exam 1
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Which of the following is not a major characteristic of fish?
gills
vertebrates
opposable thumbs
aquatic
fins
opposable thumbs
Which of the following is a common compensation mechanism for fish following a substantial and sustained drop in acclimatization temperature?
elevated unsaturated fatty acid levels to diminish membrane fluidity
decreased unsaturated fatty acid levels to diminish membrane fluidity
elevated unsaturated fatty acid levels to maintain membrane fluidity
decreased unsaturated fatty acid levels to maintain membrane fluidity
elevated unsaturated fatty acid levels to maintain membrane fluidity
What is likely to occur for tropical cardinal fishes exposed to increased temperatures associated with climate change?
decreased aerobic scope
increased aerobic scope
lower resting metabolic rates
decreased aerobic scope
Which of the following groups are most closely related to one another?
Gobiiformes and Myctophiformes
Gobiiformes and Myxiniformes
Myctophiformes and Squalimorphi
Gobiiformes and Polypteridae
Gobiiformes and Myctophiformes
Which following groups are most closely related to one another?
Gobiiformes and Polypteridae
Gobiiformes and Myxiniformes
Holocephali and Squalimorphi
Myctophiformes and Squalimorphi
Holocephali and Squalimorphi (chimeras/sharks rays)
Which of the following is not a type of fin used frequently by fish to swim?
Doral fins
Pectoral fins
Caudal fins
Anal fins
Eye fins
eye fins
In Body Caudal Fin (BCF) swimming fish species, where is the amplitude of the body wave during swimming expected to be the largest?
Middle of body
Head
Caudal area
Caudal area
or the following Body Caudal Fin (BCF) swimming fish species, which type of swimmer is likely to have the largest body wave amplitude?
Thunniform swimmers
Anguilliform swimmers
Subcarangiform swimmers
Carangiform swimmers
Anguilliform swimmers
As the velocity of muscle shortening increases, what happens to the Power generated by the muscle?
decreases to a trough, then increases at higher velocities
no change
increases to a peak, then falls at higher velocities
always doubles
increases to a peak, then falls at higher velocities
Which of the following Median and Paired Fin (MPF) swimming fish species swim primarily by oscillating their very long pectoral fins?
Labriform swimmers
Mobuliform swimmers
Rajiform swimmers
Mobuliform swimmers
Which of the following is an accurate description of a convective step in the Oxygen Cascade for most teleost fish?
Gill ventilation
Mitochondria use Oxygen to make ATP
Oxygen moving down its partial pressure gradient from from blood into cells
Oxygen moving down its partial pressure gradient from water into gill’s blood
Gill ventilation
Which of the following is an accurate description of a diffusive step in the Oxygen Cascade for most teleost fish?
Heart pumping
Gill ventilation
Oxygen moving down its partial pressure gradient from water into gill’s blood
Oxygen moving down its partial pressure gradient from water into gill’s blood
Which of the following is the main site of gas exchange in most teleost fish?
Gill arch
Secondary lamellae
Primary lamellae
Dorsal aorta
Secondary lamellae
How many gill arches do most teleosts have?
between 15 and 20
always just one
between 4 and 7
they only come in pairs, each fish has 2 only
between 4 and 7
If ventilatory stroke volume increases, what happens to the volume of water a fish can pump across its gills?
decrease
increase
no change
increase
If the surface area of secondary lamellae increases, what happens to the oxygen uptake rate of a fish?
decrease
no change
increase
increase
If the diffusion distance across the secondary lamellae increases, what happens to the oxygen uptake rate of a fish?
decrease
increase
no change
decrease
An increase in gill surface area causes which of the following to be true for freshwater teleosts?
increases ion loss and decreases water influx
decreases ion loss and increases water influx
increases ion loss and increases water influx
increases ion loss and increases water influx
For Crucian carp, exposure to hypoxia has been shown to cause which of the following?
increased gill surface area and increased inter lamellar cell masses
increased gill surface area and decreased inter lamellar cell masses
decreased gill surface area and increased inter lamellar cell masses
increased gill surface area and decreased inter lamellar cell masses
During a metabolic acidosis caused by high levels of exercise, which of the following is an accurate description of what happens to oxygen delivery to tissues in fish?
blood pH decreases, shifting the oxygen equilibrium curve to the right, and aiding oxygen unloading from hemoglobin
blood pH stays the same, shifting the oxygen equilibrium curve to the left, and inhibiting oxygen unloading from hemoglobin
blood pH increases, shifting the oxygen equilibrium curve to the left, and aiding oxygen unloading from hemoglobin
blood pH decreases, shifting the oxygen equilibrium curve to the left, and inhibiting oxygen unloading from hemoglobin
blood pH decreases, shifting the oxygen equilibrium curve to the right, and aiding oxygen unloading from hemoglobin
Which of the following areas would have the highest blood oxygenation levels?
atrium
dorsal aorta
ventricle
bulbous arteriosus
dorsal aorta
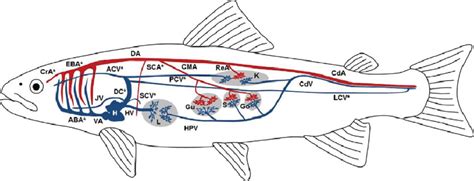
Which of the following is a realistic hematocrit for teleosts?
3%
60%
30%
90%
30%
Which of the following areas of the central cardiovascular system of fish are “directly separated by” the atrioventricular valves (“directly adjacent to”)?
atrium and ventricle
sinus venosus and ventricle
atrium and sinus venosus
sinus venosus and conal valve
atrium and ventricle
Where is the compact layer of myocardium found in fishes?
surrounding the sinus venosus
surrounding the spongy layer of the ventricle
within the sinus venosus
within the spongy layer of the atrium
surrounding the spongey layer of the ventricle
In excitation-contraction coupling of myocardial cells, what ion dominates inward ion flow into cells causing depolarization of the sarcolemma’?
Na+
Cl-
Ca2+
K+
Na+
In excitation-contraction coupling of myocardial cells, what inward flow of ions maintains contraction and can be increased through adrenergic stimulation with adrenaline (epinephrine)?
Cl-
K+
Ca2+
Na+
Ca2+
If a fish species has coronary arteries, where do they originate from?
efferent branchial artery
afferent branchial artery
ventral aorta
dorsal aorta
efferent branchial artery
How does a vascular rate conserve metabolic heat?
metabolic heat is produced in higher levels in the liver, with antiparallel flow of blood through liver
metabolic heat is conserved in the tissues where it is produced, with antiparallel flow of blood through exercising muscles
oxygen is pumped into blood at high levels by special oxygen producing cells, thus conserving heat
metabolic heat is conserved in the tissues where it is produced, with antiparallel flow of blood through exercising muscles
How does cardiac output change during intense swimming?
heart rate decreases due to reduced vagal tones and increased adrenergic stimulation
heart rate increases due to reduced vagal tones and decreased adrenergic stimulation
heart rate decreases due to reduced vagal tones and decreased adrenergic stimulation
heart rate increases due to reduced vagal tones and increased adrenergic stimulation
heart rate increases due to reduced vagal tones and increased adrenergic stimulation
Which of the following is directly correlated to increased aerobic capacity of a fish?
heart size
gill secondary lamellae thickness
sinus venosus color
heart size
Which of the following groups of fish has internal body fluid composition that is hyposmotic to its surrounding environment?
elasmobranch
hagfish
saltwater teleost
freshwater teleost
saltwater telost (boney fish)
Which of the following scenarios correctly describes typical electrochemistry of an individual vertebrate animal cell?
high intracellular K+, high extracellular Na+, high intracellular protein levels, high extracellular Cl-, leaky outward K+ current dominates resting membrane potential
high intracellular K+, high extracellular Na+, high intracellular protein levels, high intracellular Cl-, leaky outward Na+ current dominates resting membrane potential
high intracellular K+, high extracellular Na+, high intracellular protein levels, high intracellular Cl-, leaky outward Cl- current dominates resting membrane potential
high extracellular K+, high extracellular Na+, high extracellular protein levels, high extracellular Cl-, leaky inward K+ current dominates resting membrane potential
high intracellular K+, high extracellular Na+, high intracellular protein levels, high extracellular Cl-, leaky outward K+ current dominates resting membrane potential
For saltwater (marine) teleosts, which of the following is not a regulated response to maintain ionic and/or osmotic homeostasis? (Which of the following is not correct or not true)
actively drinking large amounts of saltwater
excretion of divalent ions in urine and feces
active branchial uptake of NaCl into the body
active branchial uptake of NaCl into the body
Which of the following apical branchial transport proteins utilized for Na uptake has been found in nearly all freshwater fish ionocytes and in marine elasmobranch gills?
HCO3- and Chloride exchanger
Na+/Ca2+ exchanger
Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE)
Na+/K+ exchanger
Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE)
Which of the following is a primary function of the saltwater teleost kidney?
excess divalent ion absorption
water reabsorption using aquaporins
water secretion using Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE)
respiration
water reabsorption using aquaporins
Which of the following is an example of mechanical breakdown of food in fish?
pharyngeal teeth grinding food
pepsin, the primary proteolytic enzyme of digestion
digestive enzymes produced in enterocytes
pharyngeal teeth grinding food
Which of the following is an example of the primary functions of the stomach in Loricariid fishes (armored South American catfish)?
digestion and circulation (blood pumping)
digestion and respiration
bile production
digestion and salt production
digestion and respiration
Which of the following types of fish has a spiral valve?
zebrafish
clownfish
shark
tuna
shark
Which of the following best describes the functions of the buccal cavity in fish?
Produce hormones for regulating carbohydrate, amino acid, and lipid uptake
Enterocyte proliferation, enzyme production, nutrient transport and storage
Chemical and enzyme production and secretion
Filtration, mechanical digestion, mucus production, respiration
Filtration, mechanical digestion, mucus production, respiration
Which of the following best describes the functions of the liver in fish?
Chemical and enzyme production and secretion
Produce hormones for regulating carbohydrate, amino acid, and lipid uptake
Enterocyte proliferation, enzyme production, nutrient transport and storage
Filtration, mechanical digestion, mucus production, respiration
Chemical and enzyme production and secretion