NLN-PAX Science
1/440
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
441 Terms
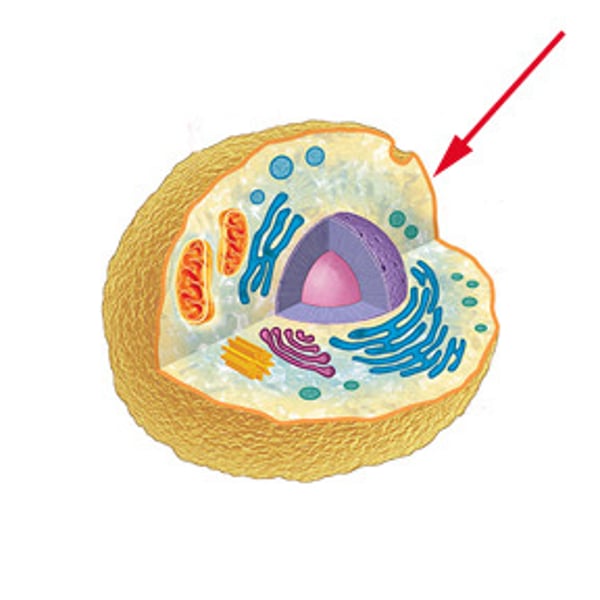
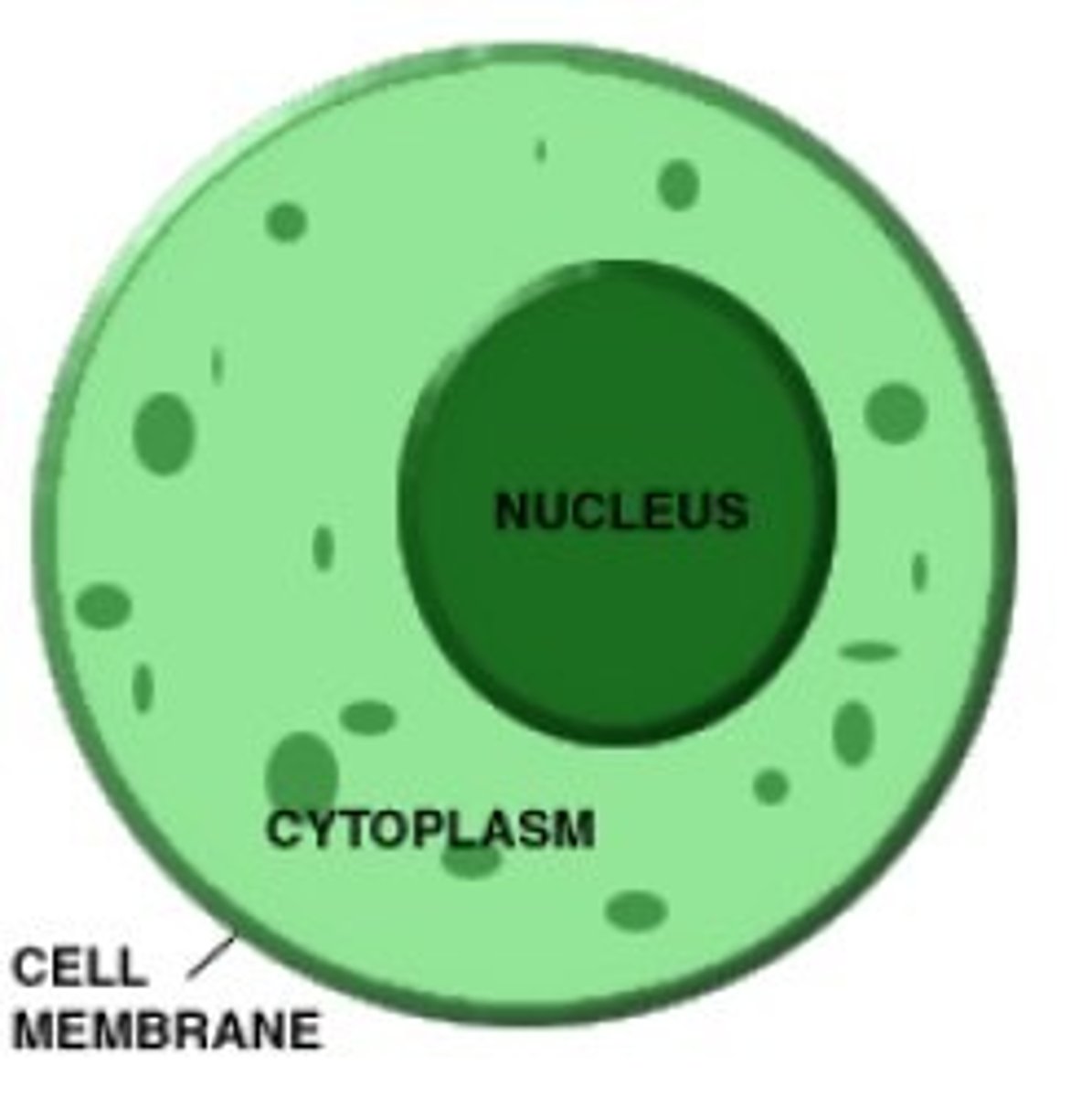
Cell
the smallest living unit and the basic unit of function and structure for all living things.
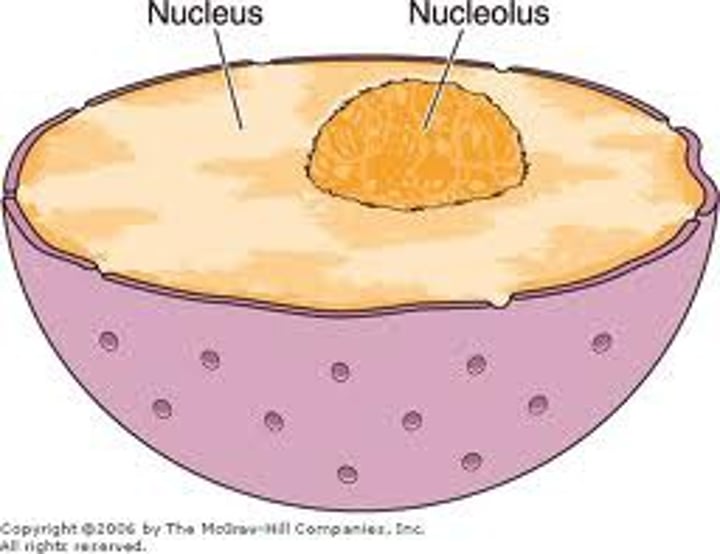
Nucleus
contains the genetic information, or DNA, and controls the activities of the cell.
Plasma (cell) membrane
separates the contents of the cell from the surrounding fluid (interstitial fluid)
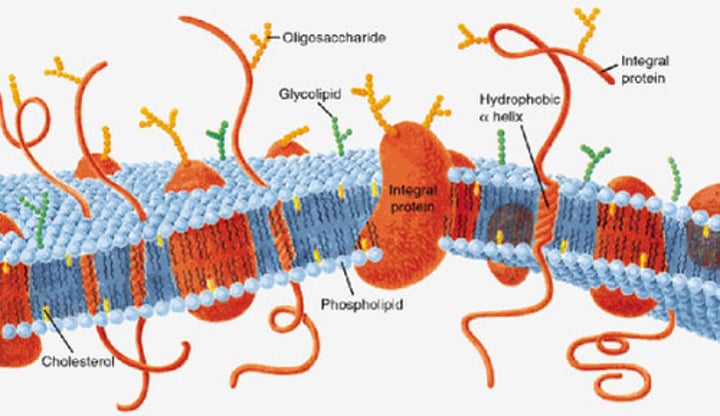
Semipermeable membrane
refers to the selective nature of the plasma membrane. It contains pores and channels that allow only particles of the right size or the right chemical nature to pass through.

Interstitial fluide
contains substances such as amino acids, sugars, fatty acids, hormones, neurotransmitters, and salts.
Cytoplasm
is the fluid matrix found between the plasma membrane and the nucleus that acts as scaffolding for the organelles.
Organelles
(little organs) are specialized units in the cell that per form certain functions.
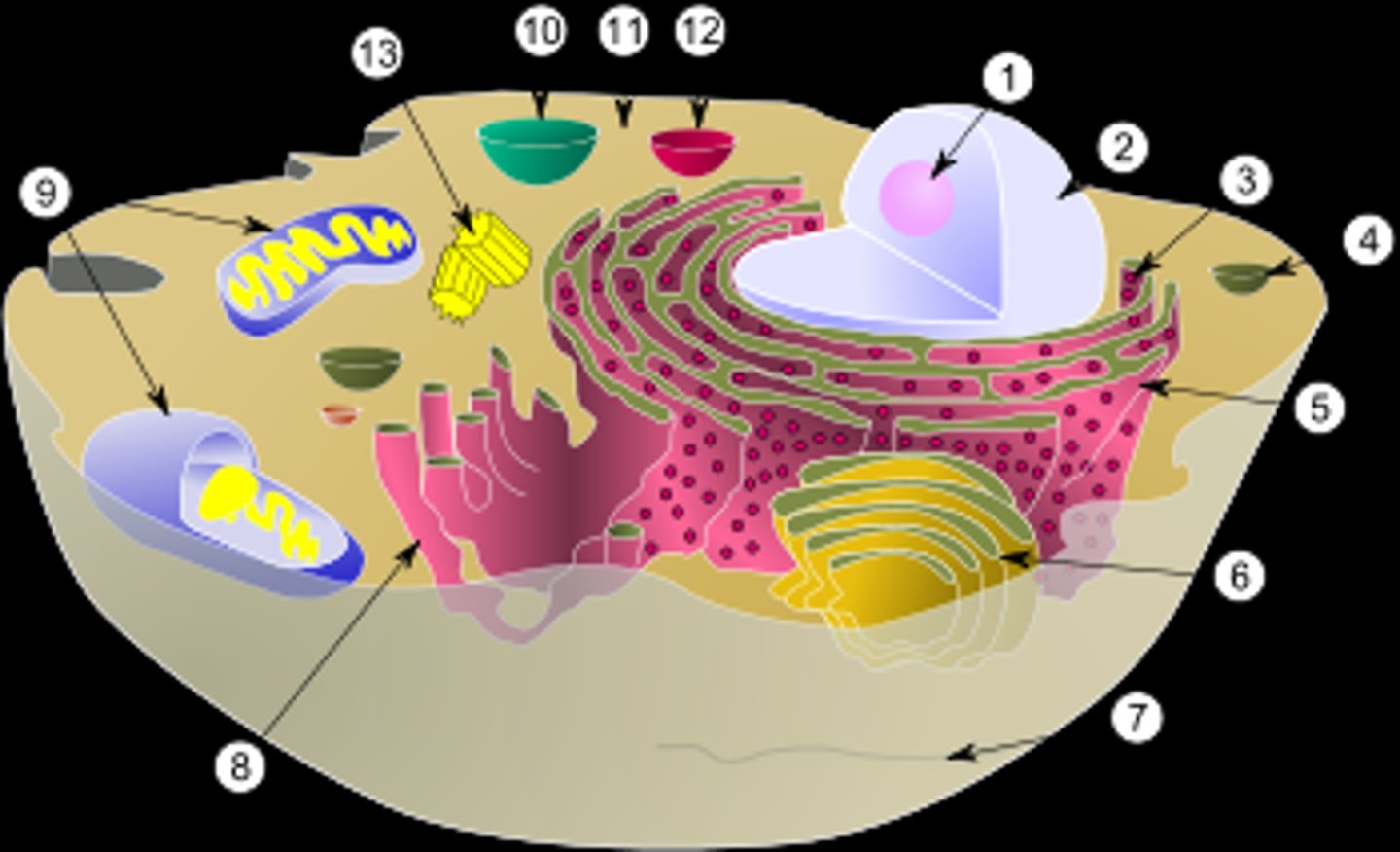
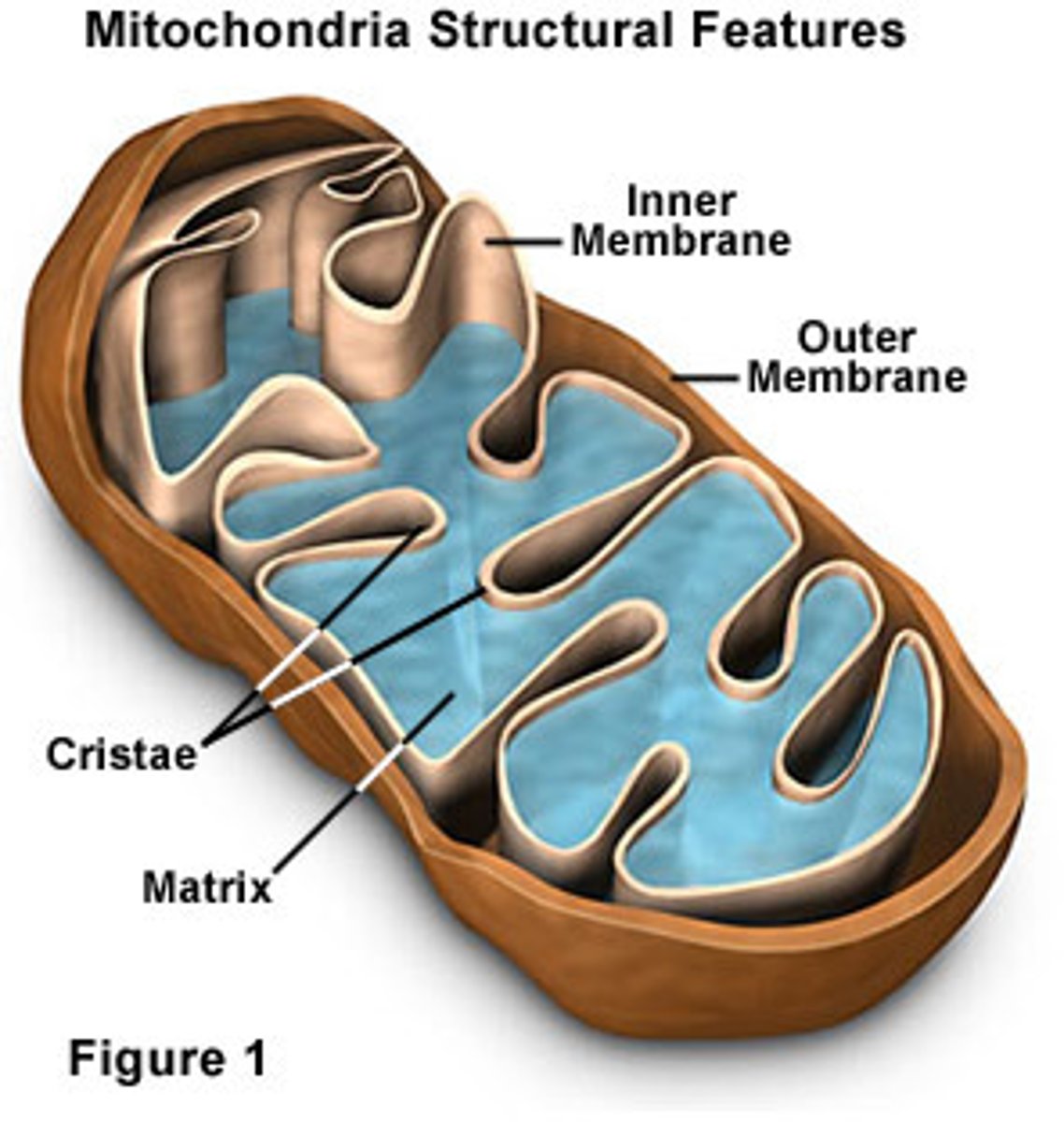
Mitochondria
are the locations for cellular respiration, that is, the conversion of food to energy at the cellular level. The site of energy production and of most of its ATP.
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
the chemical the cell uses to store and transfer energy within itself.
Ribosomes
are the sites of protein synthesis in the cell
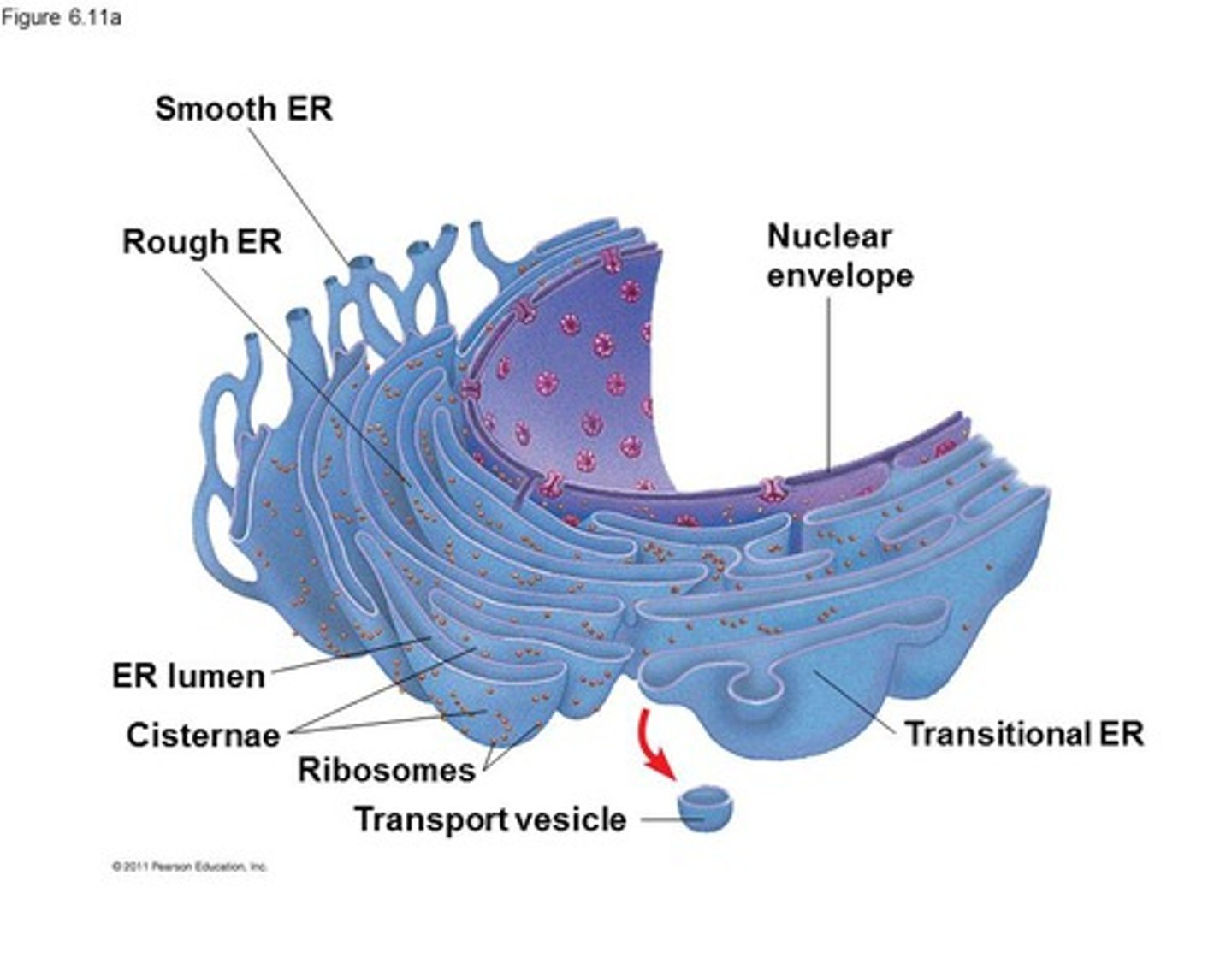
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Ribosomes are attached. Serves as a means for transport within the cell and is made up of many channels. Rough endoplasmic reticulum named for the fact that it has ribosomes on its surface, serves to store and deliver the proteins made by the attached ribosomes. Smooth ER is free of ribosomes it performs varying functions in different cells, including the storage of enzymes and minerals and the folding of proteins, among other things. It is thought to be involved in the detoxification of chemicals and the metabolism of fats.
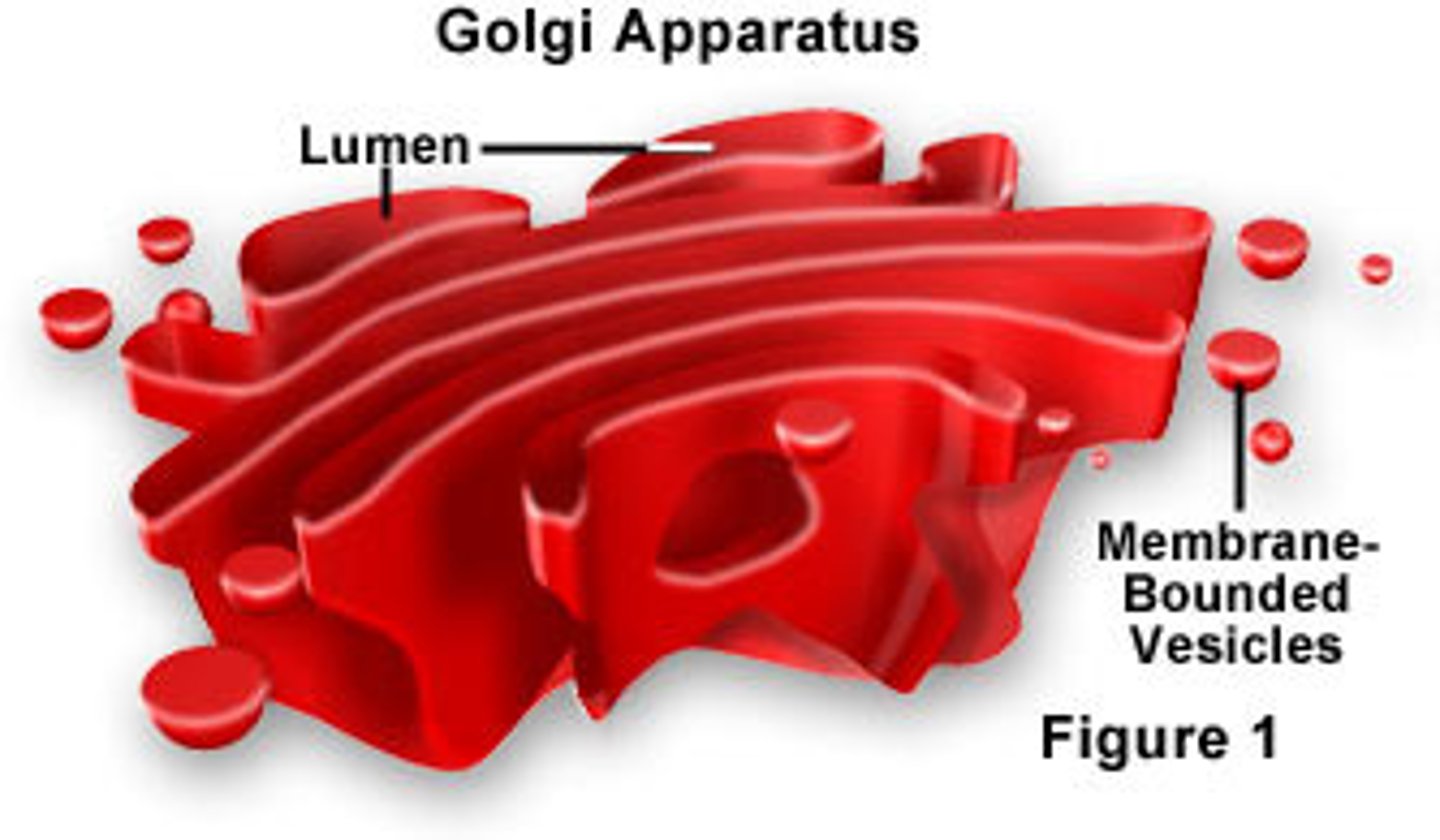
Golgi complex
modifies and packages proteins destined for use in the cell or for export from the cell.
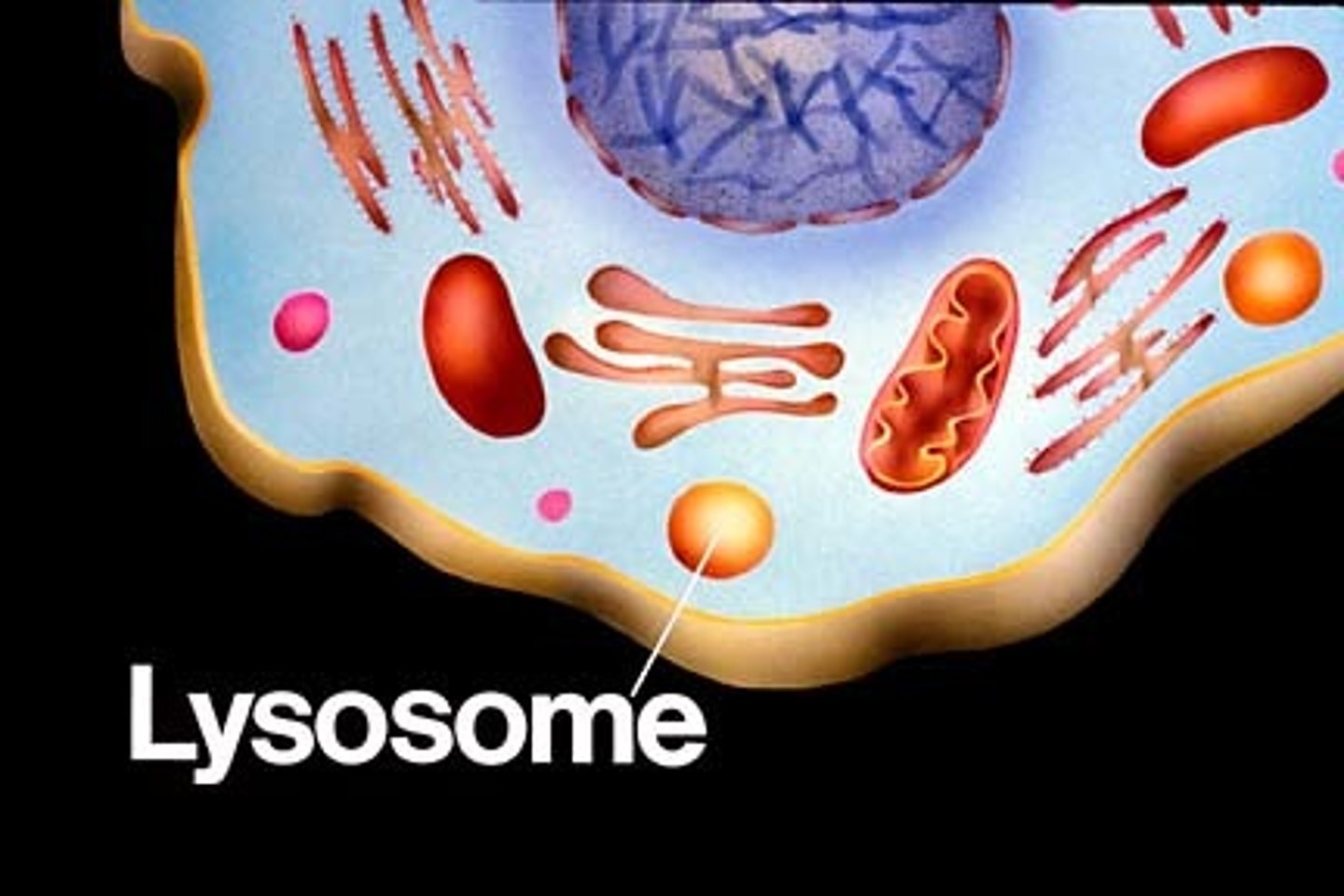
Lysosomes
are sacs that contain strong digestive enzymes. These sacs are responsible for digesting cell structures that are no longer living or that are malfunctioning, and for digesting waste.
Cell wall
Only plant cells have them. It is responsible for the protection of the cell, the maintenance of the shape, and water balance.
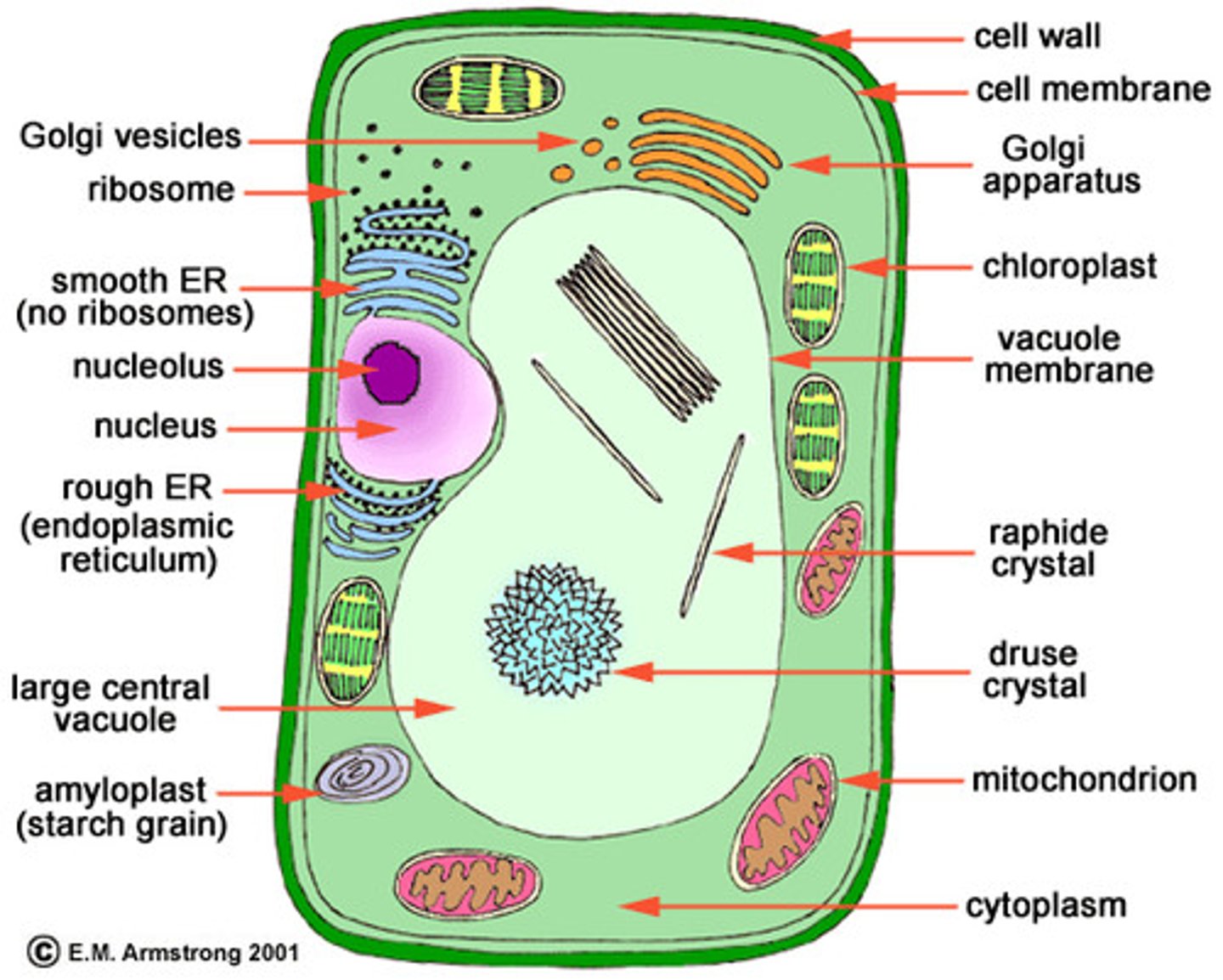
Chloroplasts
contain chlorophyll, which is necessary for photosynthesis.

Vacuoles
plant cells also often large ones. Which are compartments in the cytoplasm that act as places for secretion, excretion, and storage.
Chromatin
DNA is in this loosely structured form when it is not dividing
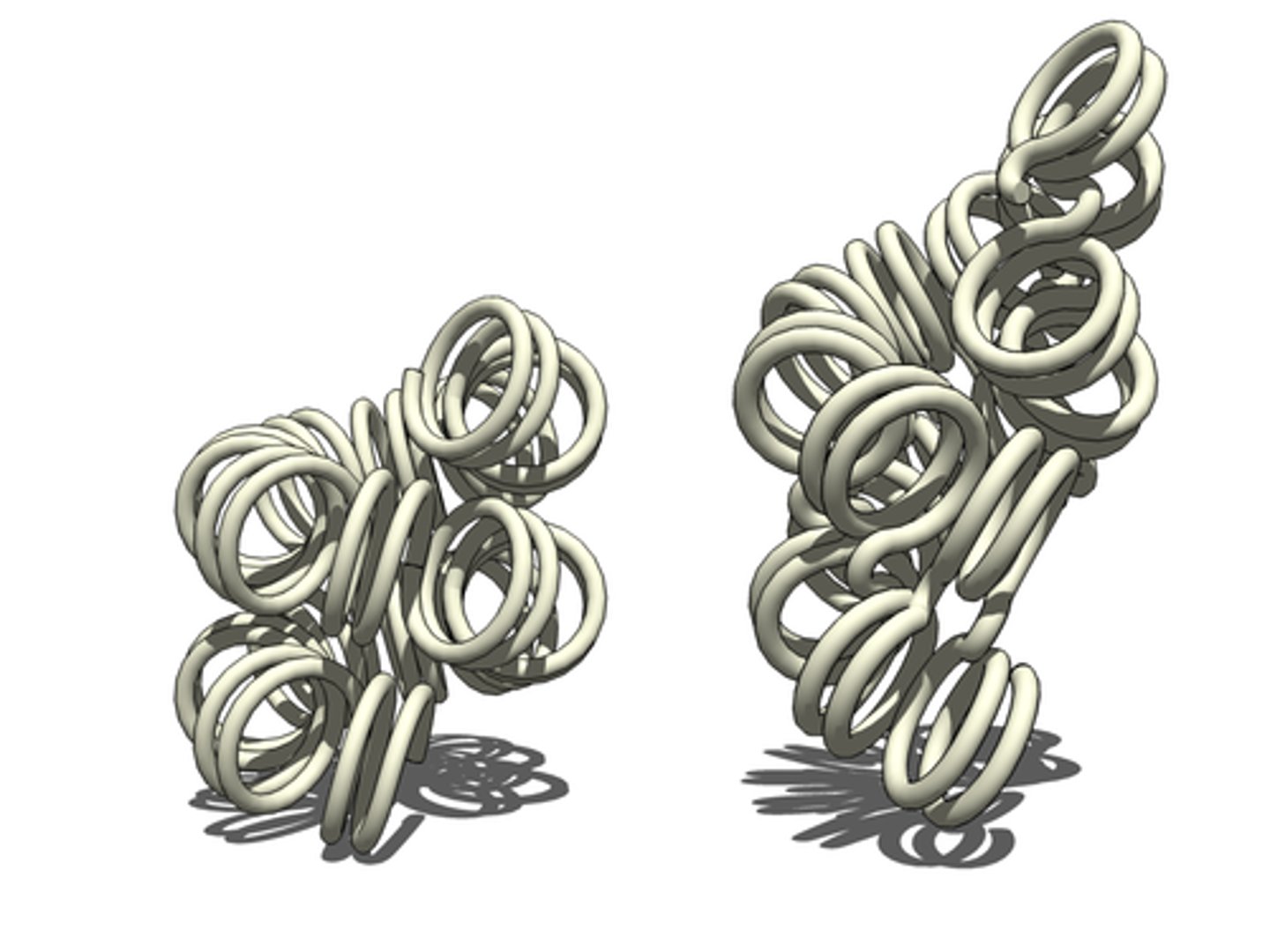
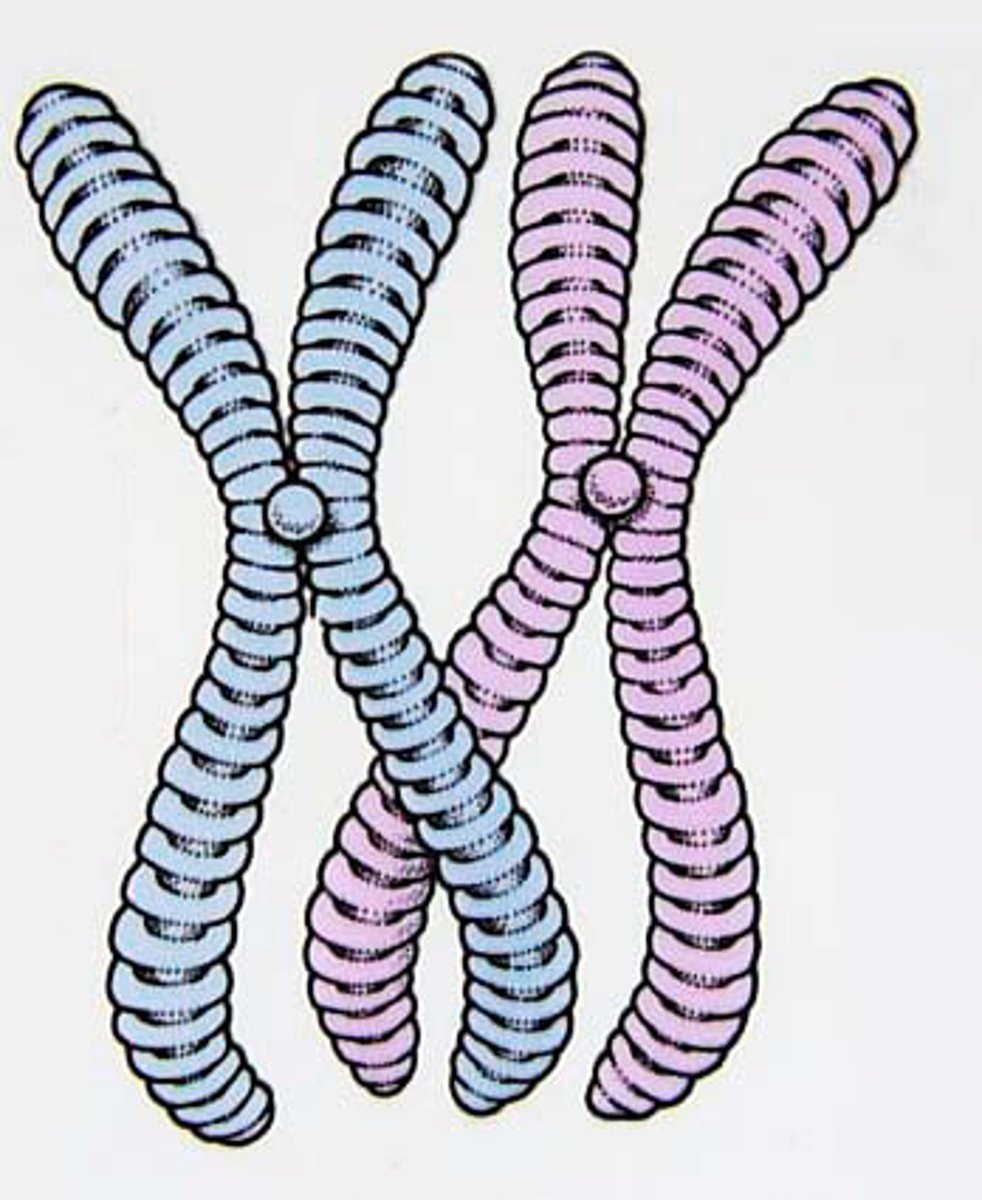
Chromosomes
DNA is seen in condensed rod-shaped bodies when the cell is dividing
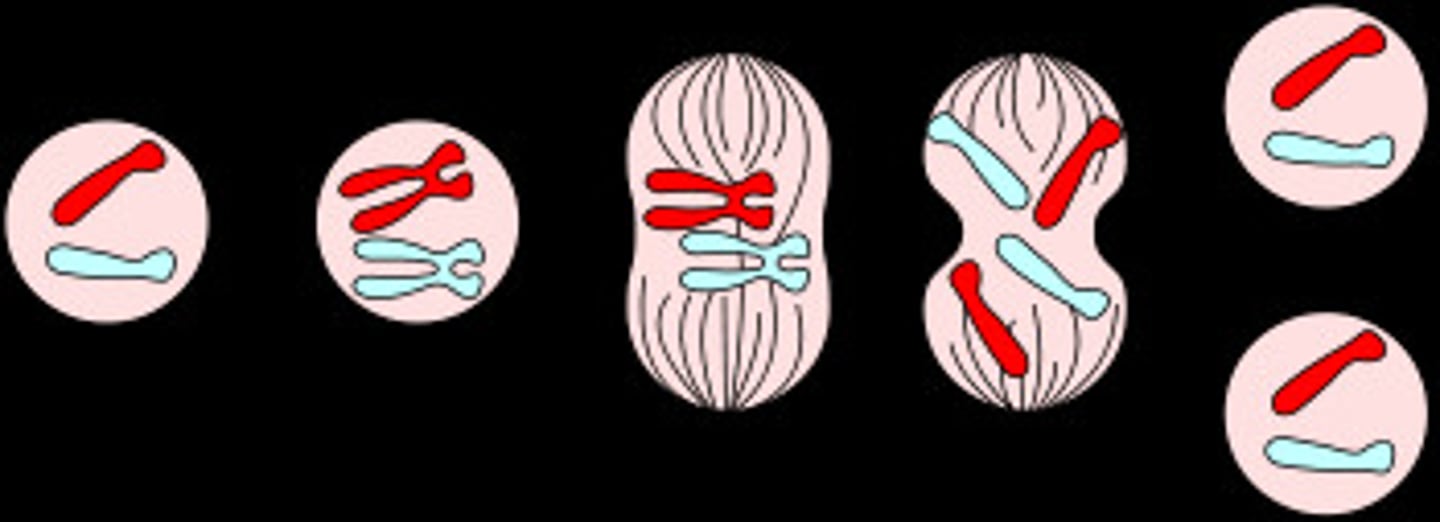
Mitosis
When cells divide, the appropriate amount of genetic material must be passed on to the new, or so-called daughter, cells. In somatic (non reproductive) cells, the new cells are identical copies of the parent cells. This is achieved by a doubling of the chromosomes prior to division. It is useful in the growth and repair of our bodies.
Zygote
the cell created by the union of a sperm and egg contains a full set of chromosomes, half from each parent.
Meiosis
Another type of division takes place in the production of gametes. It contains half of the normal number of chromosomes. It consists first of doubling of chromosomes and then two subsequent divisions. Thus the products are four daughter cells, each with half the normal number of chromosomes.
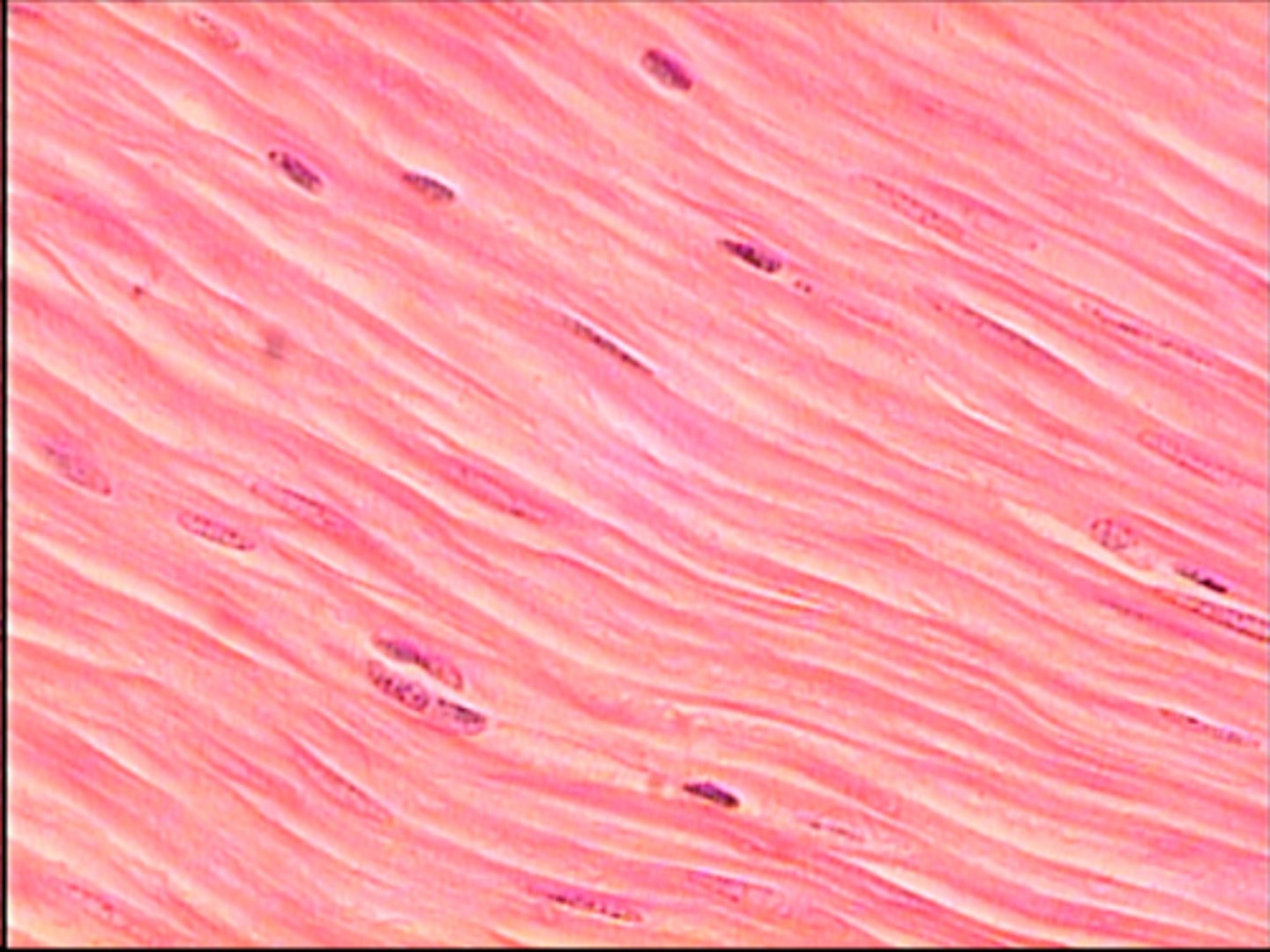
Muscle tissue
skeletal, cardiac, and smooth
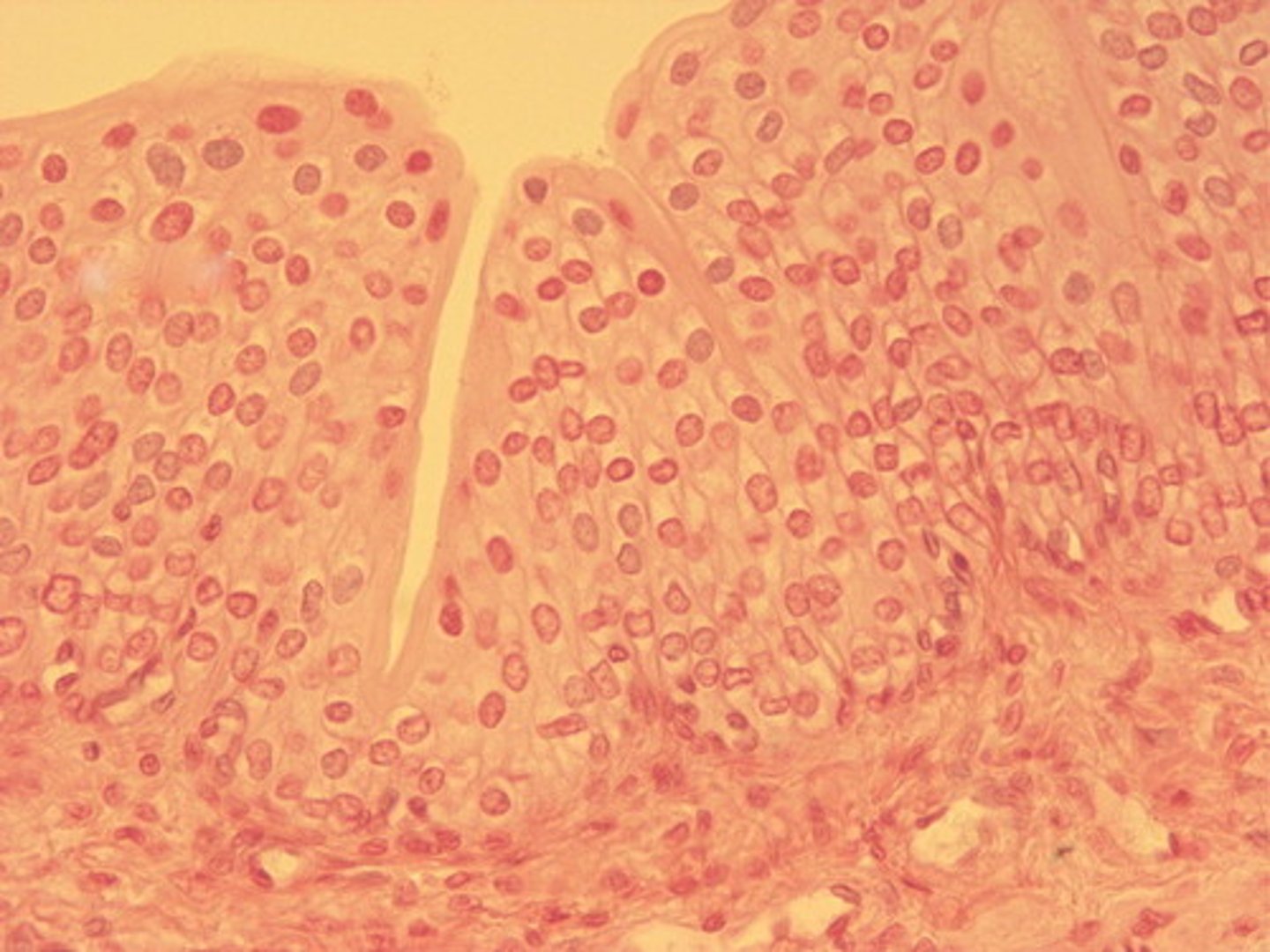
Epithelial tissue
skin, the lining of organs
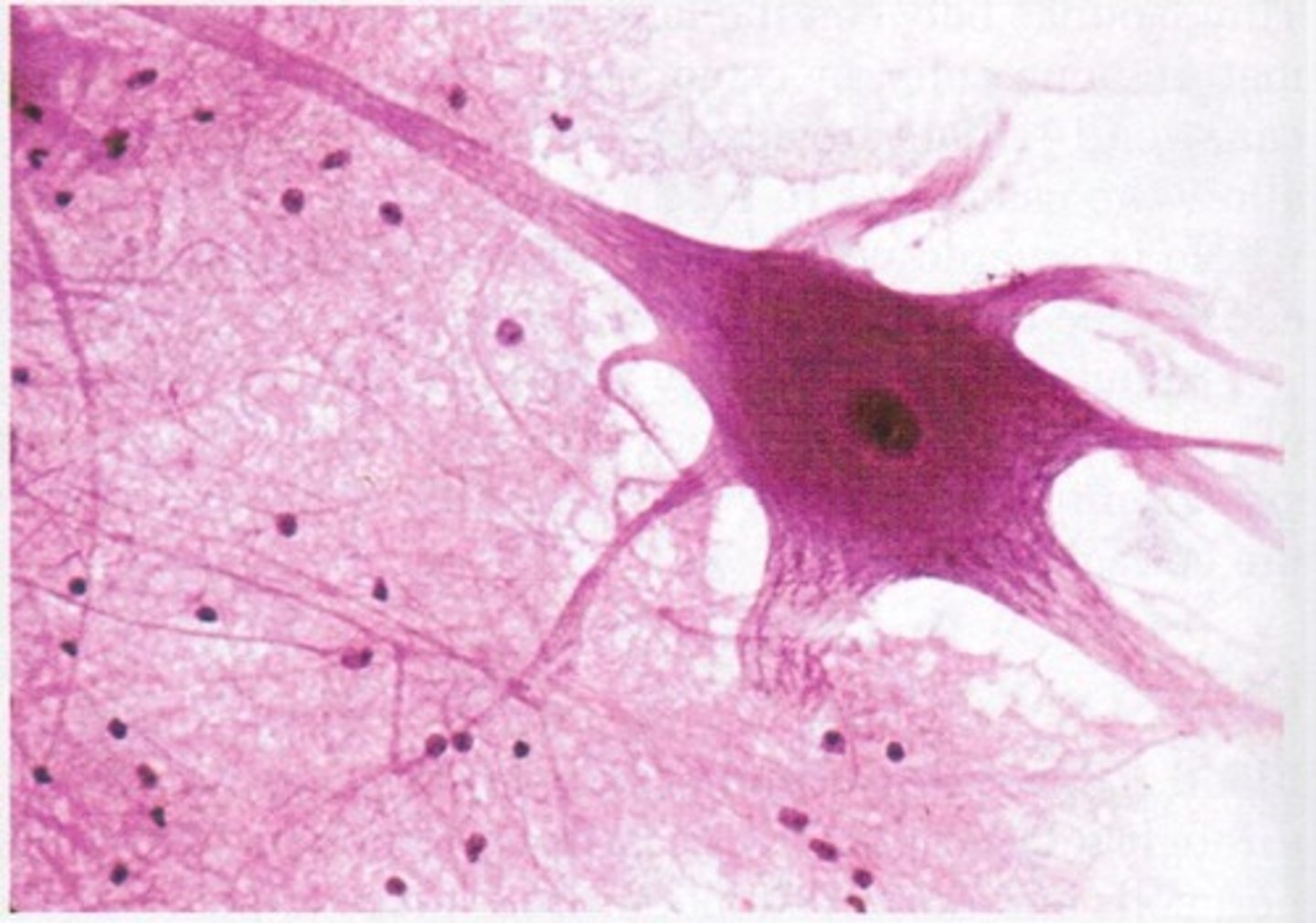
Nervous tissue
neurons
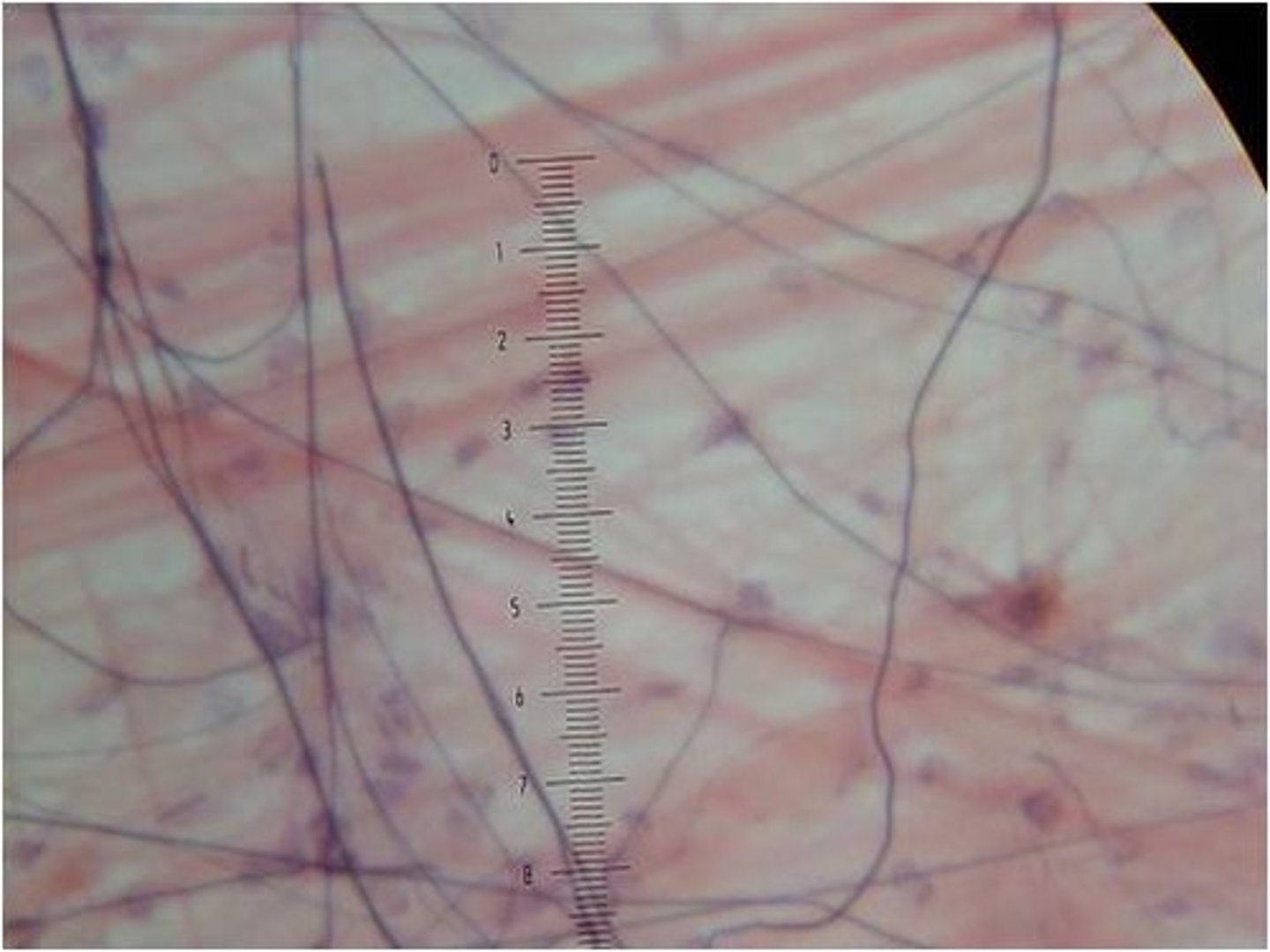
Connective tissue
cartilage, blood, fat, bone
Organ
performs a specialized function in the body.
Organ system
made up of a number of organs working together to carry out a major function.
Organism
the highest level of organization such as the human body

Evolution
is a theory regarding the processes that have produced the biological diversity we see today.
Natural selection
the process by which the traits that promote or enhance an organism's ability to survive and reproduce are passed on to following generations.
Adaptation
For natural selection to occur, organisms must have variations, some of which give the individuals having them an advantage in the struggle for survival. The struggle for survival occurs because each generation of a species produces more offspring than can survive. In this struggle, the individuals best suited to their environment survive ("survival of the fittest") and pass on the traits to their offspring
Fossil record
consists of remnants or traces of organisms from past geologic ages.

Vertebrates
animals with backbones
Biogeography
the geographical distribution of plants and animals

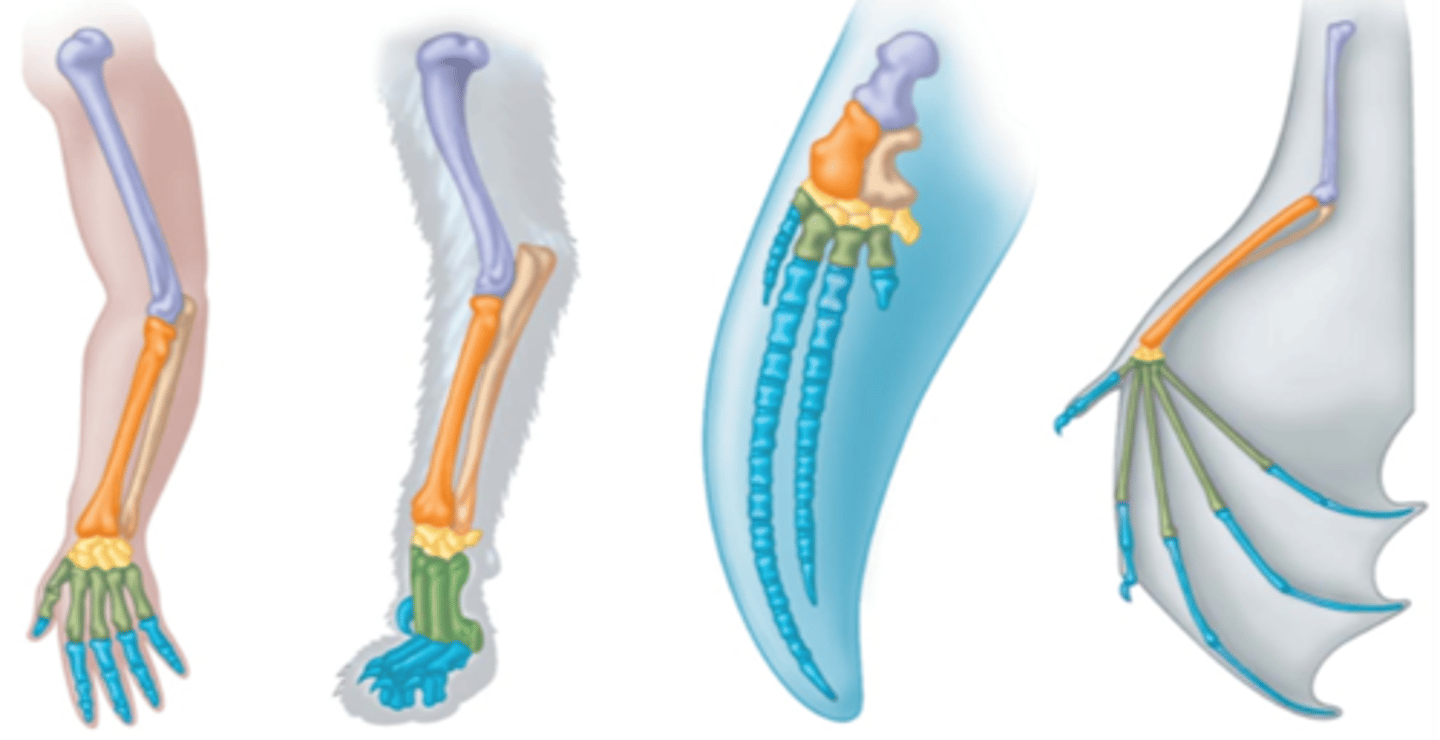
Comparative anatomy
the comparison of organisms' structures
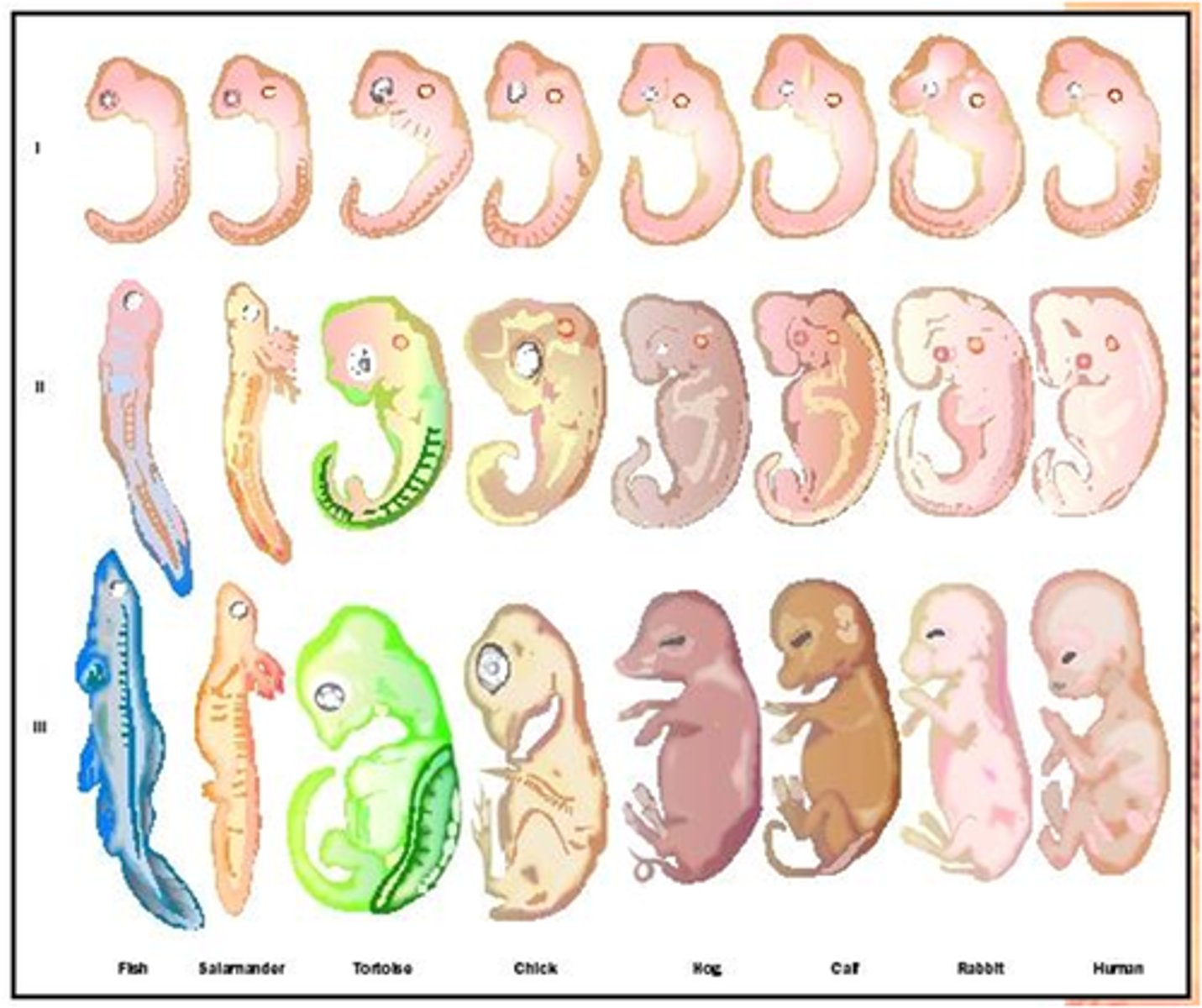
Comparative embryology
the comparison of organisms' embryos
Molecular biology
biology at the molecular level
Taxonomy
the study of scientific classification. Species are grouped according to their similarities and differences.
King Phillip Came Over For Good Soup
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Kingdom
animal, plant, monera, protist, and fungi
Monera
Bacteria
Protist
Protozoa, algae, and some molds

Fungi
Molds, muchrooms, yeasts, and the like

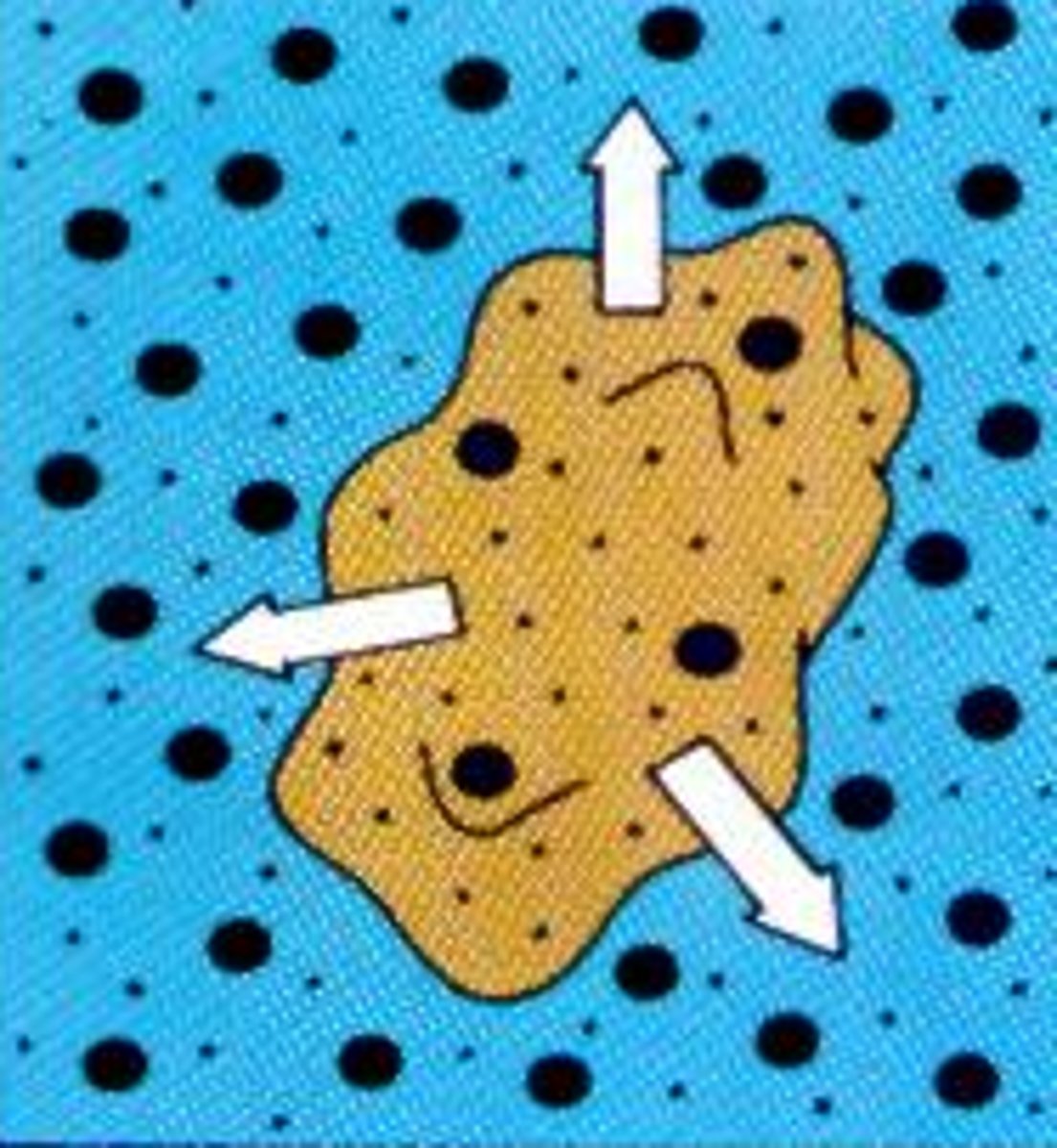
Active transport
involves the use of energy in the form of ATP to move substances across the membrane
Passive transport
does not require energy and makes use of didffusion and filtration
Diffusion
particles move in a random manner, spreading evenly throughout an available space and moving from regions of high concentration to those of low concentration.
Osmosis
A specific type of diffusion is that of water. Water moves from an area of high water concentration (or low concentration) to an area of low water concentration (high particle concentration
Isotonic
When the solute concentration of the water is the same as that inside the cell. Thus, the amount of water that leaves the cell and the amount that enters it are equal.
Hypertonic
When the solute is more concentrated outside the cell than inside it. Water leaves the cell due to osmosis; it moves from the high-water/low-particle concentration to low-water/high-particle concentration. As a result, the cell shrinks.

Hypotonic
If the solute concentration outside the cell is lower than that inside the cell. Water flows into the cell (again high-water/low-particle concentration to low-water/high-particle concentration). If the flow continues long enough, the cell bursts.
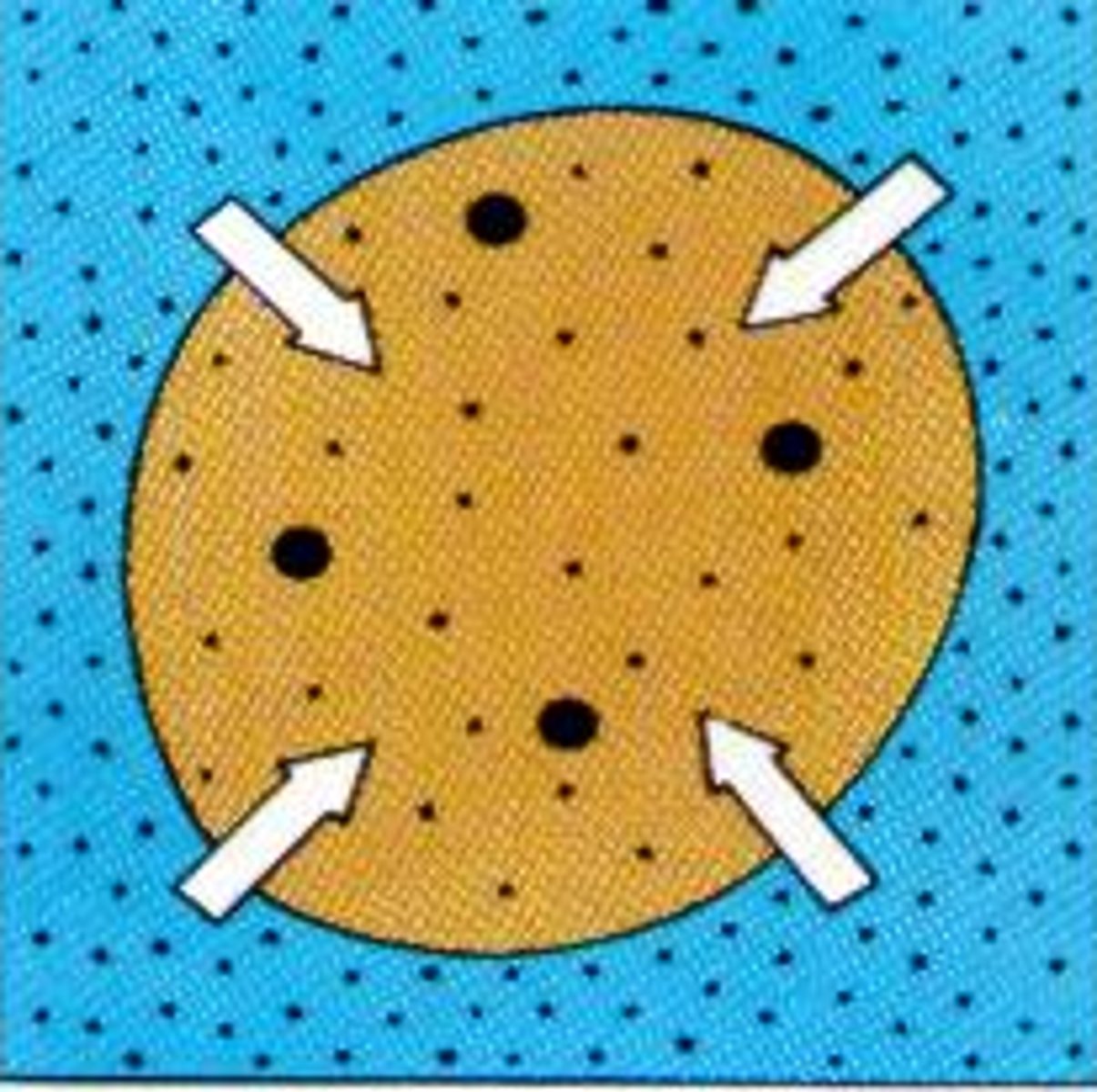
Filtration
the movement of water and solutes through the membrane by fluid, or hydrostatic, pressure.
Autotrophs
are organisms that produce their own food from inorganic substances. Plants are these.

Heterotrophs
obtain their food by consuming plants or other animals. They are also referred to as consumers.

Primary consumers
may be herbivores or omnivores

Secondary consumers
are carnivores or omnivores that eat herbivores

Tertiary consumers
are carnivores that eat other carnivores or omnivores

Herbivores
plant eaters

Omnivores
plant and meat eaters

Carnivores
meat eaters

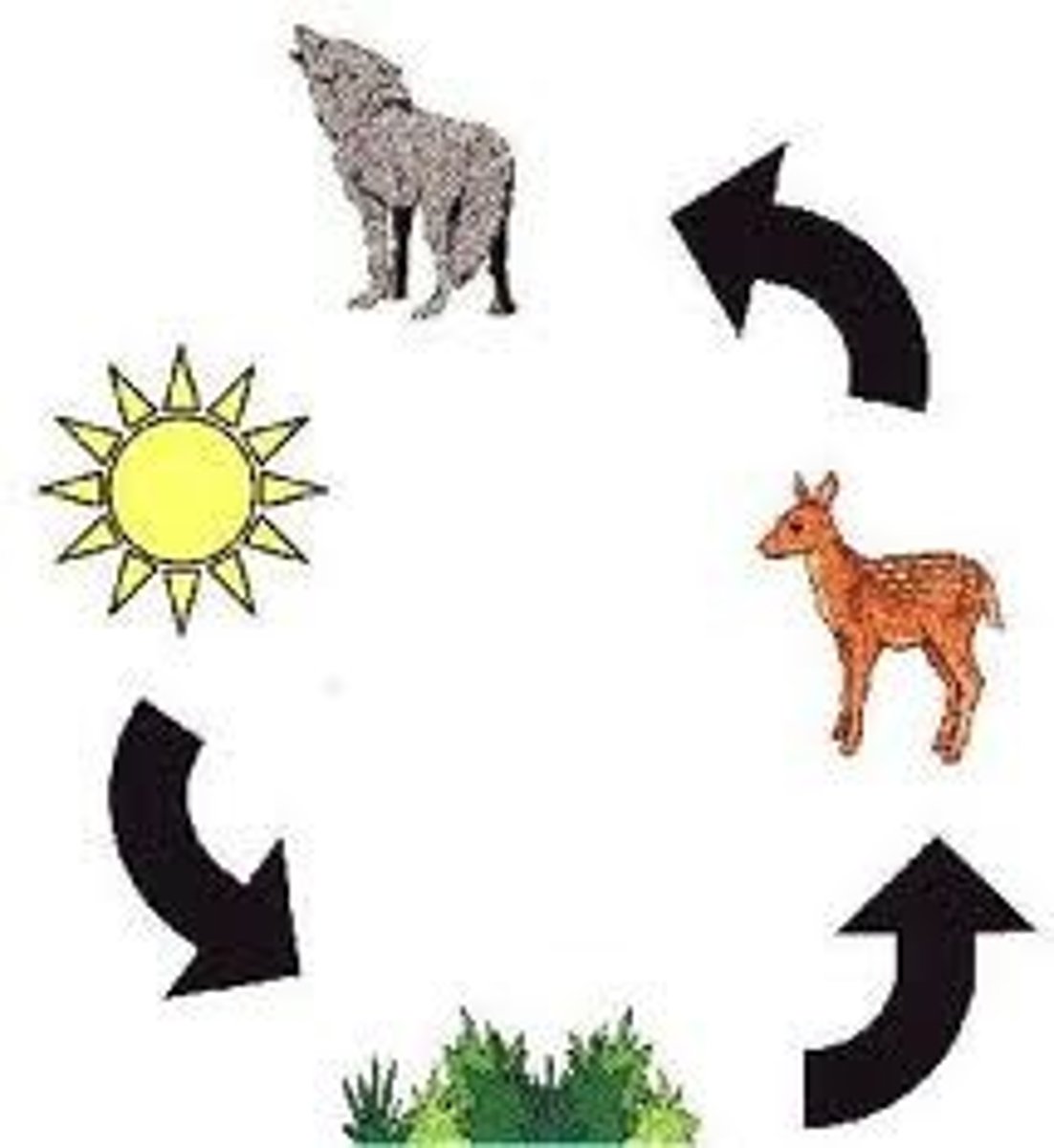
Trophic levels and ecosystem
These divisions, which are made on the basis of how the organism meets its nutritiional needs. The autotrophs are the most improtant trophic level in the ecosystem and are known as producers; the other levels are mad eup of the different types of consumers.
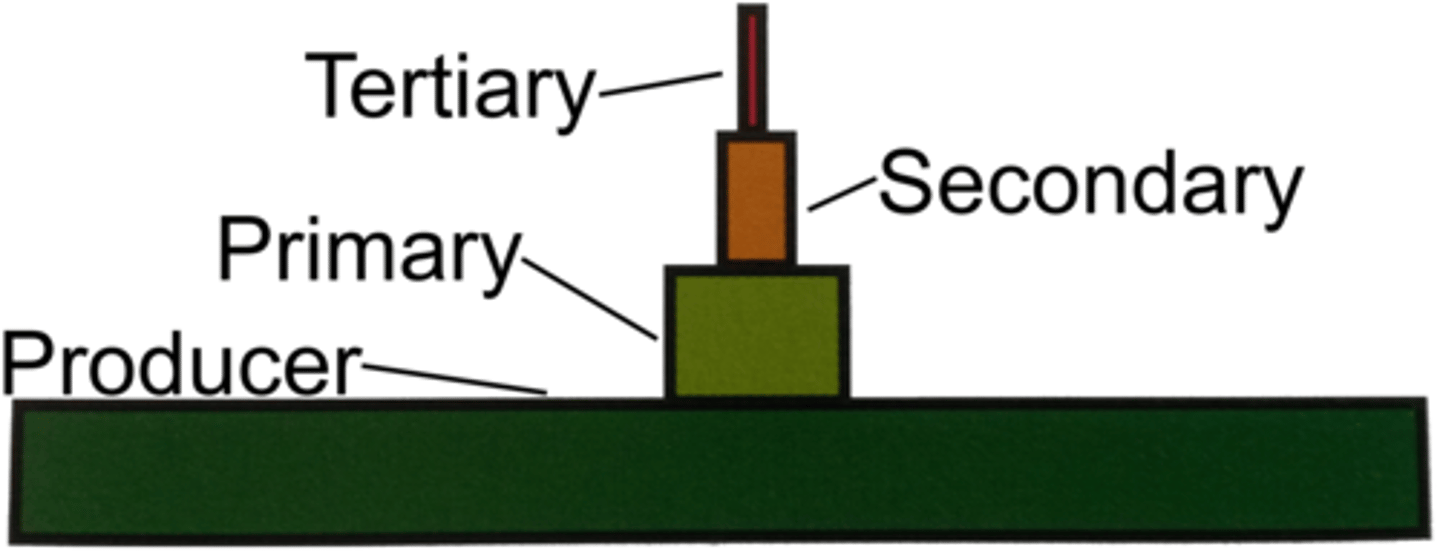
Food chain
The path along which food is transferred from level to level.
Food web
The interrelationship of many food chains
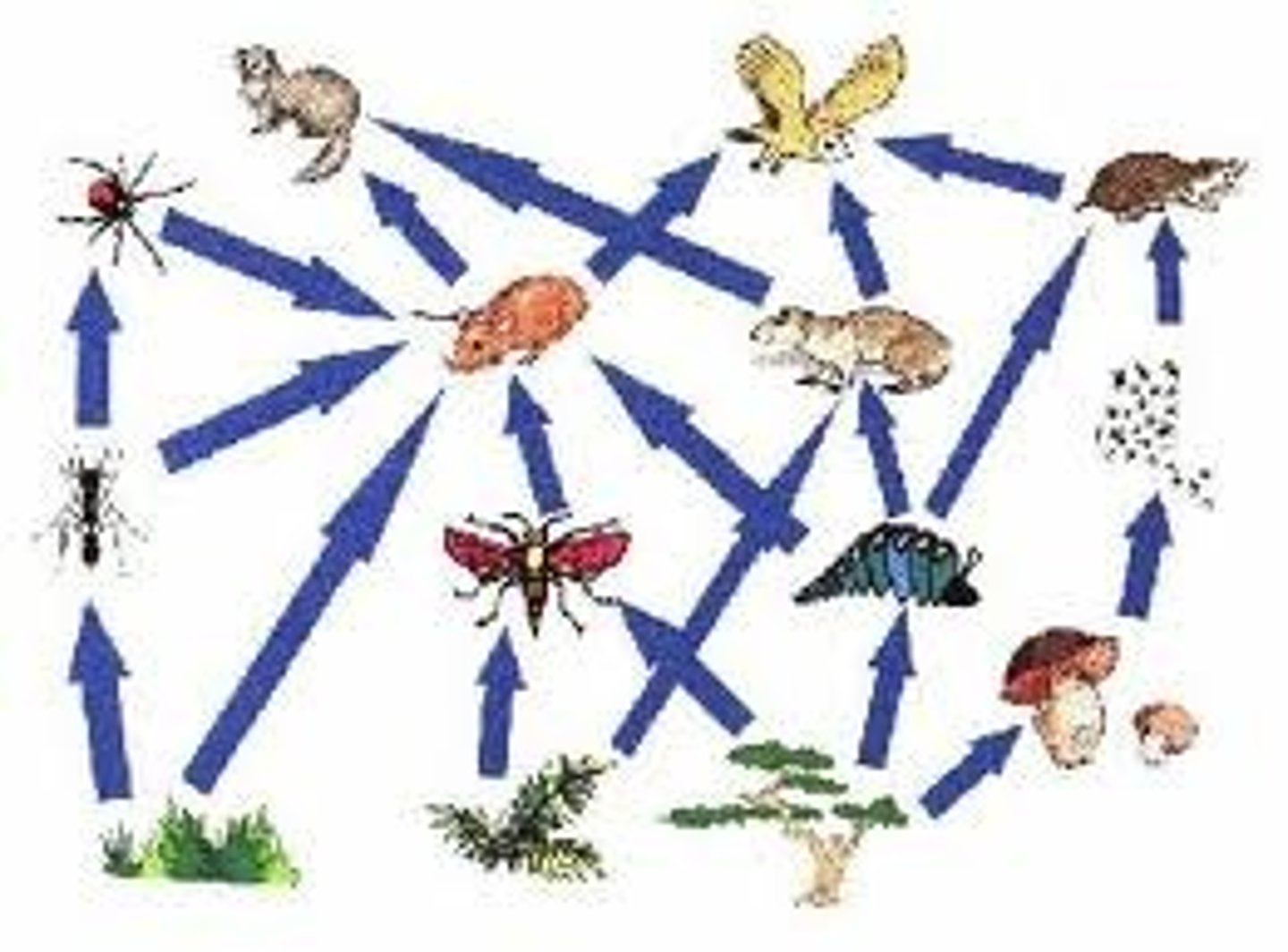
Decomposers
An important role in an ecosystem is played by organisms such as bacteria and fungi, which consume nonliving organic material and release inorganic material. Thus material is recycled through the ecosystem, and inorganic material is made available to the plants.

Biotic factors
include the living parts of the ecosystem
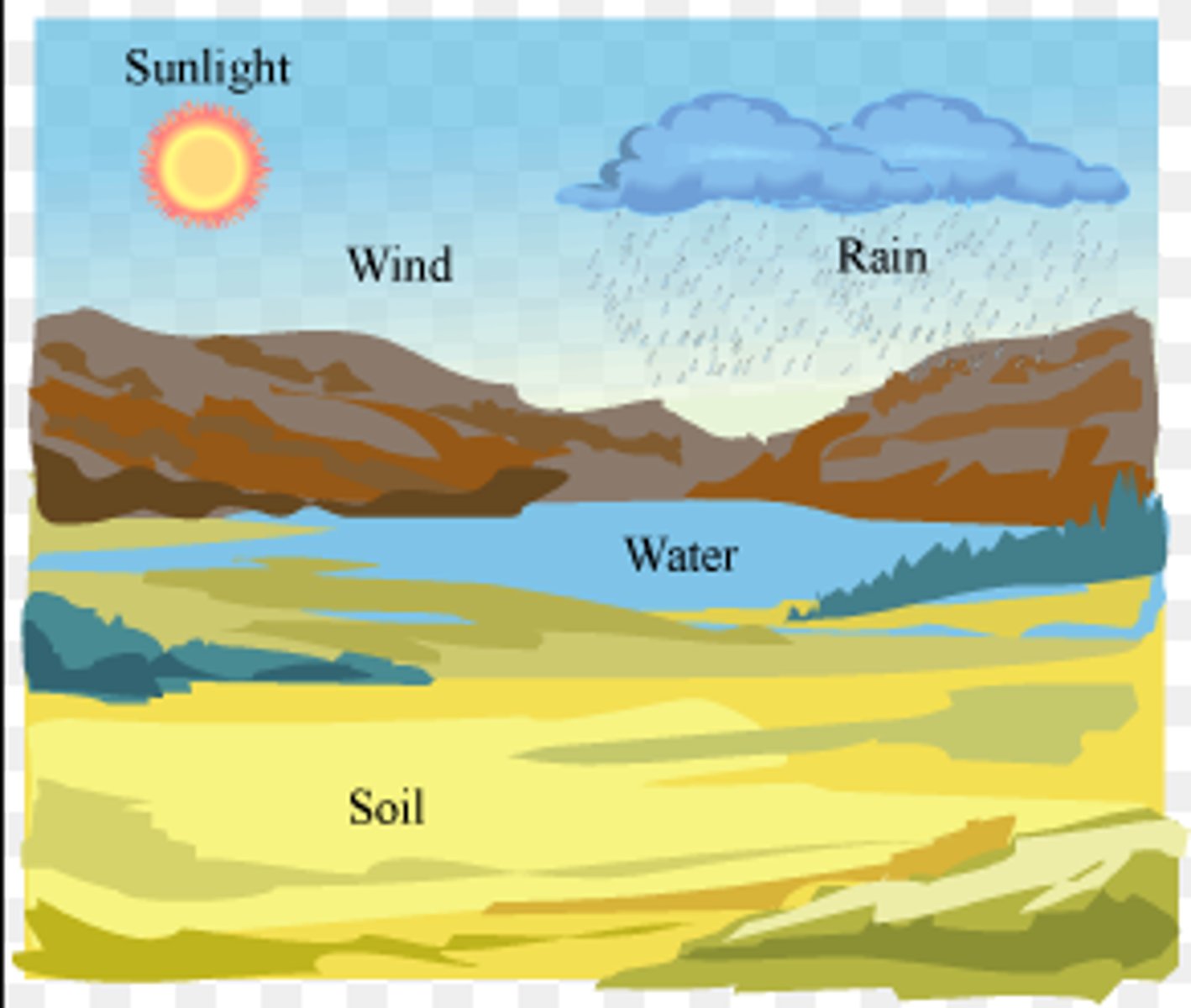
Abiotic factors
nonliving influences, such as temperature, humidity, or soil composition.
Predator
Eats prey

Prey
gets eaten

Symbiosis
separate species living together

Parasitism
In which one species benefits and one species is harmed, such as a tapeworm in a human host

Commensalism
in which one species benefits and one is unaffected, such as a remora and shark

Mutualism
in which both species benefit, such as lichen, which is made up of a fungus and an alga and is found on a tree or rock

Biosphere
the entire portion of our planet that is inhabited by living things in a variety of ecosystems and communities
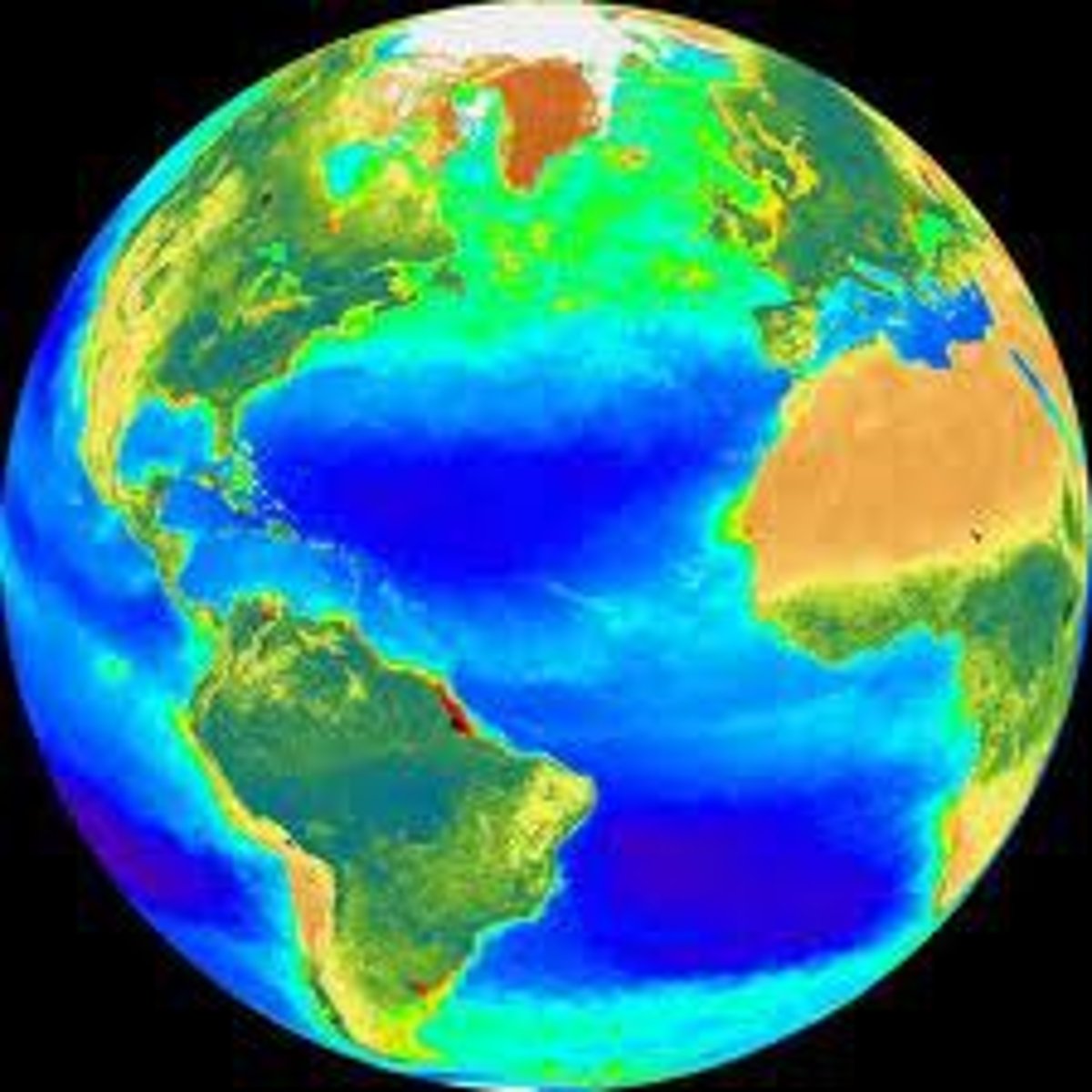
Biomes
Within the biosphere are groups of ecosystems that are common to the various types of geographical areas.
Deserts
have little precipitation and are more arid than all of the other biomes

Tropical rain forests
typically have a relatively constant temperature (68F-90F), constant daylight length throughout the year, high humidity, and abundant rain (200-400 cm/year). These forests are known for their biodiversity, having more species than any other area of the world. Trees grow very tall and there is great competition for light. Little light reaches the forest floor.

Deciduous forests
are usually found in the temperate, midlatitude regions of the world, where the air contains enough moisture to support the growth of large trees. Deciduous tress, such as oaks and maples, are ones that drop their leaves during the dry months. The temperatures in this biome can range widely from season to season.

Coniferous forests
(taigas) are found at high and cool elevations, where the seasons consist of short summers and long, chilly winters. These areas are characterized by conifers, such as pine, and firs, which do not shed their leaves in the cold, dry months.

Tundras
are characterized by very cold temperatures and high altitude. Here the conditions allow shrubs and bushes to grow, but no trees.

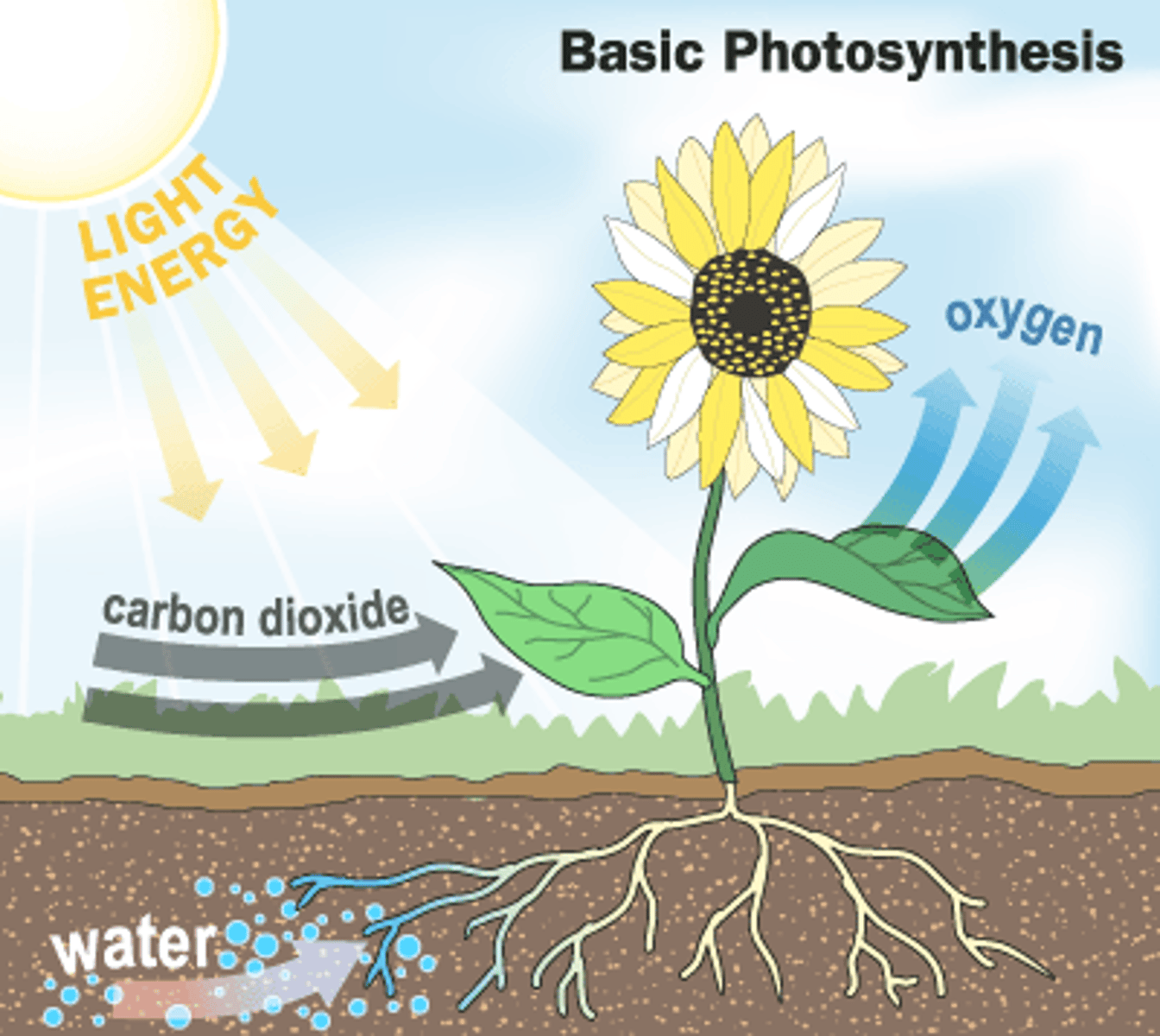
Chlorophyll
Pigment in plant cells that absorb light energy. This energy drives the synthesis of food molecules.

Photosynthesis
To produce their own organic molecules from inorganic molecules in the environment
Cuticle
Covers the stems and leaves of most plants are covered by it. Which is a waxy layer that helps prevent water loss through evaporation.

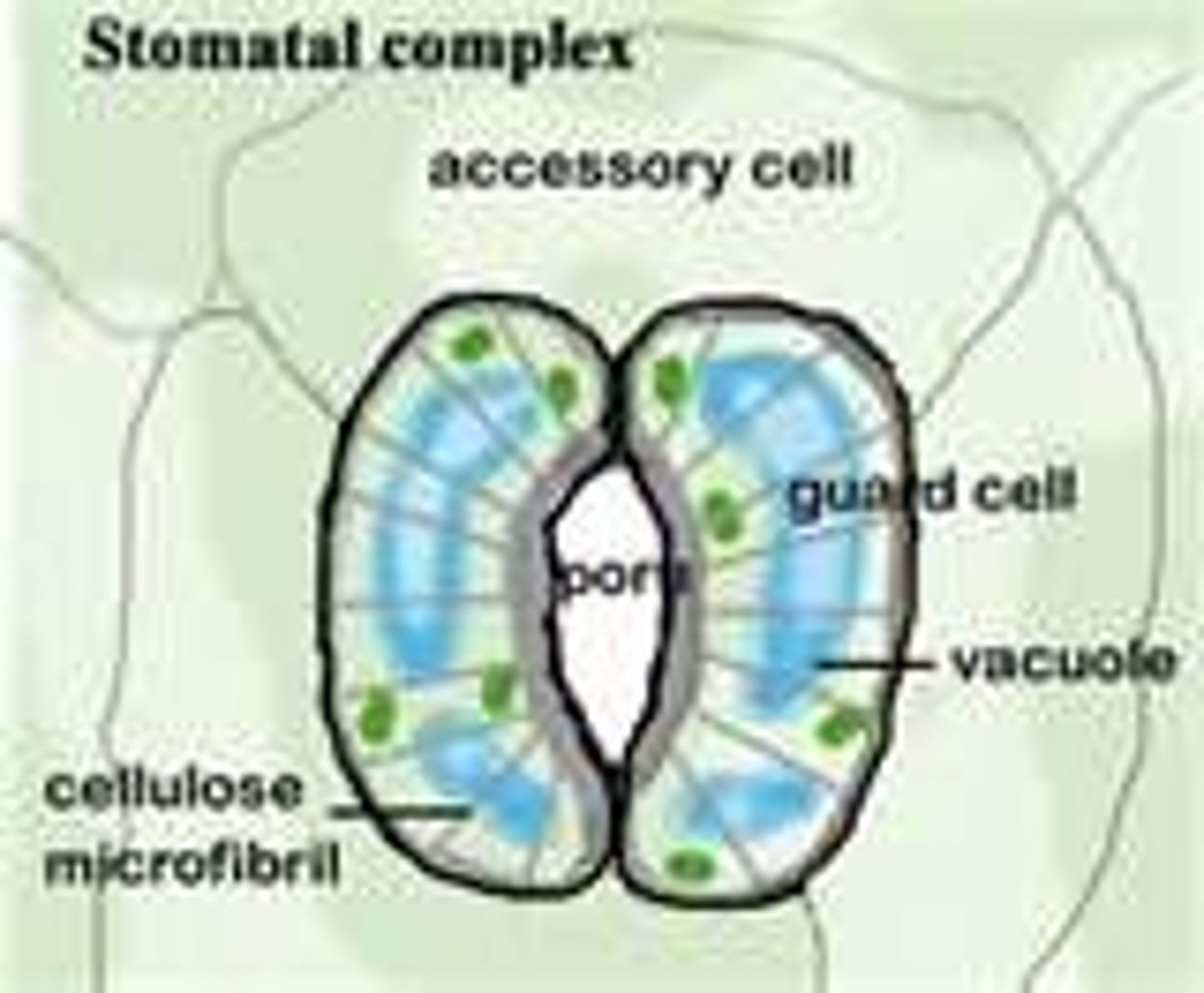
Stomates
Pores on the lower surface of the leaves that allow carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen to be released during photosynthesis without losing too much water
Angiosperms
flower in flowering plants; responsible for reproduction

Sepals
encase the flower before it blooms

Petals
useful in attracting pollinators

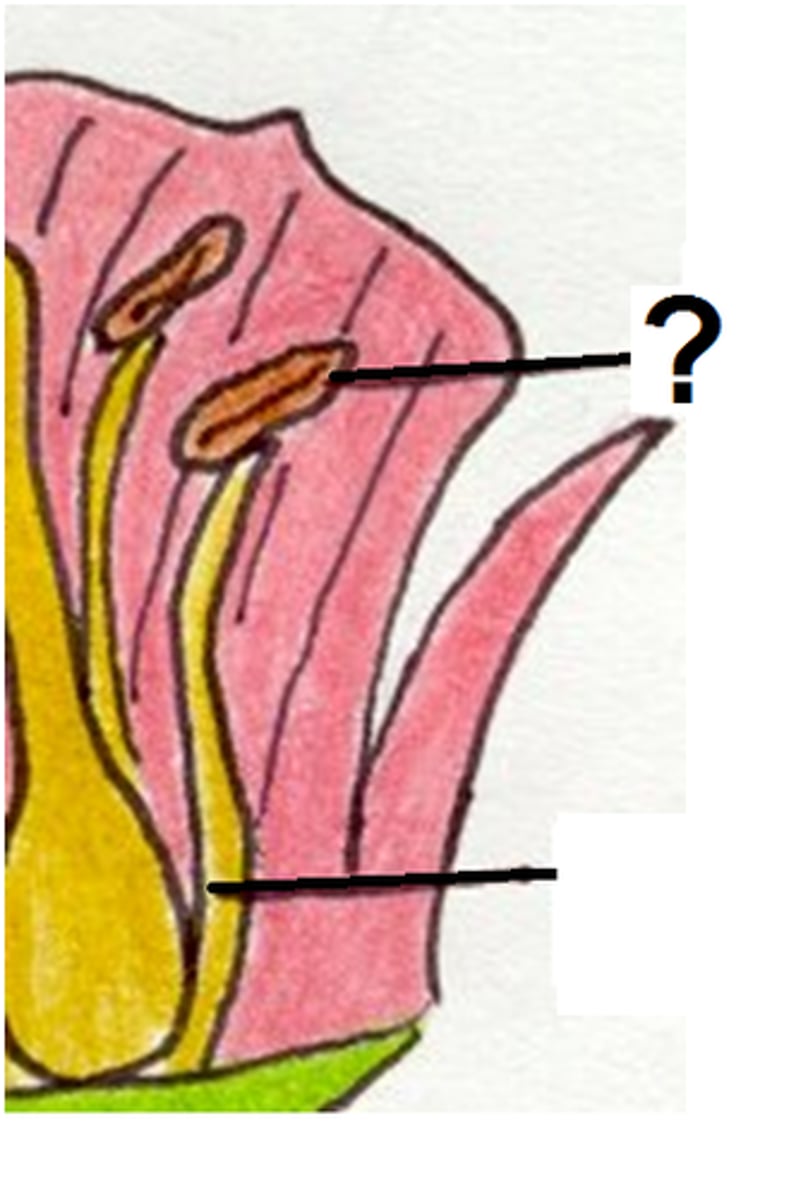
Stamin
Consists the filament, which supports the anther

Filament
Support the anther
Anther
where the pollen is produced
Pistil
Consists of the stigma, the style, and the ovary
Stigma
receives pollen

Style
leads to the ovary
Ovary
contains the 0vules and where fertilization occurs
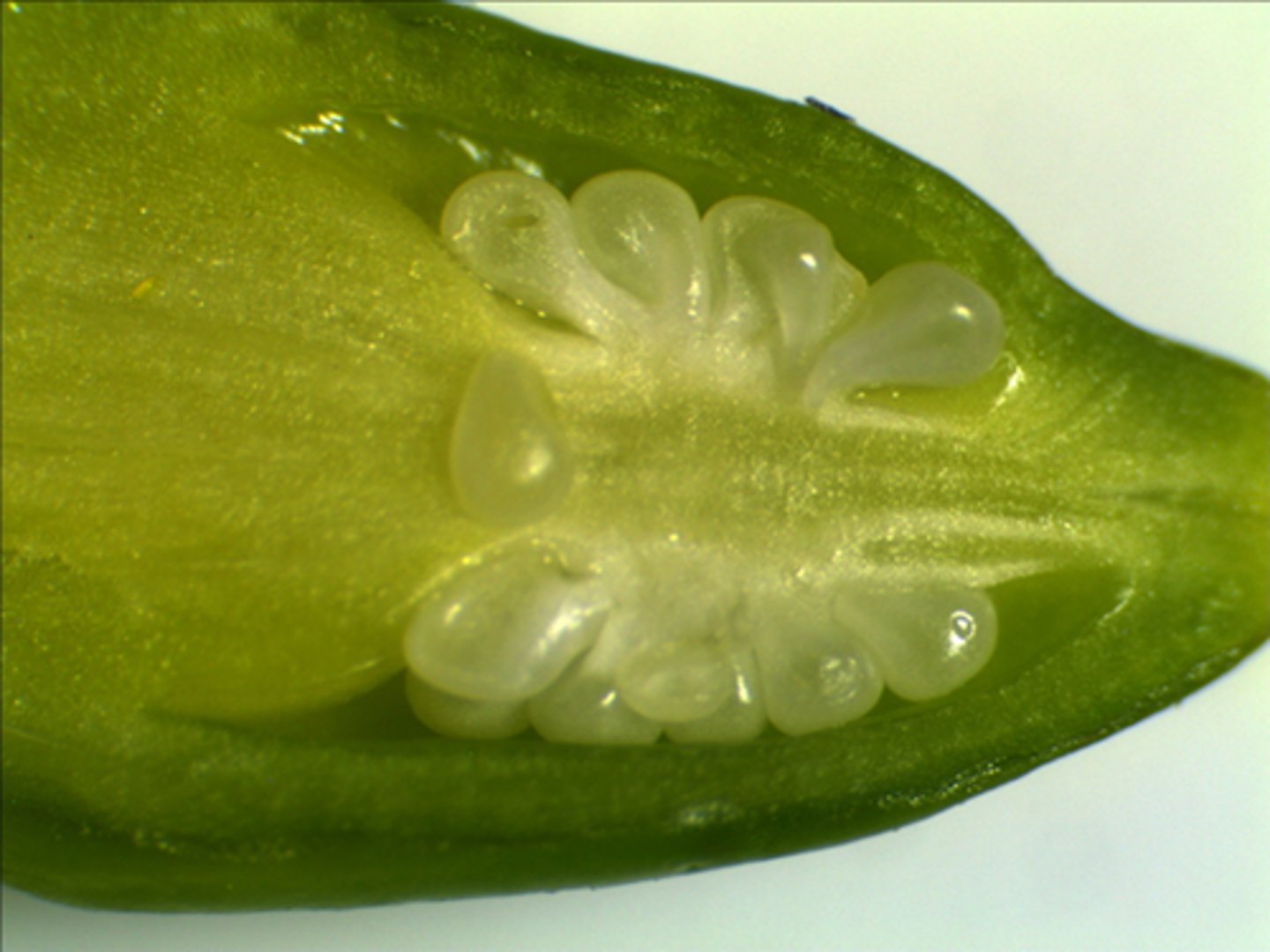

Ovules
after fertilization they become seeds
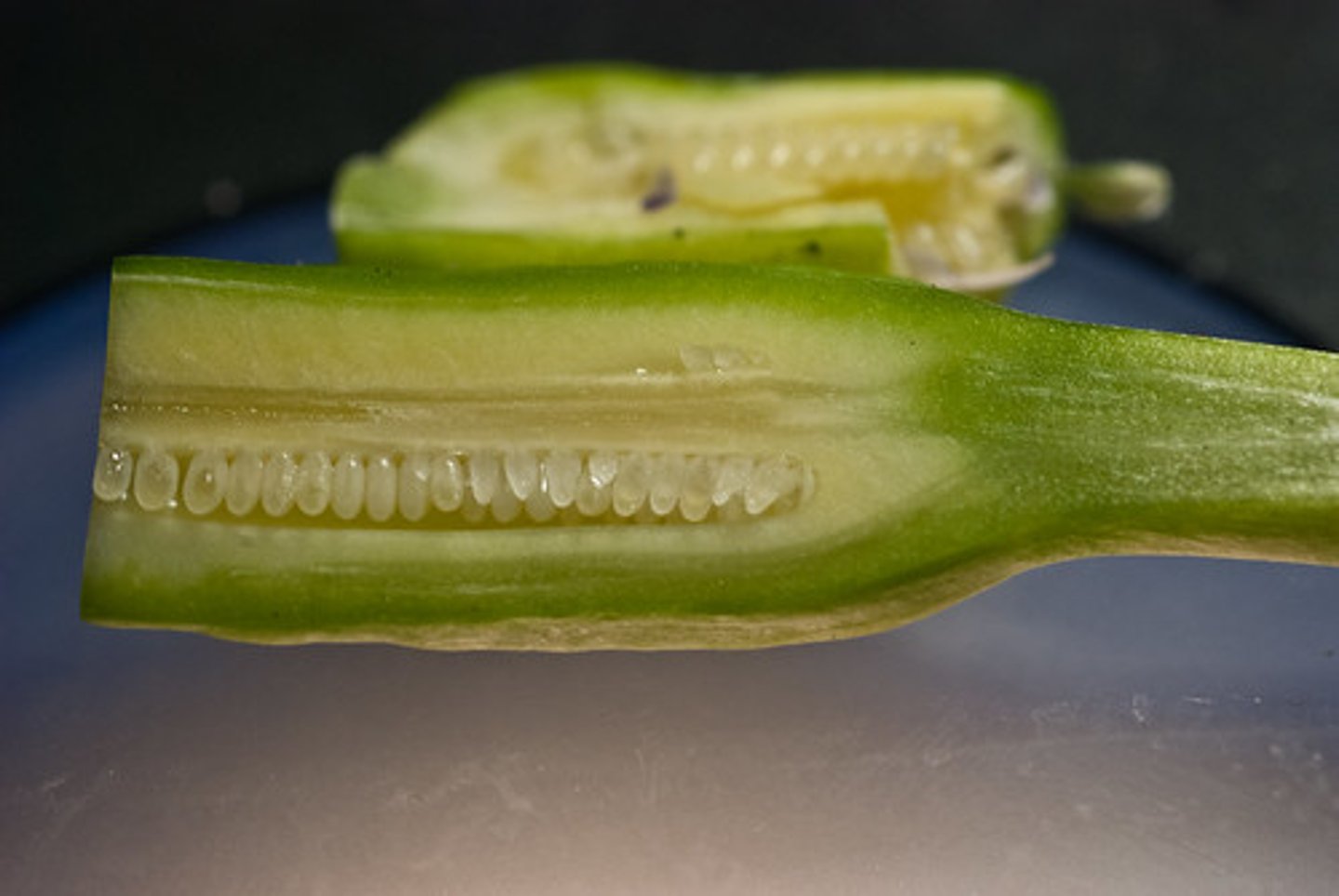

Seeds

Fruit
After fertilization, the walls of the ovary thicken to protect the seed

Genes
A set of instructions that all living things possess. These determine the characteristics of an organism. These are located on chromosomes.
Alleles
Genes are found in pairs
Homozygous
An individual with two identical genes for a trait is called a purebred.
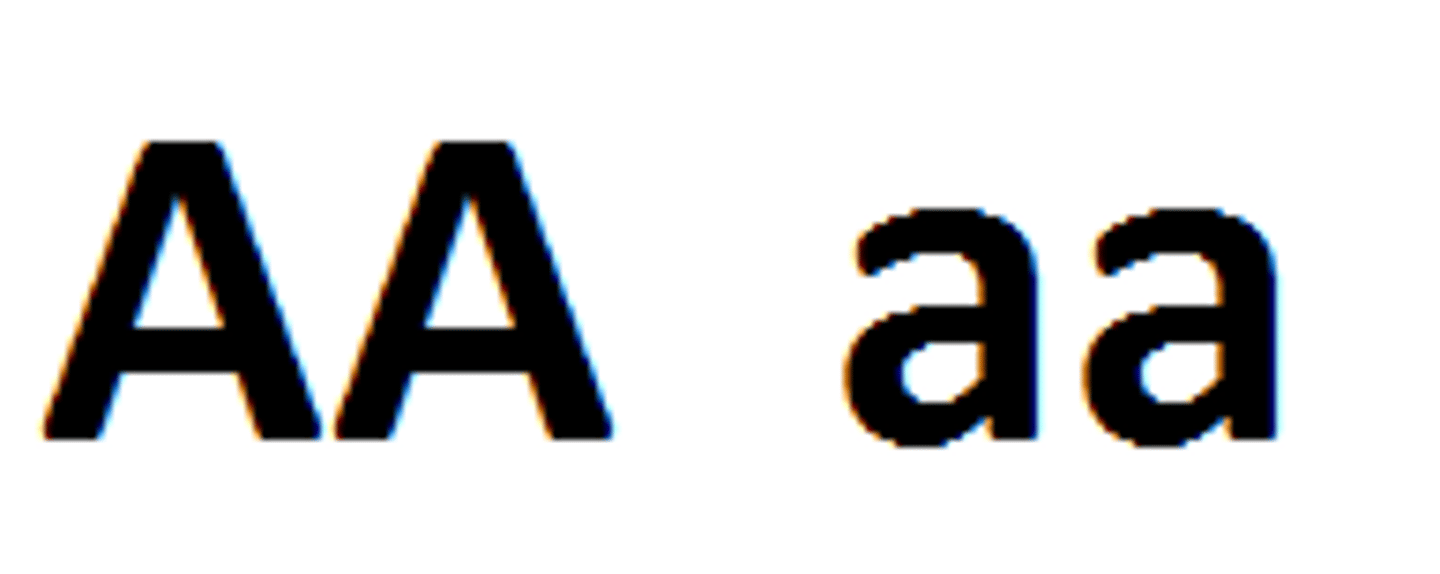
Dominance
When individuals with contrasting traits are crossed, one trait, called the dominant trait, is expressed, and the other trait, called the recessive trait, is masked.
Heterozygous
contain one allele for tall and one for short. The allele for tall (T, the dominant gene) is expressed, and the allele for short (t) is hidden.
Phenotype
appearance