V12: Theories of Emotion
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is emotion? (General as a lot of definitons)
Lasts seconds or minutes, not hours or days (short lasting)
Not affective disorders or personality temperaments
May be accompanied by facial expressions, physiological responses
Occur in response to actions, people, thoughts
What are the five components of emotion
Subjective feelings
Difficult to test (ethically, predictably, take a while to come down from i.e. elicit extreme sadness then happiness)
Physiological response
e.g. heart racing
Expressive behaviour
e.g. smiling
Cultural difference in expression
Appraisal
Interpretation i.e. ‘this is bad’
Action tendencies
e.g. avoid something disgusting
What are the three main theories of emotion and what question do they look at
Evolutionary
What do emotions do for us?
Appraisal
Why do the same circumstances cause different emotions?
Psychological constructionist
Why is there huge variation in how emotions look and feel?
What framework can be used to compare the three theories of emotion (more if I’m writing essay)
Antecedents of an emotion
What causes them
Biological givens
Innate emotional capabilities
The integration of emotional experience
How components of emotion fit together
Evolutionary approach (who it’s based from, how it’s observed, its main argument)
Based on the writings of Darwin (1972)
Observational approach
Humans and animals emotional expression
Main argument
Argued for universality and functional adaptation (including communication)
i.e. they serve an adaptive (beneficial) function
Evolutionary: Antecedents (cause)
Emotions come when we detect a threat to survival OR opportunity for reproduction
Signal stimuli (environmental indicator)
Indicate an adaptive problem
i.e. a high cliff, a potential mate
Emotion associate with action tendencies
Make someone ready to execute action like running when threatened
Who added to the evolution theory antecedents
Plutchik (1980)
Theory of actions taken in response to adaptive problems, their associated emotions, and outcomes
Outcome = Functional problem the emotion is solving (i.e. Protection, Reproduction, Exploration, etc.)
Evolutionary: Basic Emotions AND what makes an emotion ‘basic’?
Small list emotions that are innate, quick, and automatically caused by signal stimuli
What makes an emotion ‘basic’?
Universal expression
Not just facial i.e. rubbing someone’s arm when they are upset
Discrete physiology
Different physical pattern of response from respective emotions
Presence in other primates
Automatic evaluations of the environment
Not cognitive effortful
What criteria is mainly used to test ‘basic’ emotions
Universal expression AND discrete physiology
What are Ekman’s 6 basic emotions
Anger
Disgust
Happiness
Fear
Sadness
Surprise
What evidence did Ekman have for his 6 basic emotions and what were some limitations of it
Those were recognised by secluded tribe in Papua New Guinea
Limitations (methodological)
What is the criteria for something to be considered universal?
Is it truly universal or just similarities between the cultures
Emotions used are exaggerated, is recognition the same for spontaneous expression?
In what theory of emotions do some argue that basic emotions can combine to make other emotions
Evolutionary
Evolutionary study on physiological response of basic emotions (Discreet Physiology)
Ekman et al. (1990)
Directed Facial Action Task
P’s asked to contract specific muscles in their face
Allows emotional expression without specific reference to it
Results
The basic emotions show different physiological response patterns
Anger, Fear, and Sadness associated with increased HR
Everything BUT Happiness and Surprise associated with increased skin conductance
Replicated in Indonesian P’s not exposed to Western Culture (Levenson et al., 1992)
Physiological considerations other than skin conductance and HR of the six basic emotions in the evolutionary theory
Anger
Increased blood flow to arms and hands
Fear
Increased blood flow to legs and feet
Happiness
Neurotransmitter release, dampening effects of negative emotions
Disgust
Triggers gag reflex, restricts airflow to olfactory receptors
Evolutionary theory: Affect Programs (how the components of emotions come together)
Affect Program
Integrated automatic emotional response that is built into our body through evolution
Like a pre-set response that tells the body what to do when faced with a particular event
Argues they are innate, but can change through individual experience and knowledge gain
What cause emotions (antecedants) under evolutionary theory
Signal stimuli
What are biological givens in evolutionary theory
Basic emotions (universal, discrete physiology, automatic)
How is emotional experience integrated in evolutionary theory
Affect programs (co-occurrence of emotional components)
Appraisal theories: Antecedents (causes)
Very few stimuli cause the same emotion in everyone
Emotions are determined by how an individual appraises their circumstances
Appraisal
Mental process which allows detection and evaluation of stimuli and how they affect your well-being
Appraisals in appraisal theories
Explain the variation in emotional life
Determine the intensity and quality of components of emotion
Are unconscious, but part of them can become conscious
Scherer’s (1984) five dimensions of appraisals
Novelty (how new the thing is)
Valence (positive or negative)
Goal relevance
Agency (control)
Norms (social norms)
Ecologically valid study in appraisal theory looking at antecedents
Scherer and Ceschi (1997)
Interviewed people who had genuinely lost their luggage at the airport
Asked how they felt before and after they visited the luggage desk
Asked about appraisals non-directly
Results
Variation in emotions experiencing the same objective event
Goal relevance best predicted emotions
Appraisal theories: Biological givens
Scherer argues for a distinction between primary and secondary appraisals:
Primary = fast, clear-cut, innate
Secondary = higher-order, learned
i.e. Snake
Primary = dangerous!
Secondary = not poisonous
How did Scherer split his five components of appraisals into primary and secondary?
Primary
Novelty
Valence
Secondary
Goal relevance
Agency
Norms
Appraisal theories: Integration of emotional experience
All emotion components do not necessarily occur together
Reisenzien et al. (2013) found that emotions and expressions did NOT reliably co-occur
What causes (antecedent) emotions under appraisal theories
Specific appraisal patterns (can differ across people)
What are the biological givens emotions under appraisal theories
Valence and novelty appraisals
Integration of emotional experience (how components of emotion fit together) under appraisal theories
Components are independent (unlike evolutionary theory)
Psychological Constructionism: Antecedents
Barrett (2017)
Emotions are not passive reactions, but actively constructed
Emotions caused by applying learned categories to experience
Categorisation
Mental process by which we take experience and give it meaning
Can explain cross-cultural variations
CONTEXT SPECIFIC
Same physiological profile can be attributed to vastly different things depending on context
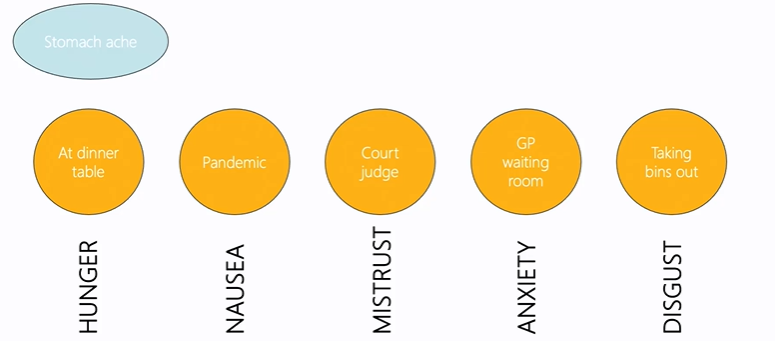
Psychological Construtionism: Biological givens
Core Affect
Composed of two dimensions
Valence: Pleasant vs. Unpleasant
Activation: Activated vs. Deactivated
Thought innate BUT influenced by personal experience
Can be a mood, emotion, symptom, body state, or an evaluation
Alexithymia
Difficulty naming emotions
Psychological Constructionism: Biological givens study
MacCormack and Lindquist (2019)
P’s rated hunger, shown context image (negative or neutral), then asked to rate pleasantness of pictograph
Results
With increasing hunger, increased unpleasantness ratings BUT only with negative context image
Conclusion
Not hunger itself causing the negative evaluations, it’s the context

Psychological Constructionism: Integration of emotion
Emotions don’t have fingerprints, each expression of anger in an individual will be different
Emotions you experience are not inevitable consequences of your genes
HR changes inevitable, interpretation is not
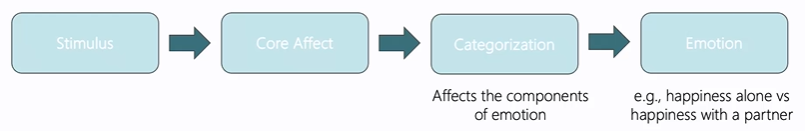
What causes emotions in psychological constructionism theories
Categorisation of affect responses
What are the biological givens in psychological constructionism theories
Core Affect
What is the integration of emotional experience in psychological constructionism theories
Components are independent