Business and Environmental Sustainability & Ethical Decision Making Flashcards
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary from chapters 9 and 10, focusing on business sustainability, ethical decision-making, and ESG principles.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Backcasting
Imagining a sustainable future and working backward to determine the steps needed to achieve it.
Closed Loop Production
A system where waste is reintegrated into production, mimicking natural cycles to eliminate waste.
Conservationist
Advocates for the prudent and sustainable use of natural resources to ensure long-term availability.
Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) Standards
Regulations that set average fuel efficiency requirements for a manufacturer’s fleet of vehicles.These standards aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve fuel economy over time.
Cradle-to-Cradle Responsibility
A business model where companies take responsibility for recycling or incorporating repurposing products at the end of their lifecycle.
Eco-Efficiency
Maximizing productivity while minimizing resource use and environmental impact.
Introduced at the Rio Earth Summit in 1992, the concept is a way business can contribute to sustainability by reducing resource usage in its production cycle.
“Doing more with less”
The "Factor Four" principle suggests that businesses can reduce their ecological footprint and improve economic efficiency through enhancements in lighting, building design, product design, and distribution channels.
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)
A framework for evaluating a company’s sustainability and ethical impact beyond financial performance.
Preservationist
Views nature as having intrinsic value beyond human use, advocating for its protection for aesthetic, spiritual, or ecological reasons.
Service-Based Economy
Focuses on providing services rather than selling products, encouraging durable and recyclable designs.
Sustainable Business Practices
Strategies that balance economic success with environmental and social responsibility.
Sustainable Development
Meeting present needs without compromising future generations’ ability to meet theirs.
Sustainable/Green Marketing
Promoting products based on their environmental benefits, ensuring transparency and avoiding greenwashing.
Triple Bottom Line
Measuring success by economic, environmental, and social performance.
Three Pillars of Sustainability
Economic (profitability), Environmental (planet health), Social (human well-being).
Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (COSO)
A framework for internal controls and risk management to improve corporate governance and financial reporting.
Conflict of Interest
When personal interests interfere with professional judgment.
Control Environment
The ethical culture of an organization, including integrity, competence, and accountability.
Corporate Governance
Structures ensuring fair, accountable, and transparent management of a corporation.
Gatekeeper
Professionals who ensure market integrity by enforcing rules.
Insider Trading
Illegally trading stocks using non-public, material information for personal gain.
Internal Controls
Processes to ensure accurate financial reporting and compliance.
Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX)
U.S. law mandating financial transparency, auditor independence, and internal controls.
Trust
Ethically warranted reliance on others.
Greenhouse Gases (GHGs)
Gases like CO₂ that trap heat in the atmosphere, driving climate change.
‘Who Cares Wins’ Evolution
Originally 9 elements (2004), now expanded to broader ESG metrics.
Voluntary ESG?
Report advocates for mandatory integration into business practices.
Duty of Care
Acting with reasonable diligence.
Duty of Good Faith
Loyalty to the organization’s mission.
Duty of Loyalty
Prioritizing the organization’s interests over personal gain.
SSEI (Sustainable Stock Exchanges Initiative)
Promotes ESG reporting in capital markets; key elements include transparency and investor engagement.
COP 21 (2015 Paris)
Paris Agreement to limit global warming.
COP 28 (UN climate summit)
Latest UN climate summit.
UNFCCC
UN Framework Convention on Climate Change.
CSR vs. ESG
CSR is voluntary philanthropy; ESG is measurable, integrated into core operations.
ISO/TC 322
Standardizes sustainable finance terminology
Nili Gilbert’s View
Climate action requires capital allocation—investing in green tech is critical.
ESG Rating Systems
Vary by agency, leading to inconsistency and ratings confusion.
UN SDGs
17 goals to achieve global sustainability by 2030.
The preservationist approach supports that the environment should be preserved from use as a commodity.
True
Reason: This is the belief of this approach
Sustainable business and sustainable economic development try to create new ways of doing business in which business success is measured in terms of economic, ethical, and environmental sustainability. This is often called the
triple bottom line approach
The Natural Step uses an image of a funnel, with two converging lines, to depict the opportunities available in the age of sustainability. According to this metaphor, businesses that _____ will succeed in emerging successfully from the funnel.
The given image represents the Natural Step's funnel that depicts the relationship between business and sustainability. While A represents the resources necessary to sustain life, B represents _____.
aggregate worldwide demand
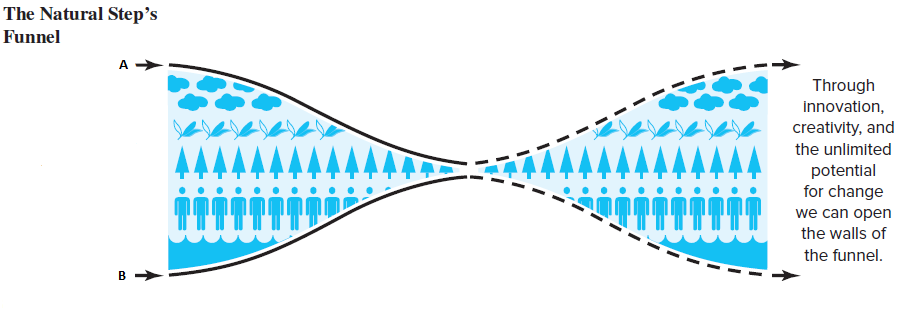
Identify the guidelines that firms should follow if they are to evolve toward a sustainable business model.
1. Eliminate waste within biosphere limits.
2. Extract resources at replenishment rates.
3. Use renewable energy.
The principle of “doing more with less” is sometimes called
eco-efficency or resource efficiency.
True or false: Contemporary environmental issues highlight the need for self-interested reasoning in protecting nature, as life-supporting systems depend on a delicate environmental balance.
TrueFalse
Humans came to appreciate the self-interested reasons for protecting the natural environment by the late 19th century. The _____ , the first phase of modern environmentalism, advocated a more restrained and judicious approach to the natural world.
Conservation movement
IIn the context of animal rights, identify true statements about the view that animals and all living things deserve respect and dignity.
It recalls the utilitarian tradition and asserts the duty to minimize pain.
It considers inflicting unnecessary pain as an ethical wrong.
Identify the possible and appropriate means for meeting business’s enviromental responsibilities.
government regulation
efficent markets
In his popular book People or Penguins: The case for optimal pollution, William Baxter put forth the argument that there is an optimal level of pollution that would best serve society’s interests and that this optimal level is best attained by it to _____.
a competitive market
According to the suggestions of professor Patrick Murphy for marketing to develop sustainable distribution channels for products, ___ ___ refers to the growing marketing practicec of taking back one’s products after their useful life.
reverse channel(s)
Identify market failures causing environmental harm in the market-based approach to environmental challenges.
The lack of markets for creating a price for important social goods
the presence of externalities
____ ____ fuel economy (CAFE) is the sales-weighted average fuel economy, expressed in miles per gallon (mpg), of a manufacturer's fleet of passenger cars or light trucks.
corporate average fuel economy (CAFE)
Which of the following are true of the environmental laws enacted in the United States during the 1970s?
They set standards shifting the burden from the threatened to those causing harm.
They established regulatory standards to prevent species extinction and pollution.
Defenders of the market-based approach to resolving environmental challenges contend that ____.
environmental issues are economic issues that deserve economic solutions
According to the suggestions of professor Patrick Murphy, which of the following will be emphasized by new sustainability options in marketing distribution channels that involve transportation, distribution, and inventory?
Alternative fuel technologies and fuel efficiency
More efficient and localized distribution channels
Increased reliance on electronic rather than physical distribution
In the context of the market-based approach to resolving enviromental challeneges, which of the following is market failure that can lead to serious environmental harm?
The differnce between individual decisions and group consequences
In the context of governance, identify the reasons why excessive executive compensation suggests evidence of a failure of corporate boards to fulfill their fiduciary duties.
In many cases, executive compensation lacks correlation with performance.
Little evidence supports excessive compensation as necessary for performance incentives.
§201 (consulting)
prohibits various forms of professional financial services that are found to be consulting and not auditing.
§301 (indpt audit committees)
It requires a public company audit committees to be independent and mandates total absence of current or prior business relationships
§307 (attorneys)
It establishes rules of professional responsibility for attorneys representing issuers before the SEC, ensuring they act in the best interests of their clients.
Identify the features of the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (COSO)
It has become one of the most broadly accepted audit systems for internal controls
It was established originally to study fraudulent reporting and later to develop standards for publicly held companies.
____ ____ refers to a process by an entity’s board, management, and staff that ensures reasonable assurance for achieving objectives in operational effectiveness, financial reporting reliability, and compliance with laws.
Internal Control
Which guidelines apply to the legal duty of care for board members under US law?
Board members are directed to use their “business judgment as prudent caretakers”.
The director is expected to be disinterested and reasonably informed and to rationally believe the decisions made are in the company’s best interest.
In the context of governance, which of the following are the reasons why excessive executive compensation suggests evidence of a failure of corporate boards to fulfill their fiduciary duties?
The chief executive officer determines the compensation received by board members, which creates a conflict of interest.
Executives are often evaluated and paid as the chair of the board of directors.
§404 (annual reports)
It requires that management file an internal control report each year along with its annual report.
§406 (senior COE)
It requires codes of ethics for senior financial officers
§407 (audit committees)
It requires audit committees to have a financial expert.
The ____ lets directors trust information and opinions only if provided by corporate officers, employees, a board committee, or other reliable professionals.
duty of care