Unit 7 Efficiency and Market Failure
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Types of Efficiency
Productive
Allocative
Productive Efficiency
Occurs when firm produces goods at the lowest possible cost, using resources efficiently.
When MC = LRAC at the minimum point of LRAC
Allocative Efficiency
Means producing the right amount of goods — where P = MC — so that society’s wants are met optimally
Total Welfare is Maximised
How is Equil. of Perfect Comp Productive and Allocative Efficient?
In SR and LR
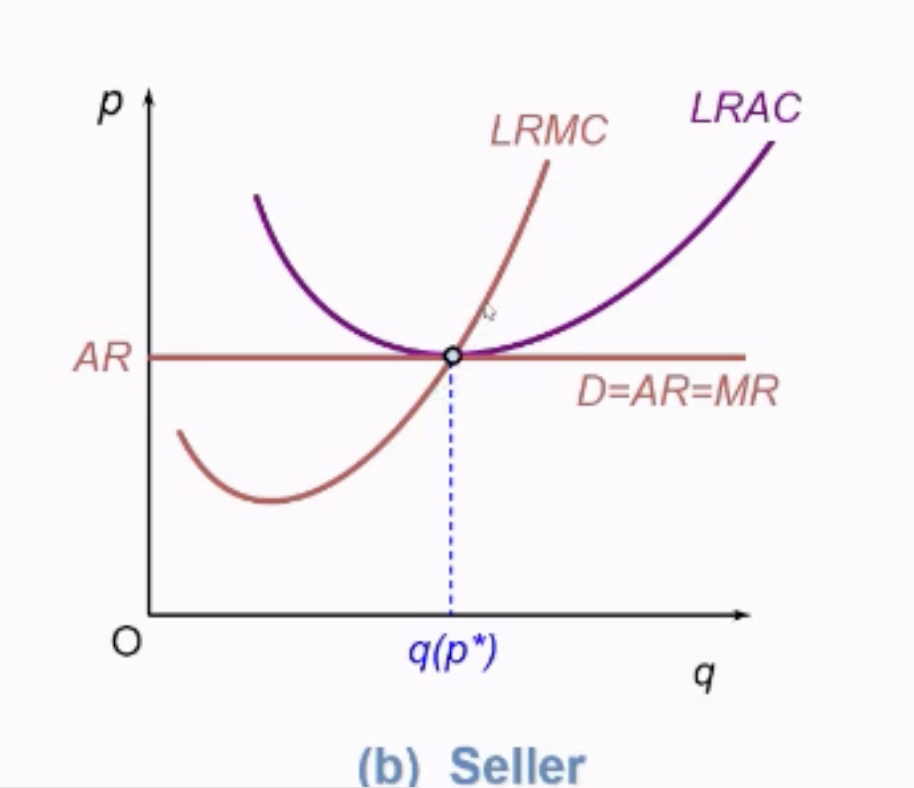
Productive, because firm produces at lowest possible cost at lowest point on LRAC
Allocative, because buyers is paying firm what it costs to produce the product
So consumers' demand is satisfied, leading to maximum total welfare.
Pareto Improvement
Situation when an allocation of resources makes one person better off without making the other person worse off
Pareto Efficiency
When resources are allocated in a way where no one can be made better off without making someone else worse off
Interpreting indifference curves in Edgeworth Box
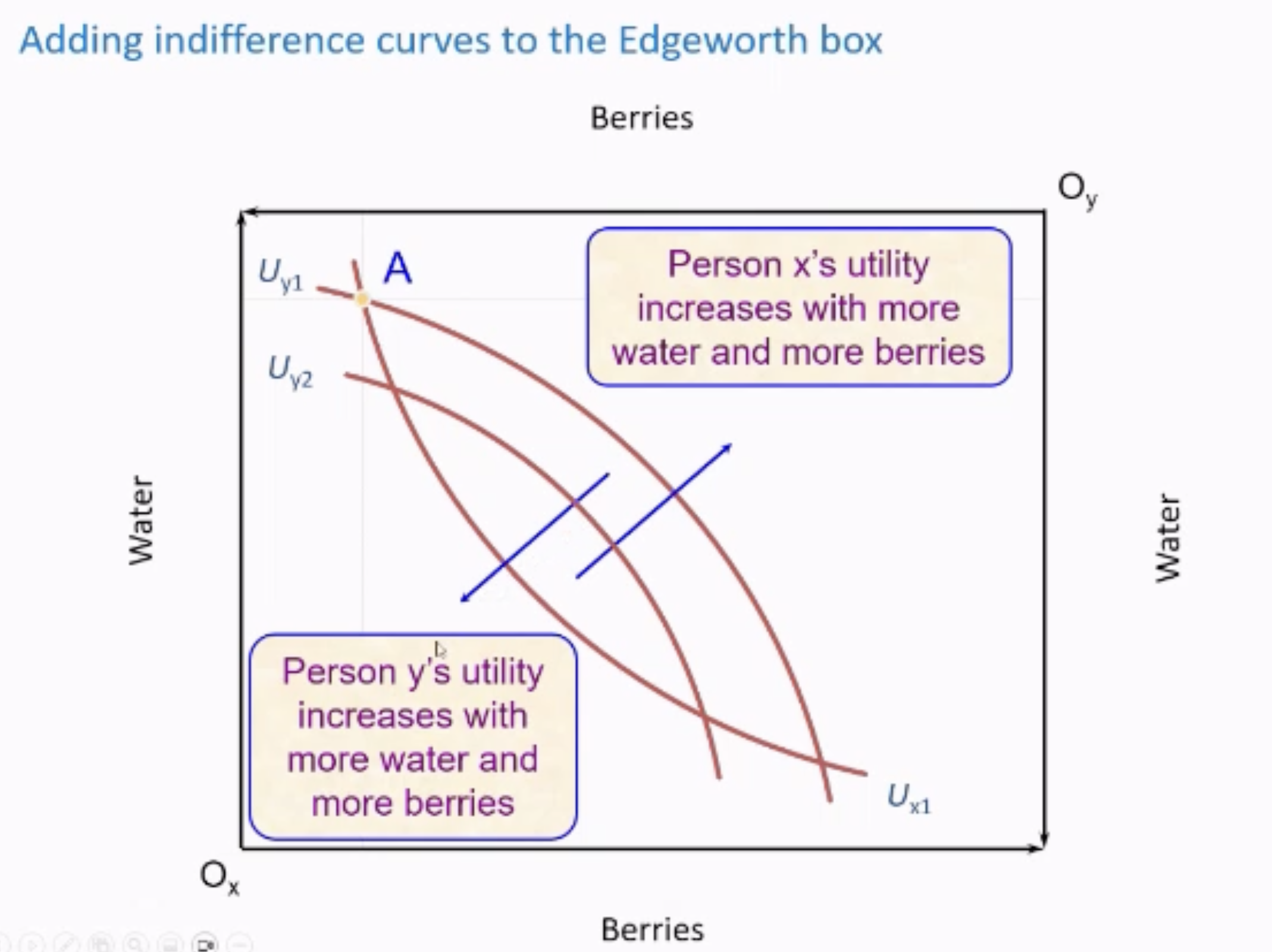
Person x’s utility Increases to top right
Person y’s utility increases to bottom left
What represent a Pareto Improvement
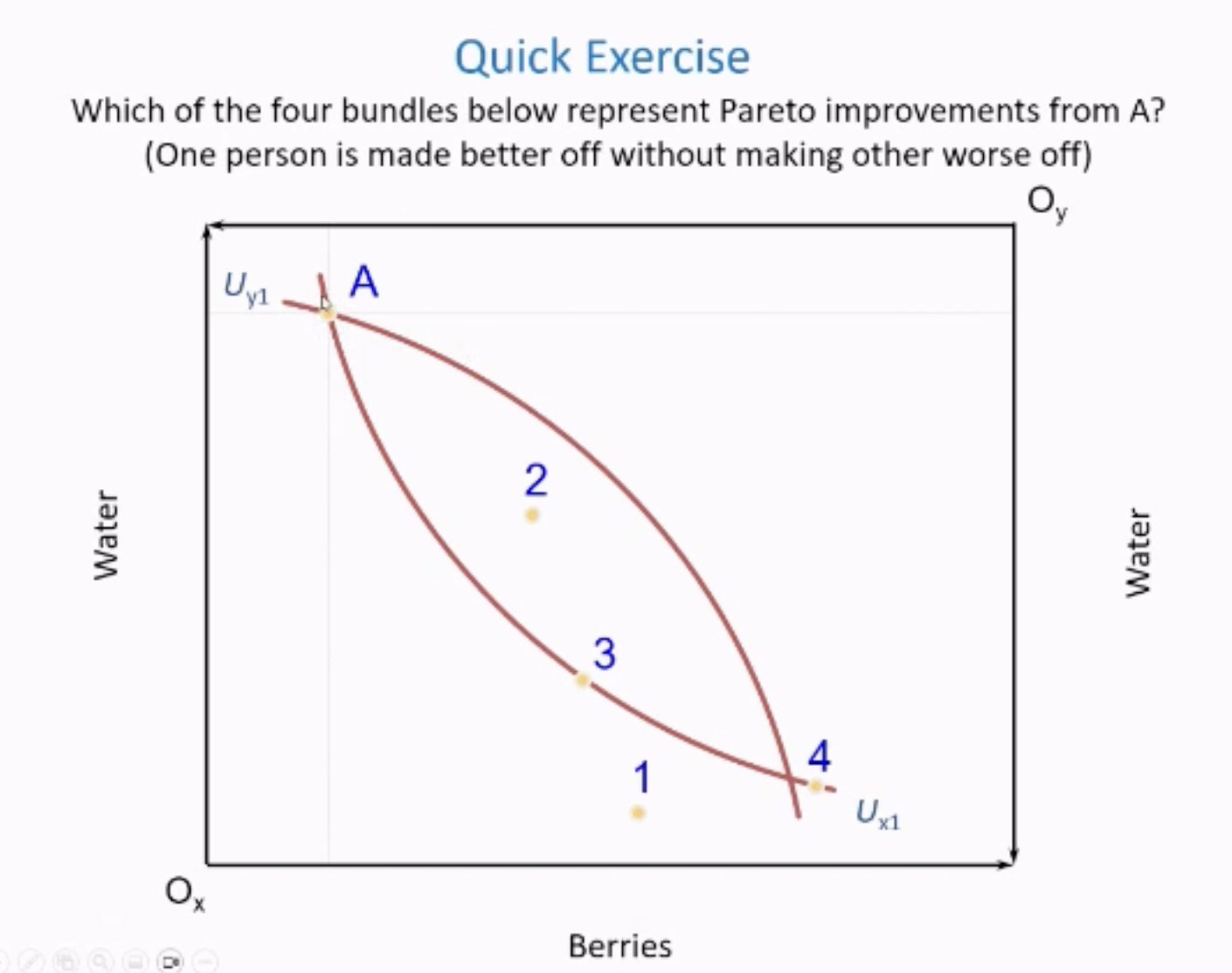
Any bundle that is on x and not beyond y
Any bundle that is within areas of indifference curves
so A, 2, and 3
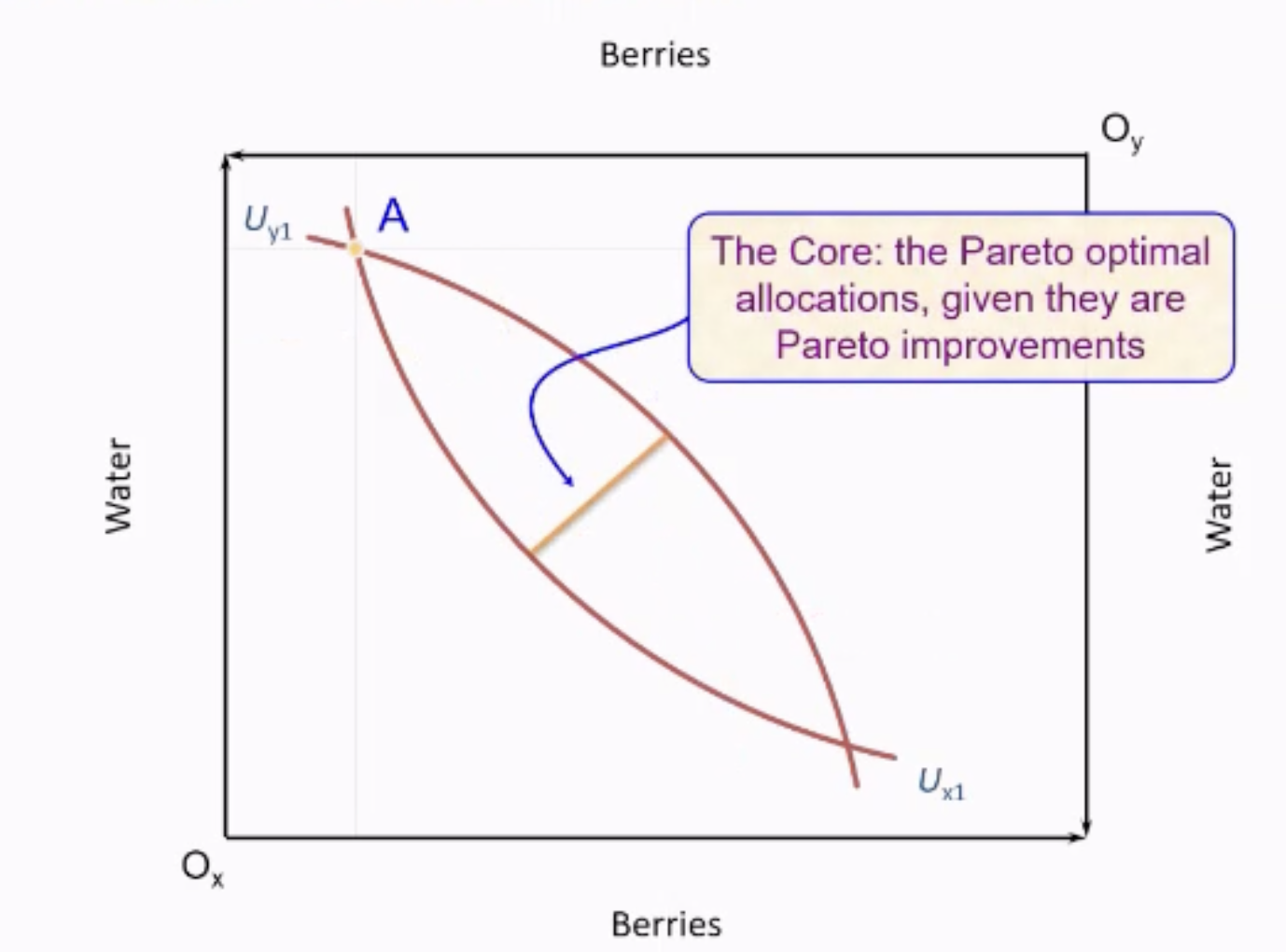
Pareto Optimal Allocation fo Resources
Private Efficiency
MPB = MPC
Marginal Private Benefit
Max price consumer is willing to pay for Good
Marginal Private Cost
Cost is the cost a producer or consumer directly pays for making or using one more unit of a good
Social Efficiency
MSB = MSC
Marginal Social benefit
Marginal Social Cost
Private and Social Effiecncy Under Perfect Comp
MSB = MPB = P = MPC = MSC
Externalities
The impact of a transaction that indirectly affects third parties.
Types of Externalities
Positive: Marginal Social Benefit (MSB)
Transaction indirectly benefits third party (e.g. G in education)
Negative: Marginal Social Cost (MSC)
Transaction indirectly harms third party (e.g. pollution, deforestation).
Types of Goods
Rival
Non-rival
Excludable
Non-excludable
Rival vs Rival Goods
Rival
One person consuming a good reduces availability for others.
Non-Rival
One person’s consumption does not limit another person’s consumption of good
Excludable vs Non-excludable
Excludable
Non-payers are prevented from using
Non-excludable
Non-payers cannot be easily excluded
Public Goods vs Private Goods vs Common Resources
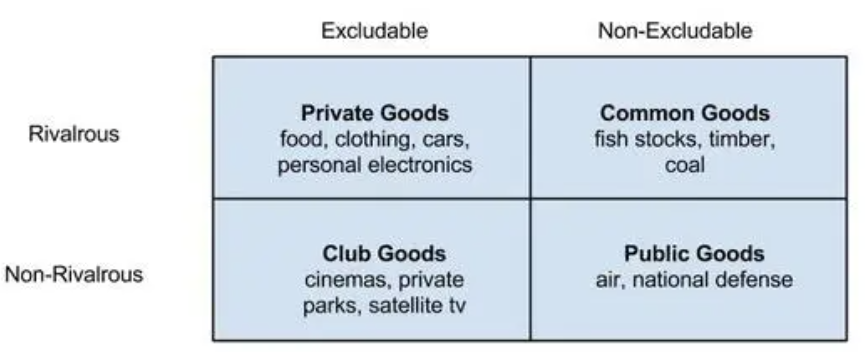
Private Goods: Rival and Excludable
food clothing, car, beer
Public Goods: Non-excludable and non-rival
air, road, ocean
Common Goods: Rival and Non-excludable
fish, timber, coal
Free Rider Problem
Why public goods are underprovided by gov
When people benefit from a good or service without paying for it, leading to underproduction or no production of that good.
e.g. Fireworks display can be seen from anywhere
Perfect vs Imperfect Information
Perfect
Consumers know price of both firms and are willing to shop at either
Imperfect
Consumers do not know prices and finding information is costly, so they are willing to shop at either firm.
Unravelling Principle
How firms have incentives to provided information to uninformed consumers under conditions of imperfect information.
Asymmetric Information
When only one party has more info than the other.
Usually when buyer has less information than sellers.
Asymmetric Goods when seller has more info
Search Goods
Experience Goods
Credence Goods
Search
Quality assessable pre-purchase
Experience
Quality assessable post purchase
Credence Goods
Quality hard to assess even post purchase
Asymmetric goods when buyer has more info
Loans
Insurance