Acid - Fast stain: Binds only to bacteria that have a waxy material in their cell walls, which is not decolorized by acid- alcohol Used for the identification of
- Mycobacterium
- Nocardia
What are the two types of Glycocalyx and what is its function
Capsule
-Slime layer
Function: contribute to virulence (prevent phagocytosis, helps form biofilms)
-------- I have a hair like structure and I allow for attachment.
Who am I?
Fimbriae
Describe Flagella structure and function
Structure: Filaments, Hook, and basal body
Function: Movement (Taxis)
What is another name of Axial filaments and where do we find them?
Also called endoflagella
- Found in spirochetes
LPS contain:
1.
2.
3.
1. O polysaccharide antigen
2. Core polysaccharide
3. Lipid A is: an endotoxin embedded in the top layer
Define Pasteurization
Pasteurization is the application of a high heat for a short time
Define Biofilm? Its Function?
Biofilm: is a matrix formed by bacterial cells which allow them to
attach to surface as well as to other bacterial cells
- Biofilms can cause infections and are often resistant to antibiotics
------------ I am involved in DNA transfer from one cell to another
Who am I ?
Pili
What does the endosymbiotic theory say?
It states that mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells were once bacteria that were engulfed by larger bacteria.
What is the path of the light from bottom to top?
Illuminator
Condenser
Specimen
Objective lens
Ocular lens
Each of the following statements concerning the gram-positive cell wall is true EXCEPT
it protects the cell in a hypertonic environment.
which of the following have a cell wall?
Fungi
fimbriae and pili differ in that
pili are used for transfer of DNA and motility.
The cell walls of bacteria are responsible for the shape of the bacteria and the difference in the Gram stain reaction.
True
cells placed in a hypotonic solution tend to lose water due to osmotic pressure.
False
spheroplasts, protoplasts, and mycoplasms are bacterial cells without cell walls.
True
spirochetes move by means of
axial filaments
which of the following structures allows a cell to survive adverse environmental conditions?
caspule
prokaryotic ribosomes are composed of two subunits of what sizes?
30S + 50S
gram negative outer membrane consists of all of the following except
lipotechoic acid
Lipid A is an
endotoxin
The DNA found in most bacterial cells:
Is circular in structure
Which of the following mechanisms will be used by a cell to move a substance from a lower to a higher solute concentration?
Active transport
When rod-shaped bacteria are arranged in chains it is called:
Streptobacillus
The cell wall around a prokaryote is to help create and maintain structure and aid in cellular respiration.
True
In a hypertonic solution, what would happen to a bacterial cell?
shrink
75% of the microorganisms are of which of the following?
Prokaryotic cells, chloroplasts and mitochondria
Which of the following organelles most closely resembles a prokaryotic cell?
Mitochondrion
Prokaryotic cells might have all of the following structures, EXCEPT FOR:
Cilium
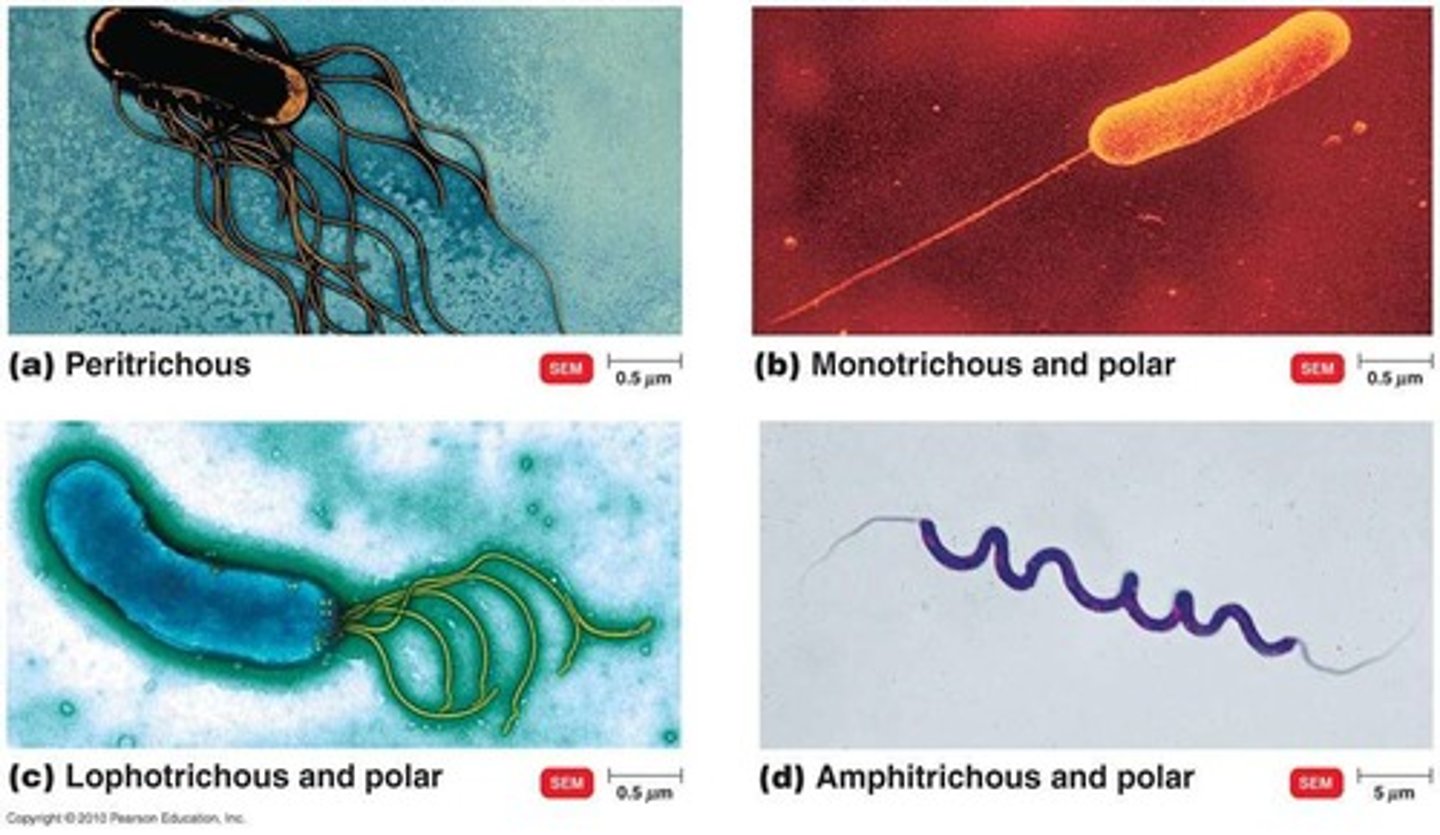
Bacteria with small bunches of flagella emerging from the same site are said to be:
Lophotrichous
Which statement about bacterial plasma membranes is NOT true?
Contains cholesterol
The process of endospore formation is sporulation, while the process of an endospore growing into a vegetative cell is:
Germination
Which type of cellular transport uses transport proteins and moves substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration?
Facilitated diffusion
What unit of measure is most appropriate for expressing the size of bacteria?
Micrometer
Which of the following is used as a mordant in staining procedures?
Iodine
The cell wall structure of Mycobacterium and Nocardia differs from gram-positive bacterial cell walls because it:
All of these choices are correct
Gram-negative bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell walls.
False
Facilitated diffusion is different from simple diffusion because facilitated diffusion:
Requires transporter proteins
The terms "run" and "tumble" are generally associated with:
Cell wall fluidity
Most prokaryotic cells reproduce:
By binary fission
Assume you stain Bacillus by applying malachite green with heat and then counterstaining with
safranin. Through the microscope, the green structures are
endospores
Pasteur used a swan-neck flasks, because he knew that:
living microorganisms contaminating the flask would be trapped in the neck
A virus measures 100 nm in length. What is its length in μm
0.1 μm
All of the following are true about Biofilms except
Biofilms formed on medical devices such as catheters do not cause infections
Which of the following describes a microorganism able to cause disease
pathogen
Your patient has a bacterial infection and you need to decide which antibiotic to prescribe. Which staining technique will you use?
Gram stain
Which of the following correctly traces the path of light through the compound microscope?
light source; condenser; specimen; objective lens; ocular lens.
Microorganisms are involved in
All of the answer choices are correct.
Which of the following places the steps of the Gram stain in the correct order? 1-Alcohol-acetone 2-Crystal violet 3-Iodine 4-Safranin
2-3-1-4
if you wanted to see internal structures of live cells, what would you use?
phase-contrast microscope
The three domains of life are Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
True
Which of the following is NOT equal to 10 mm?
1000 μm
You are studying the surface of a biofilm on a glass slide. Which microscope will you use?
scanning acoustic microscope
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
nigrosin - endospore stain
yeasts are different from Helminth because they
They are single-cell
Which physician is first associated with the use of chemical disinfectants to prevent wound infections ?
Lister
Each of the following organisms would be considered a microbe EXCEPT
ticks
___________ is not part of the four-kingdom system
Bacteria
The Koch's postulates is used in the__________
determination of the cause of a disease by scientists studying disease transmission.
You are studying a gram-negative bacteria and decided to do a Gram stain. After adding the alcohol, what is the color of the bacteria at this point?
colorless
A scientist studying helminths is working with prokaryotes.
False
why do we use a mordant in the staining process?
prevent the crystal violet from leaving the cells.
What structure does light pass through after leaving the specimen in a compound light microscope?
objective lens
Archea
Prokaryotic
Lack peptidoglycan
pseudomurein cell walls
Extreme environments
Fungi
Eukaryotes
Chitin cell walls
Absorb organic molecules for energy
Protozoa
Eukaryotes
Absorb or ingest organic molecules
Motile via pseudopods, cilia, or flagella
Free living or parasitic
Algae
Eukaryotes
Cellulose cell walls
Photosynthesis for energy
Produce oxygen and carbohydrates
Viruses
Acellular
RNA or DNA core
Core surrounded by protein coat
Replicated in a living host
Multicellular Animal Parasites
Eukaryotes
Multicellular animals
Not just microorganisms
flat and roundworms called helminths
4 Kingdoms of Eukarya
protists, fungi, plants, animals
Infectious Diseases
when a pathogen overcomes a host's resistance and disease results
Biofilms
Microbes attach to solid surfaces and grow in masses. Can grow on teeth, rocks, etc. Can cause infections and be antibiotic resistant.
Normal microbiota
prevents growth of pathogens. produce growth factors. provide resistance.
biotechnology
the use of microbes for practical applications, such as producing foods and chemicals
Recombinant DNA technology
enables bacteria and fungi to produce a variety of proteins, vaccines, and enzymes
Fermentation
the microbial conversion of sugar to alcohol in the absence of air
smear
a thin film of a material containing microorganisms spread over a slide
basic dye
the chromophore is a cation
acidic dye
the chromophore is an anion
mordant
may be used to hold the stain or coat the specimen to enlarge it
gram positive
bacteria have thick peptidoglycan walls
gram negative
have thin peptidoglycan walls
capsules
are a gelatinous covering that do not accept most dyes
endospore staining
resistant dormant structures inside some cells
Primary stain: malachite green, usually with heat
Counterstain: safranin
flagella staining
mordant and carbolfuchsin
Prokaryote
one circular chromosome
no histones
no organelles
Eukaryote
paired chromosomes
histones
organelles
polysaccharide cell walls
mitosis
prokaryote cell shapes
bacillus (rod shaped)
coccus (spherical)
spiral (spirillum, vibrio, spirochete)
star shaped
rectangular
arrangements
diplo (pairs)
staphylo (clusters)
stepto (chains)
tetrad (groups of four)
sarcinae (groups of eight)
glycocalyx
external to cell wall
made of polysaccharide and or polypeptide
capsule or slime layers
prevent phagocytosis
flagella
made of flagellin
filament, hook, basal body