BIOL 300 Discussion 5: Genome Evolution and DNA Packaging
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Introns Early Hypothesis
Genes were always interrupted
Introns Late Hypothesis
Genes started as uninterrupted
Exon Shuffling
Results in many different proteins, caused by Unequal Crossing Over and Transposons
Recombination Exon Shuffling
Mismatching portions of homologous chromosomes align during meiosis.
Transposons Exon Shuffling
AKA "Jumping Genes" is a chromosomal segment that can undergo transposition (Change position in the genome)
Result of Exon Shuffling
This shuffling can result in the evolution of a new protein.
Protein Domain
Distinct functional unit of a protein that can exist independently with a specific function
Nucleosome
a section of DNA that is wrapped around a core of proteins
Structure of Chromatin
An octamer of histones wrapped with DNA
The 4 Histone Proteins
H2A, H2B, H3, H4
Major Enzyme used in Transcription
RNA Polymerase
Major Enzyme used in Replication
DNA Polymerase
Do you need more histones to be synthesized during transcription?
No, because the number of DNA strands is the same
Do you need more histones to be synthesized during replication?
Yes, because the number of DNA strands is doubled
Histone repositioning on DNA after transcription
Simply re-form the nucleosome
How do the histones reposition
themselves on DNA after replication?
New Octamer is bound to new strand and old octamer is bound back to old strand .
FACT
dismantles nucleosomes ahead of transcribing polymerases
Histone Positioning
Histones inhibit reading of DNA and must be moved for it to be read.
Histone Phased
Histones are placed in specific location to prevent or allow the reading of certain regions.
Hypersensitive Regions Histone Positioning
Regions that are more actively being expressed, they are more easily digested by DNAses
Telomere
A region of repetitive nucleotide sequences at each end of a chromosome
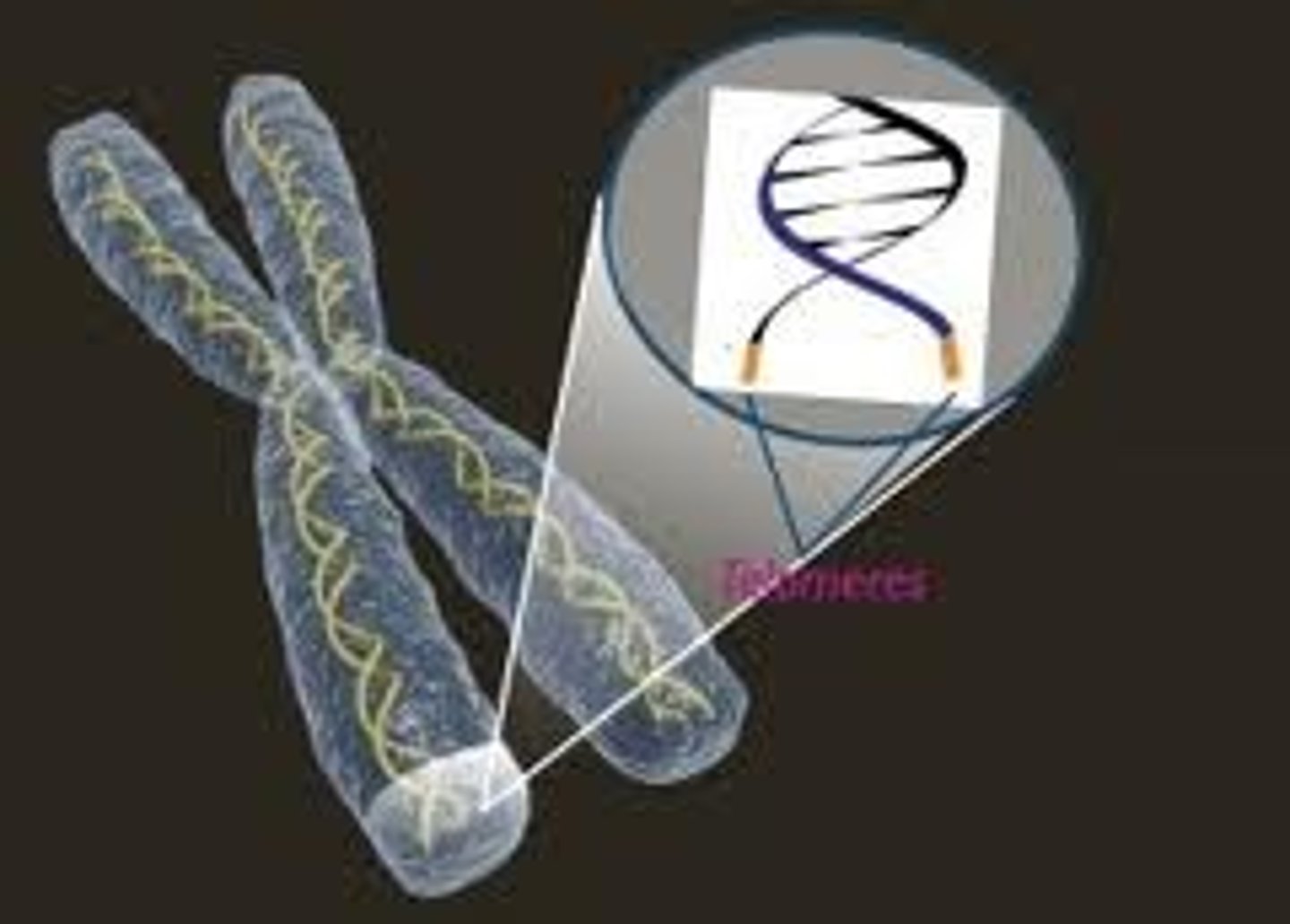
Telomerase
An enzyme that adds DNA sequence repeats to the 3' end of the DNA strand in the telomere regions
Telomere Importance
Telomeres protect eukaryotes from gene loss or mutation during replication
T Loop
Something that acts like a knot at the end of the chromosome to stabilize it
D Loop
A region of the animal mitochondrial DNA molecule that is variable in size and sequence and contains the origin of replication.
Shelterin Complex
Makes DNA inaccessible in the d-loop.