functional groups of muscles
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
prime movers
provide the majority of the force needed for movements (usually the largest muscle operating at the joint)
antagonists
are usually located on the opposite side of the joint as the prime mover
(opposes the movement to make it slower and graceful)
synergists
works with the prime mover to make movements smoother by guiding movement
(helps stabilize joints)
fixators
holds joint bones in place, projecting against injury and making movements more efficient
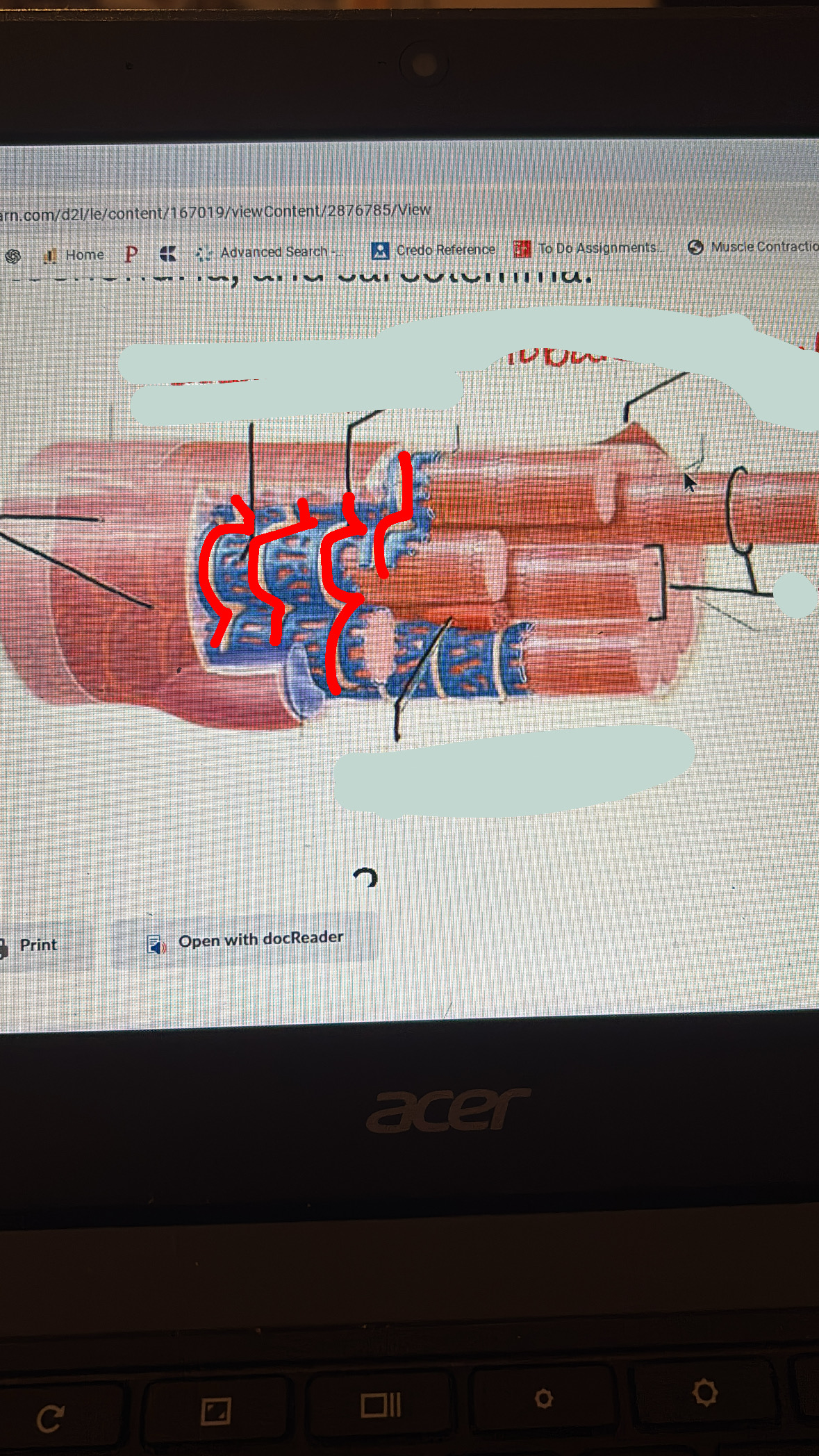
myofibril
the tubes made of a bunch of sarcomeres that allows for contraction/relaxation of the muscle
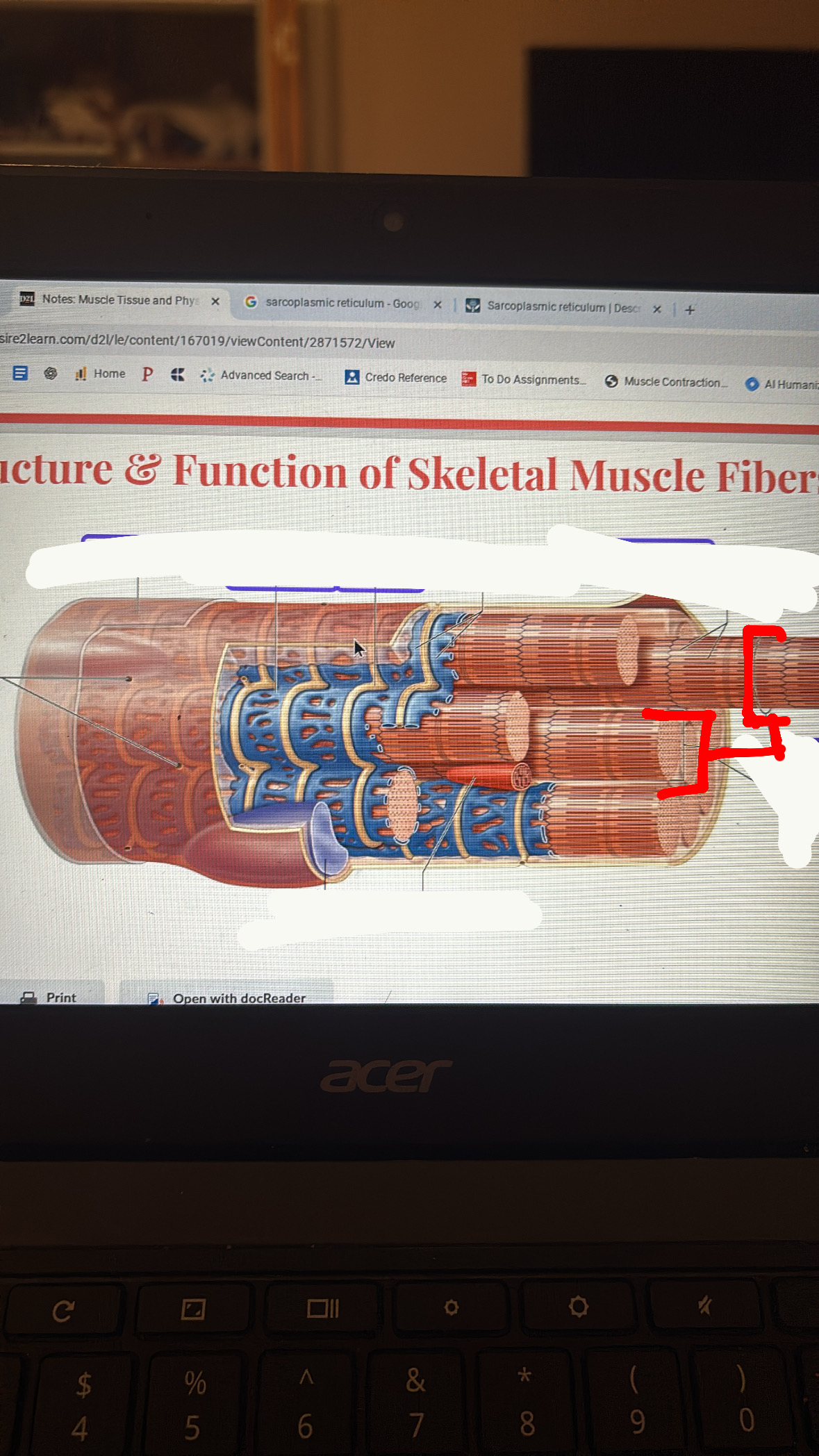
sarcoplasmic reticulum
stores Ca2+ ions that are released into sarcoplasm when stimulated
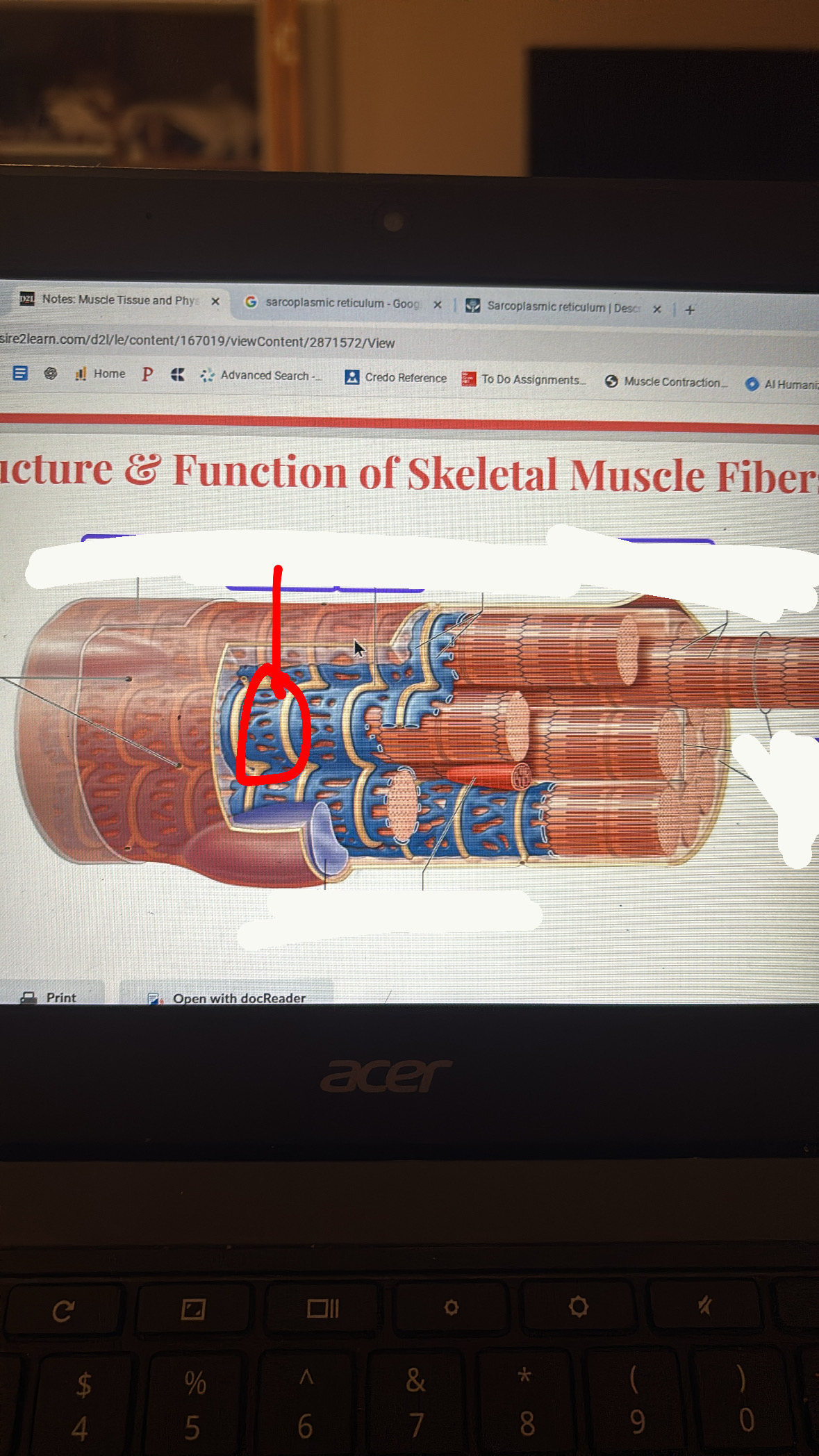
t-tubules
conducts action potentials deep in muscle cell to signal the ST to release Ca2+
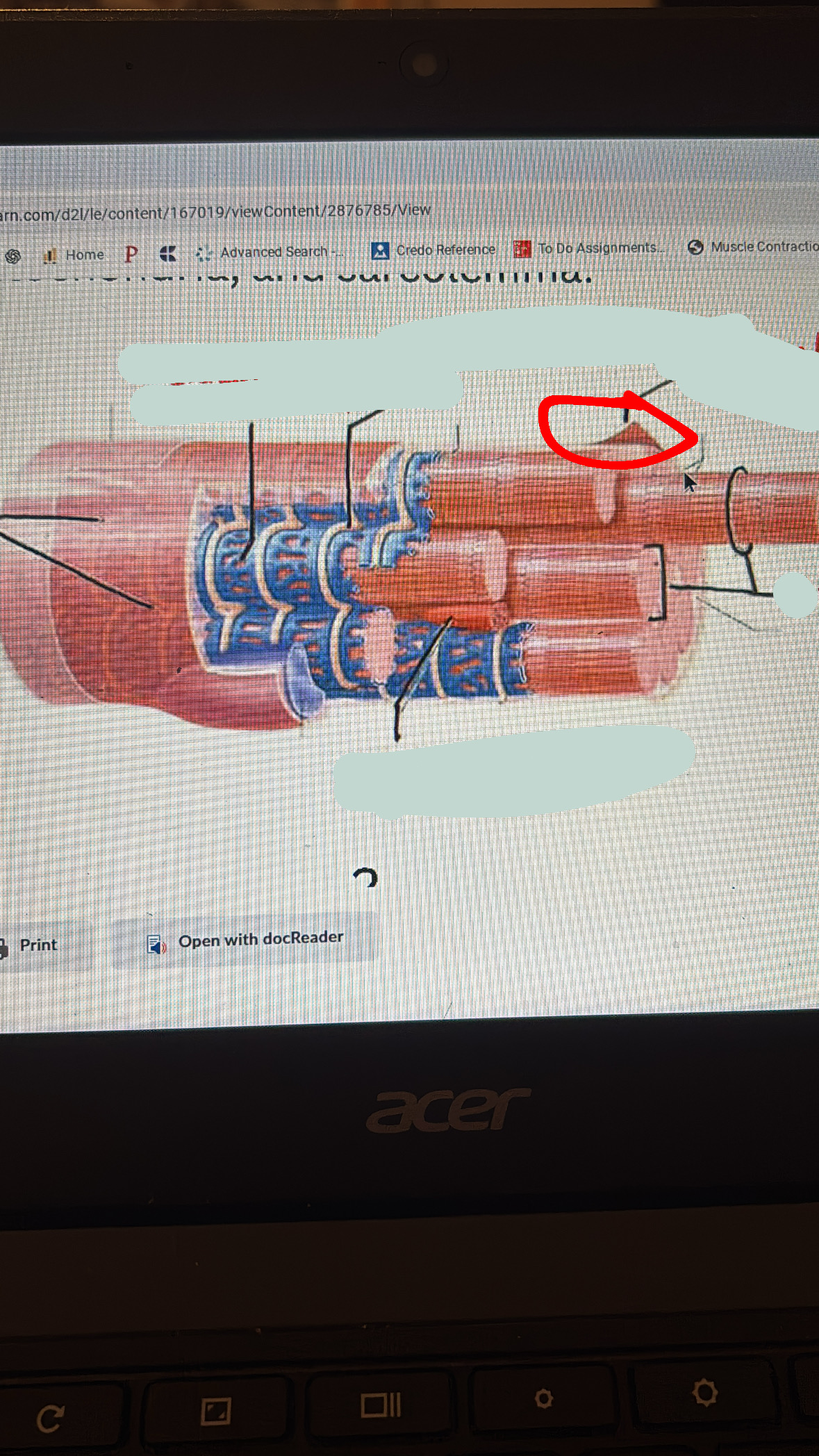
sarcolemma
cell membrane
how muscles contract
1st Ca2+ ions bind to a troponin which changes shape and causes tropomyosin to slide away from active sites of actin
2nd “cocked” myosin heads bind to actin active sites
3rd ADP and Pi are released from the myosin head and myosin head pulls the actin forward the M-line of the sarcomere in the “power stroke”
4th ATP binds to myosin head causing it to detach from actin
5th ATP is hydrolyzed (broken down) into ADP+ Pi and myosin head ”cocks” into postition to bind to actin site
troponin
holds tropomyosin in place over the actin active sites
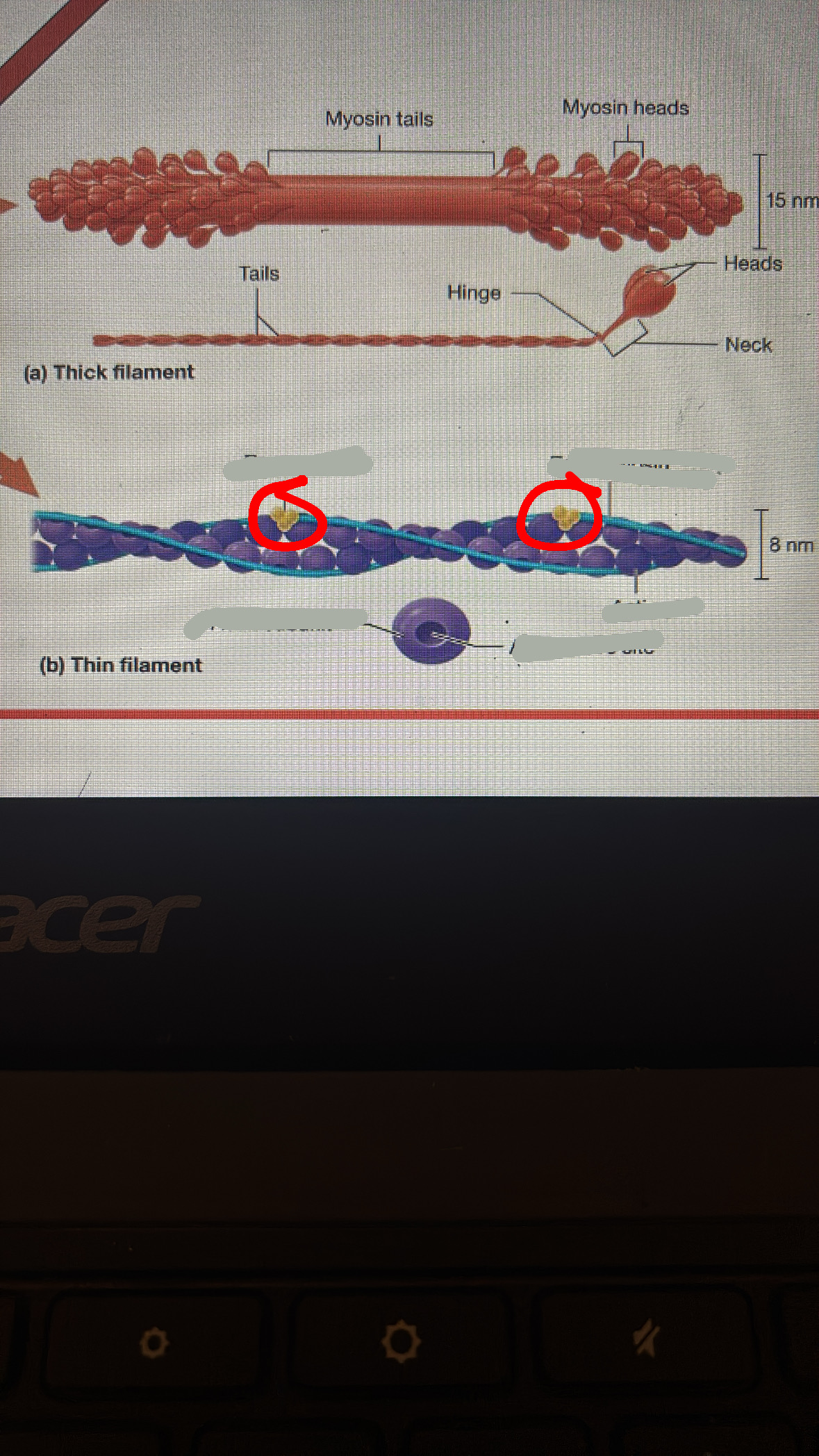
tropomyosin
the band that covers the actin active site
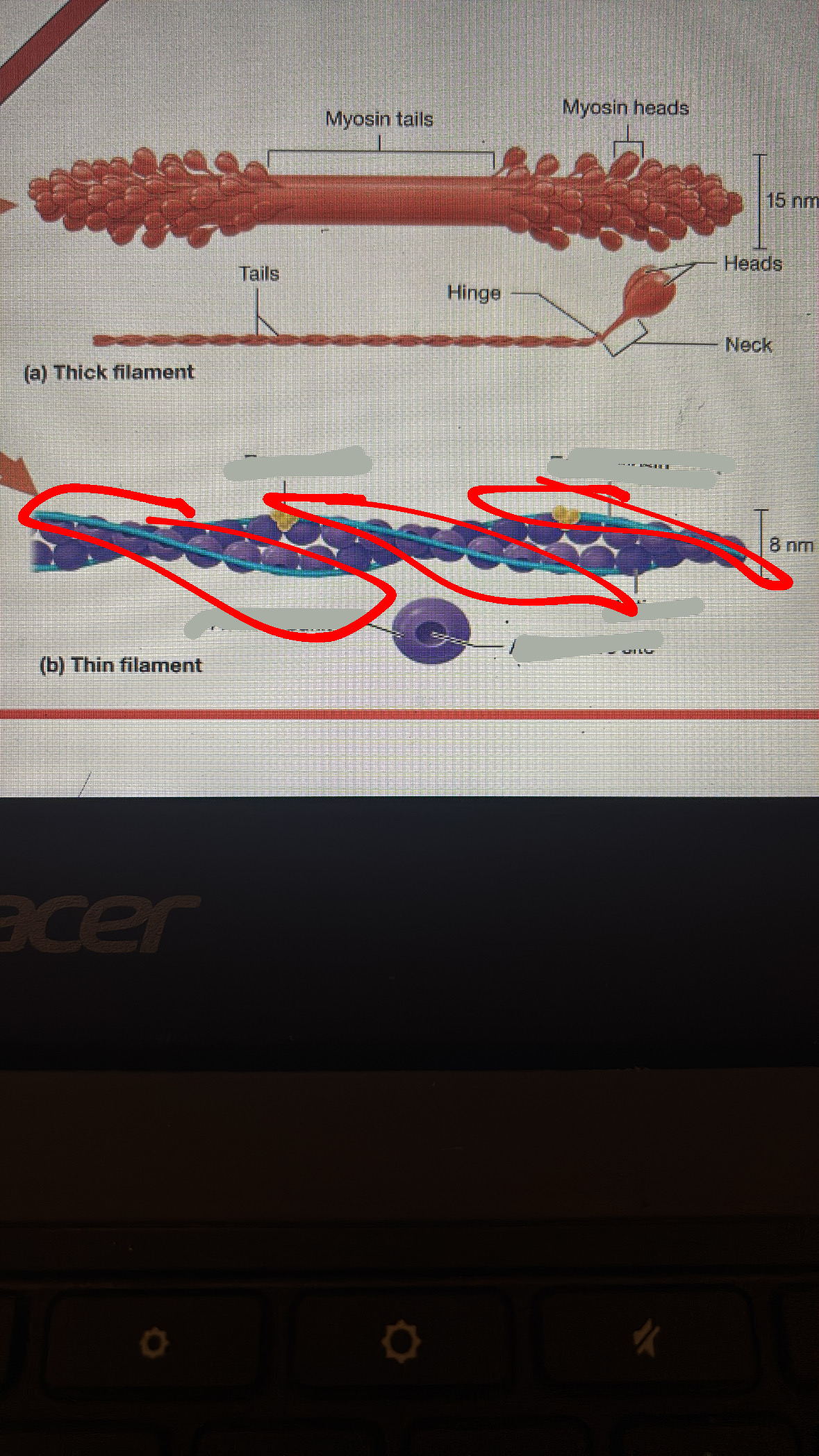
sarcomere
is a single tube from the myofibril
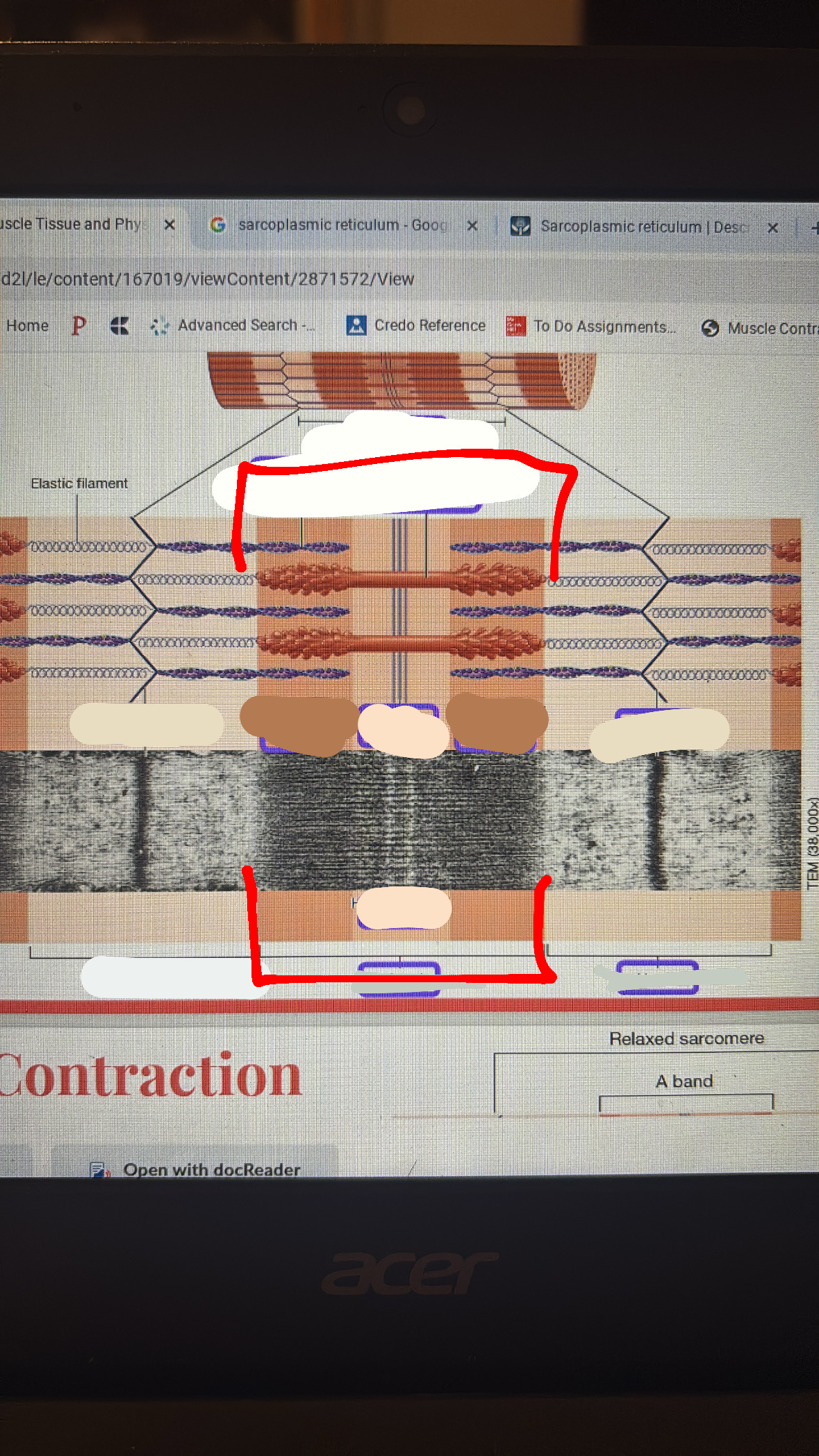
m-line
the line where only the thick filament is
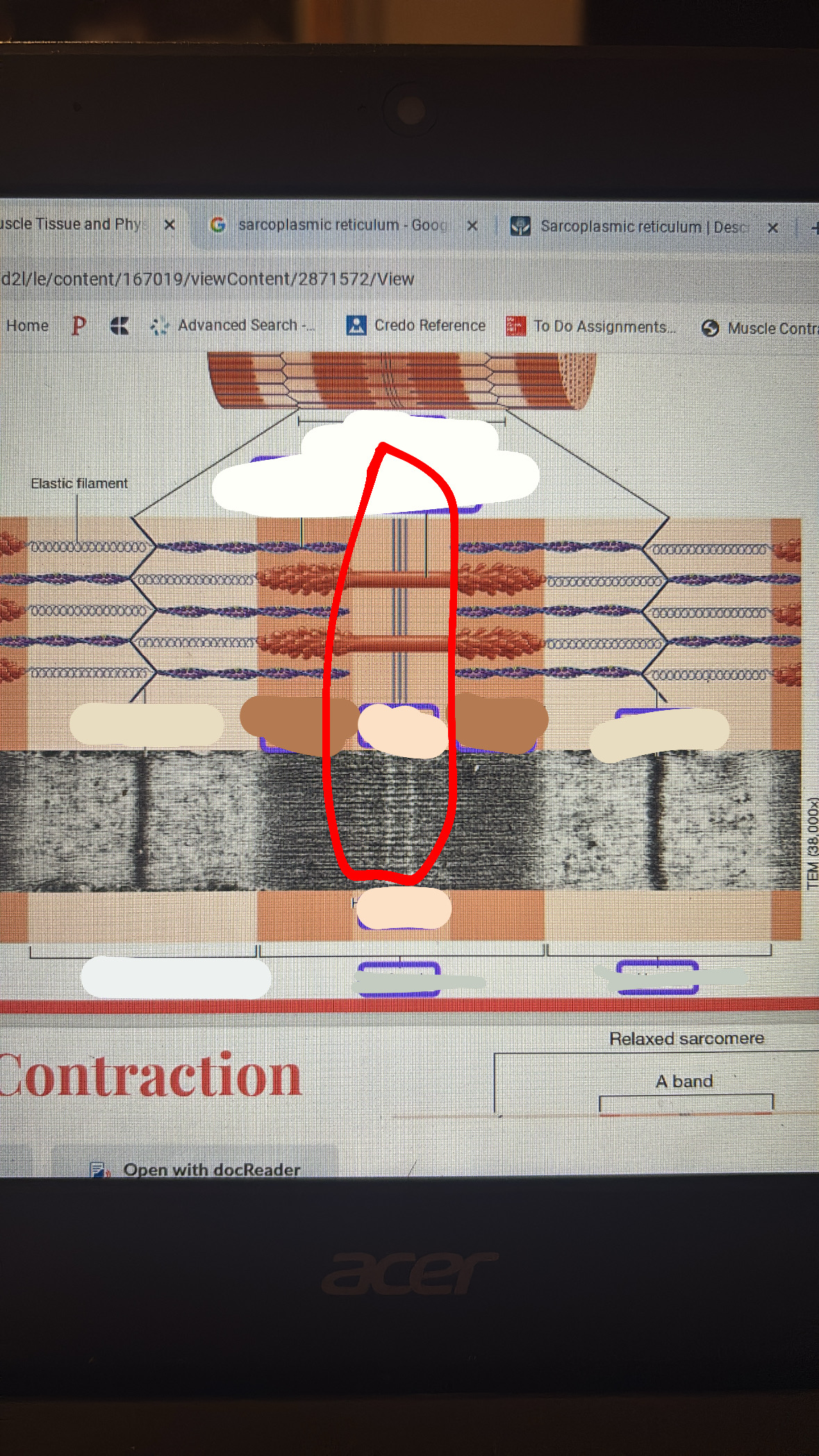
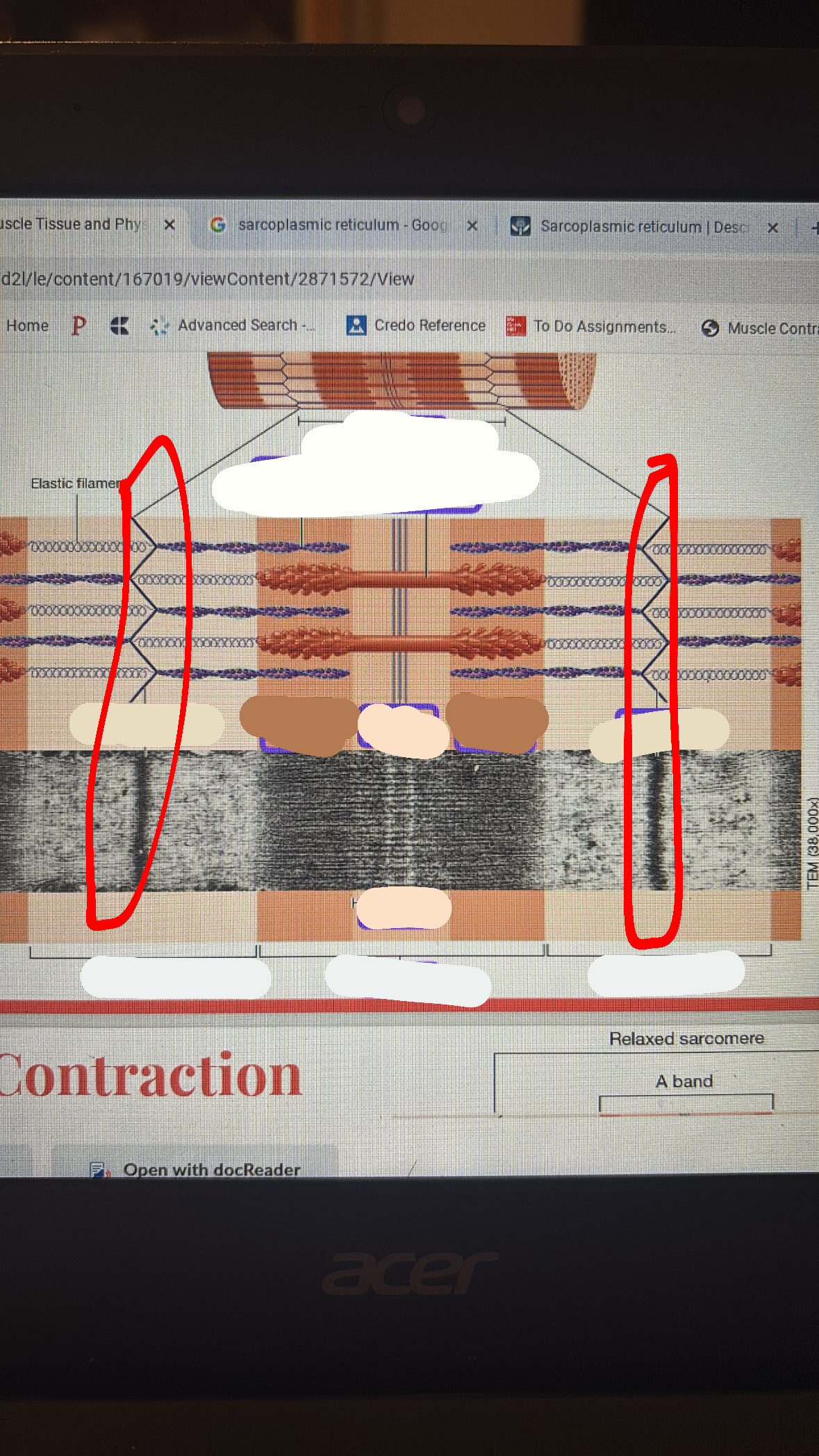
zone or overlap
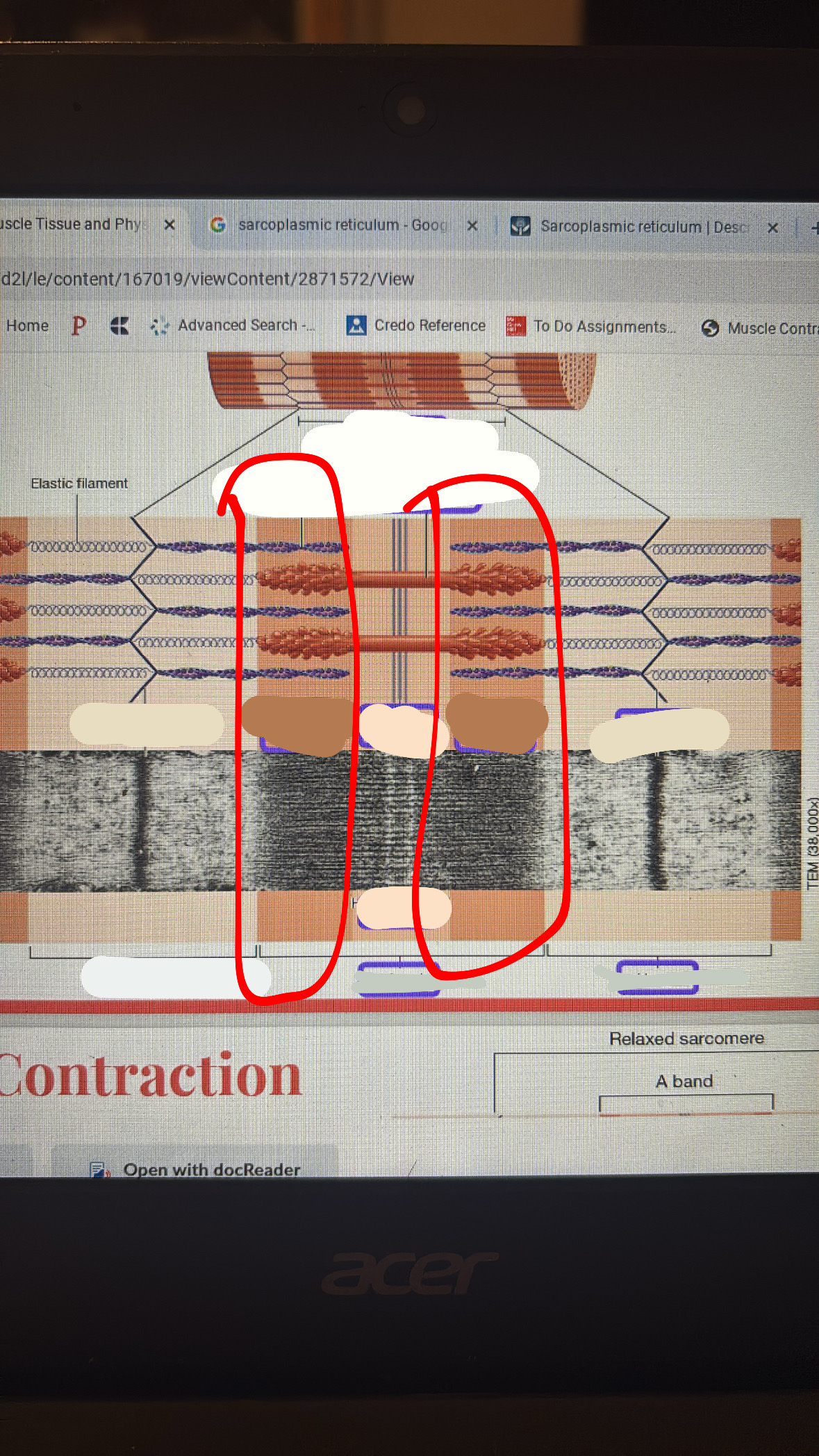
i band
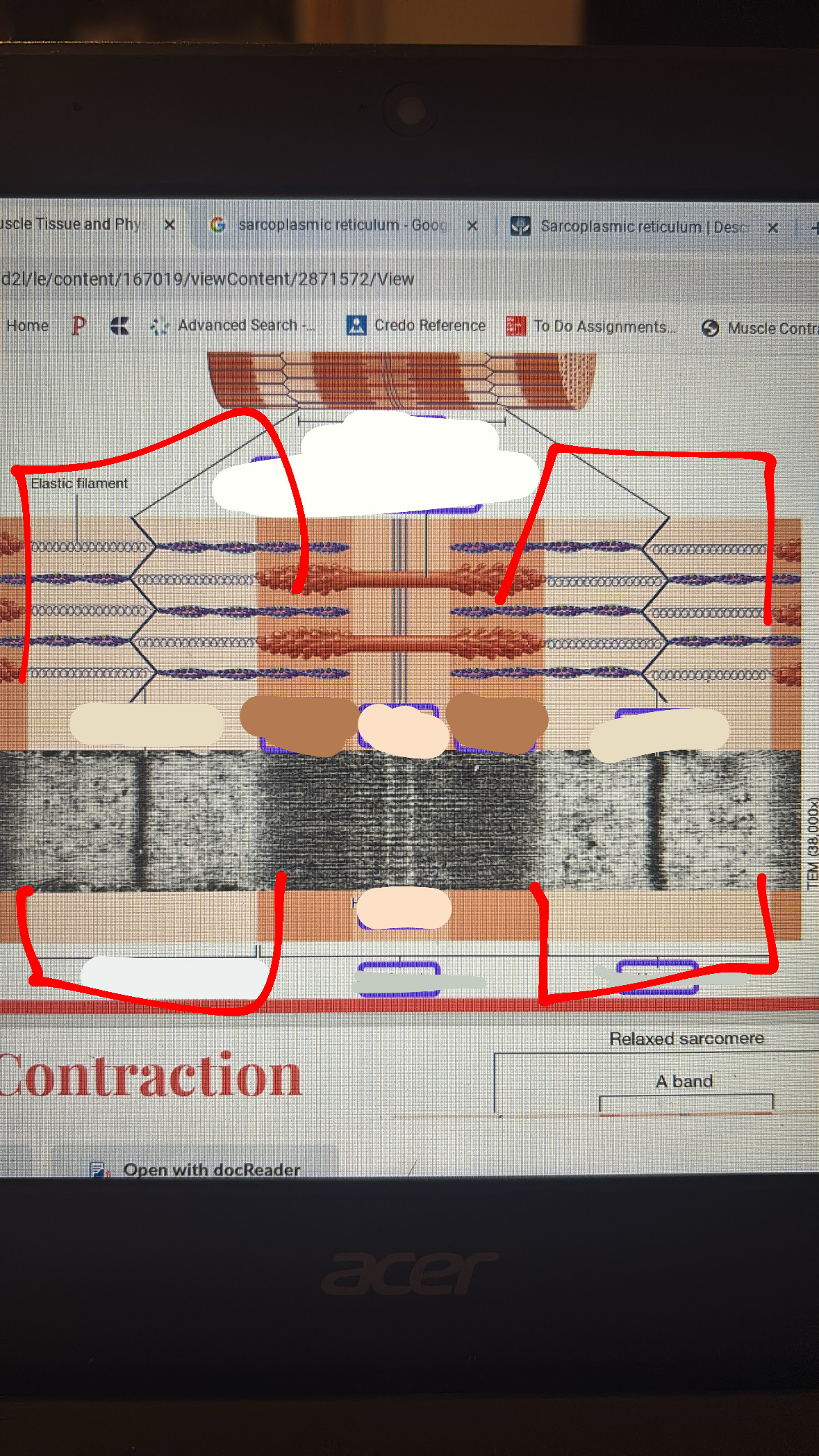
a band
z disc
secretory vesicle with acetylcholine(ACH)
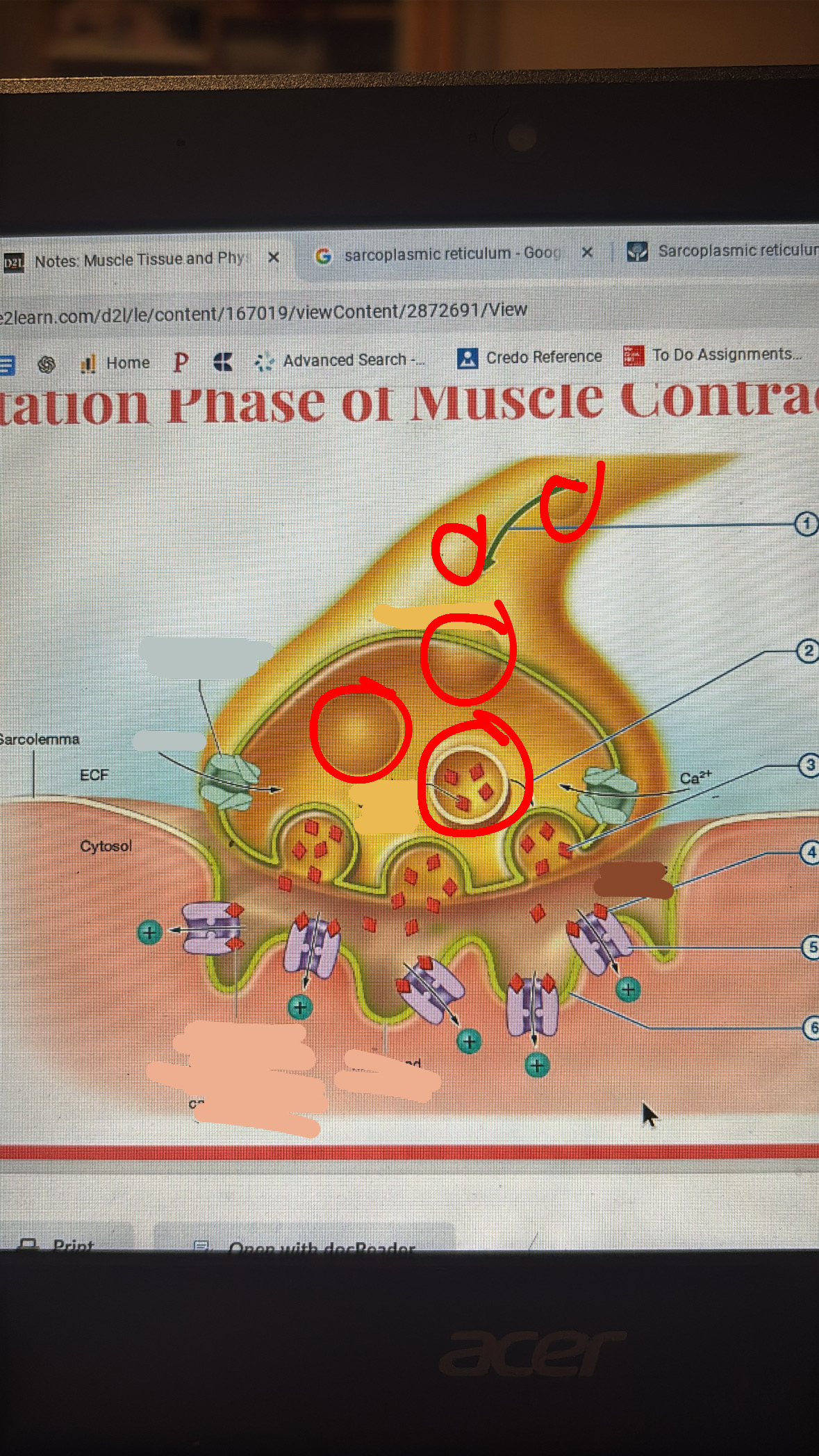
axon terminal
voltage gated Ca2+ channel
synaptic cleft
cation (+)
stimulation
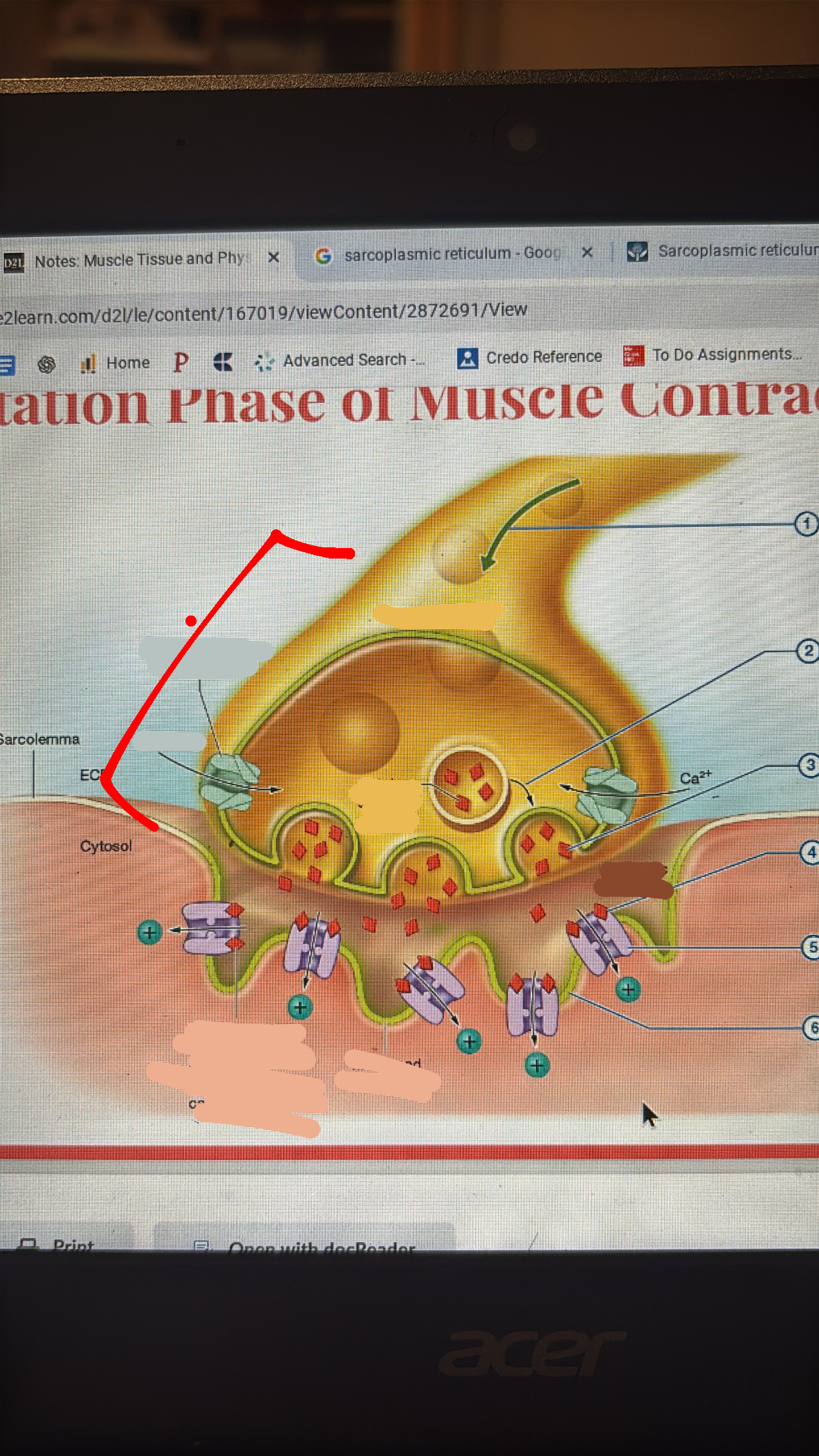
action potential arrives at axon terminal signaling Ca2+ channels to open
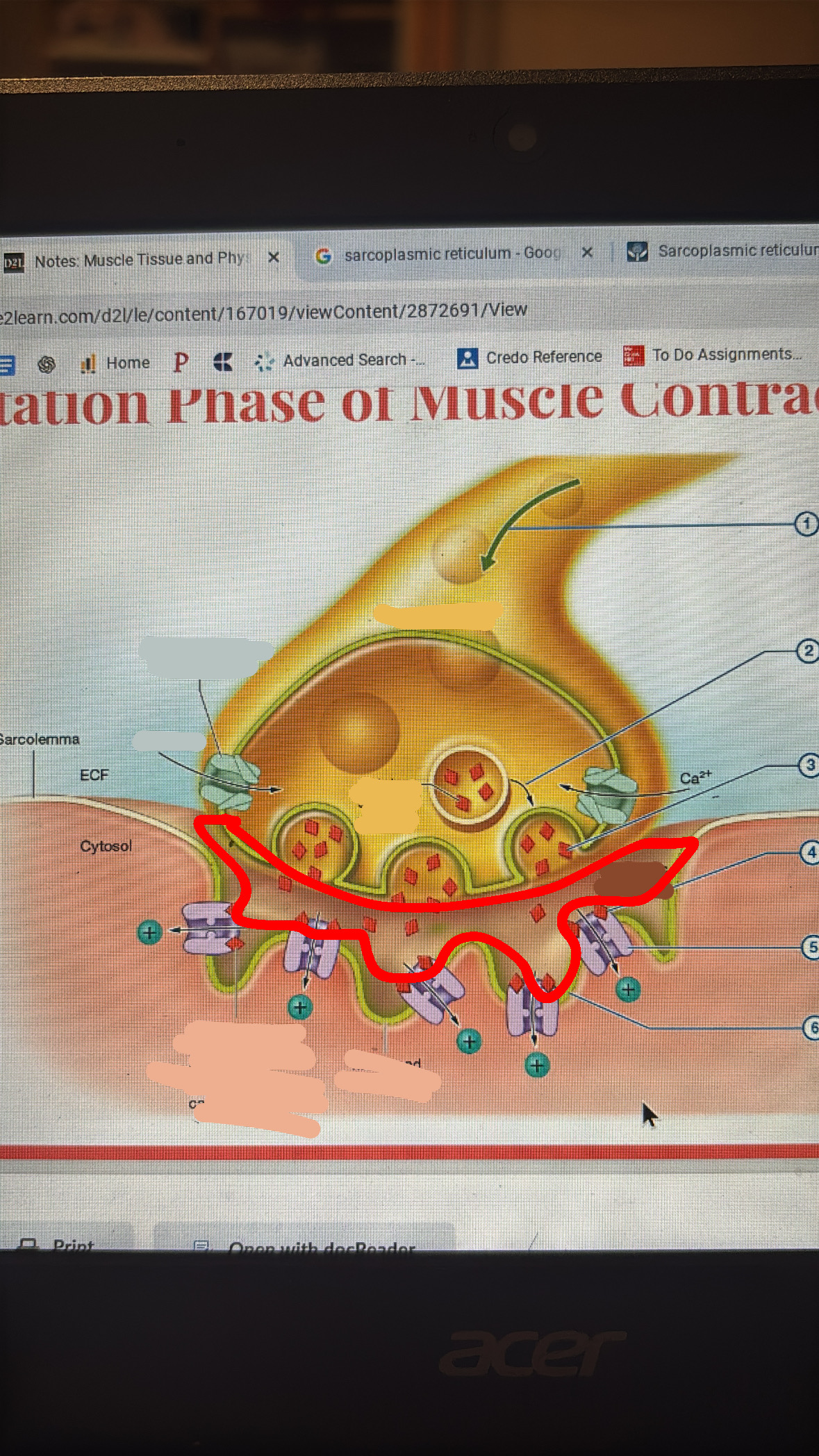
Ca2+ entry causes exocytosis to vesicles
ACH is released into synaptic cleft
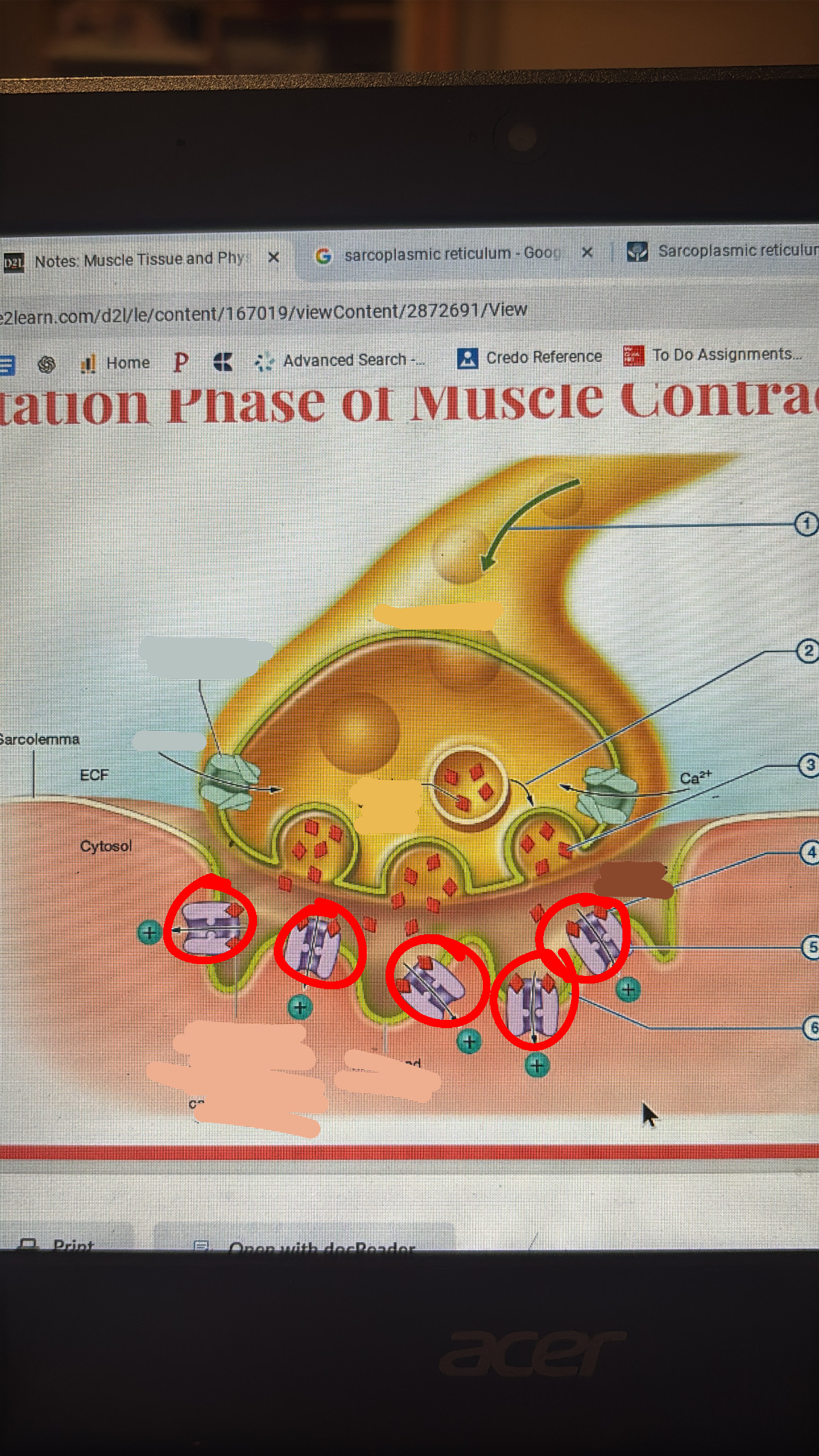
ACH binds to ligand gated cation channels in motor end plate
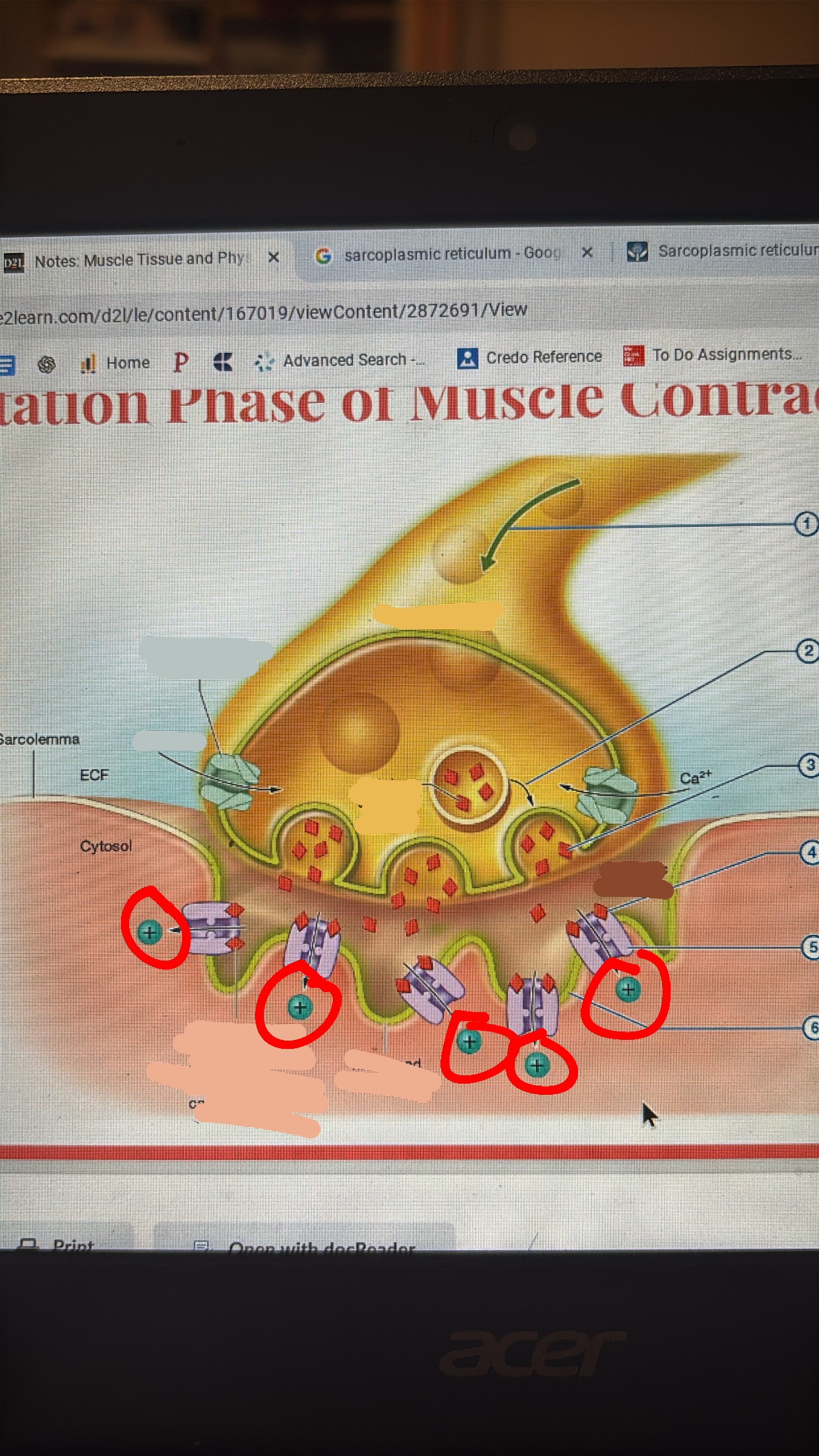
cations rush into muscle cell
cations depolarizes the sarcolemma at motor end plate initiating action potential that spreads across sarcolemma
motor unit
a group of muscle fibers that are innervated and stimulated by the same motor neuron
muscle twitch
a muscle fibers response to a single neuronal action potential
EPOC
excess post exercise oxygen consumption (in lease in ventilation rate during and for a time after exercise)
muscle fatigue
inablility to maintain a certain lever of exercise wether that be for depletion of metabolites, decreased oxygen, accumulation of certain chemicals, or environmental conditions
latent period
an action potential spreads across the sarcolemma in a muscle twitch
contraction period
increasing smuggle tension due to corssbrige cycling in muscle twitching