2nd Lab Practical AA&P
1/449
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
450 Terms
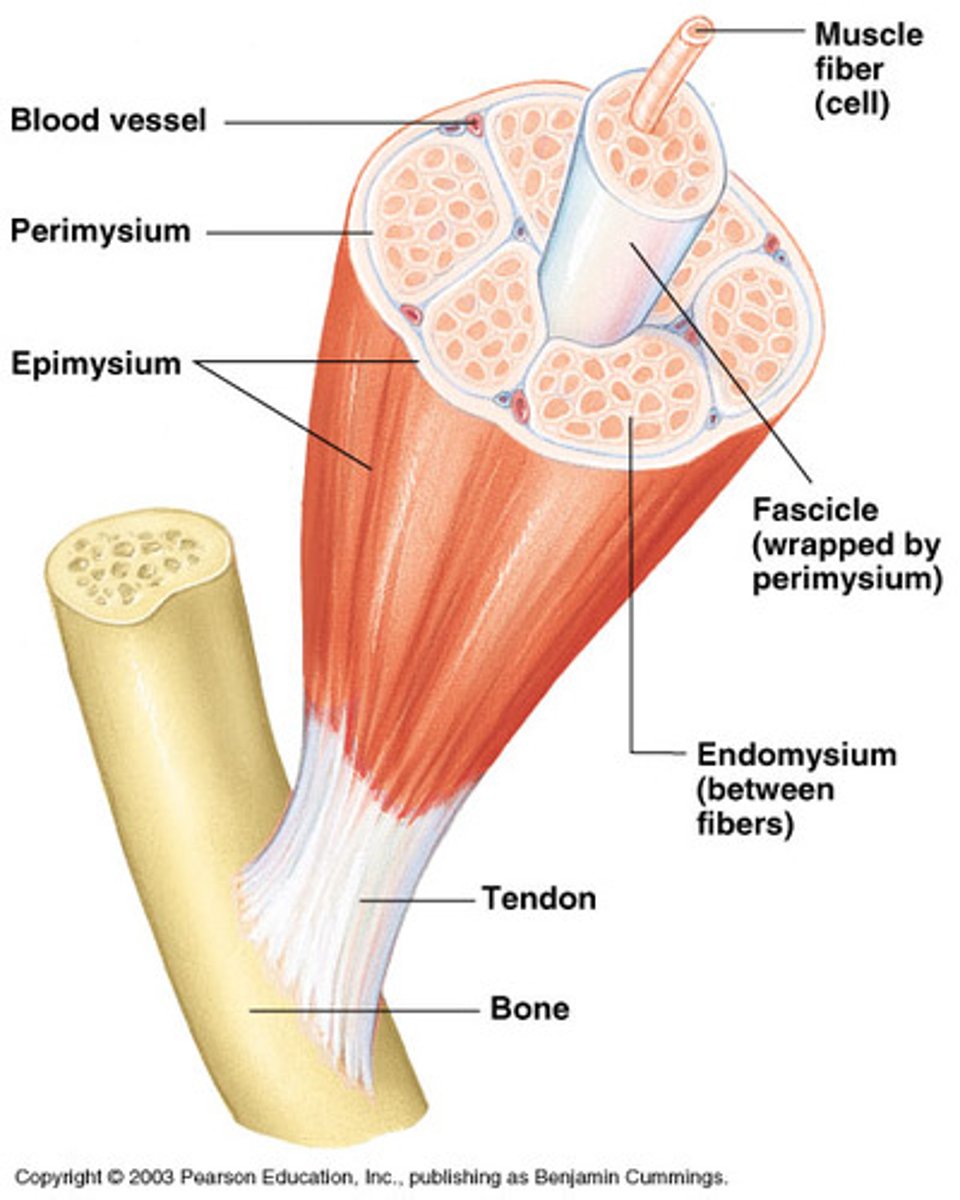
endomysium
delicate layer of connective tissue that separates individual muscle fibers ** outside of sarcolemma; it isnt on the diagram in lab*
muscle model in lab labeled
nucleus ?
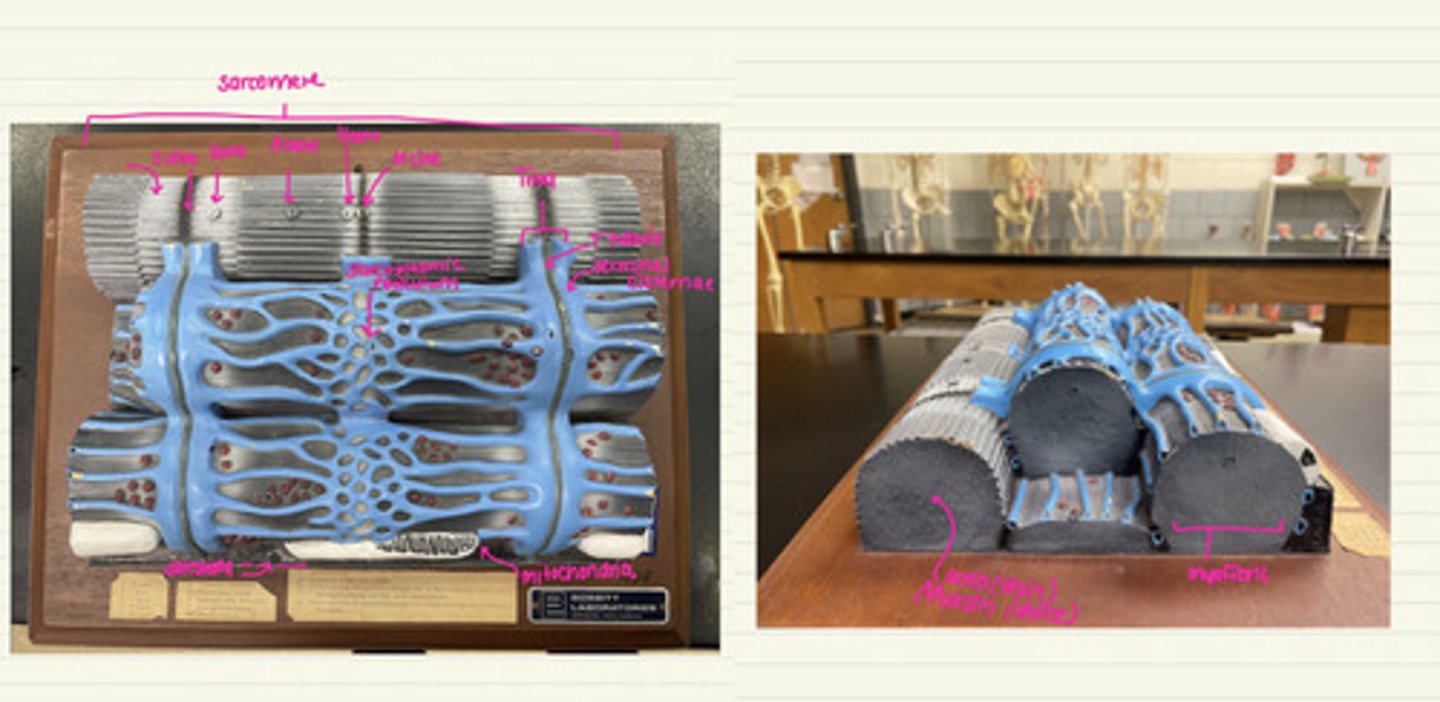

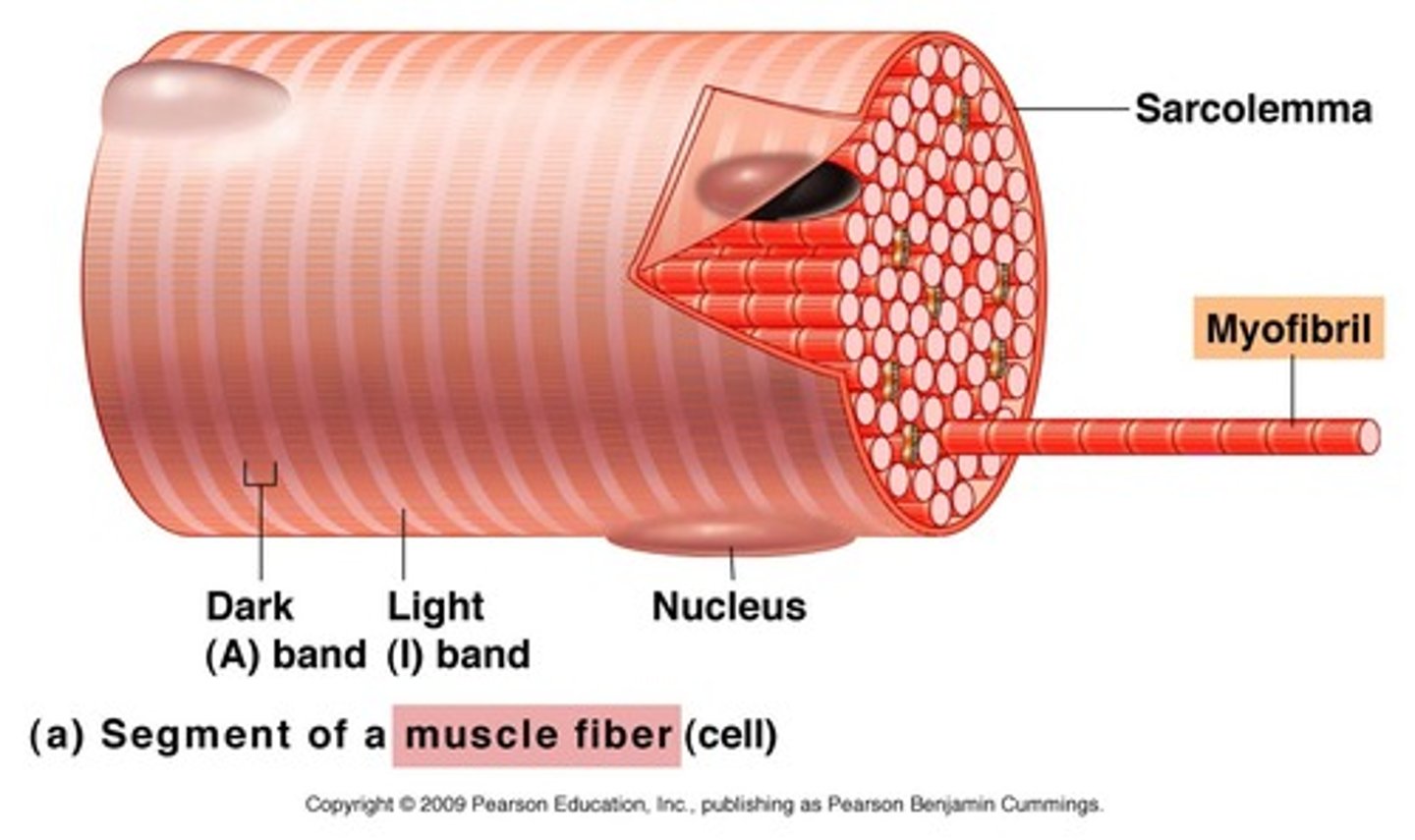
sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
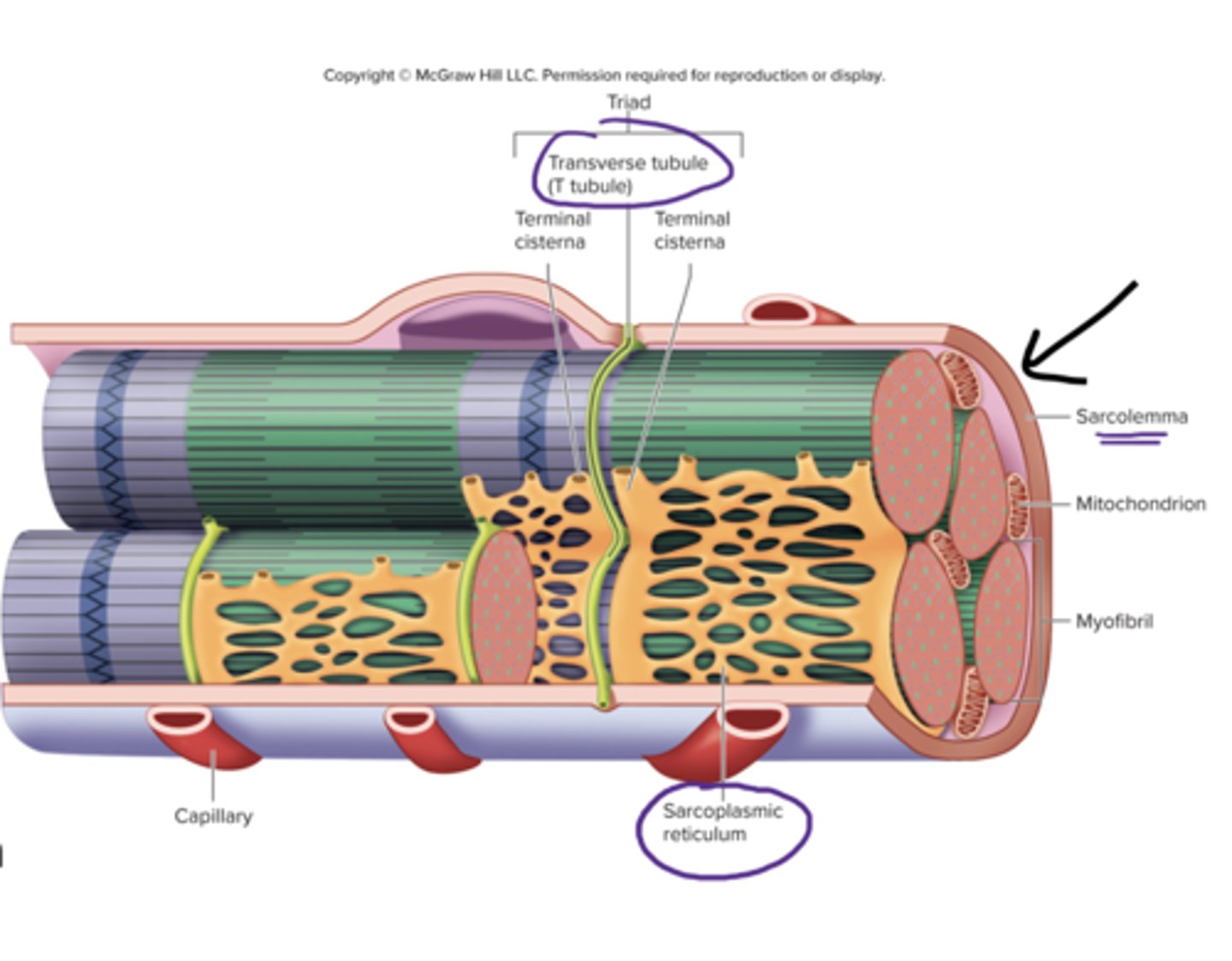
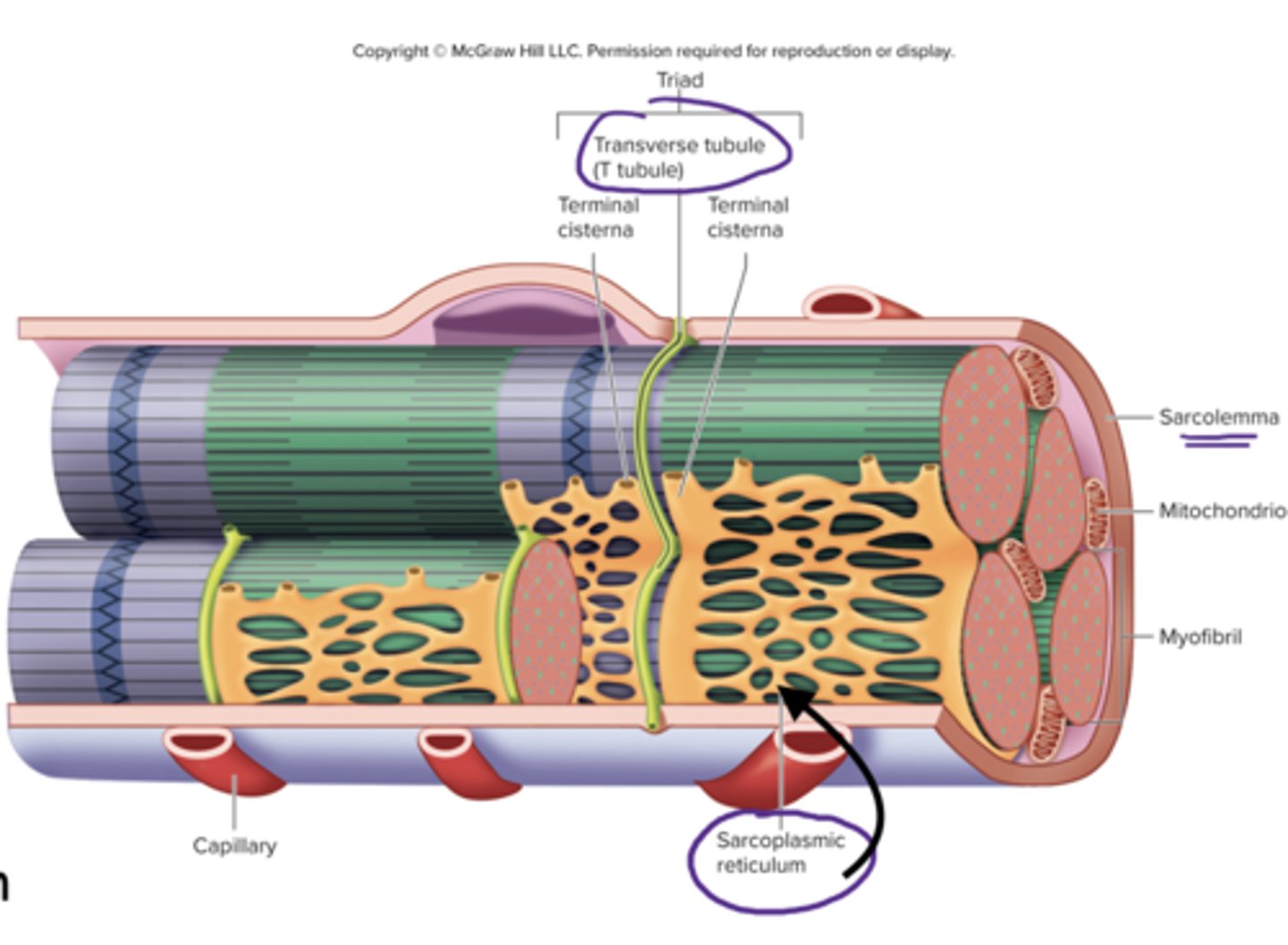
sarcoplasmic reticulum
specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum, stores Ca2+
mitochondria
produces energy
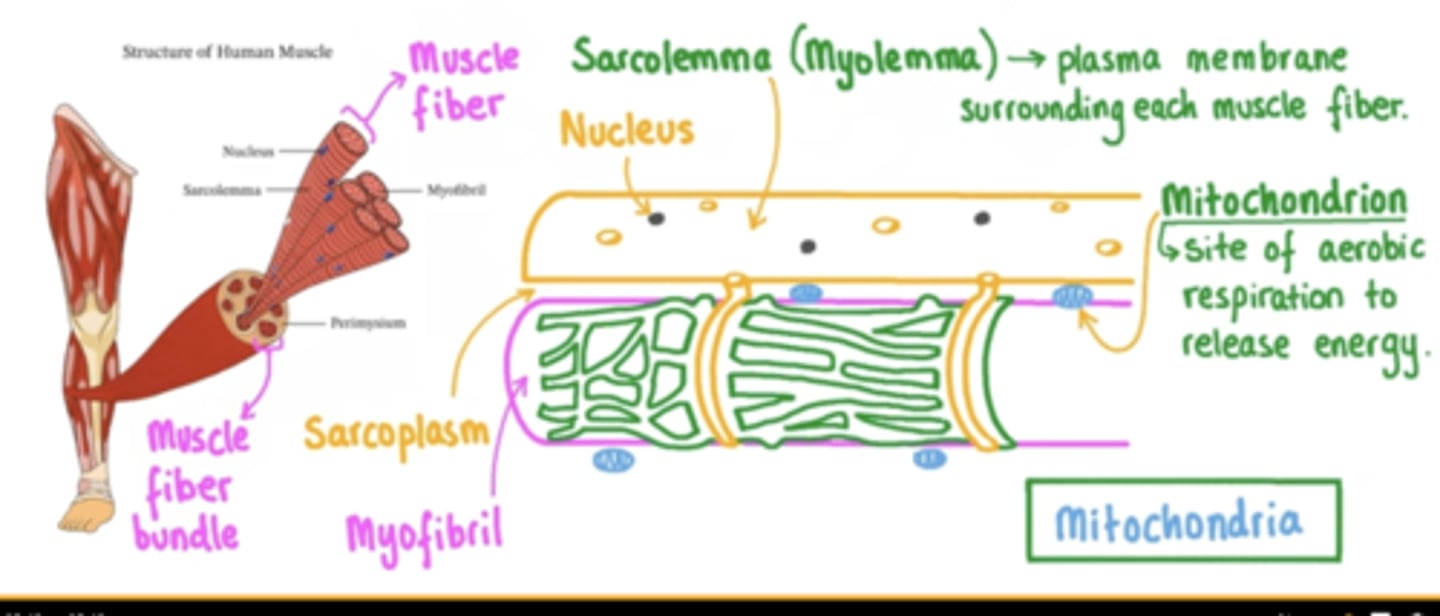
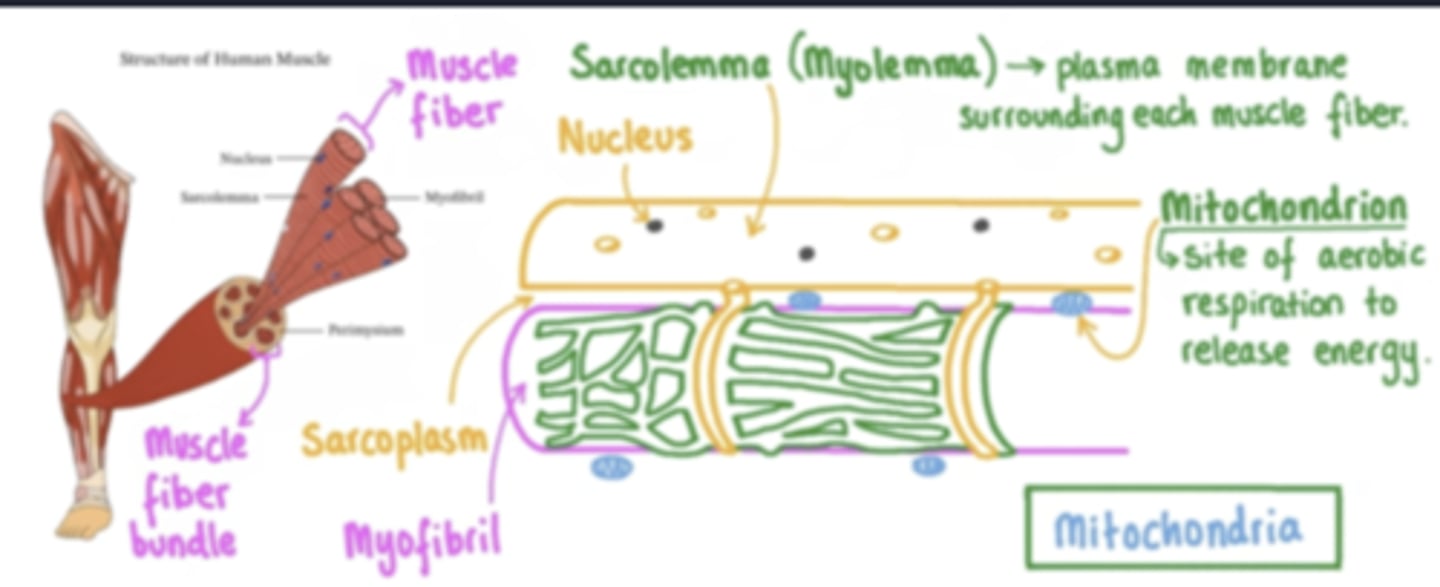
nucleus
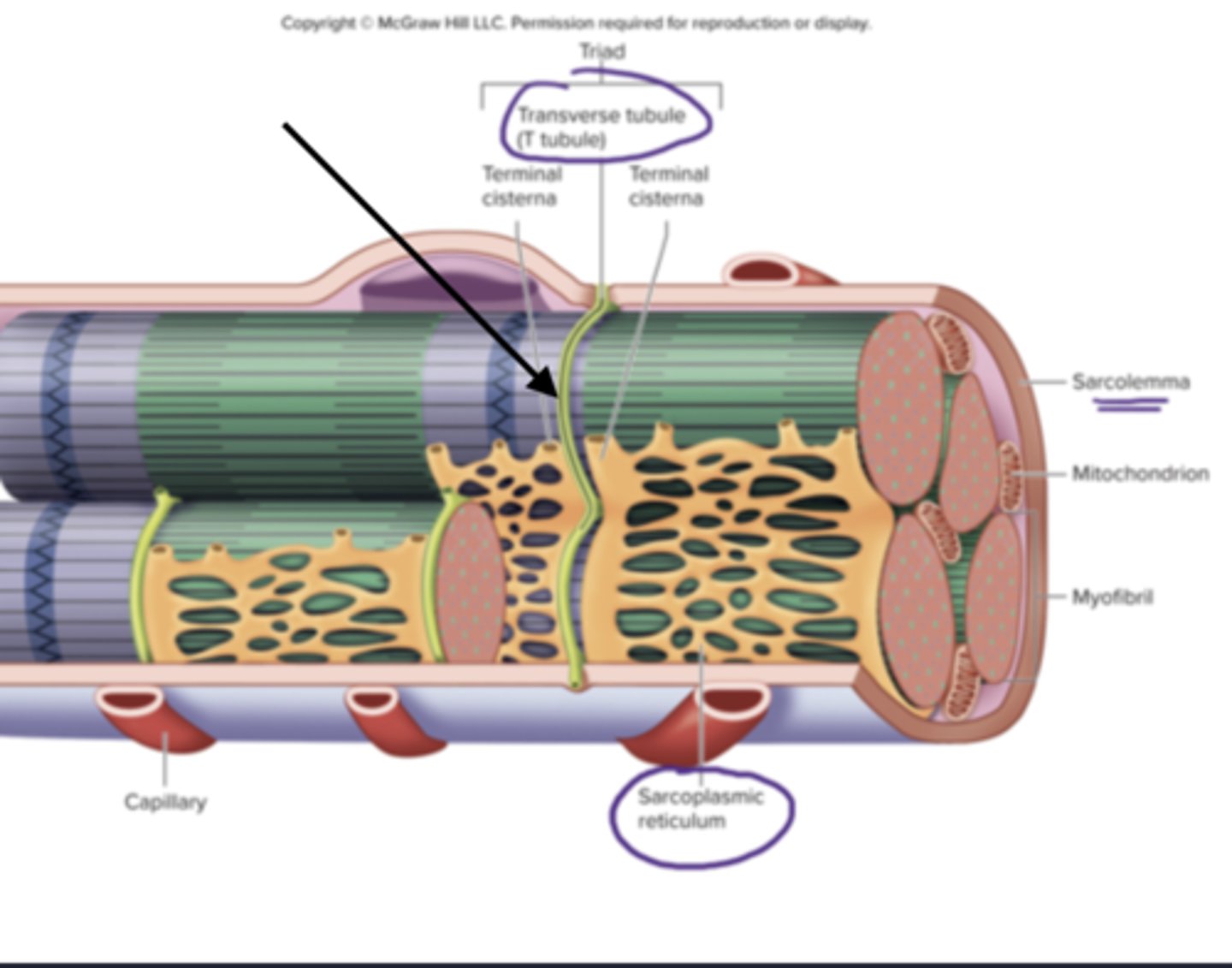
triad of skeletal muscle
1 T-tubule and 2 terminal cisternae
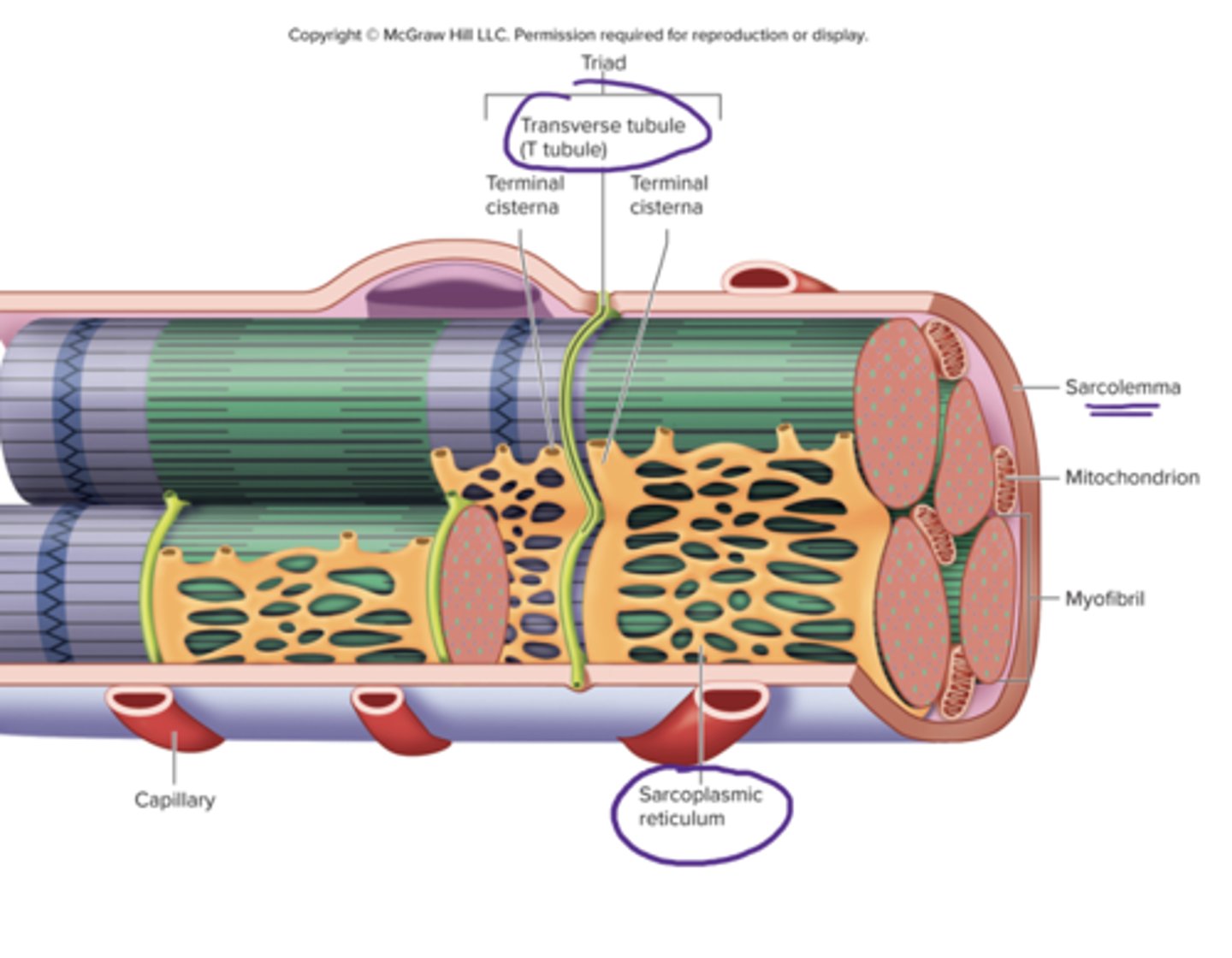
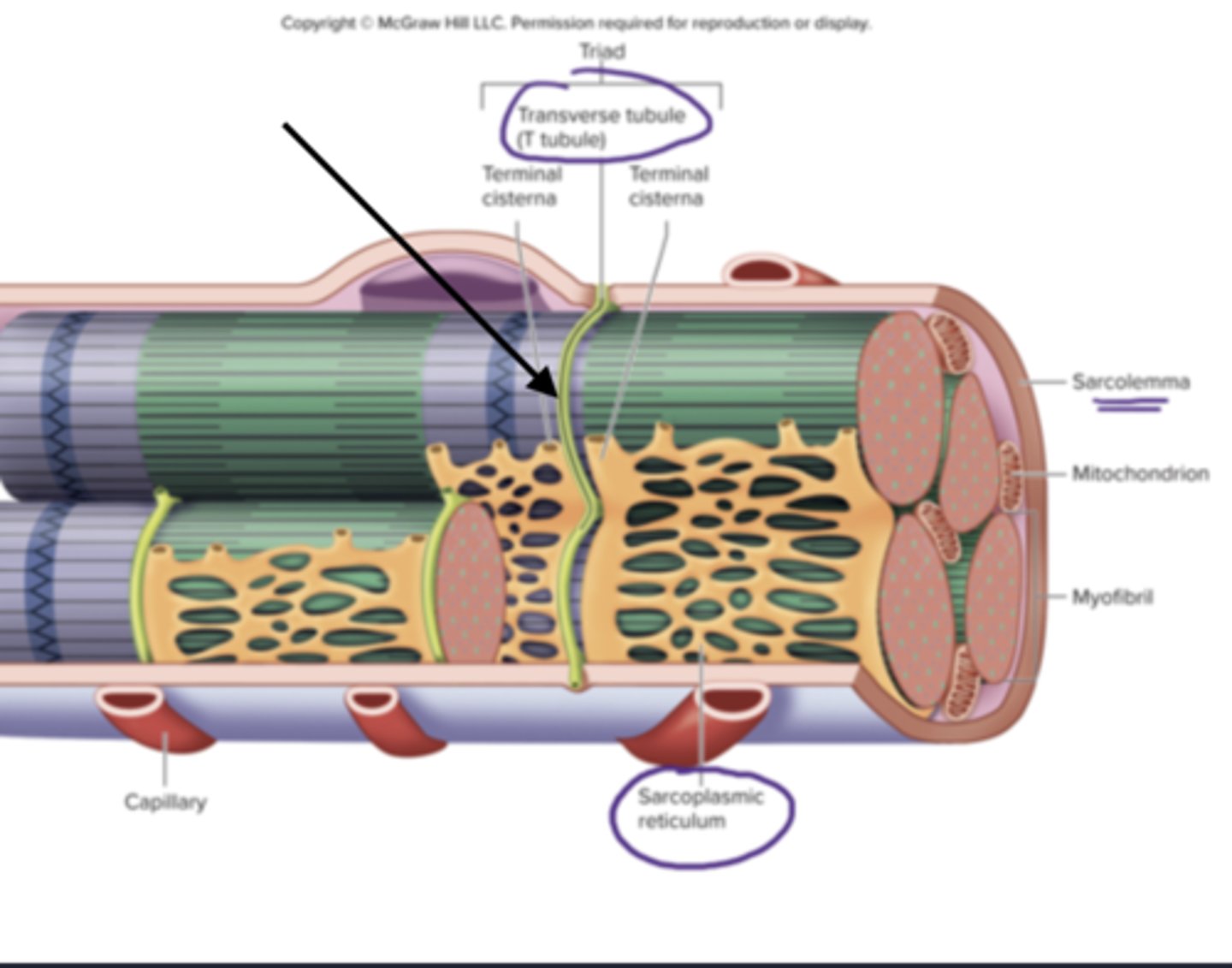
T tubules
transverse tubules
tube like inward folds of the sarcolemma, found at regular intervals among the muscle fiber, carries electrical impulses to the center of the muscle fiber
terminal cisternae
enlarged regions of the sarcoplasmic reticulum, closely associated with the t tubules (form the triad)
myofibrils
bundles of protein filaments, multiple found in sarcoplasm extending length of the muscle fiber, formed by sarcomeres joining @ ends
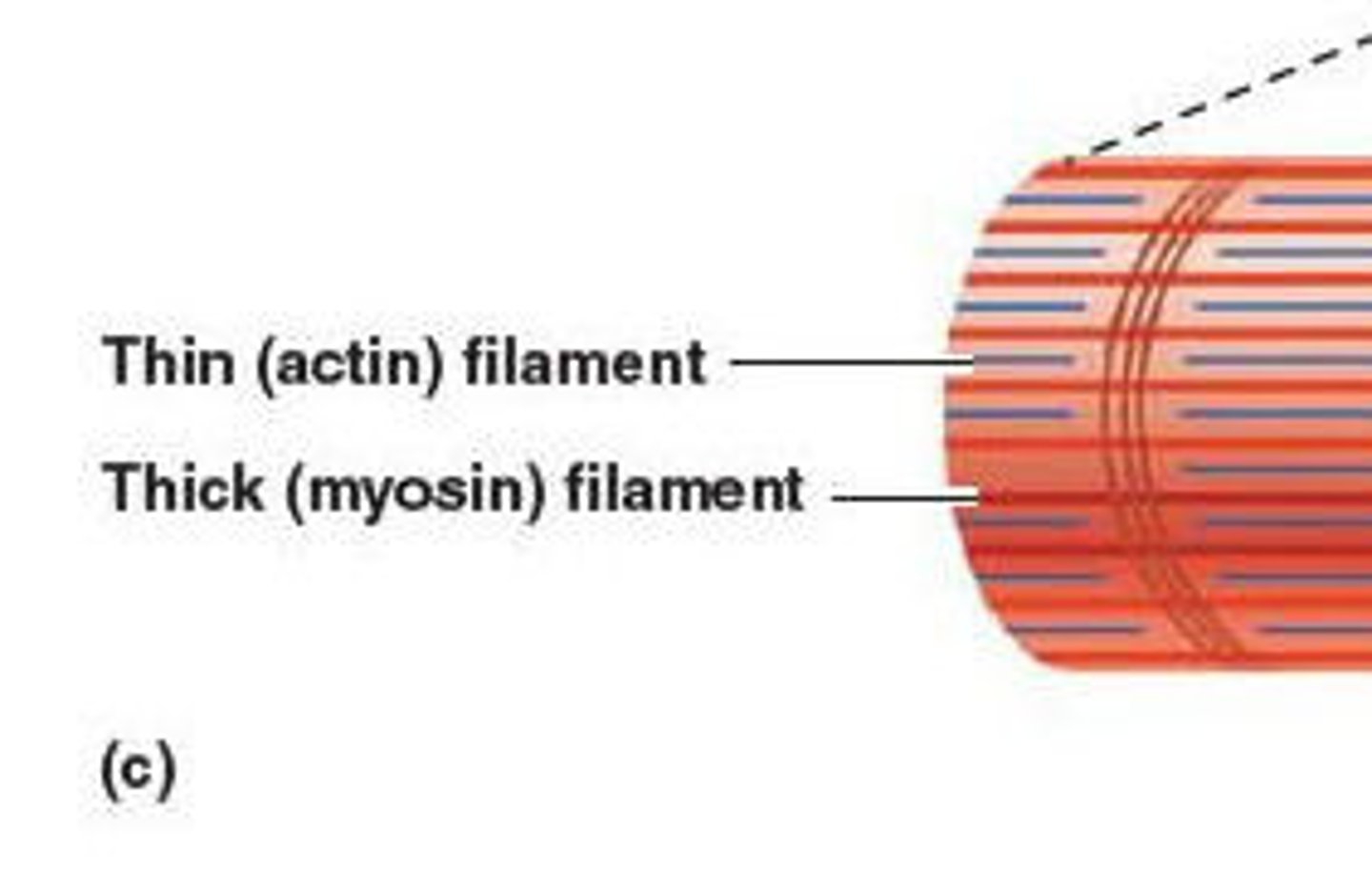
thick filament & thin filament
myosin, actin respectively
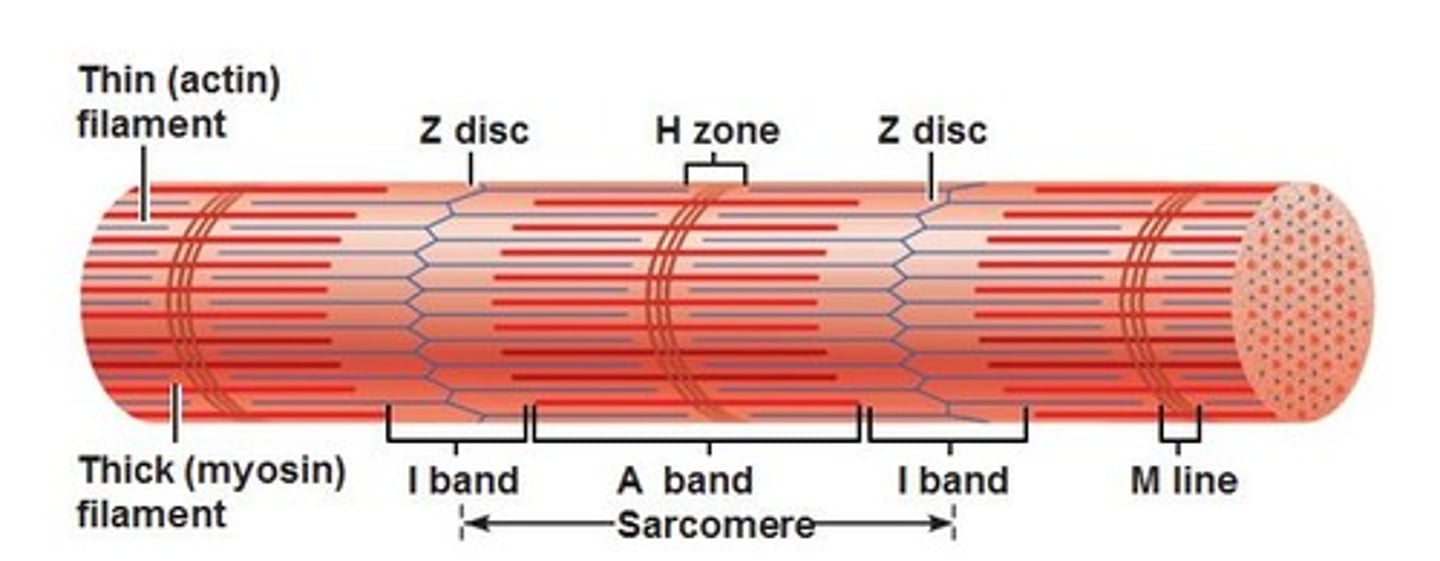
sarcomere
join end to end to form myofibrils
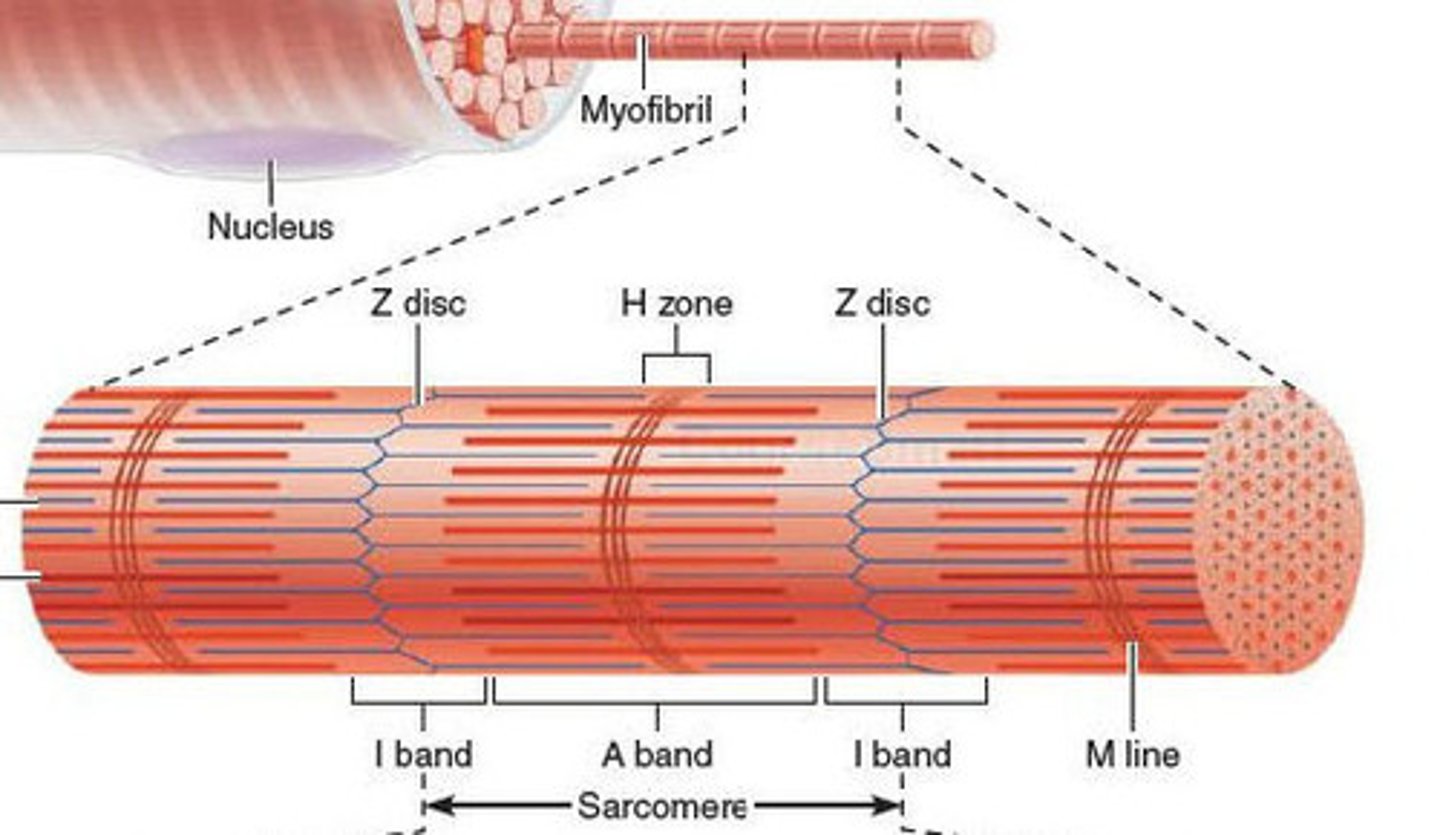
Z disc
network of proteins @ end of sarcomere, anchor actin myofilaments
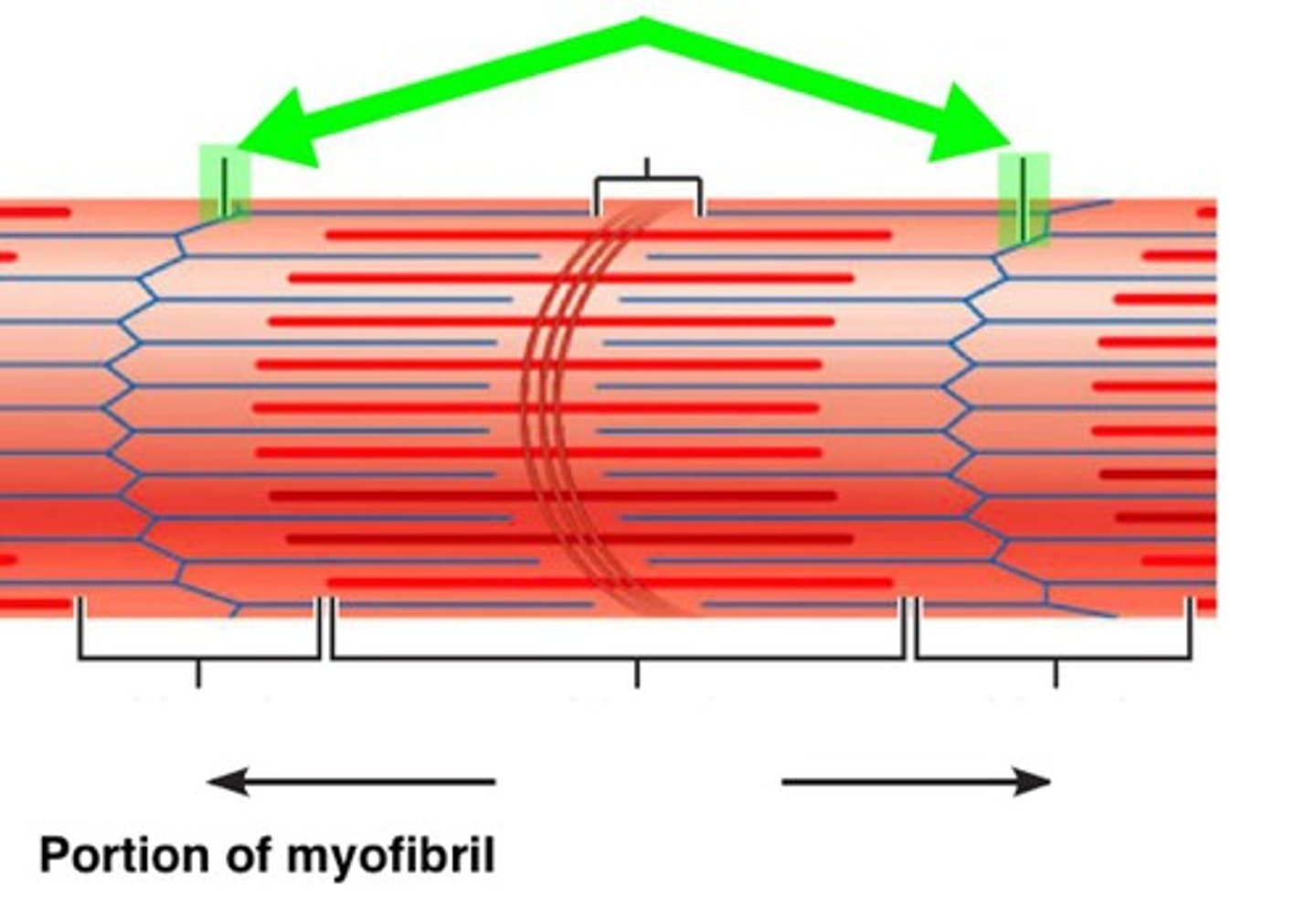
i band
light region, only actin, contains z discs
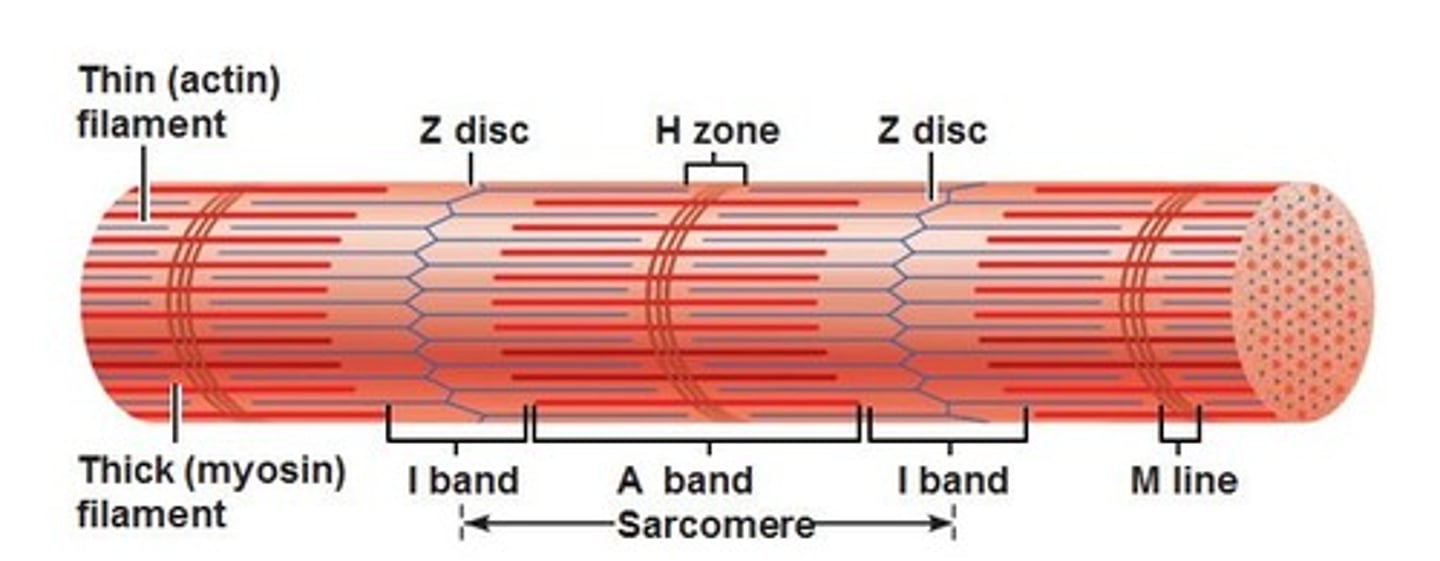
A band
dark area; extends length of the thick filaments (myosin)
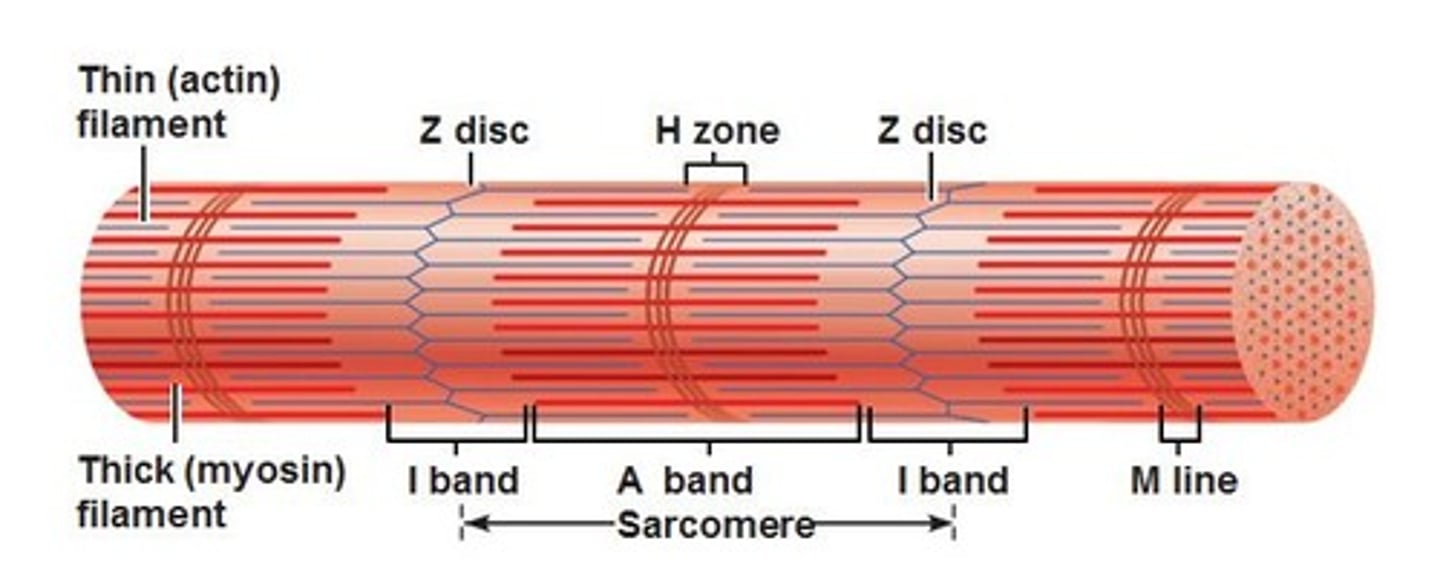
H zone
within A band, contains only myosin filaments
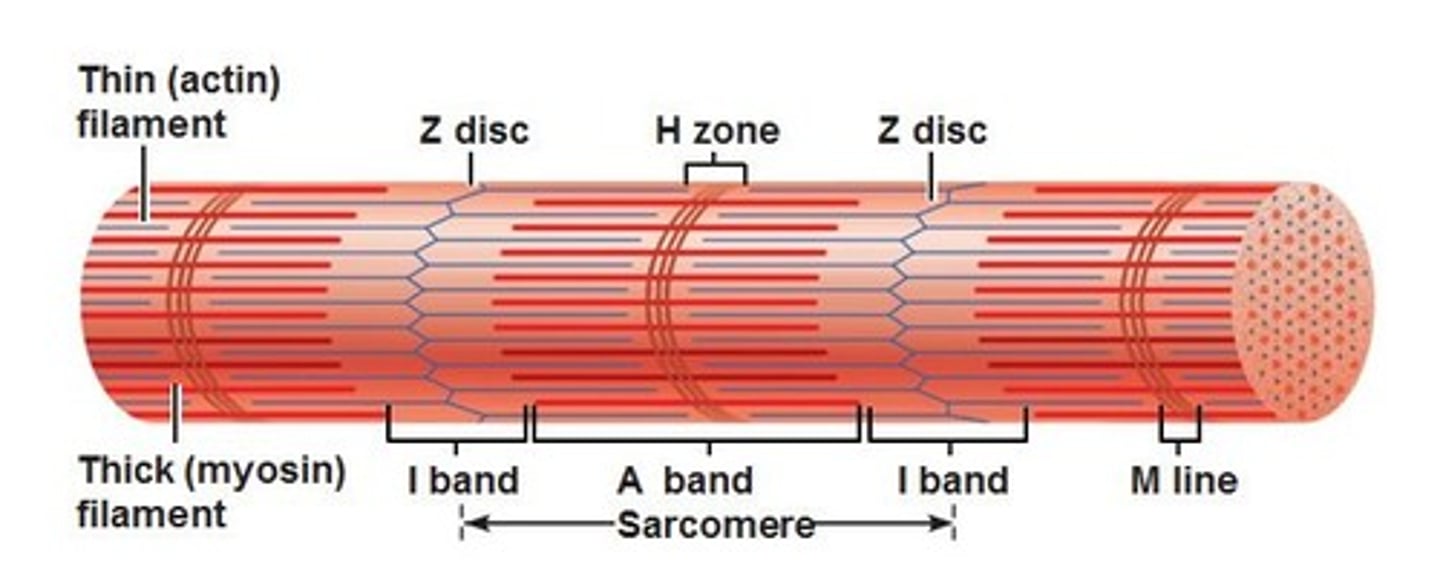
M line
delicate filaments that support myosin filaments
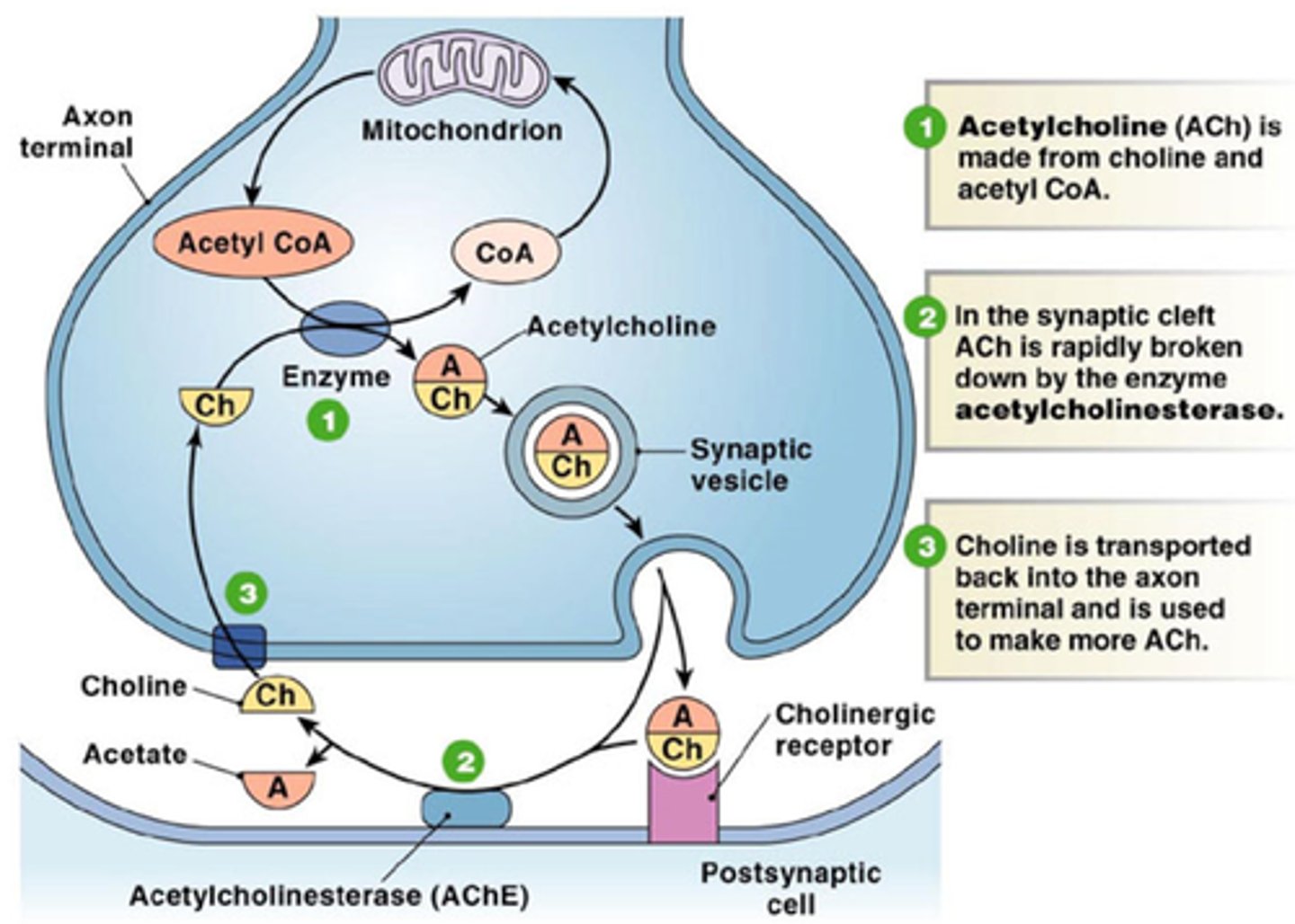
neuromuscular junction
point of contact between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber... consits of presynaptic terminal, synaptic cleft, motor end plate of postsynaptic membrane
acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter
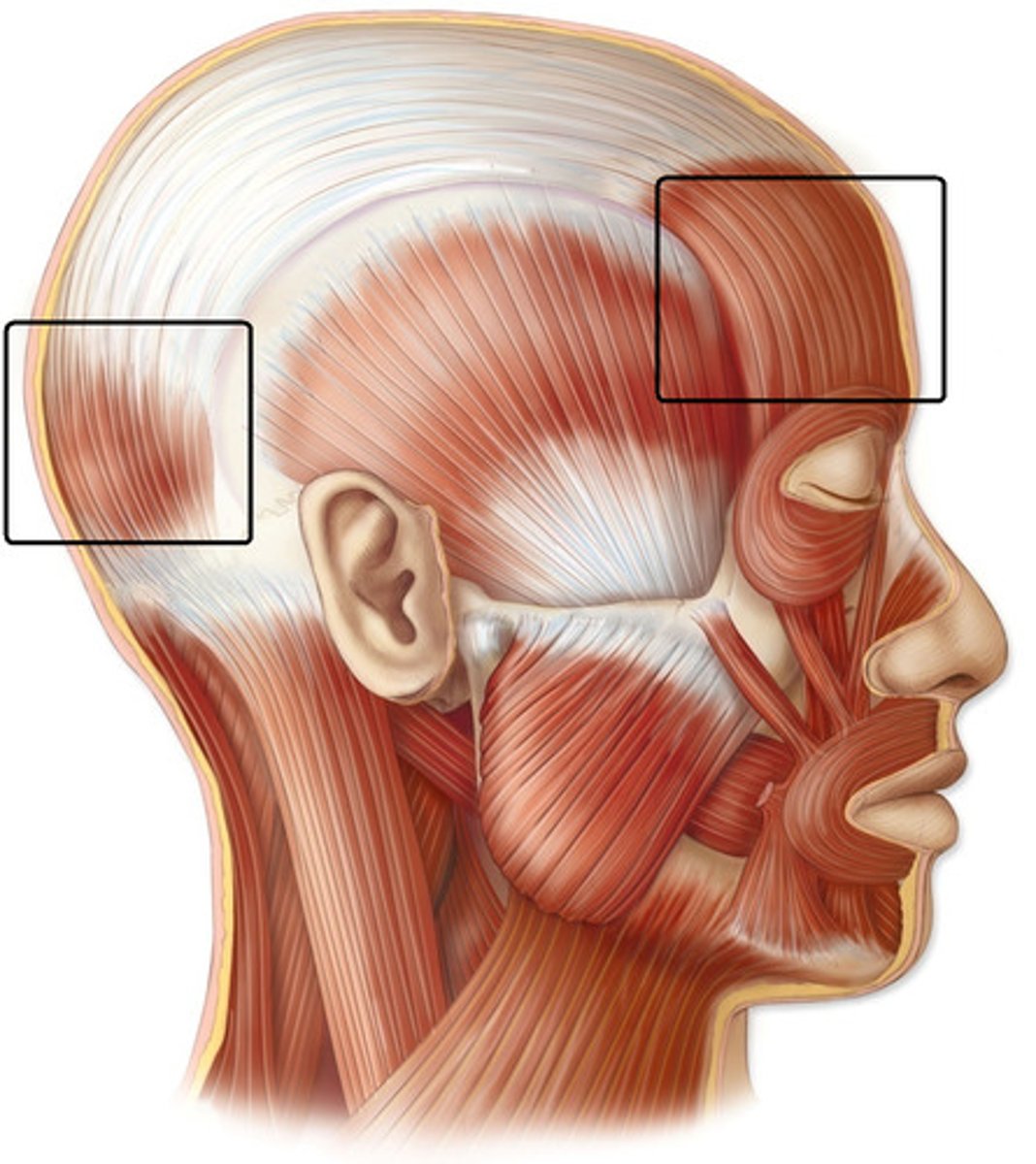
Occipitofrontalis
Origin: occipital
Insertion: skin of eyebrow, nose
Action: moves scalp; raises eyebrows; wrinkles forehead; "suprise"
temporalis muscle
Origin: Temporal fossa of temporal and parietal bones
Insertion: anterior portion of mandibular ramus and coronoid process
Function: elevates and retracts the mandible; involved in excursion
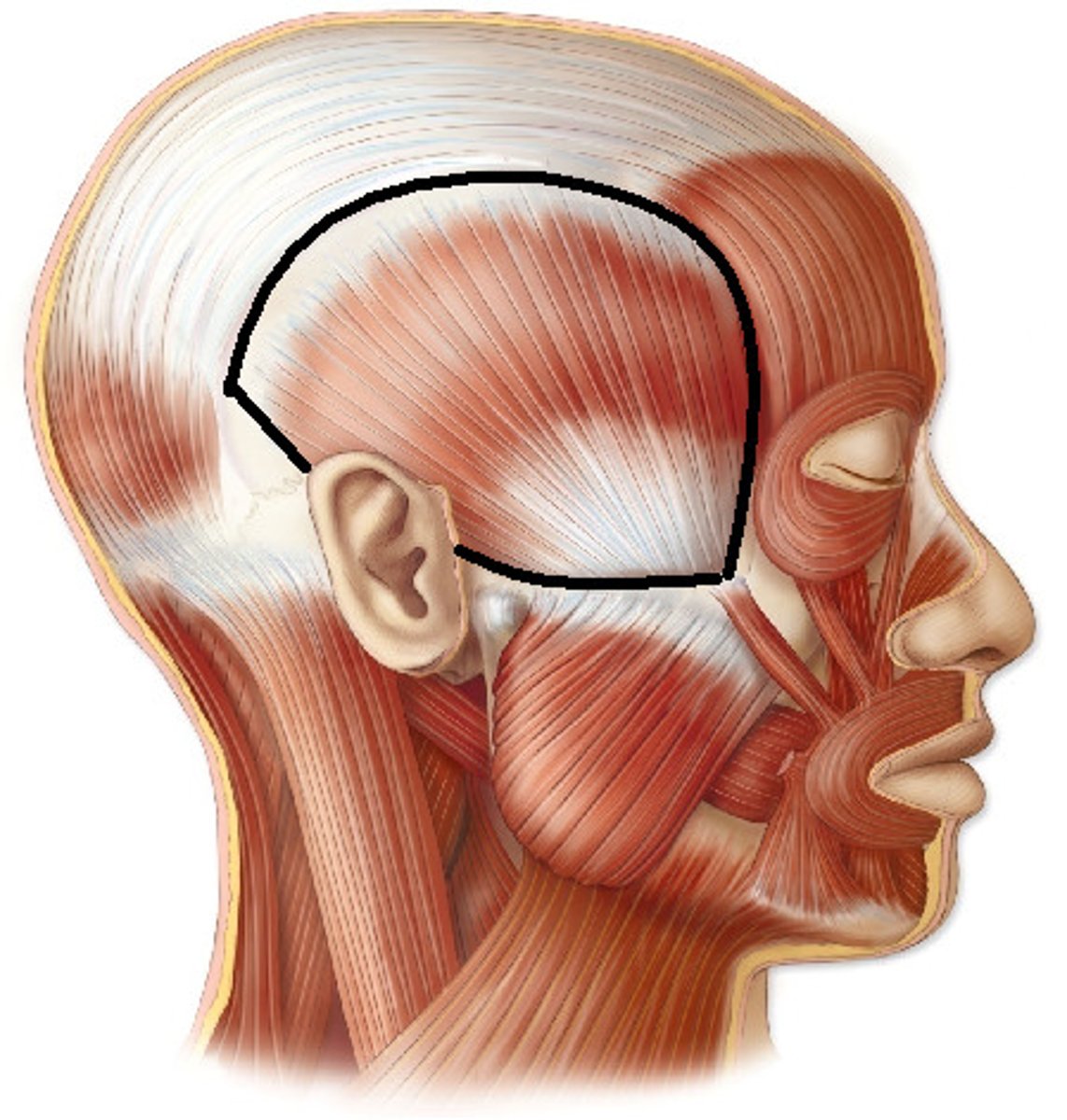
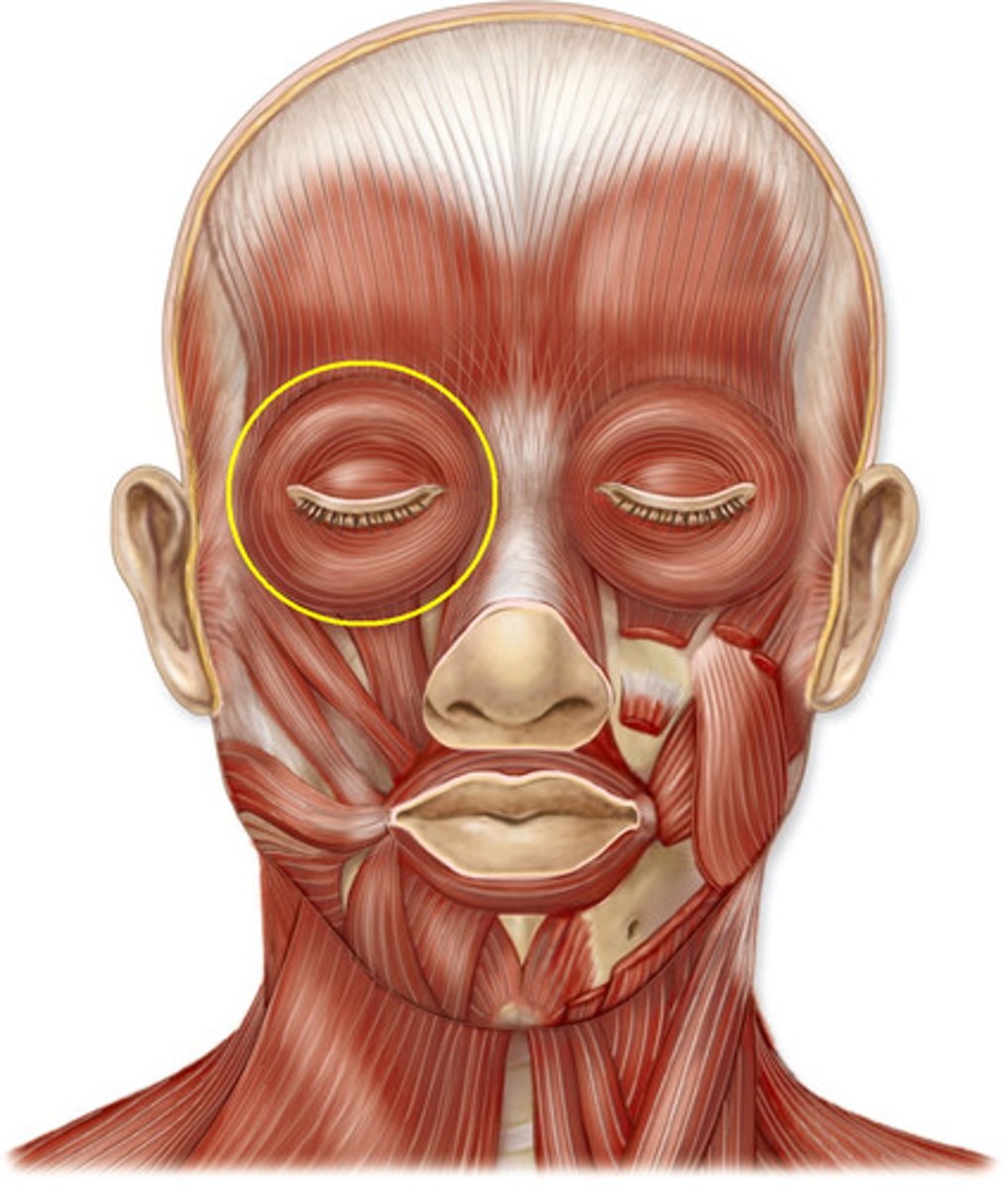
orbicularis oculi muscle
origin: maxilla and frontal bones
insertion: circles orbit and inserts near origin
function: closes eyes; blinking; winking; squinting
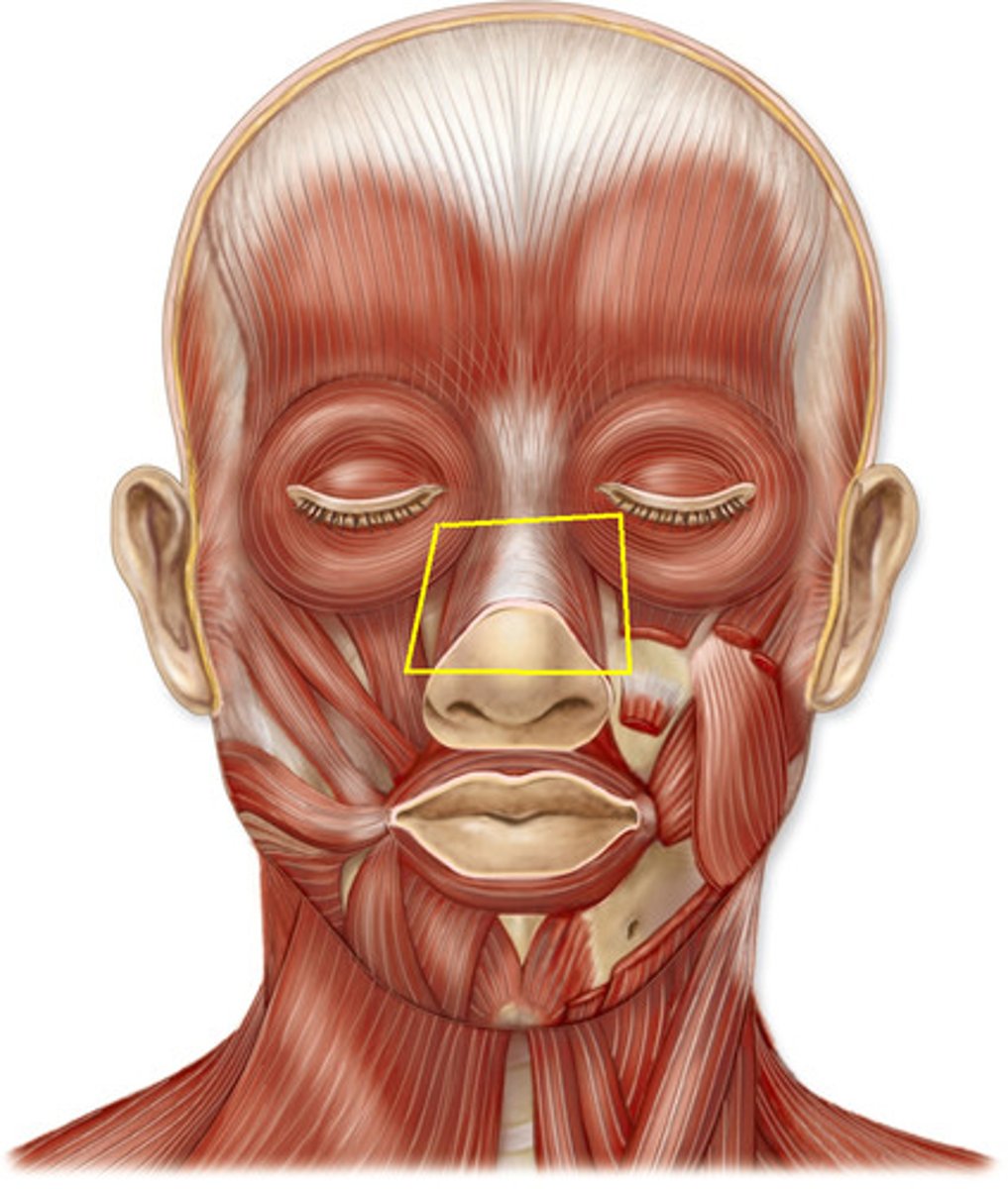
procerus muscle
origin: bridge of nose
insertion: frontalis
action: creates horizontal wrinkles between eyes (frowning)
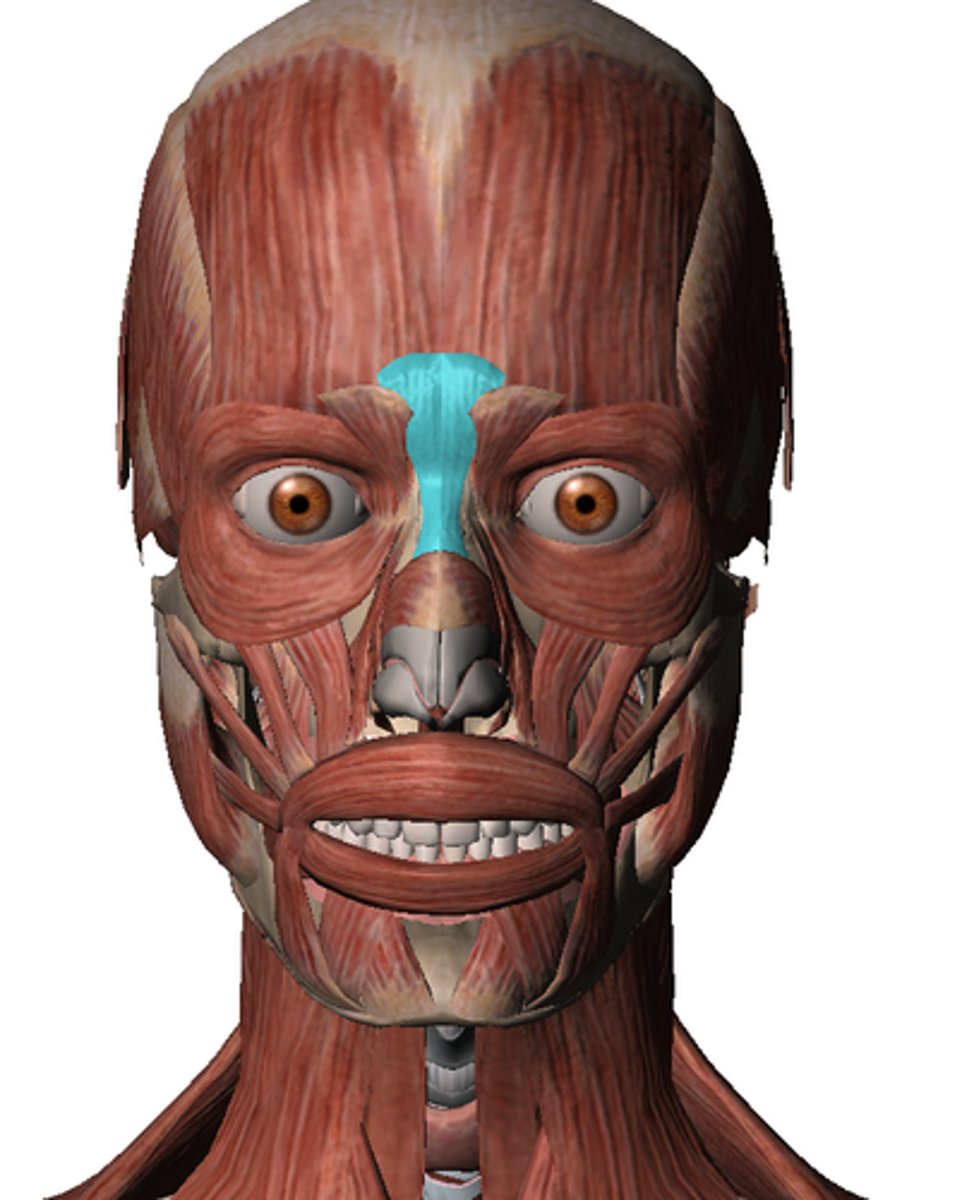

nasalis muscle
origin: maxilla
insertion: bridge and side of nose
action: dilates nostril
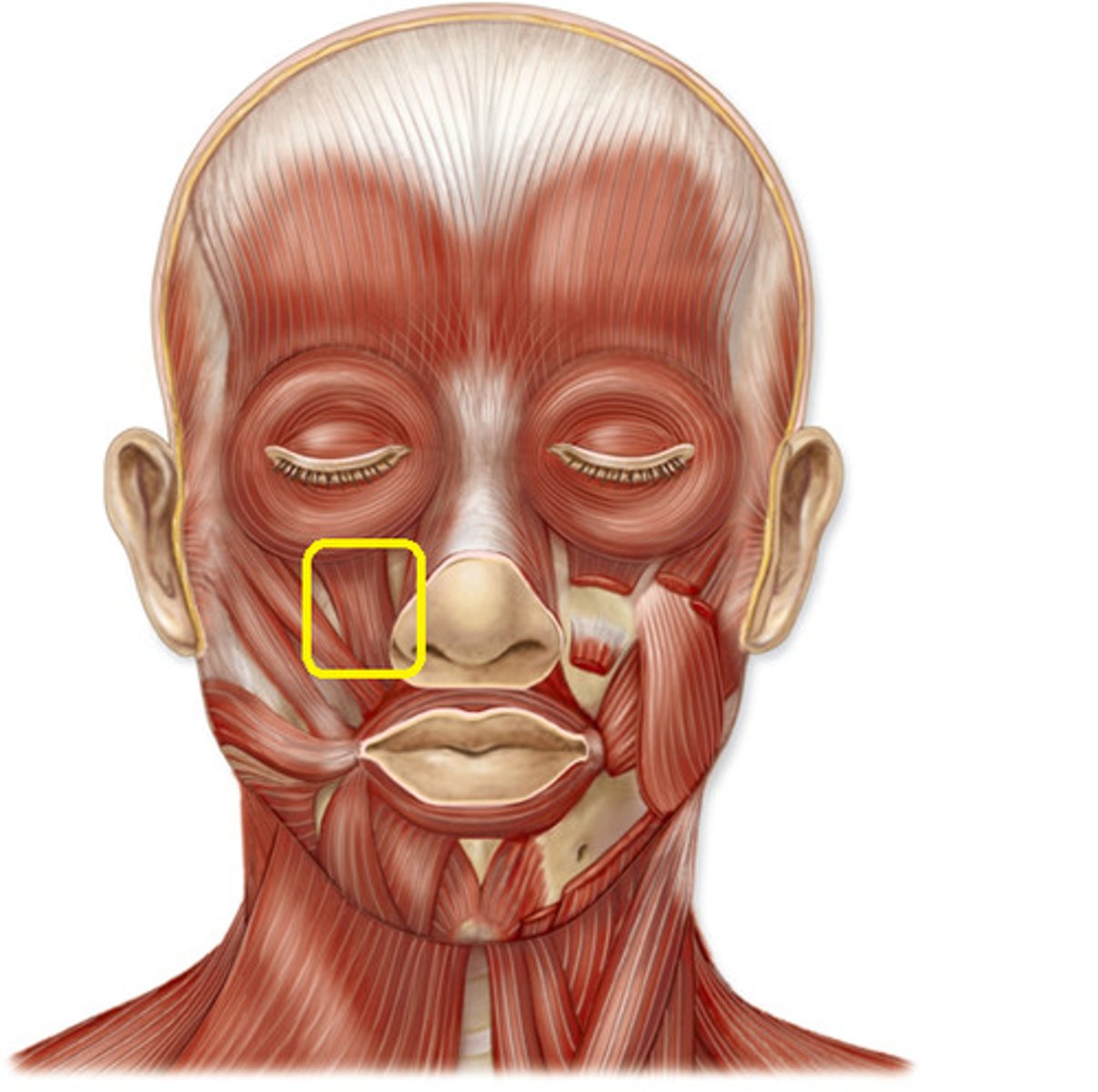
levator labii superioris
origin: maxilla
insertion: skin and orbicularis oris of upper lip
action: raises upper lip "sneer"
zygomaticus minor
origin: zygomatic bone
insertion: orbicularis oris of upper lip
action: elevates and abducts upper lip; smile
zygomaticus major
origin: zygomatic bone
insertion: angle of mouth
action: elevates and abducts upper lip and corner of mouth "smile"
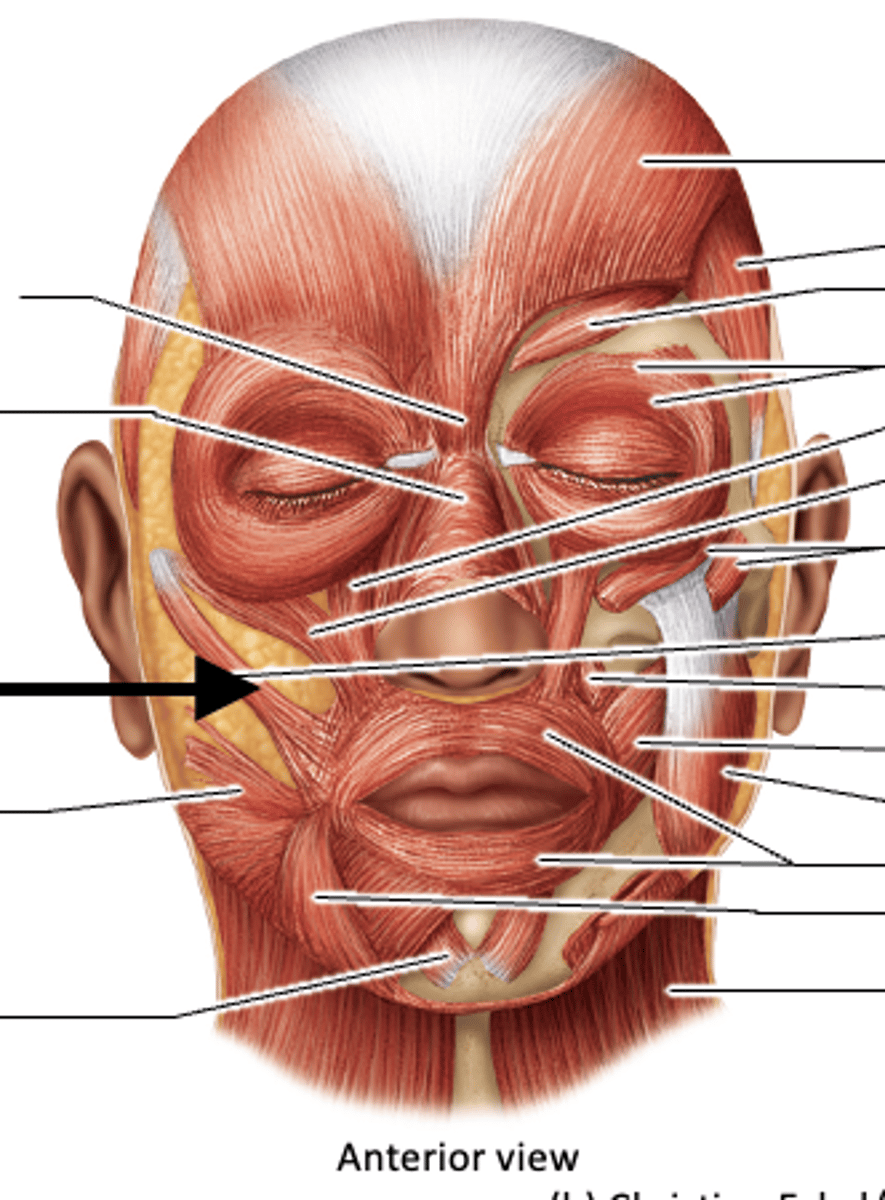
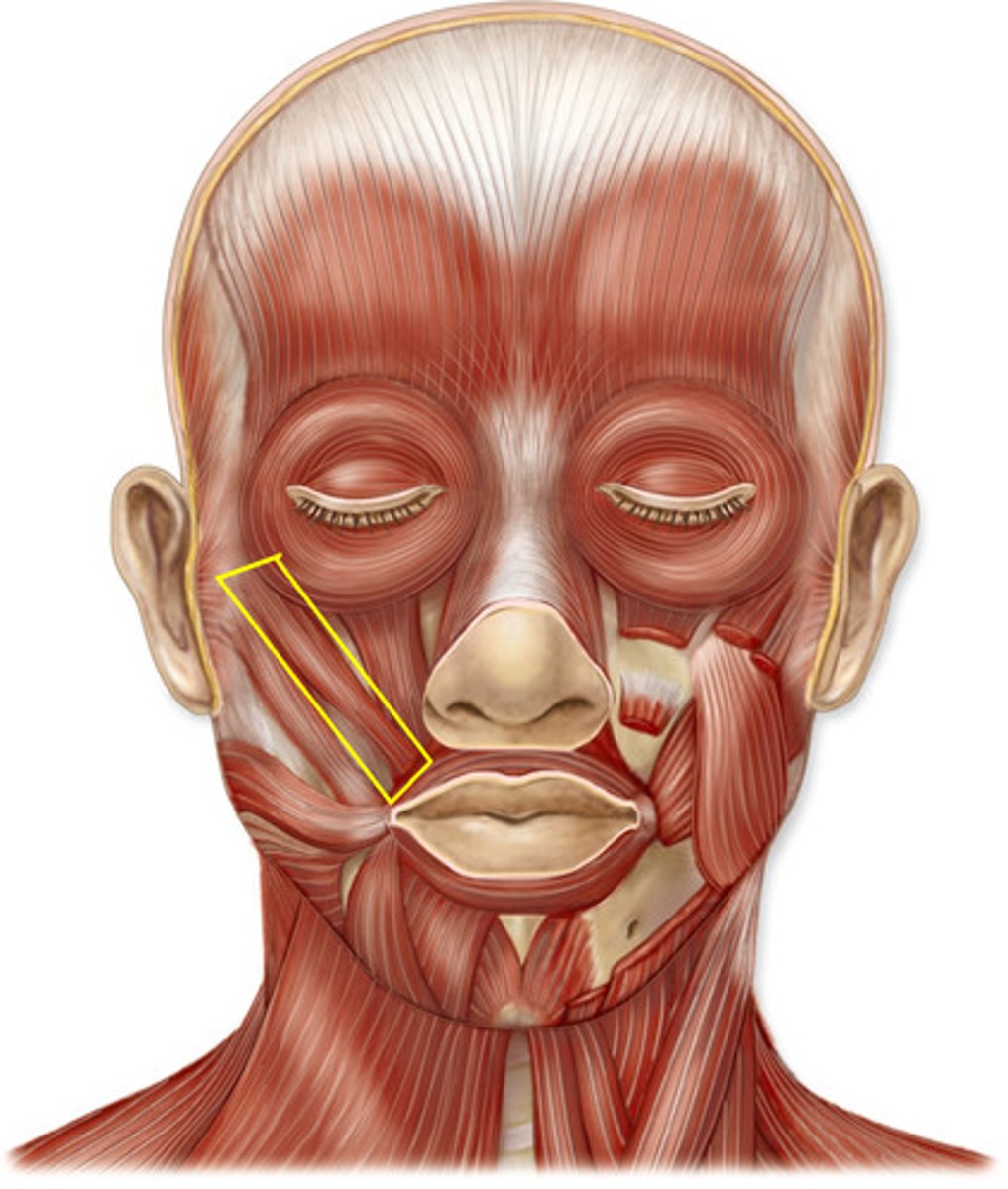
buccinator muscle
origin: mandible and maxilla
insertion: orbicularis at corner of the mouth
action: draws corners of mouth posteriorly; compresses cheek to hold food between teeth
orbicularis oris
origin: nasal septum, maxilla, mandible
insertion: fascia and other muscles of lip
action: closes and purses lip "kissing"
depressor anguli oris
origin: lower border of mandible
insertion: skin of lip near corner of mouth
action: lowers corner of mouth; frown
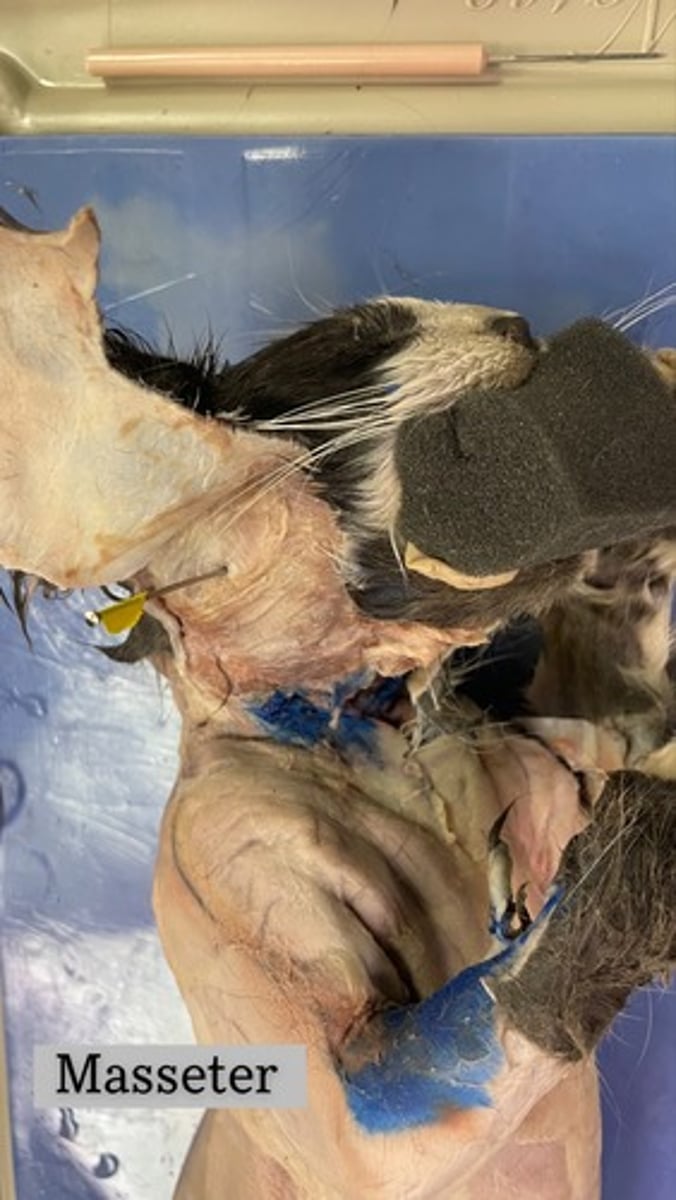
masseter muscle
origin: zygomatic arch
insertion: lateral side of mandibular ramus
action: elevates and protracts mandible; involved in excursion
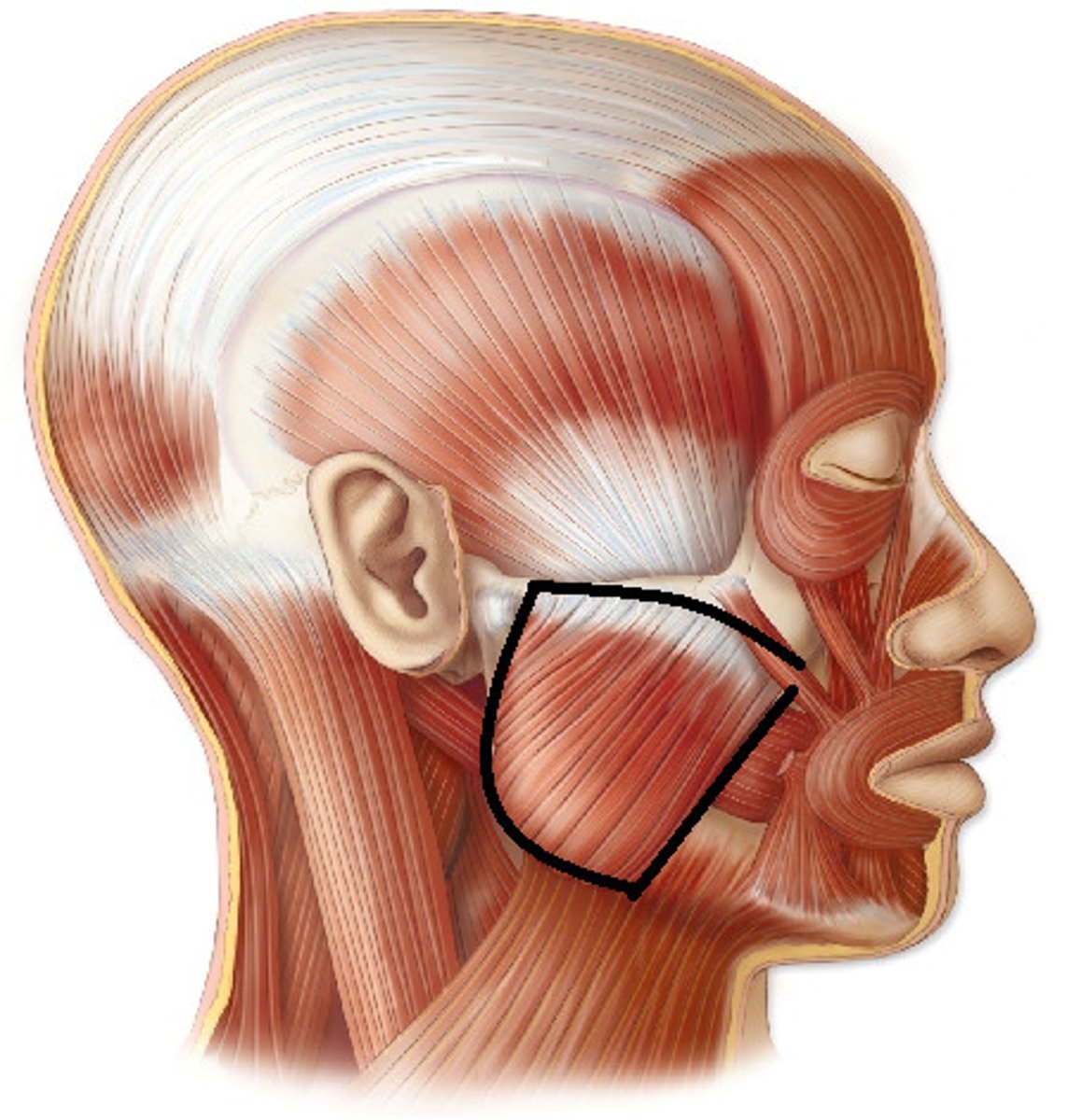
Massester on cat

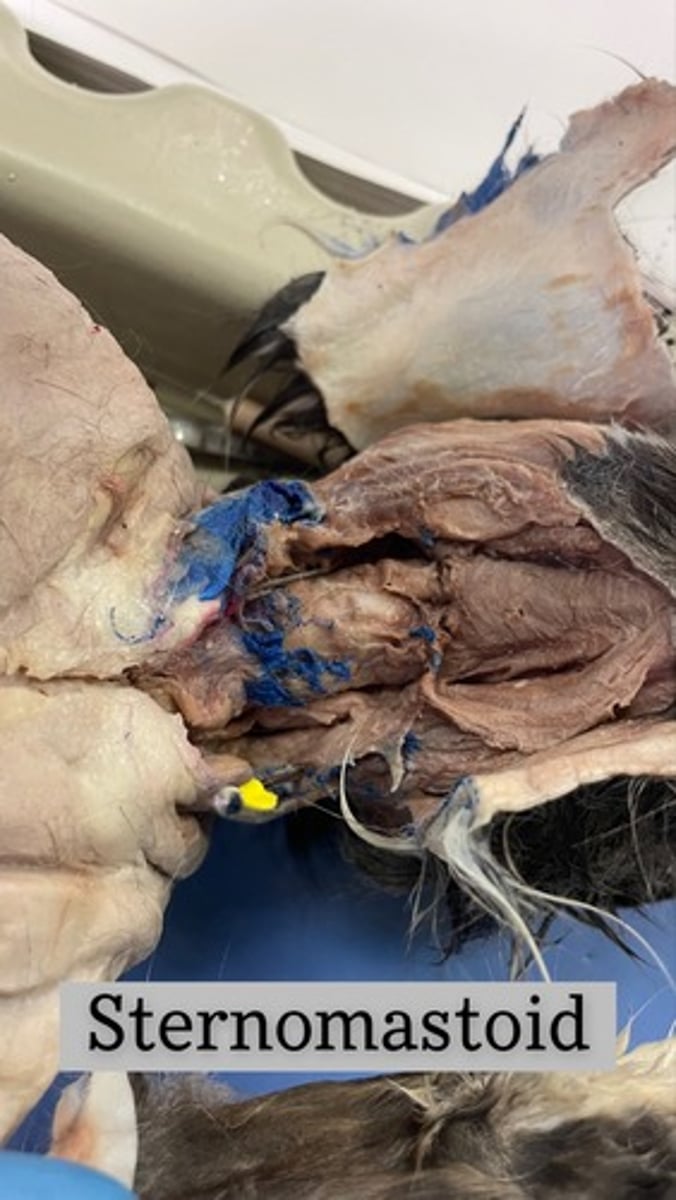
Sternocleidomastoid
origin: manubrium and medial clavicle
insertion: mastoid process and superior nuchal line
action: one contracting alone laterally flexes head and neck to same side and rotates head and neck to opposite side... both contracting together; flex neck
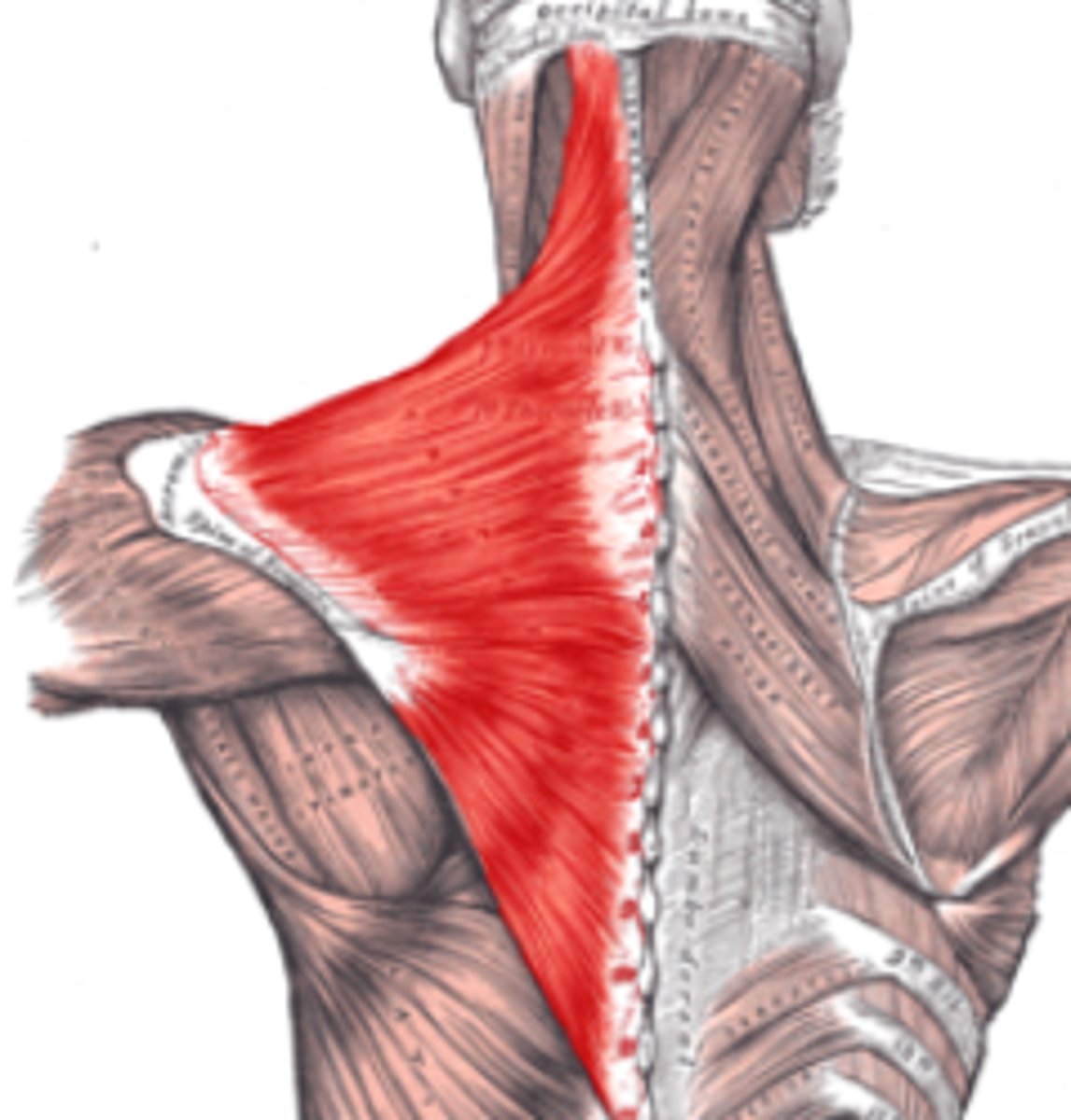
trapezius muscle
origin: occipital protuberance, nuchal ligament and spinous process of C7-T12
insertion: clavicle, acromion process, and scapular spine
action: extends and laterally flexes neck
platysma
origin: fascia of deltoid and pectoralis major
insertion: skin over inferior border of mandible
action: depresses lower lip; wrinkles skin of neck and upper chest; to express fear
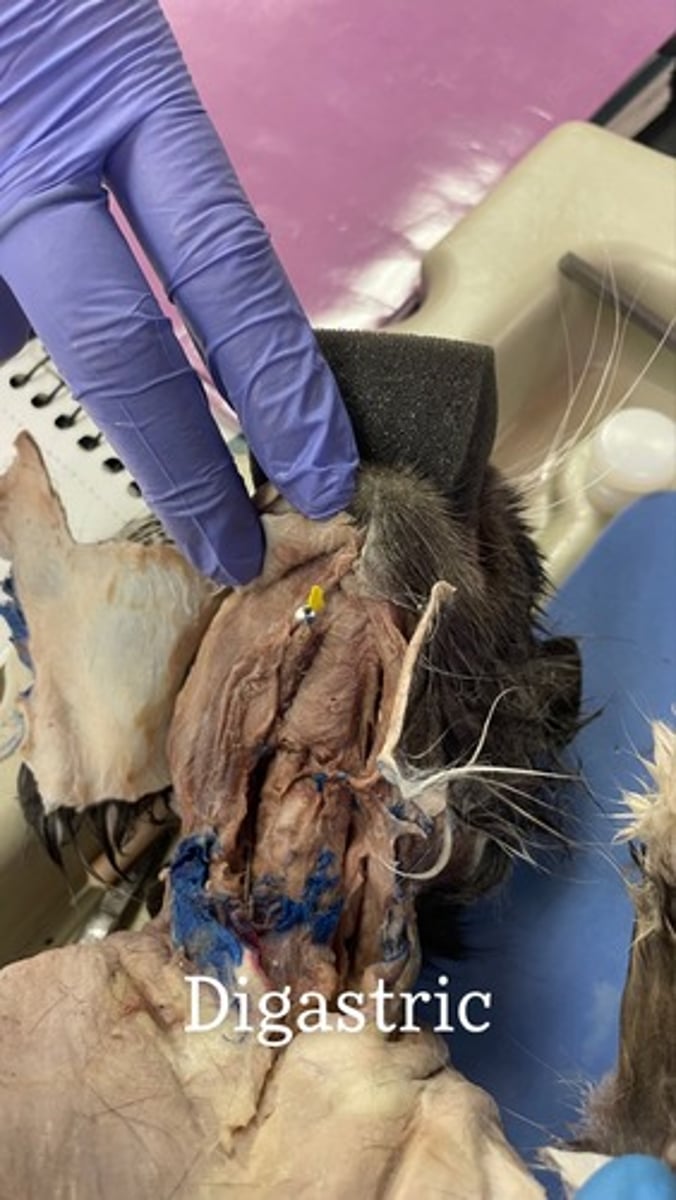
Digastric on cat
origin: mastoid process (posterior belly)
insertion: mandible near midline (anterior belly)
action: depresses and retracts mandible; elevates hyoid
Sternomastoid on cat
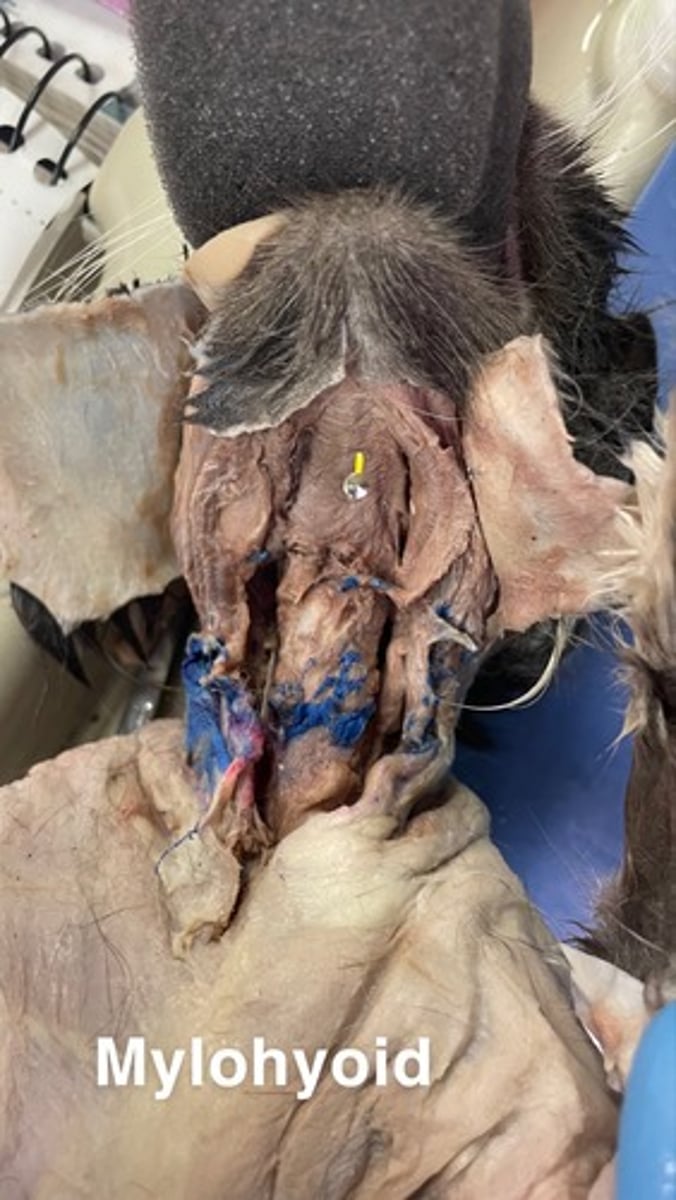
Mylohyoid on cat
origin: body of mandible
insertion: hyoid
action: elevates floor of mouth and tongue ; depresses mandible when hyoid is fixed
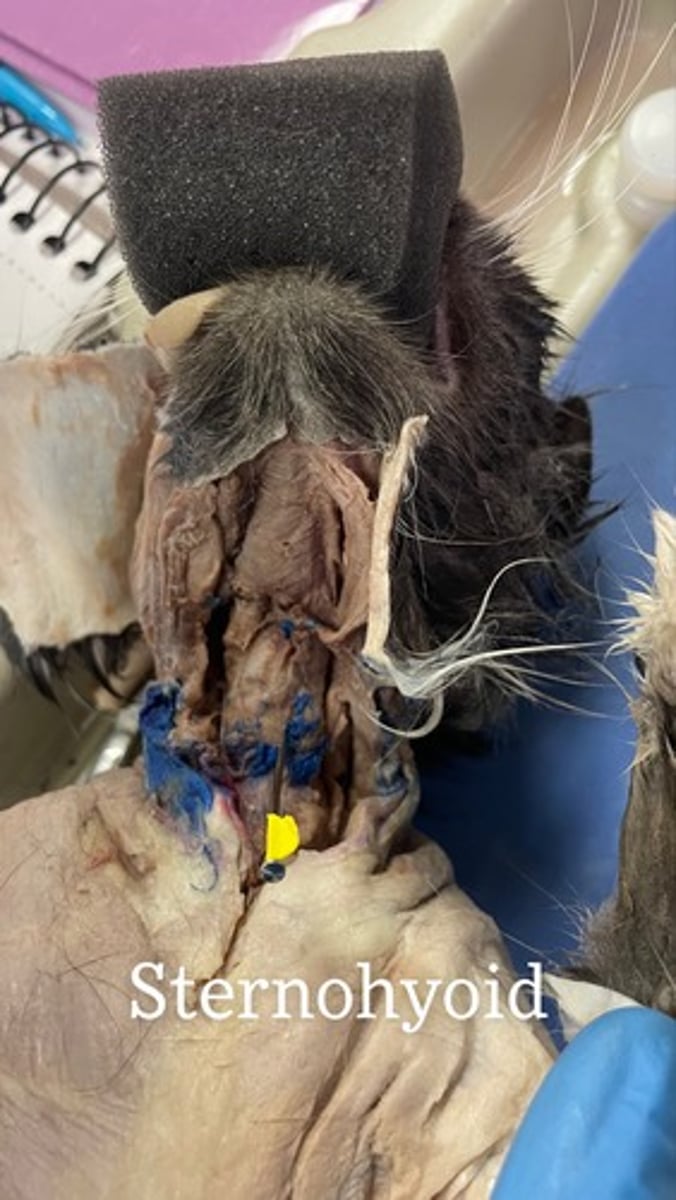
Sternohyoid on cat
origin: manubrium and first costal cartilage
insertion: hyoid
action: depresses hyoid; fixes hyoid when opening mouth
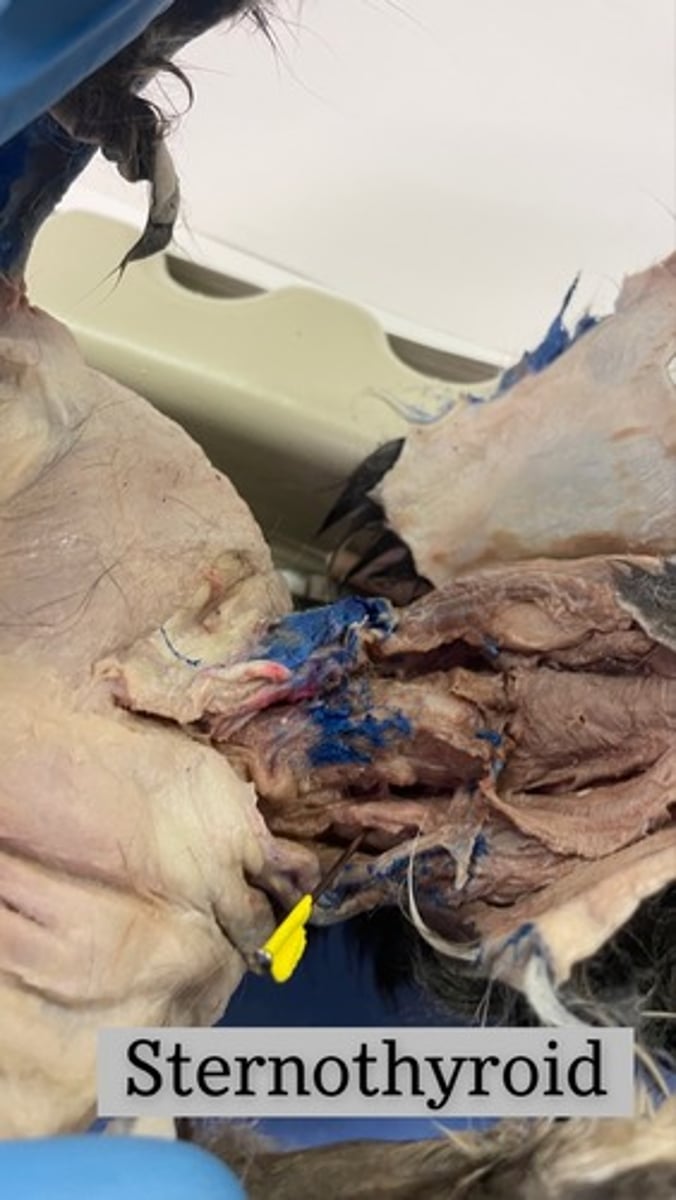
Sternothyroid on cat
origin: manubrium and first or second costal cartilage
insertion: thyroid cartilage
action: depresses larynx, fixes hyoid when opening mouth
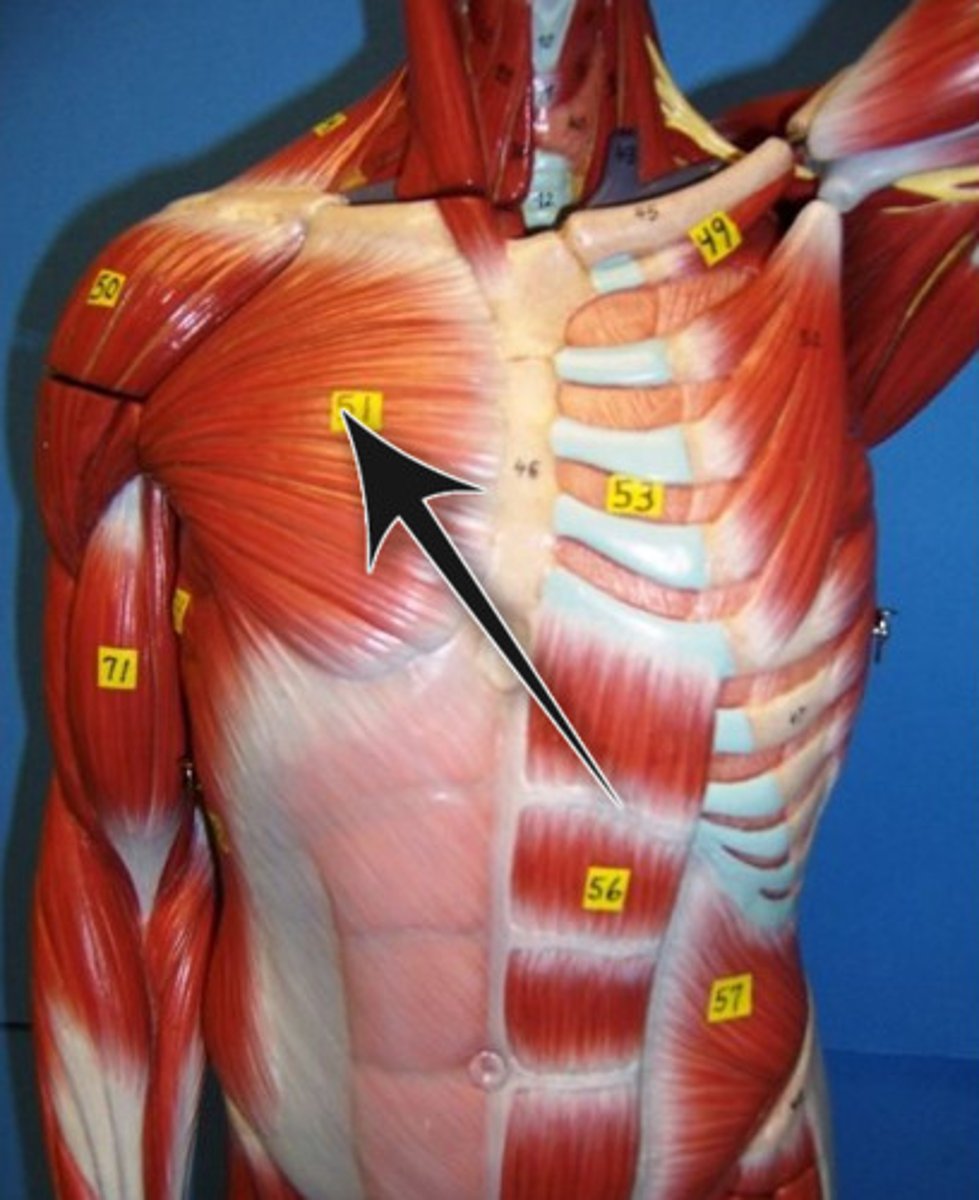
pectoralis major
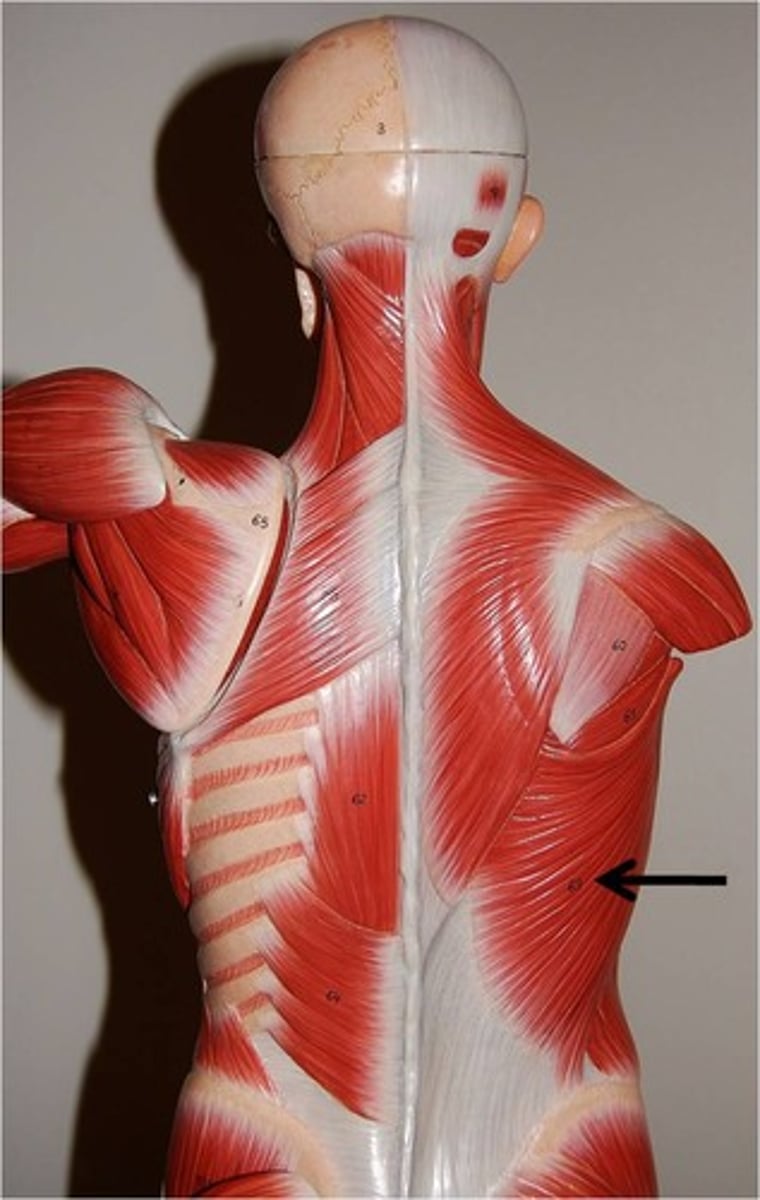
latissimus dorsi
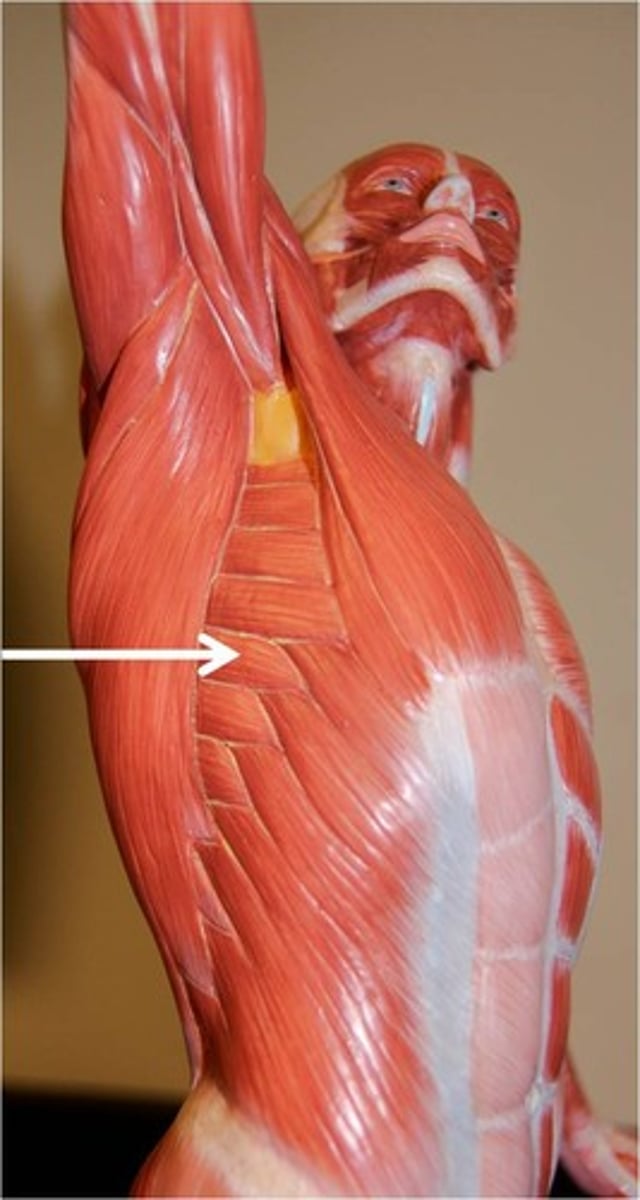
serratus anterior
external abdominal oblique
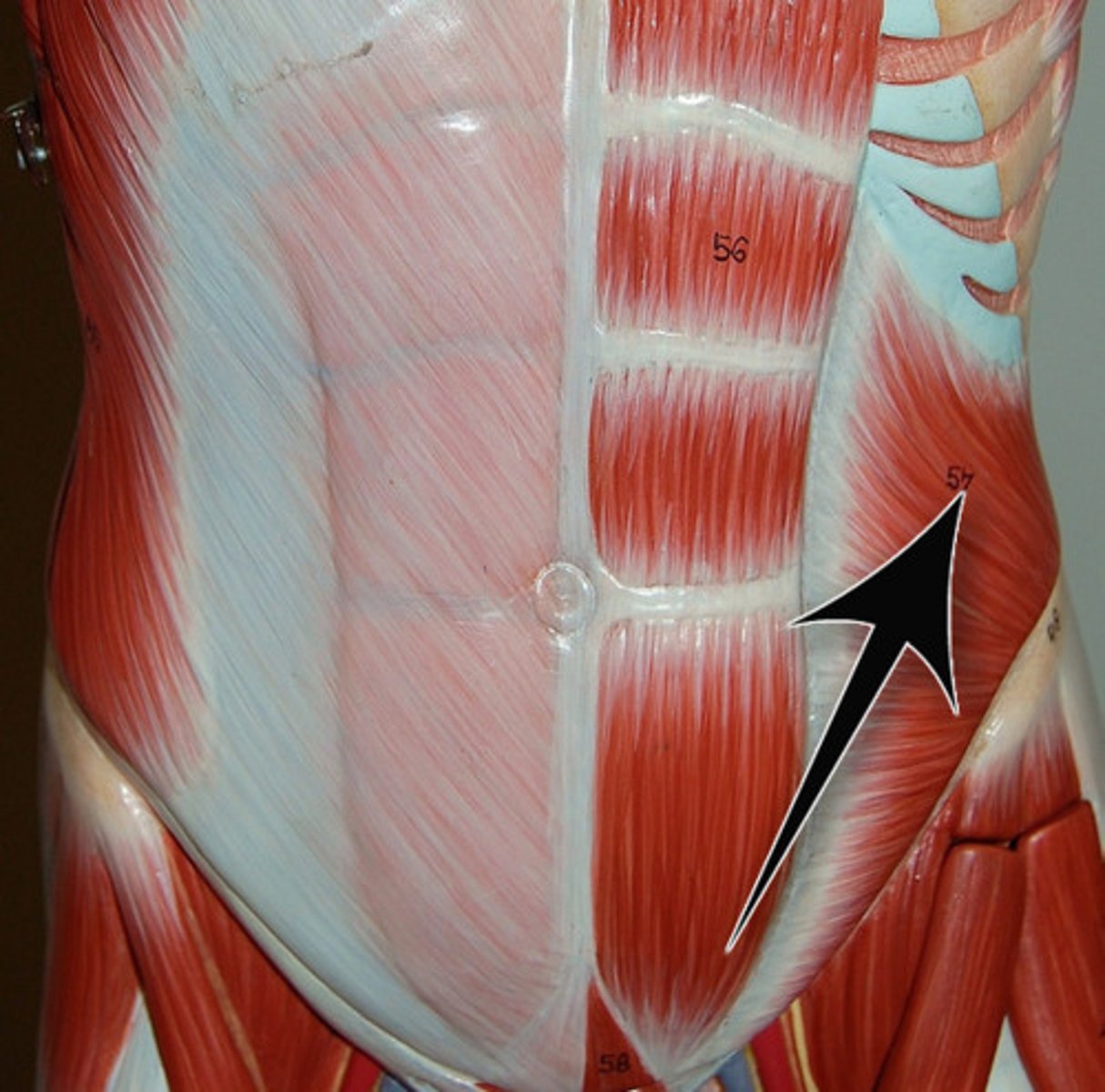
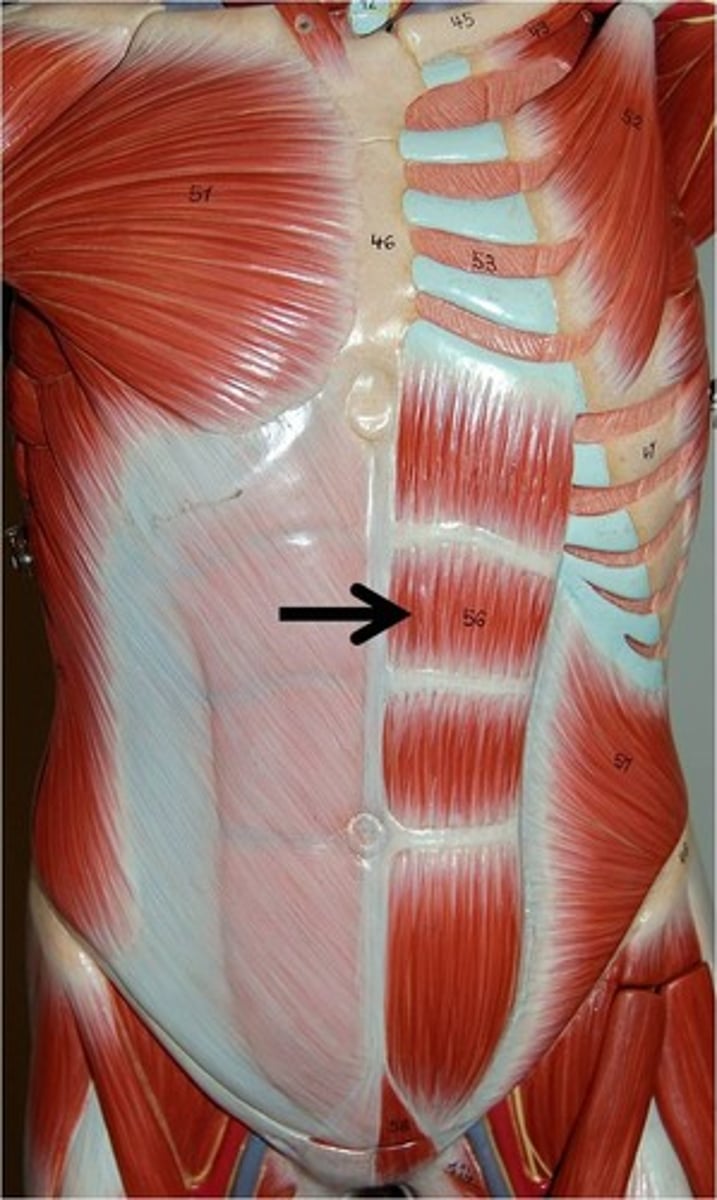
rectus abdominis
internal abdominal oblique
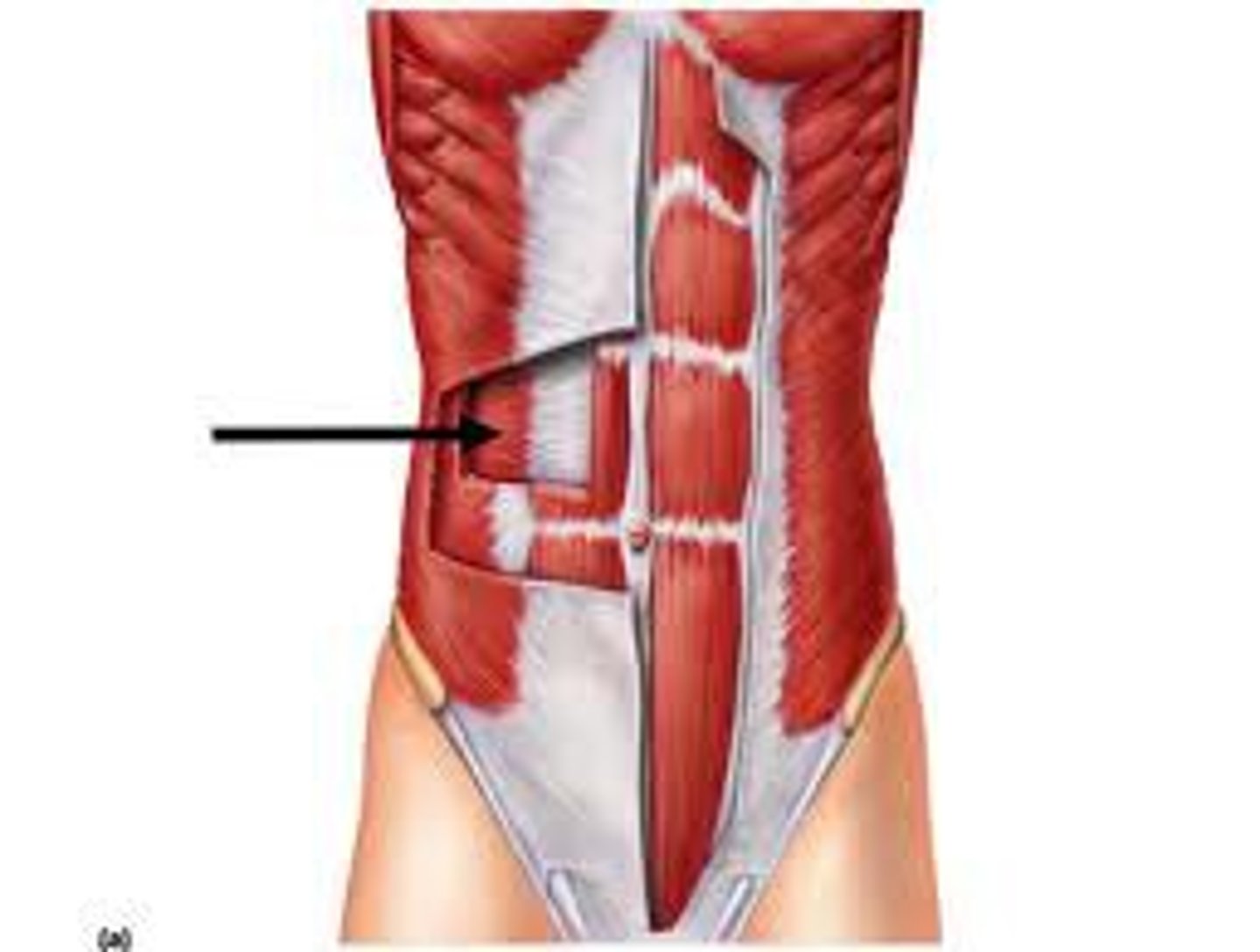
transversus abdominis
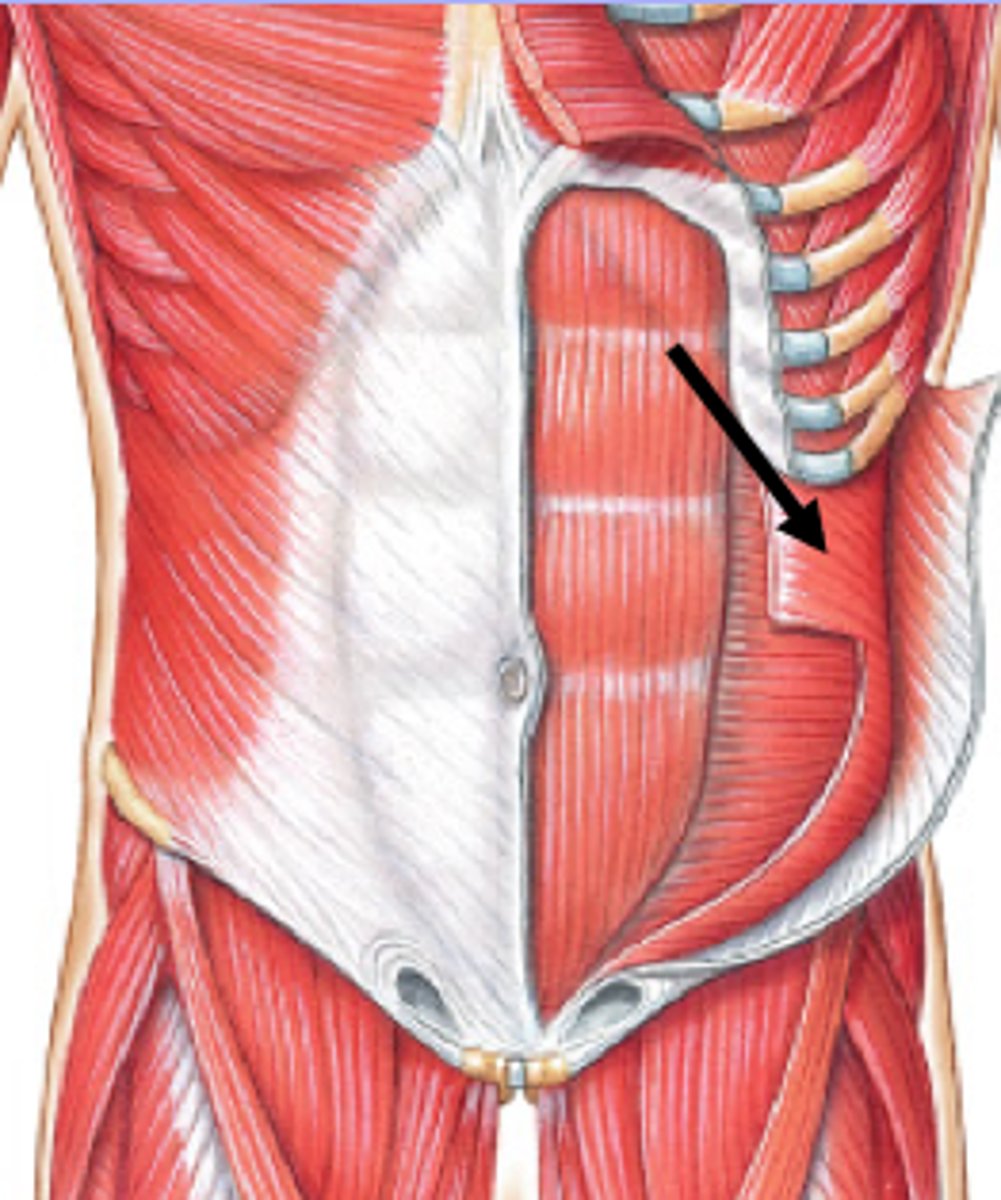
trapezius
levator scapulae
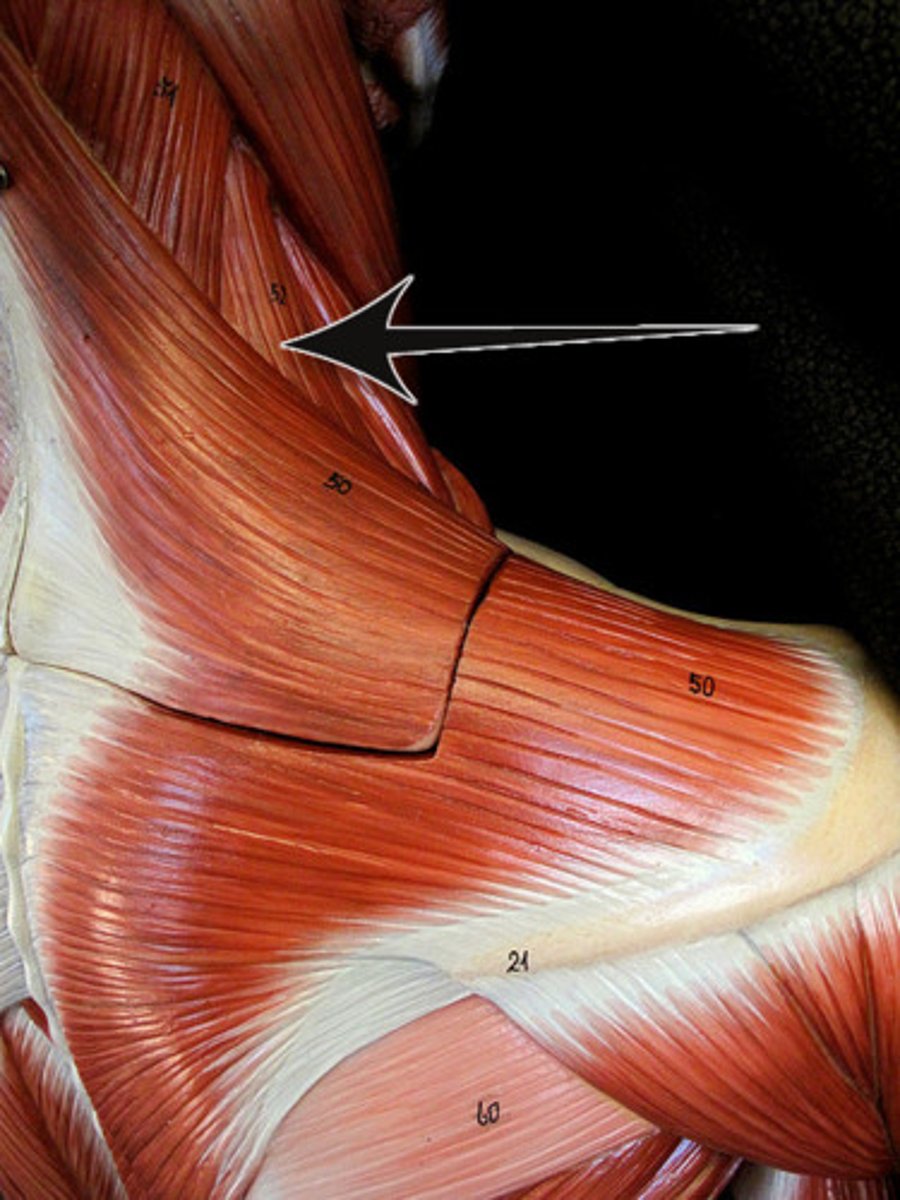
Rhombdoideus Major
rhombdoideus minor
pectoralis minor
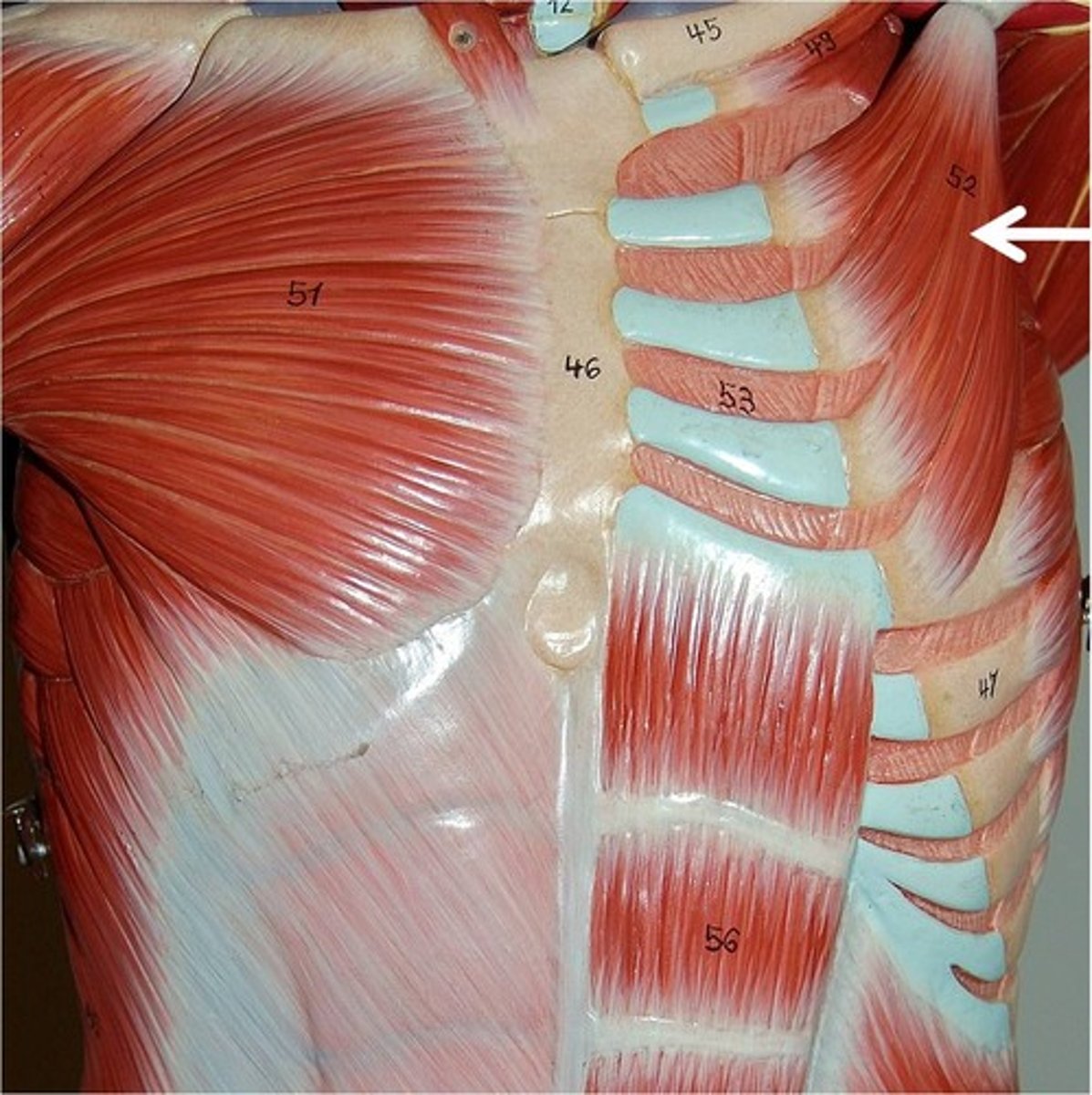
subscapularis
anterior surface of scapula
teres minor
origin: lateral border of scapula
insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
*** superior to teres major
teres major
origin: lateral border of scapula
insertion: medial crest of intertubercular groove
** inferior to teres minor
deltoid
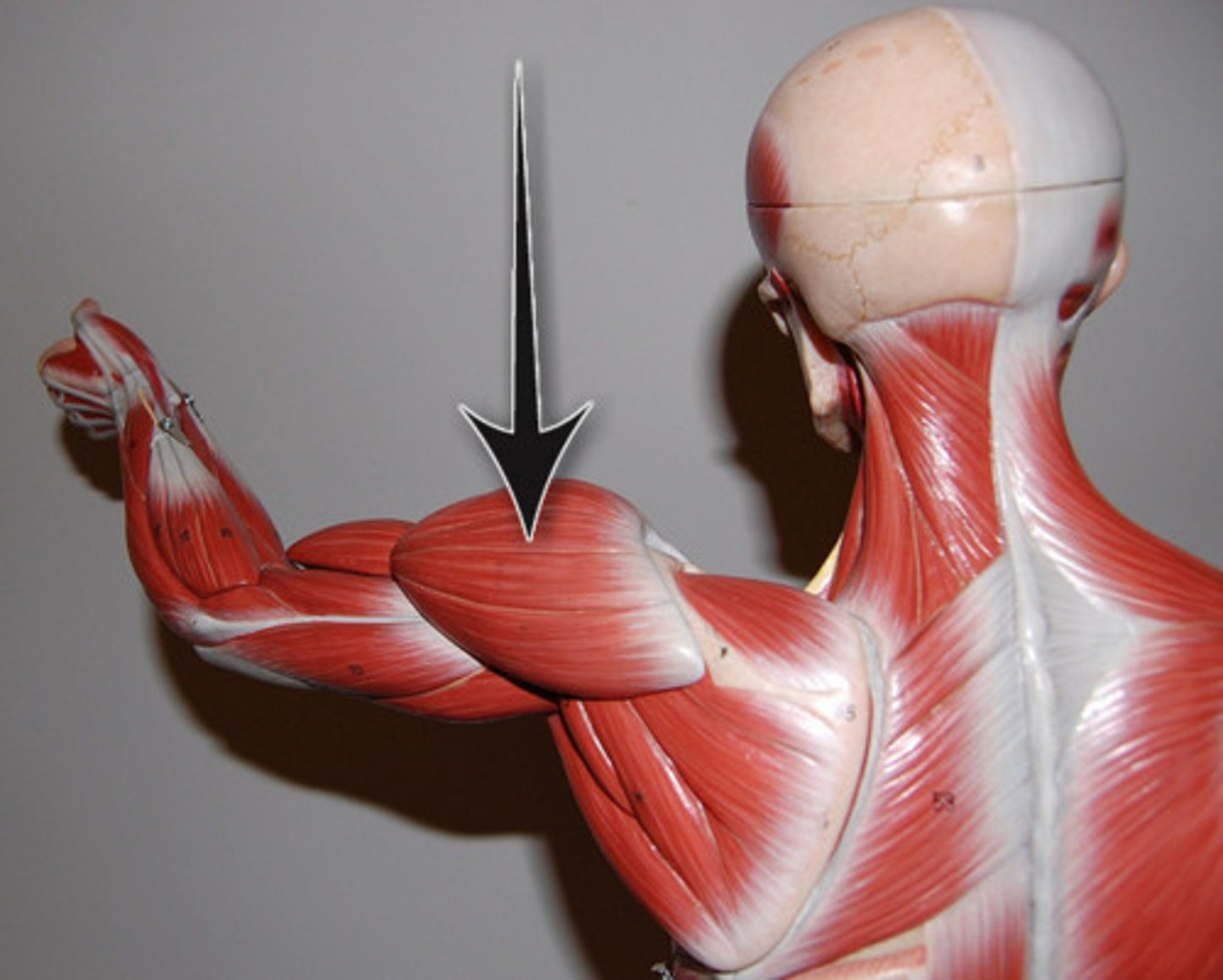
Corachobrachialis
origin: coracoid process of scapula
insertion: midshaft of humerus
** deep to short head of biceps brachii (is medial of the biceps)
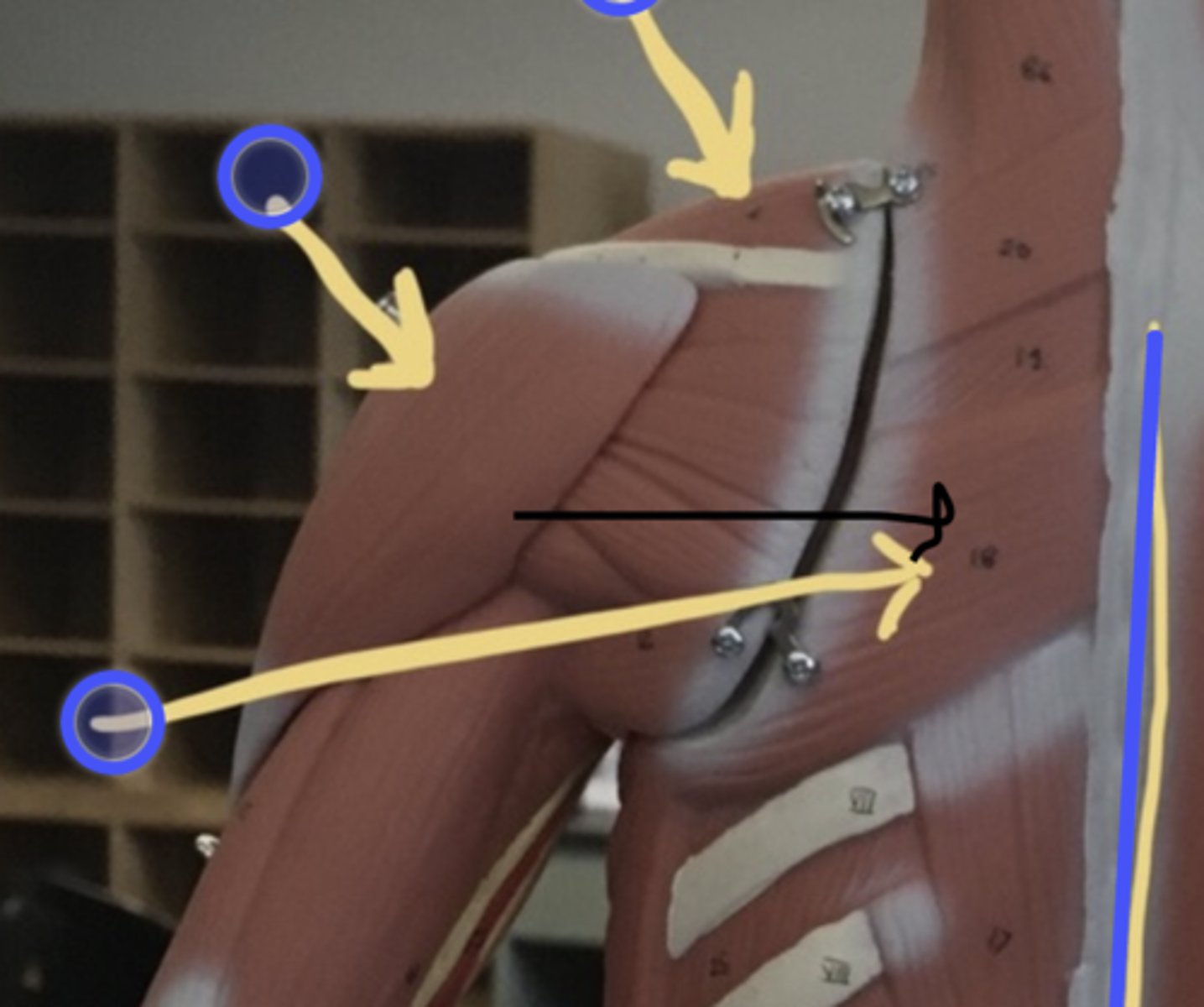
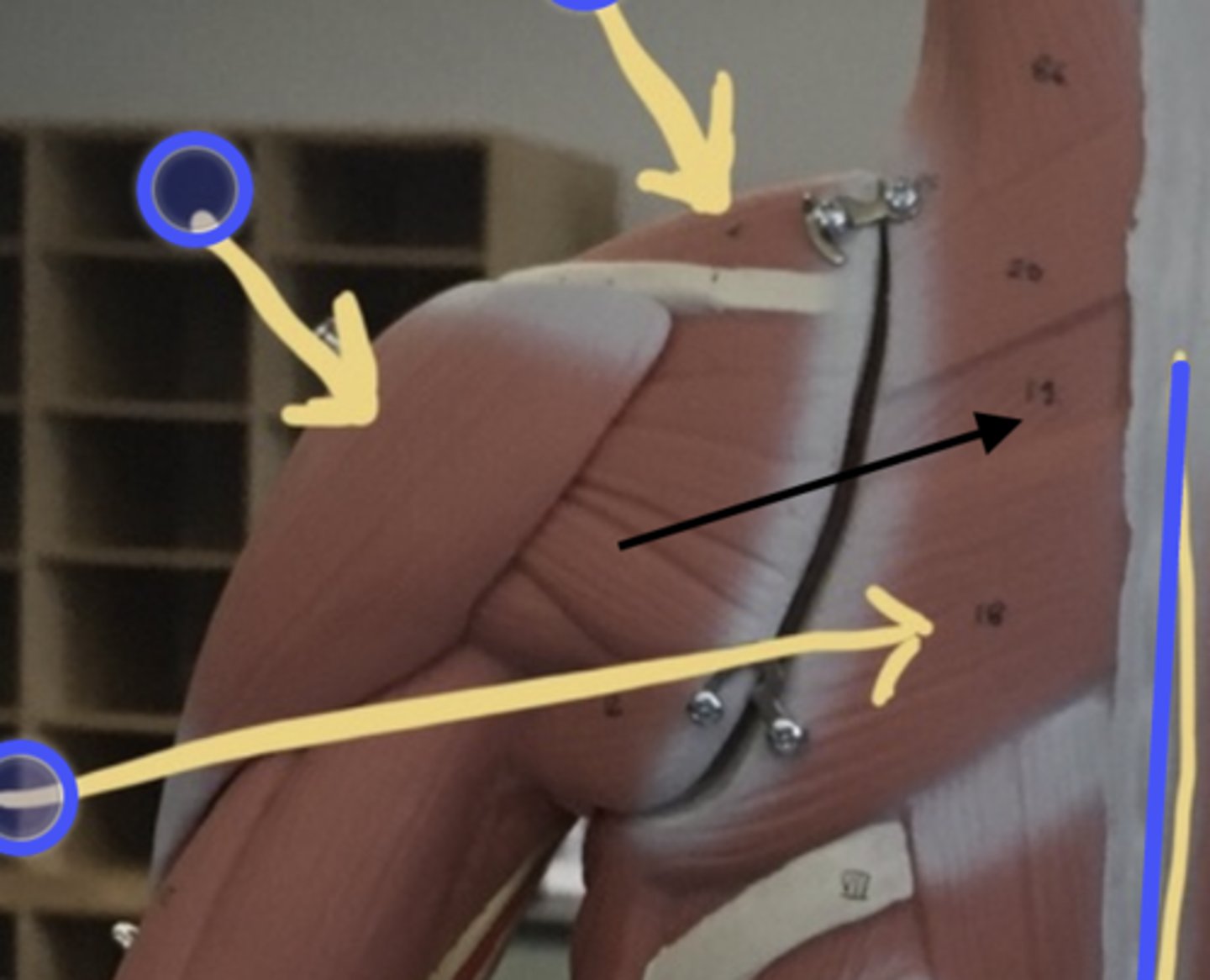
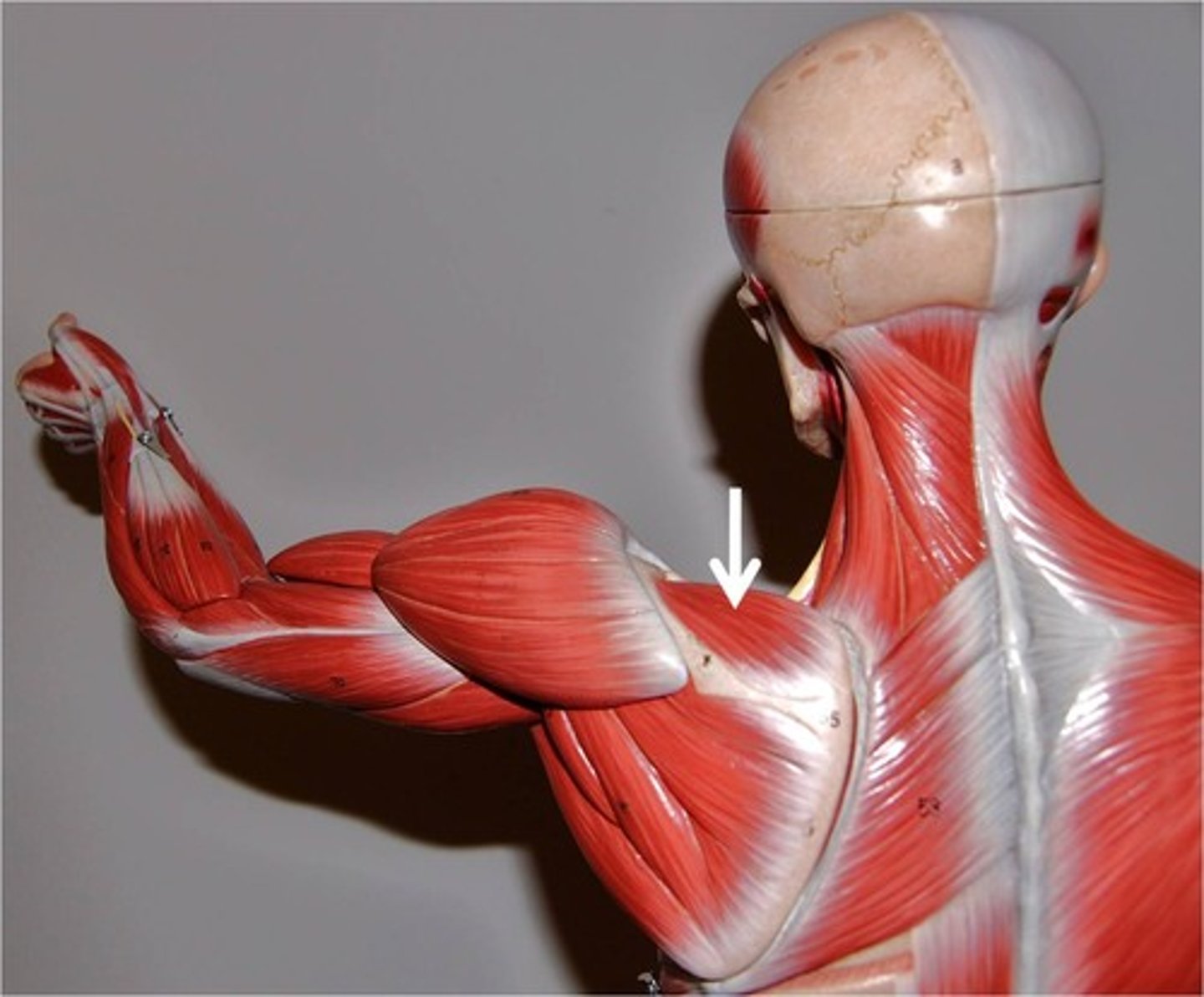
supraspinatus
origin: supraspinous fossa of scapula
insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
posterior side of scapula, superior to scapular spine
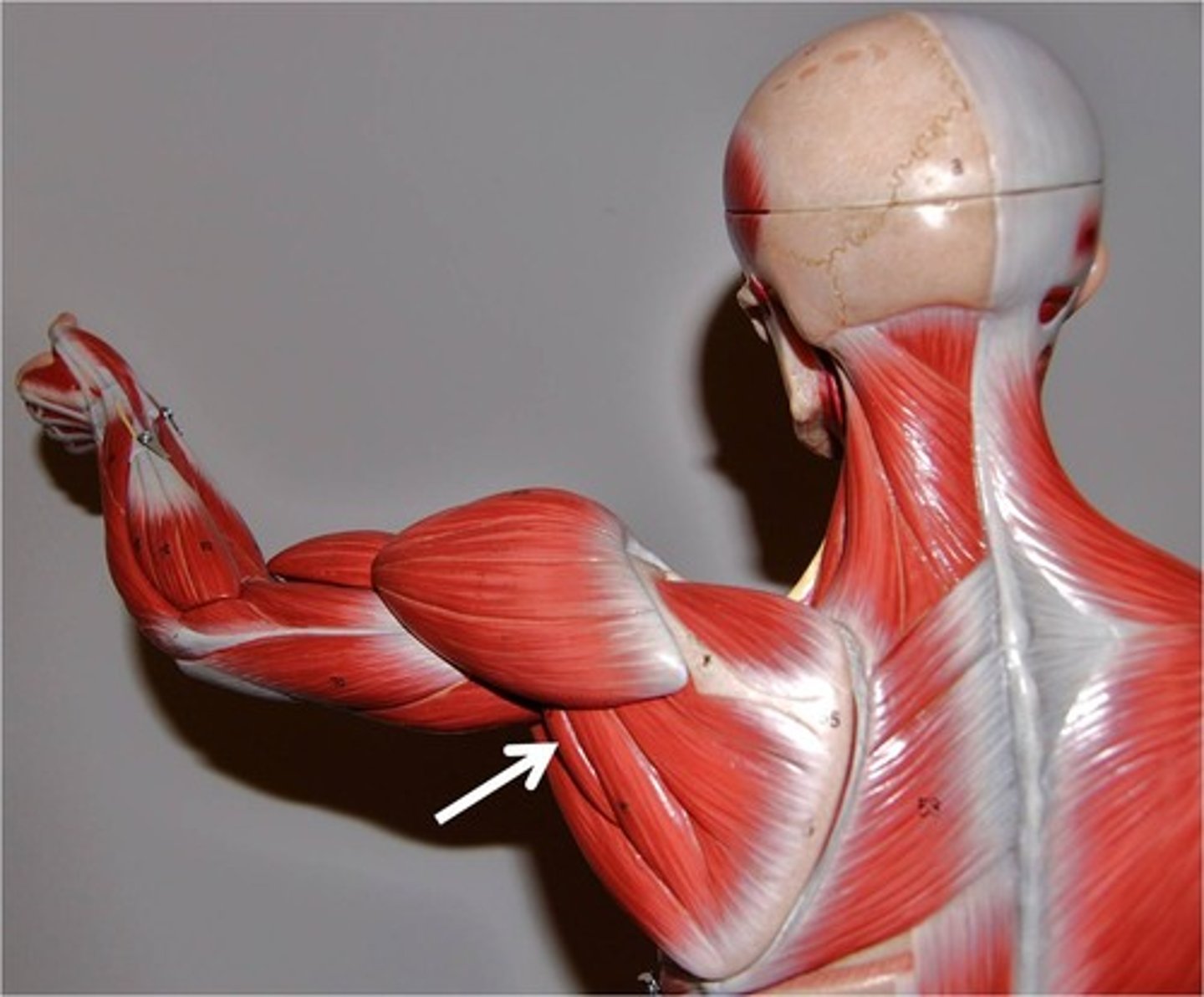
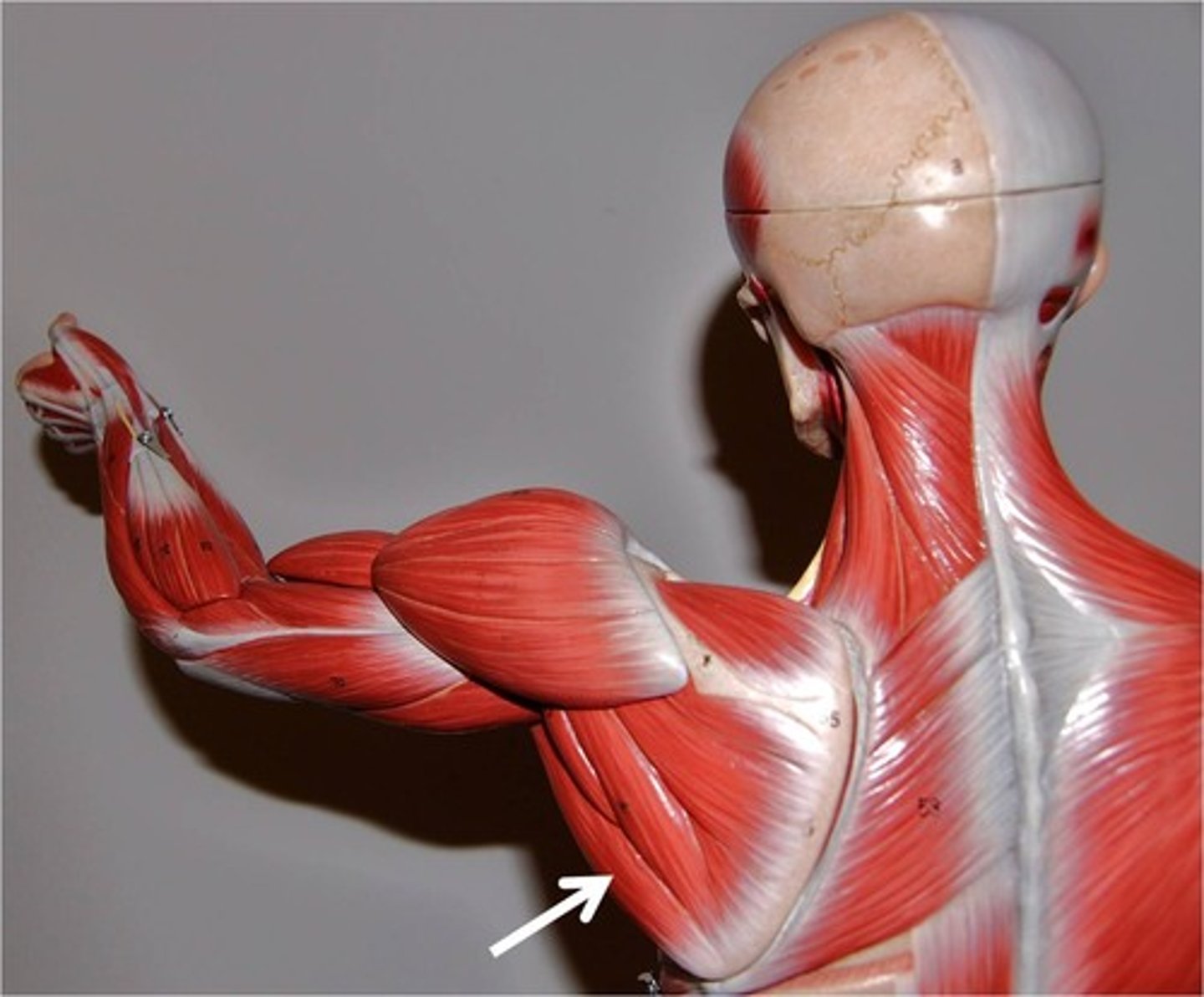
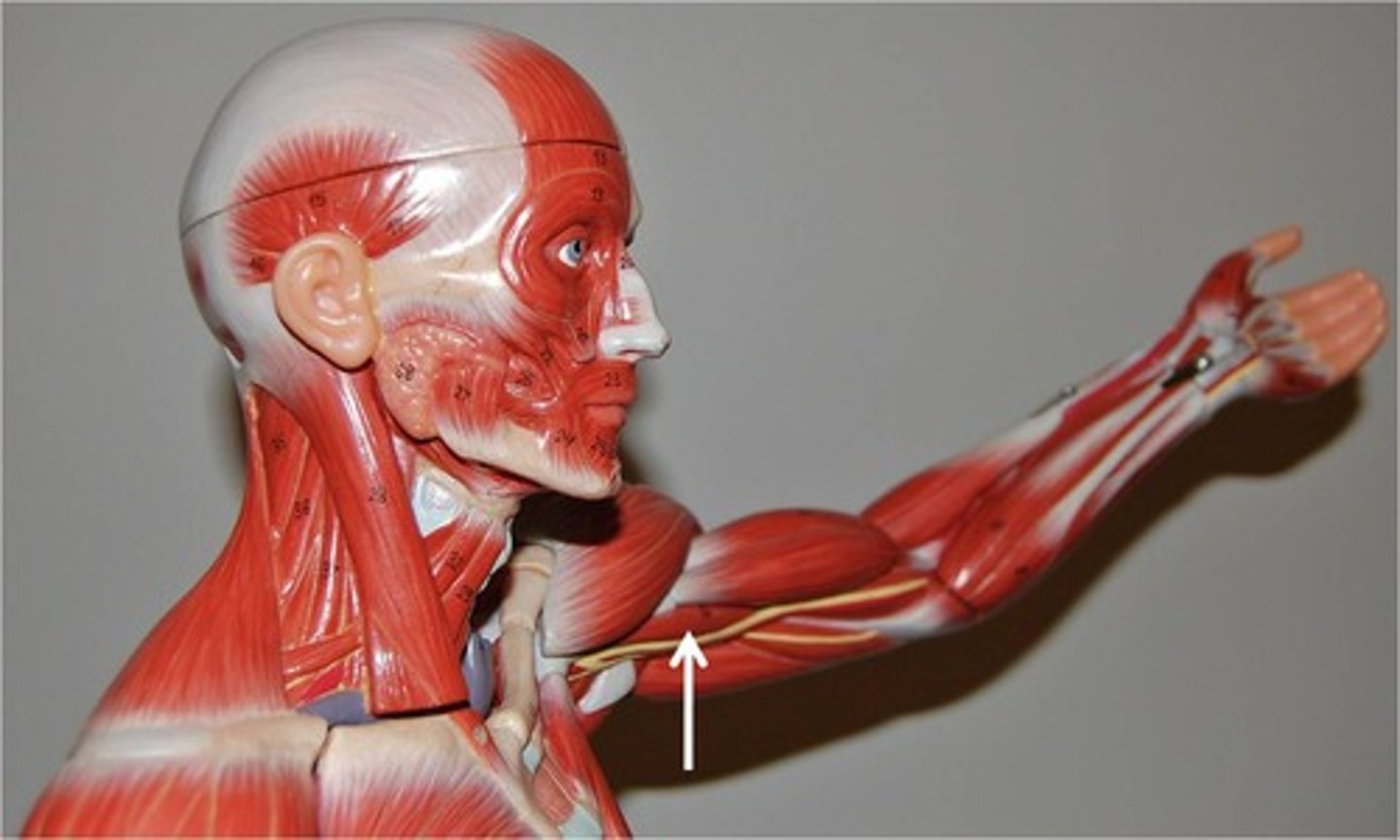
Infraspinatus
origin: infraspinous fossa of scapula
insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
inferior to scapular spine, posterior surface
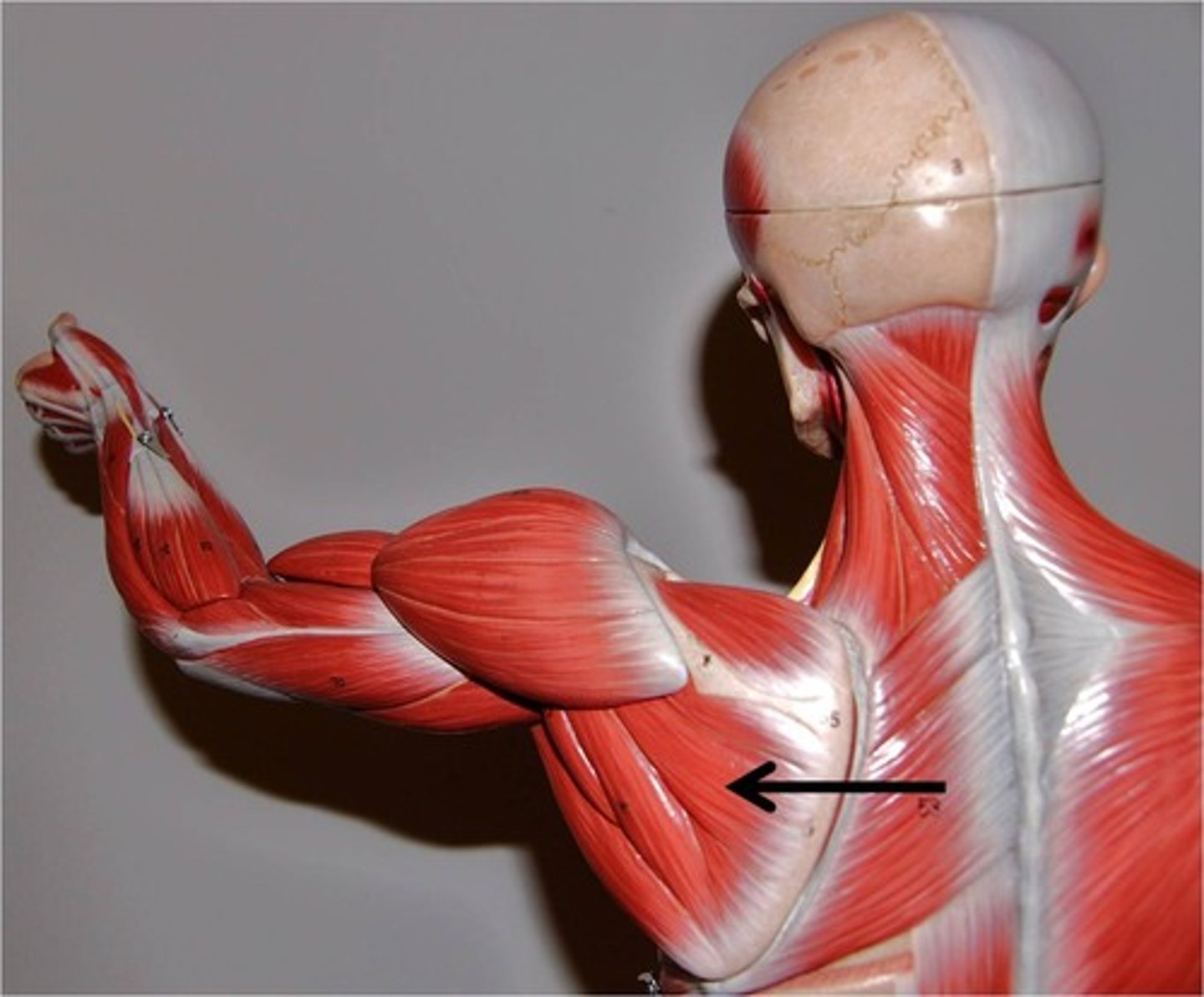
long head of biceps brachii
Origin: supraglenoid tubercle
Insertion: radial tuberosity
lateral side of biceps
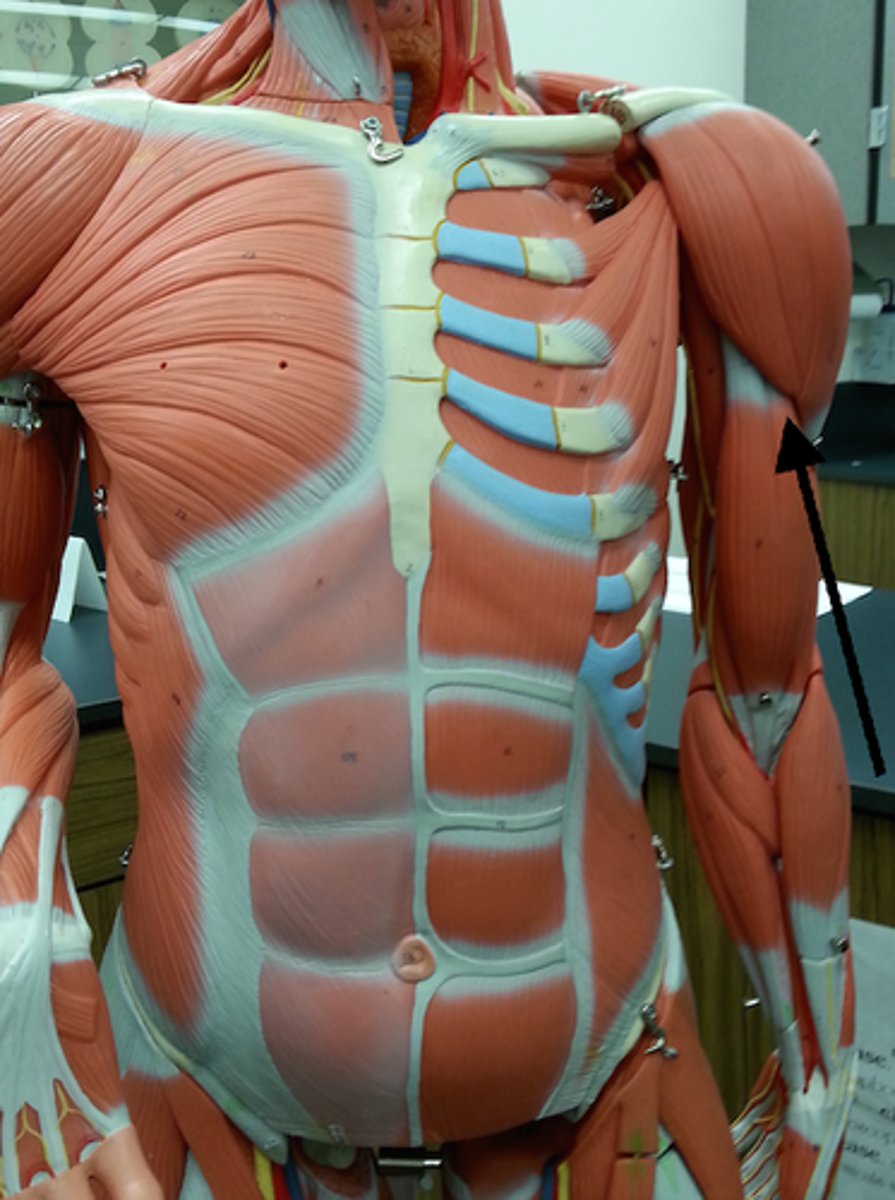
short head of biceps brachii
Origin: coracoid process of scapula
Insertion: radial tuberosity
medial head, superficial to coracobrachialis (same origin)
lateral head of triceps brachii
origin: humeral shaft
insertion: posterior surface of ulna
(olecranon fossa)
** anterior to the long head, the most lateral
medial head of triceps brachii
Origin: posterior surface of shaft of humerus
Insertion: olecranon process of the ulna
** most medial, posterior
long head of triceps brachii
Origin: Infraglenoid tubercle of lateral border of scapula
insertion: olecranon process
** between the medial and lateral heads, they all insert at the olecranon process
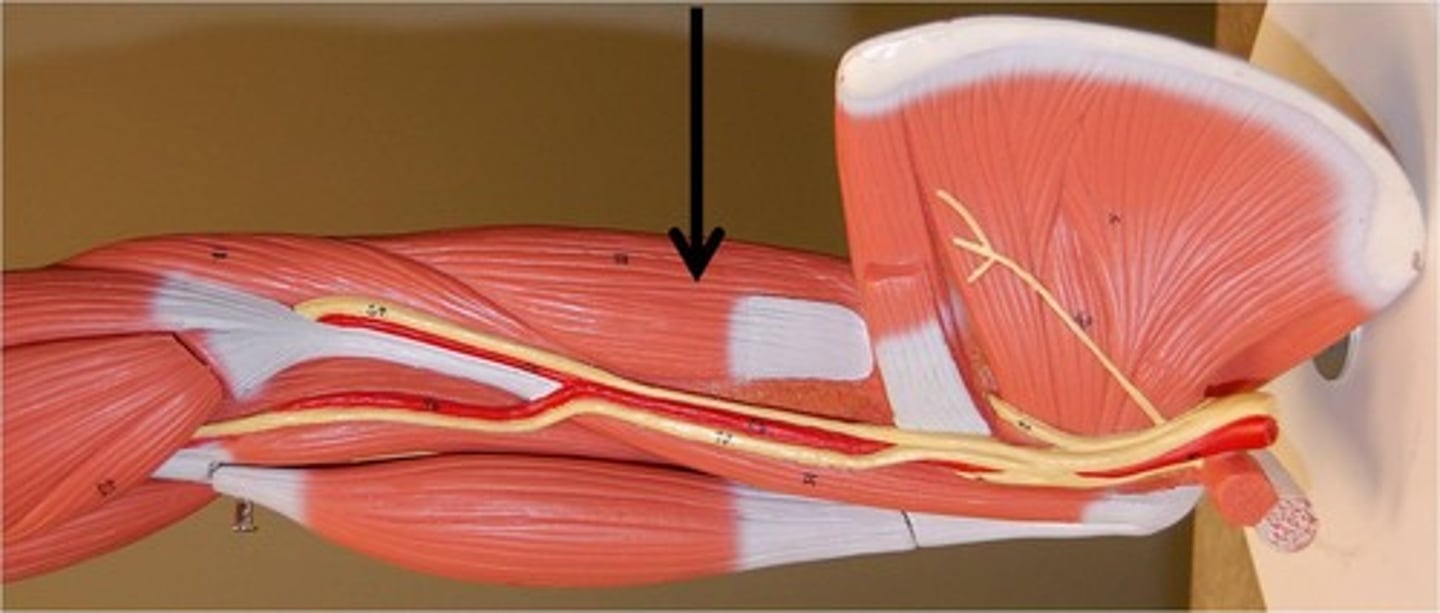
Triceps (all heads) insertion
olecranon process of ulna
brachialis
Origin: anterior surface of humerus.
Insertion: coronoid process of ulna.
*** between the biceps and triceps
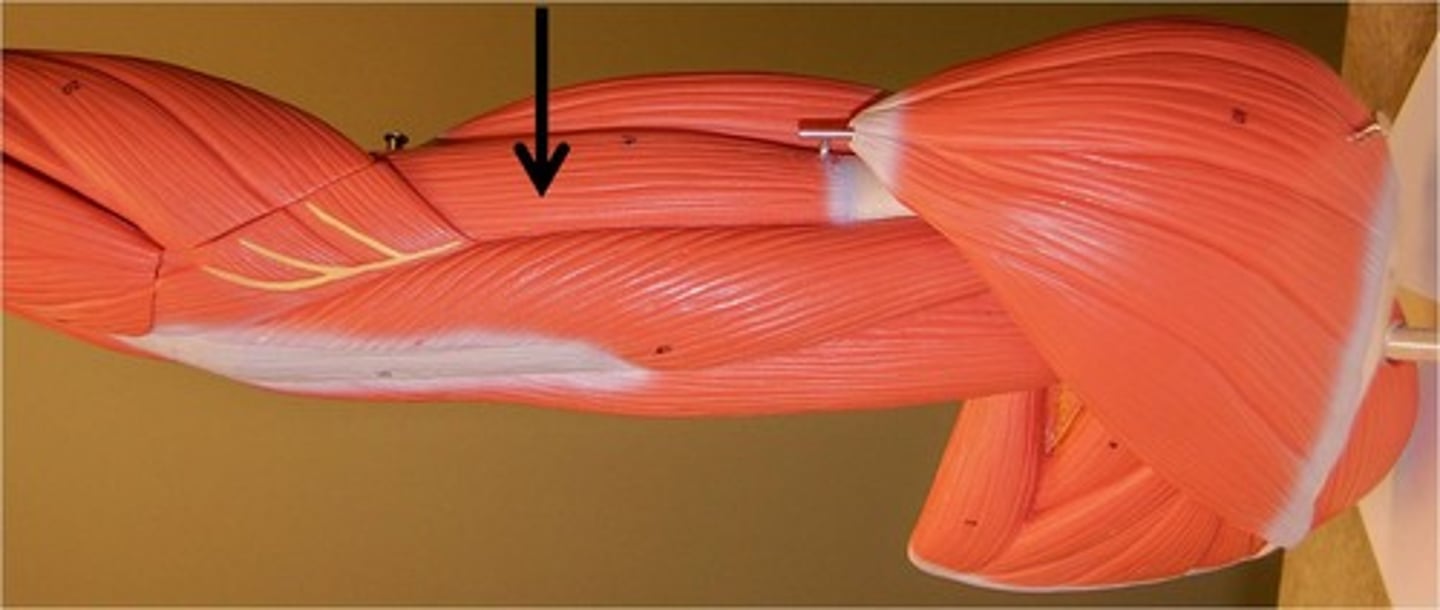
pronator teres
origin: medial epicondyle of humerus
insertion: radius
** diagonal from medial humerus to lateral radius
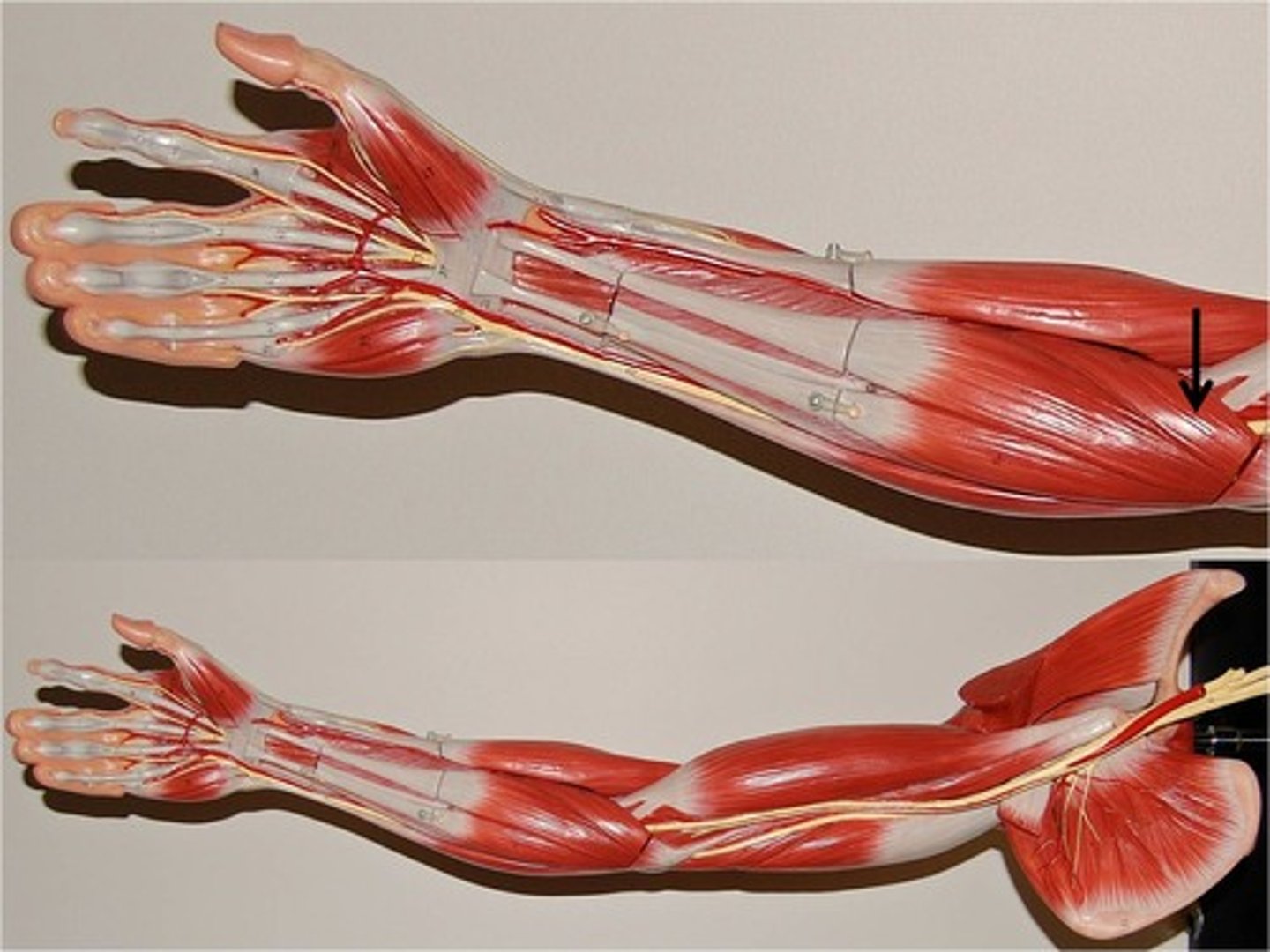
Brachioradialis
Origin: Lateral ridge at distal end of humerus
Insertion: radial styloid process
** originates at humerus, passes over brachialis, then inserts at end of radius (thumb side)
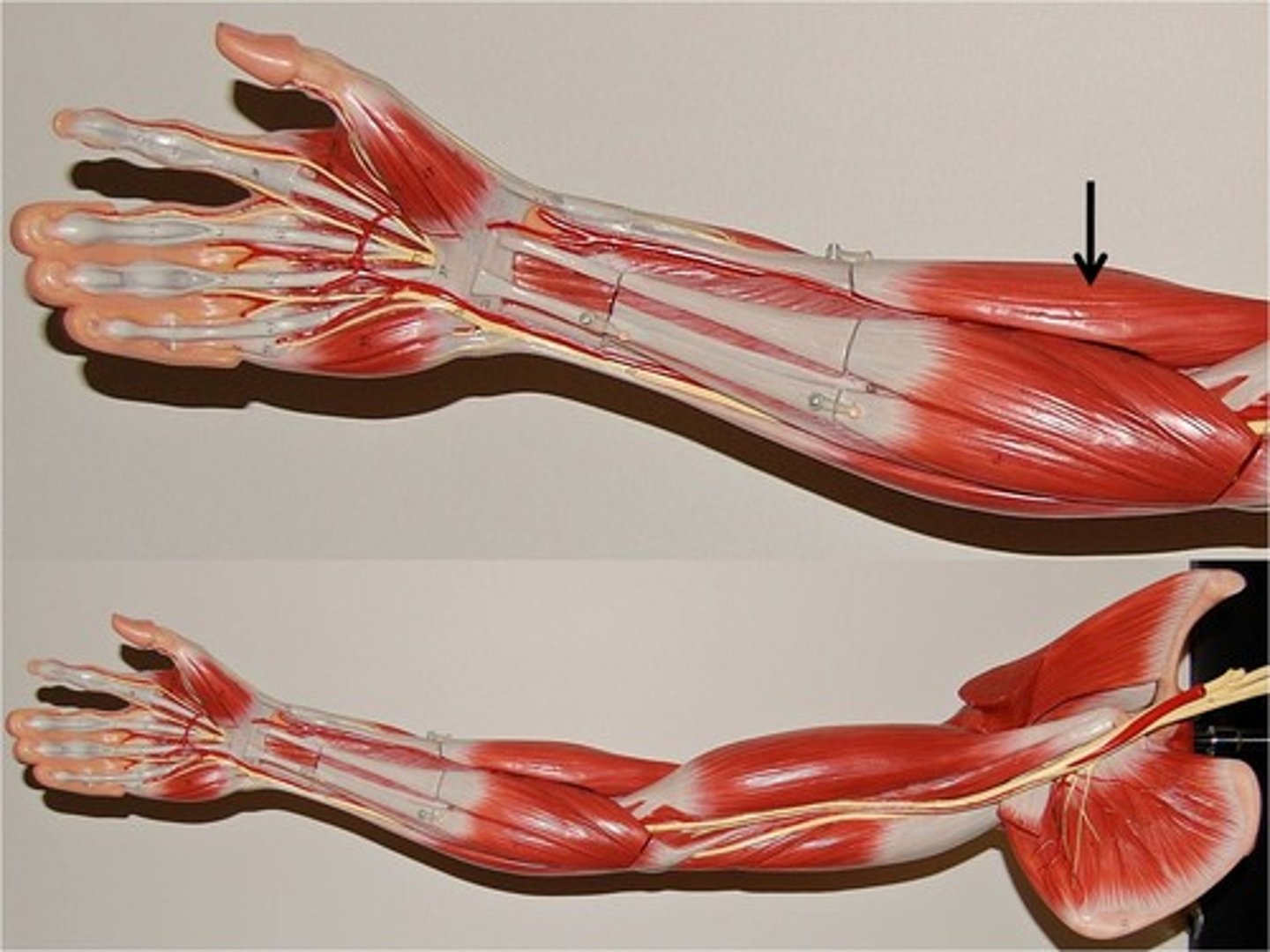
flexor carpi radialis
Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: Bases of second and third metacarpal bones
** most superficial, central in anatomical position
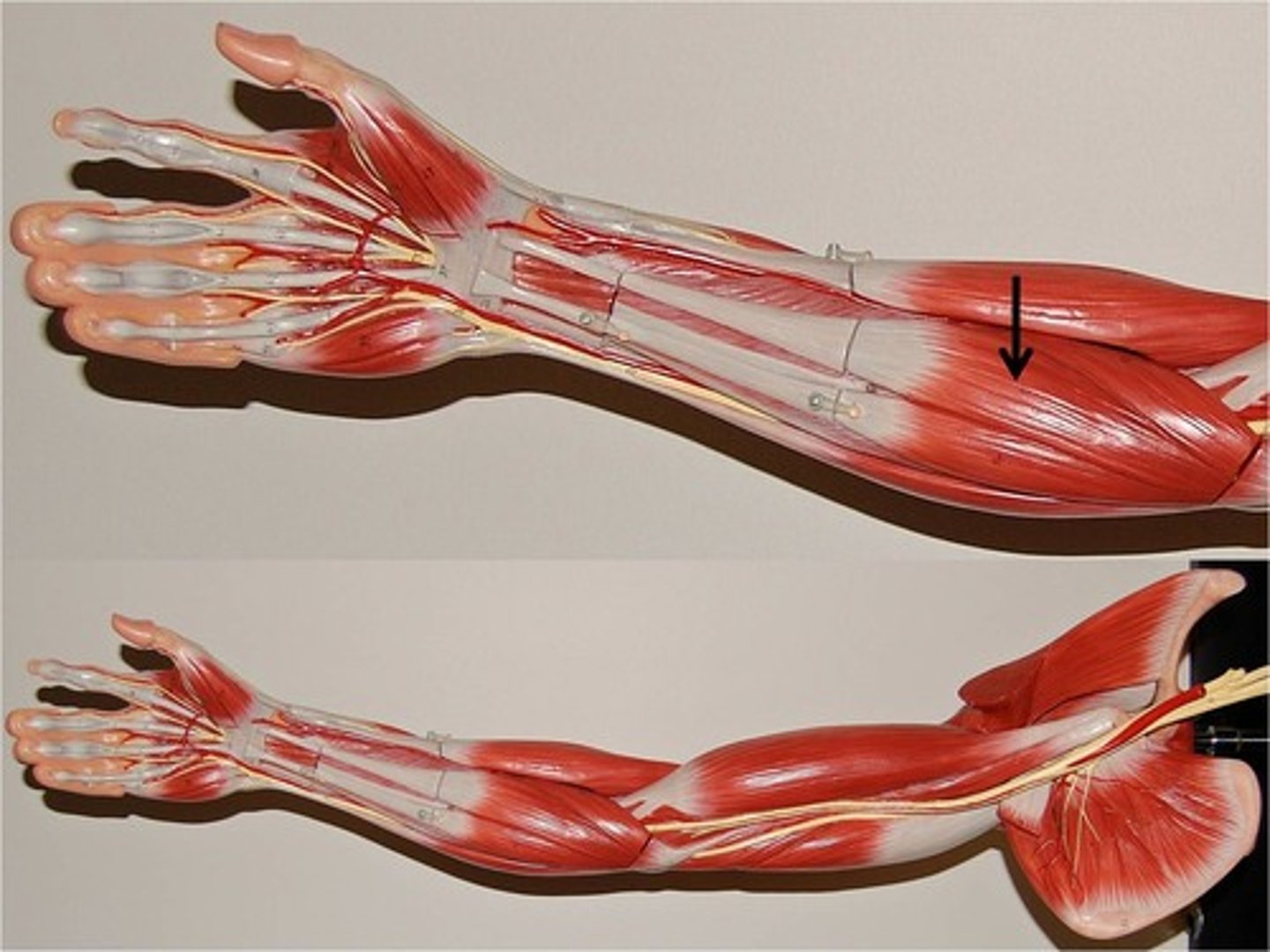
flexor carpi unlaris
** medial, pinky side to flexor carpi ulnaris, superficial
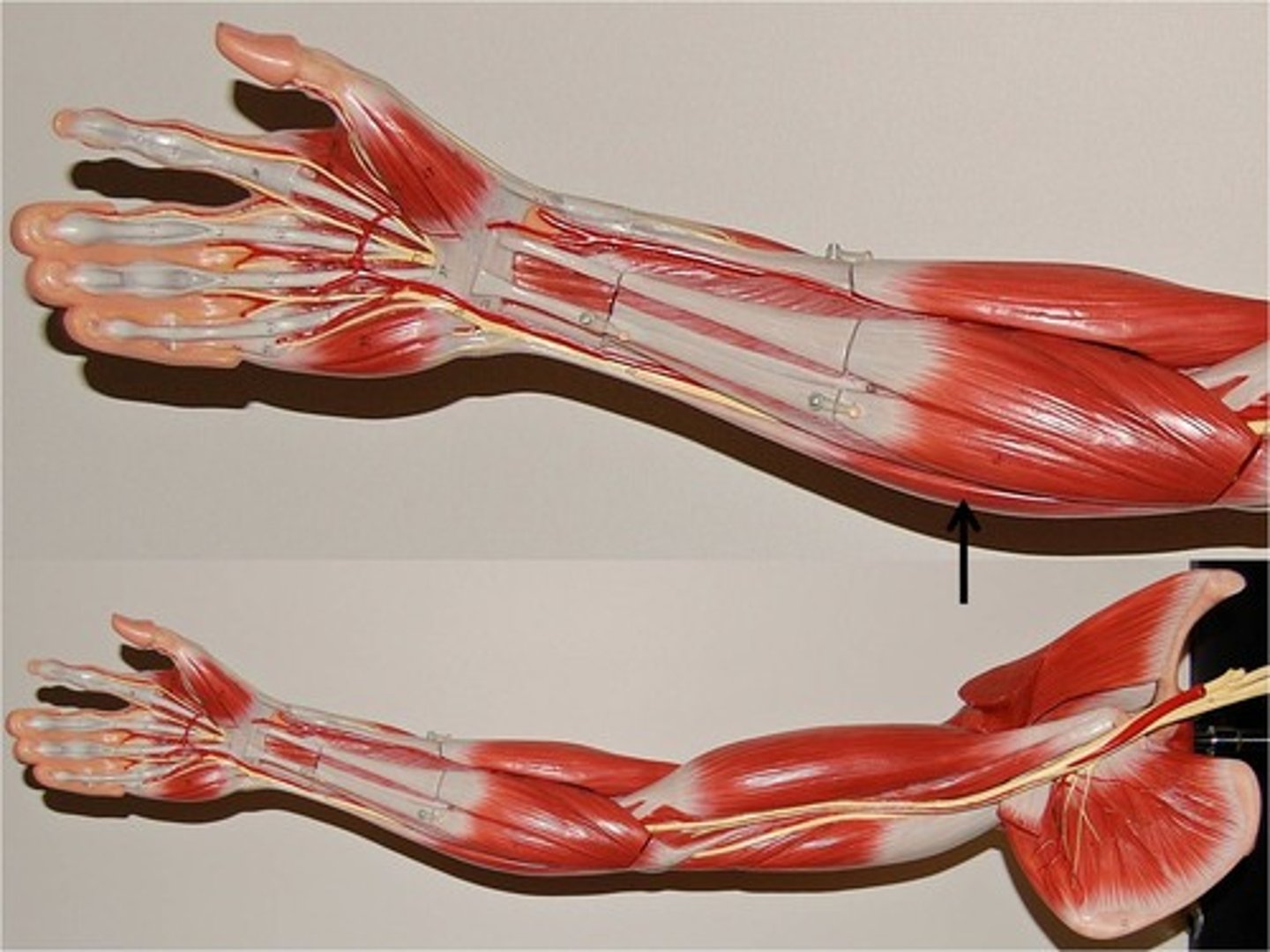
palmaris longus
between flexor carpii radialis and ulnaris
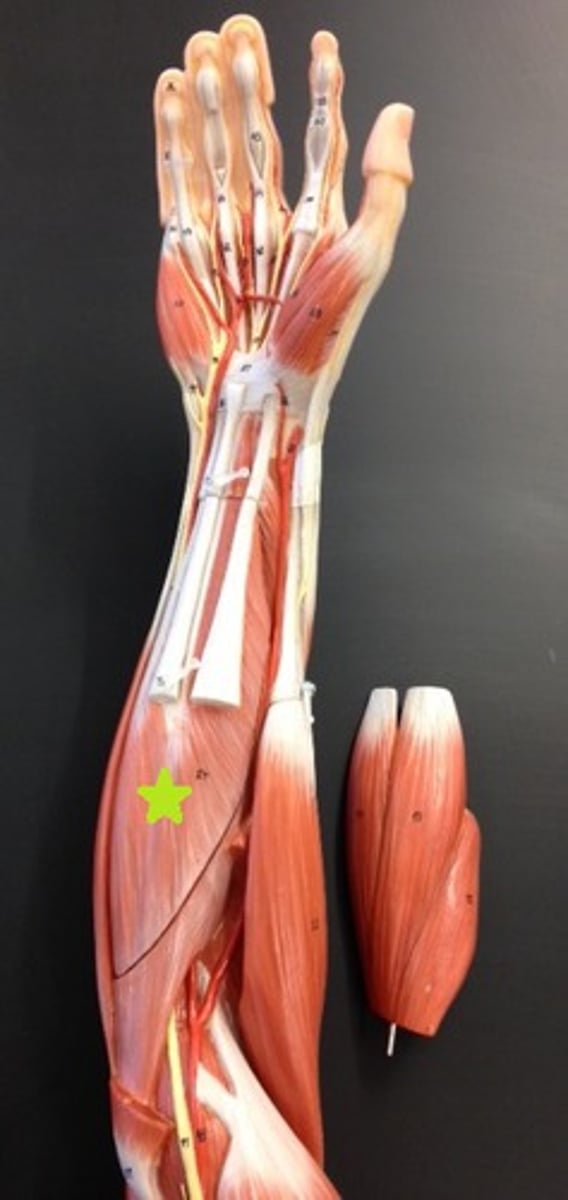
3 superficial forearm muscles
flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, and palmaris longus, these being superficial in anatomical position
flexor digitorum superficialis
under the flexor carpi radialism palmaris longus, and flexor carpi ulnaris -- so this is still a flexor so iti is superficial but it is a deeper flexor,
its own level
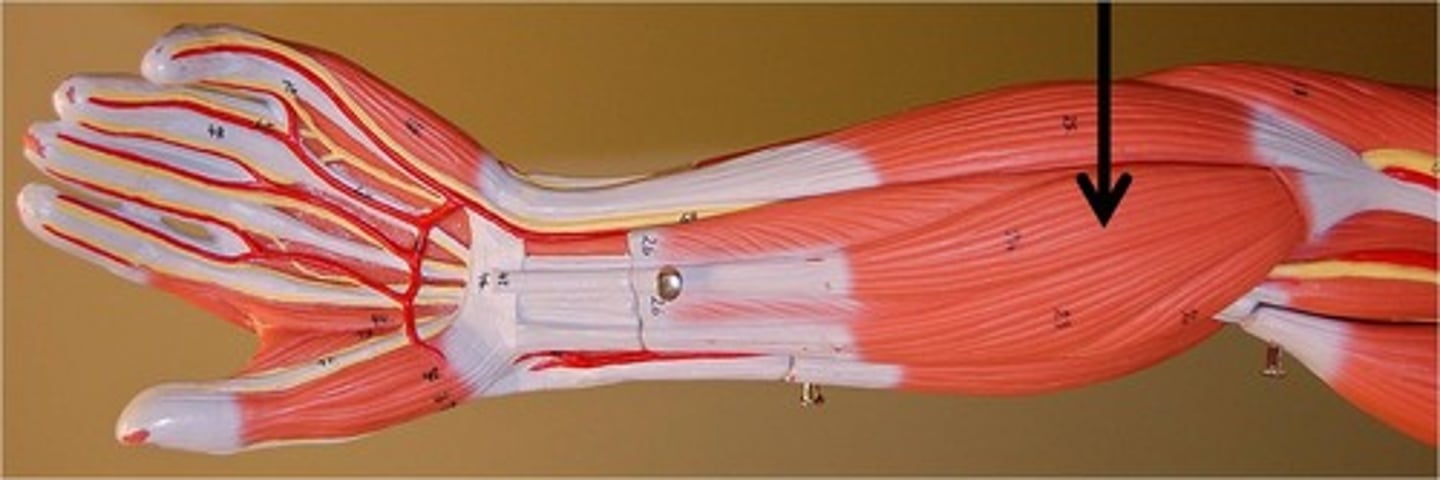
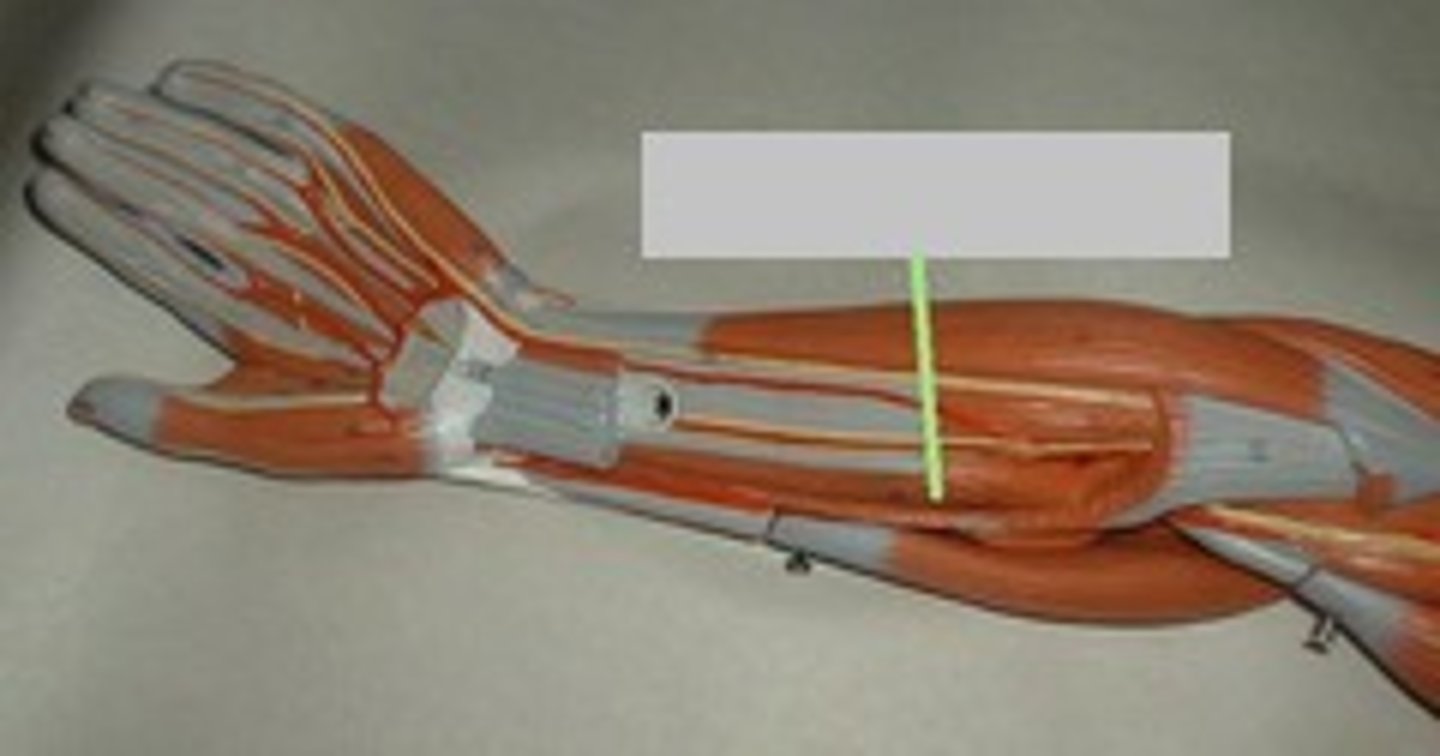
supinator
Origin: Lateral epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: Radius
** short muscle on same level as flexor digitorm superficialis
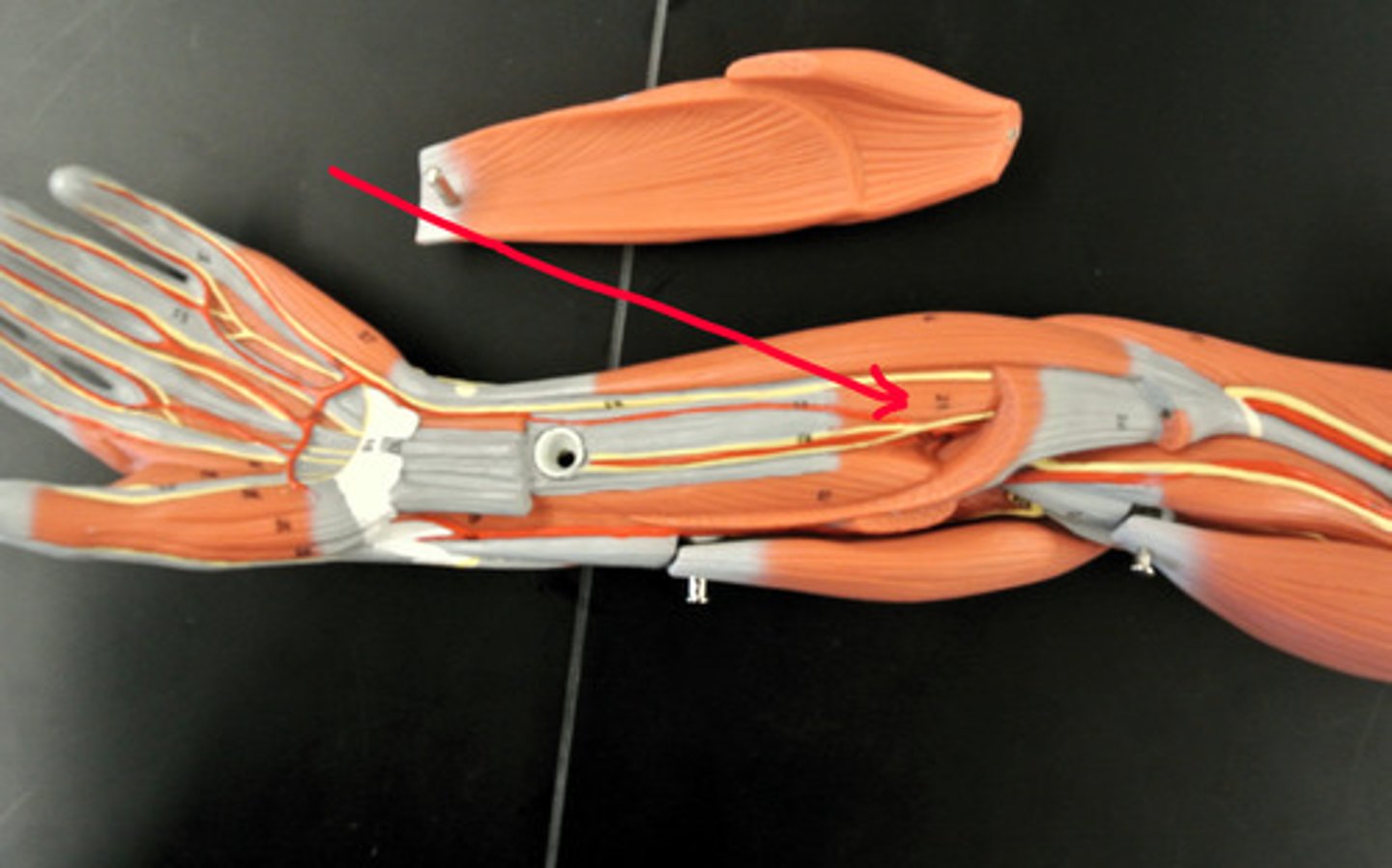
flexor pollicis longus
origin: radius
insertion: distal phalanx of thumb
flexor digitorum profundus
deeper than flexor digitorum superficialis
Deep layer of flexor forearm
flexor digitorum profundus, flexor pollicus longus,
extensor carpi ulnaris
deepest in anatomical position, but superficial posteriorly
extensor digitorum
large, central, on posterior surface
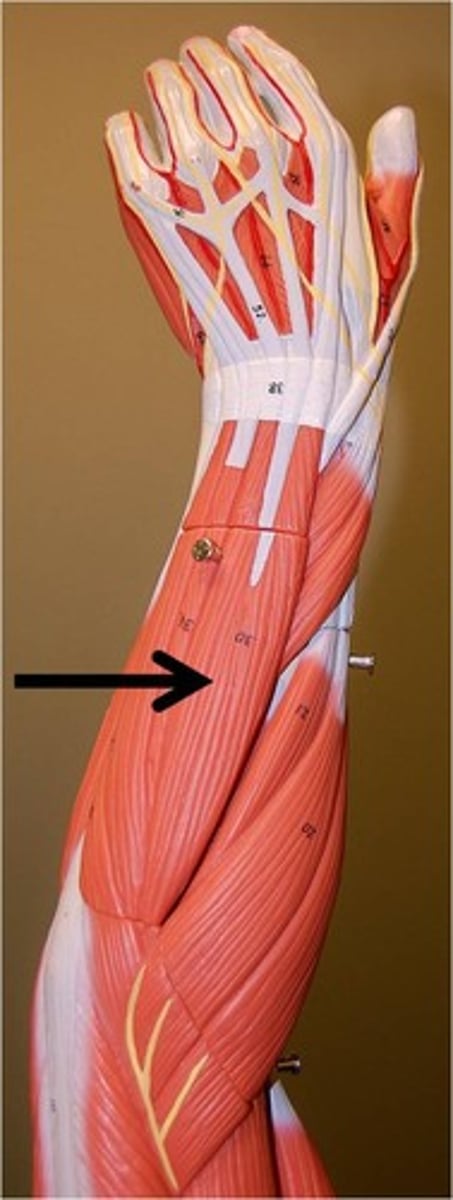
extensor carpi radialis longus
closer to thumb than brevis, posterior surface, thumb side
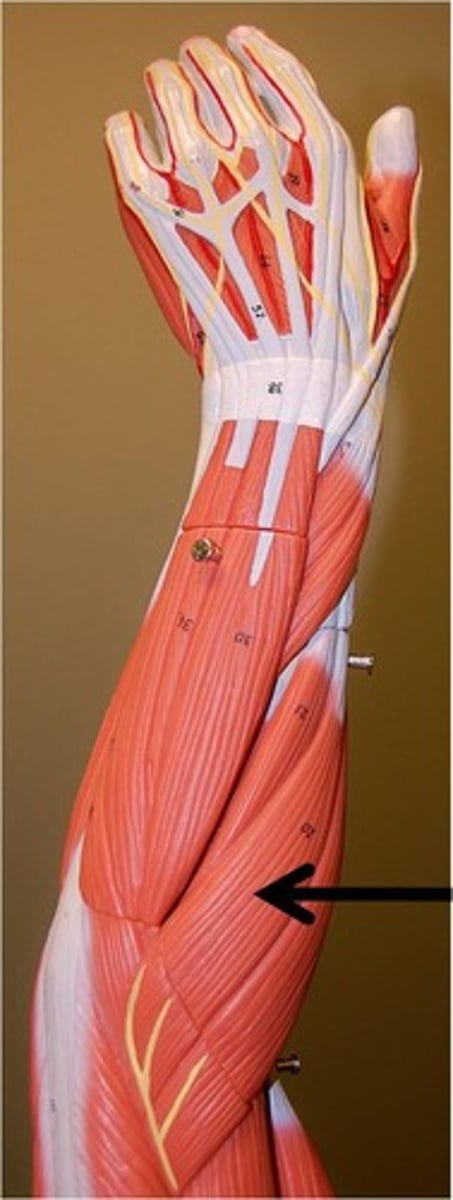
extensor carpi radialis brevis
medial to the longus when in anatomical position so it is closer to first finger
gluteus maximus

gluteus medius
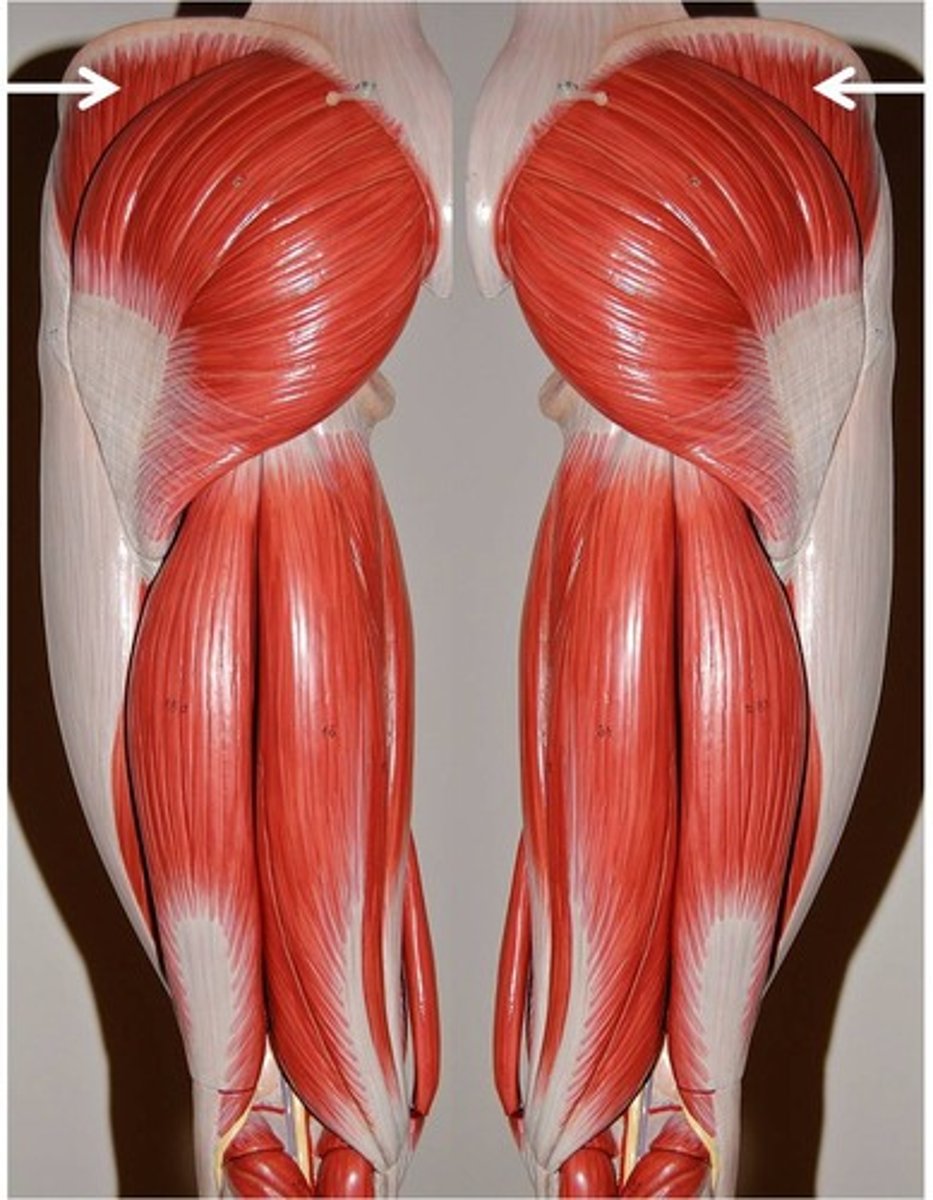
gluteus minimus
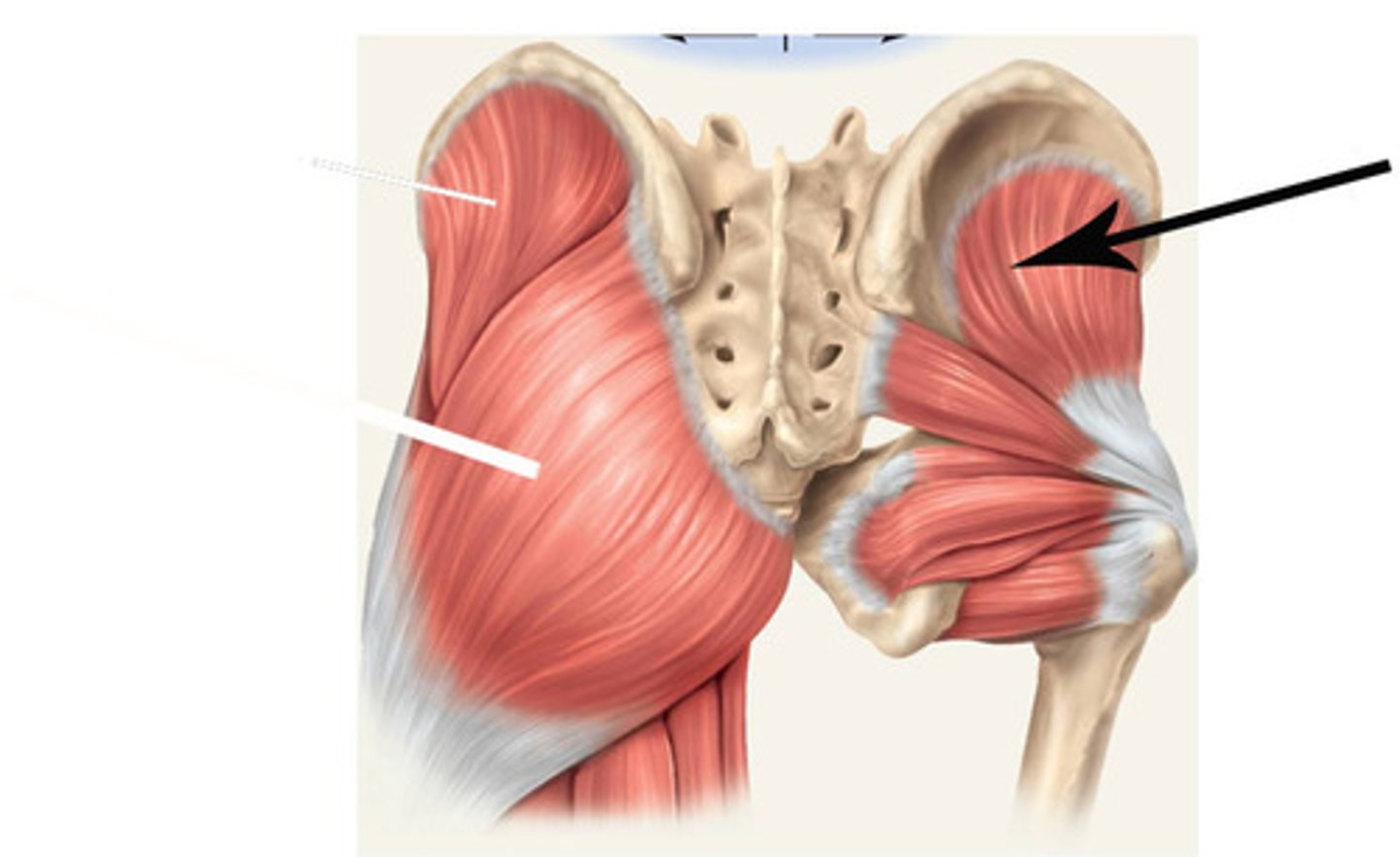
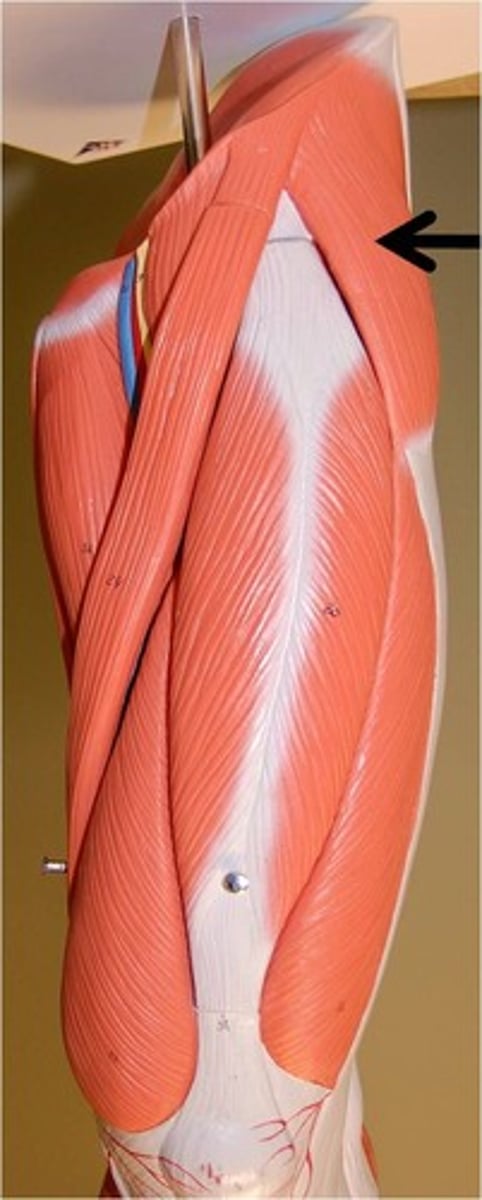
tensor fasciae latae
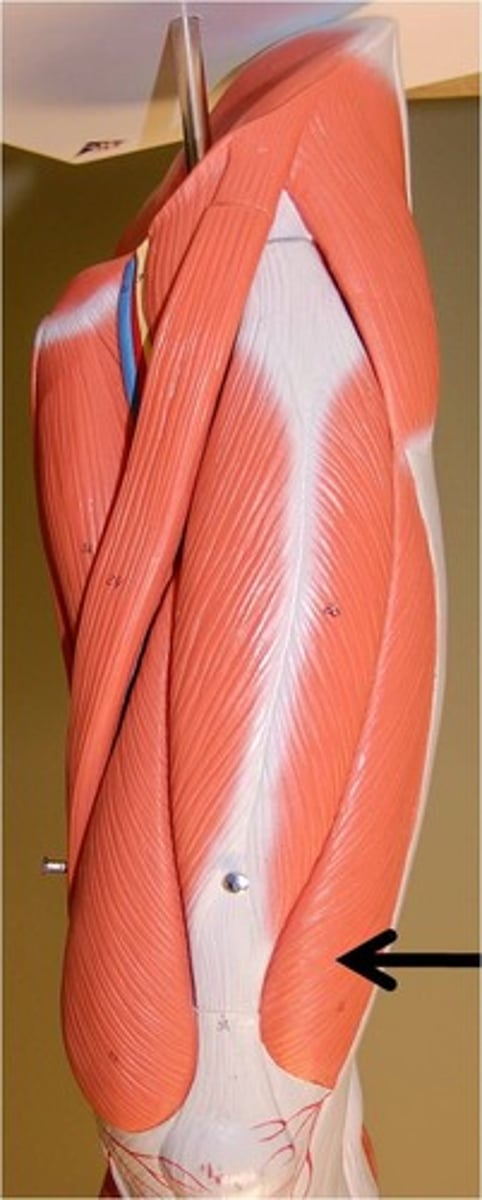
vastus lateralis
rectus femoris
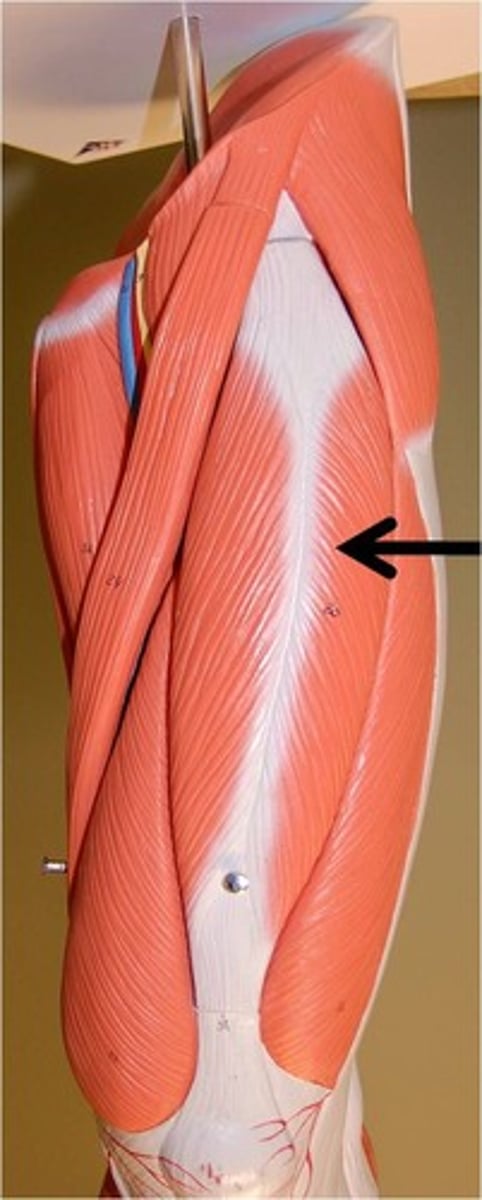
vastus medialis
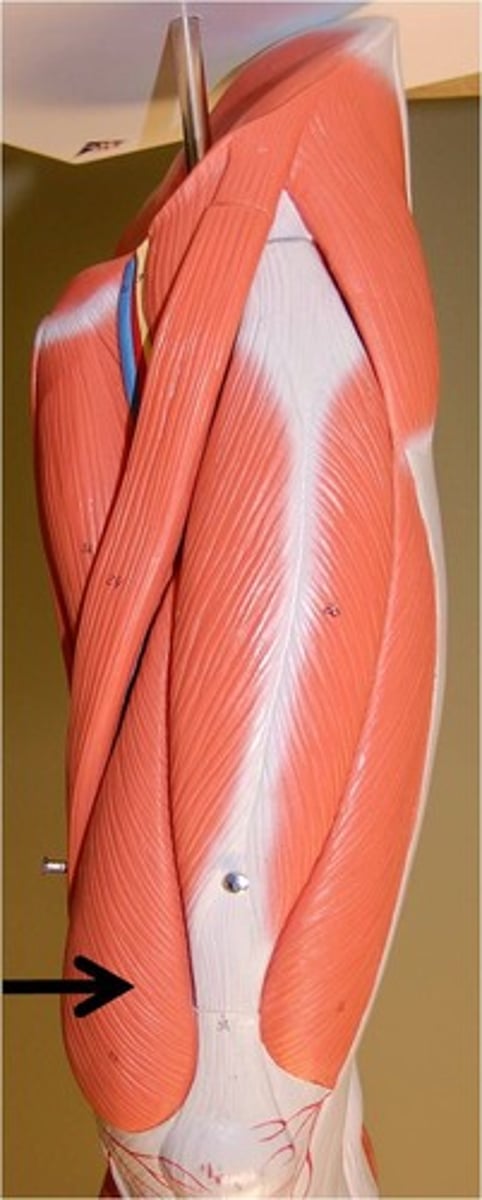
sartorius
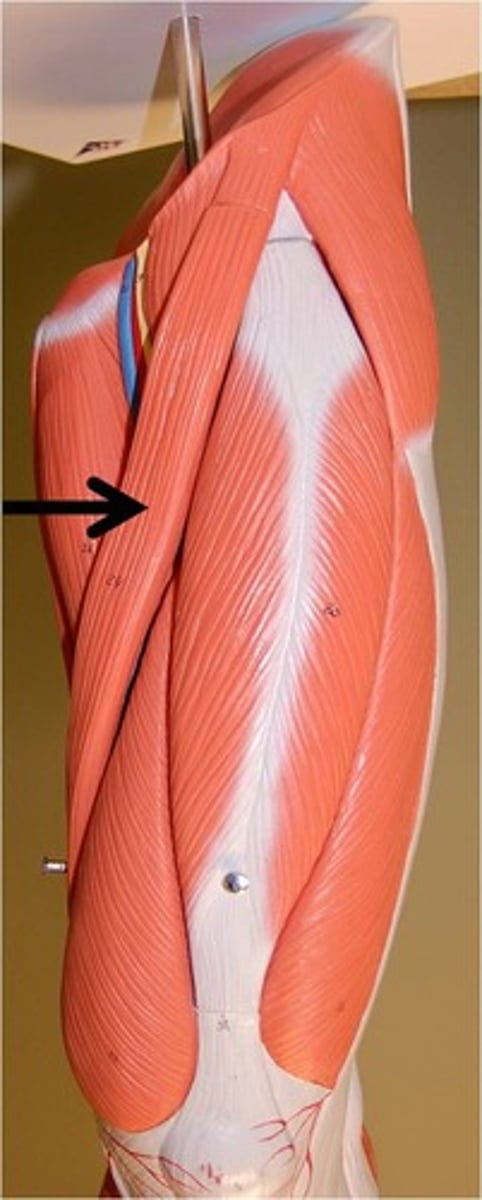
adductor longus
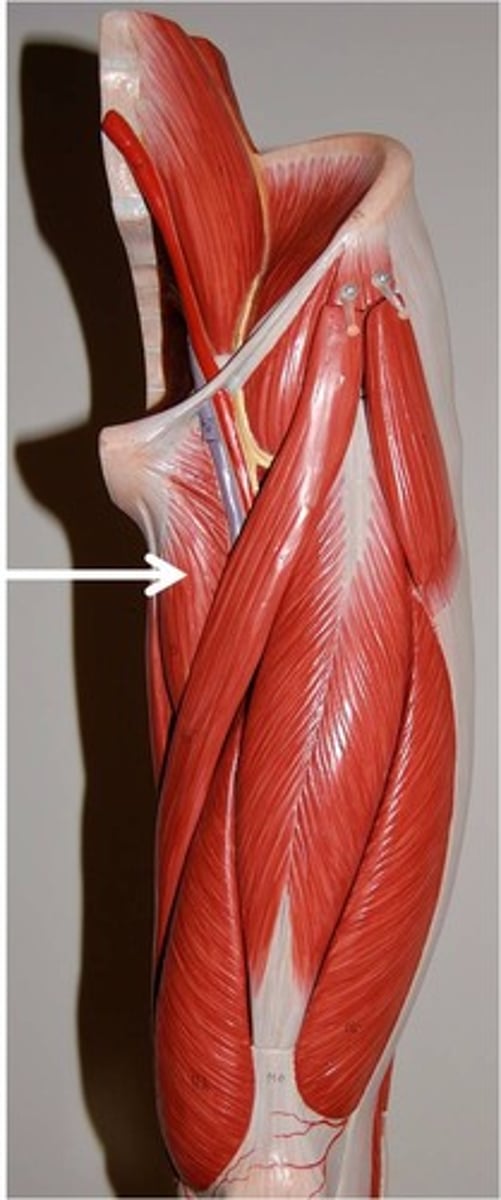
gracilis
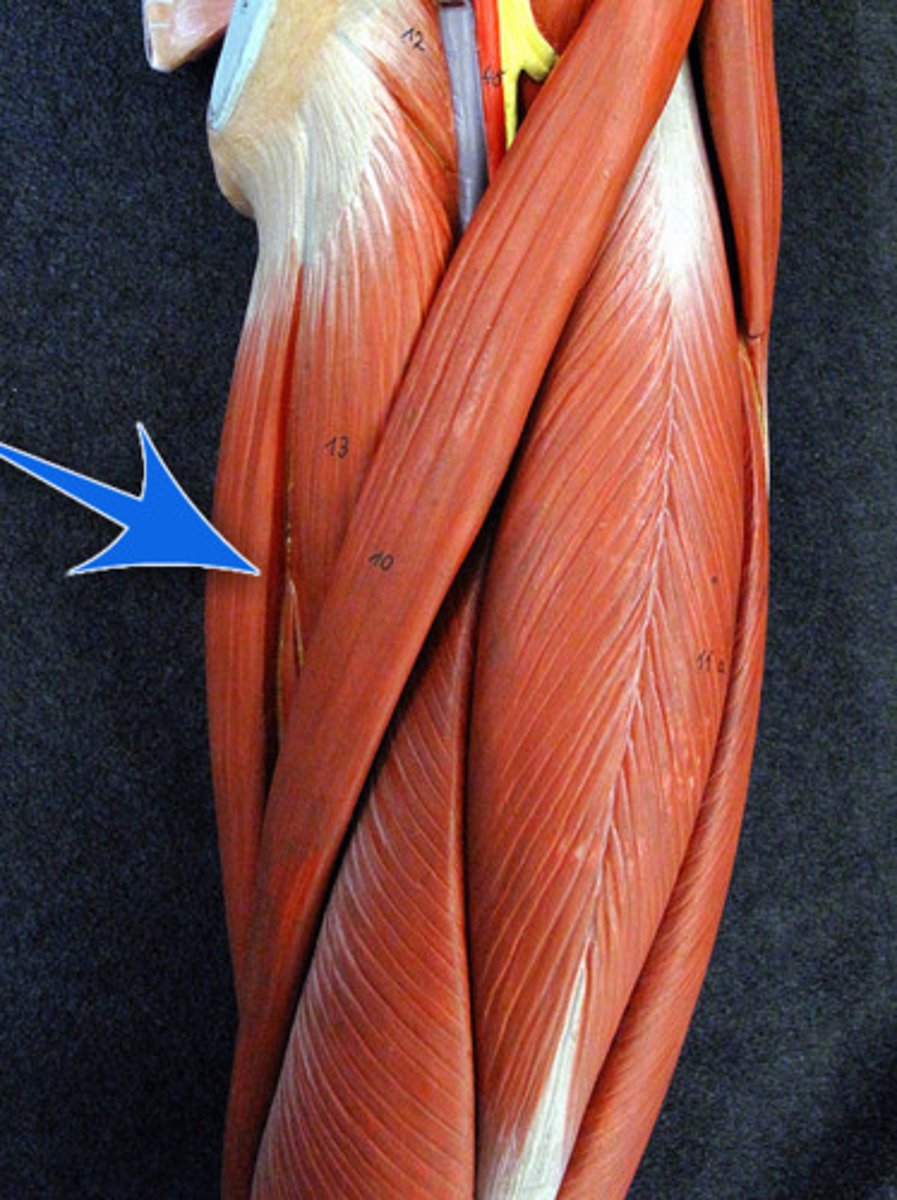
adductor magnus
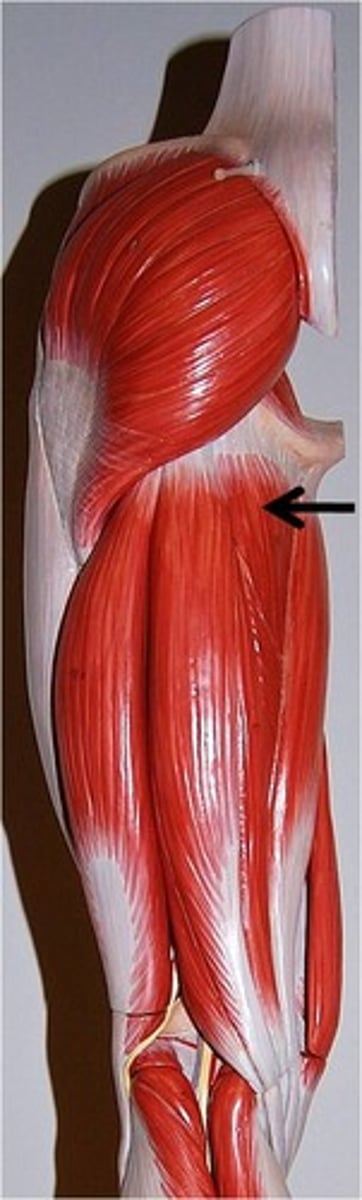
Semimembranosus (red diagram)
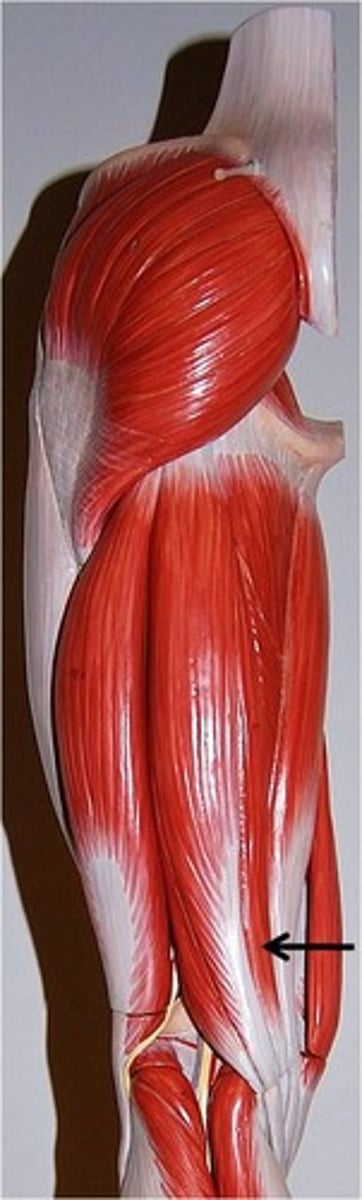
Semitendinosus (red diagram)
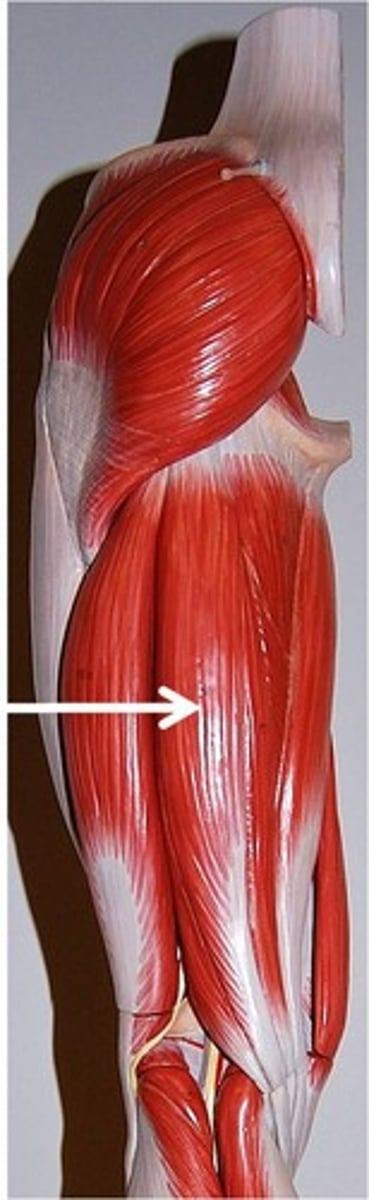
long head of biceps femoris
long head is posterior to short head
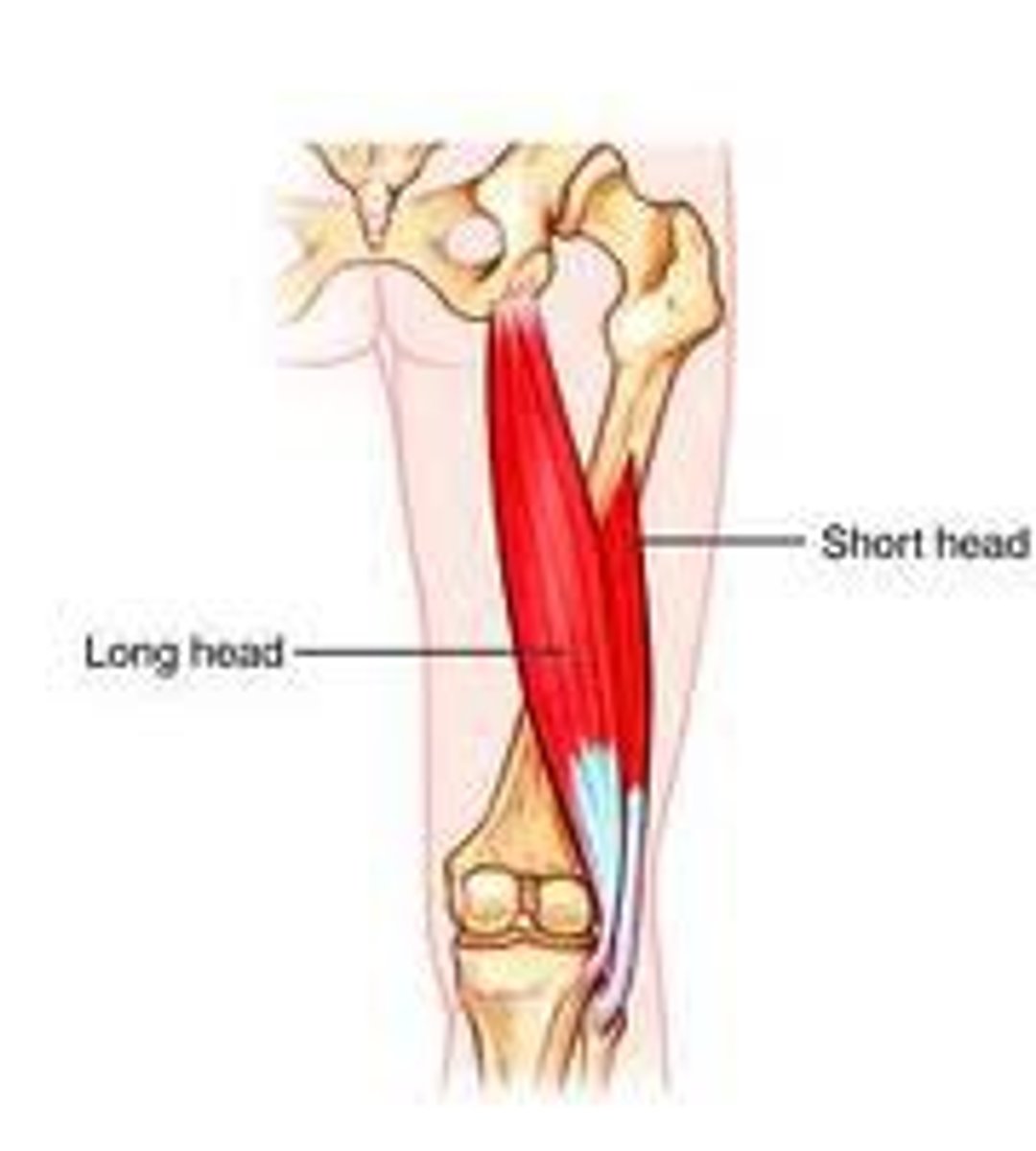
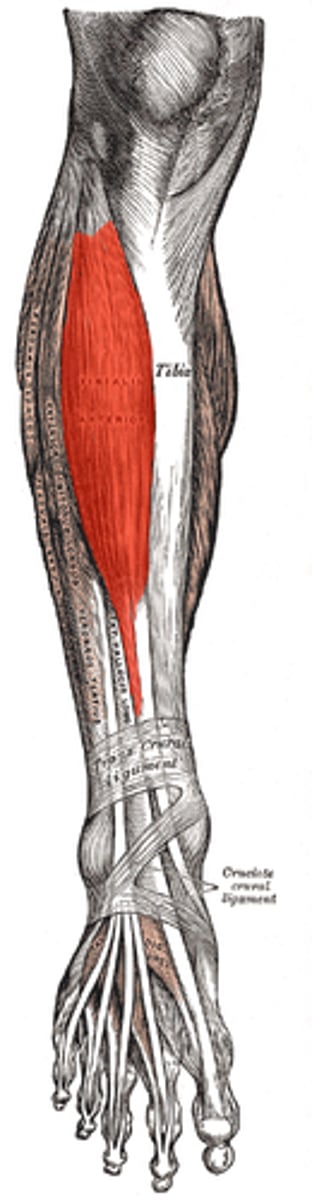
tibialis anterior
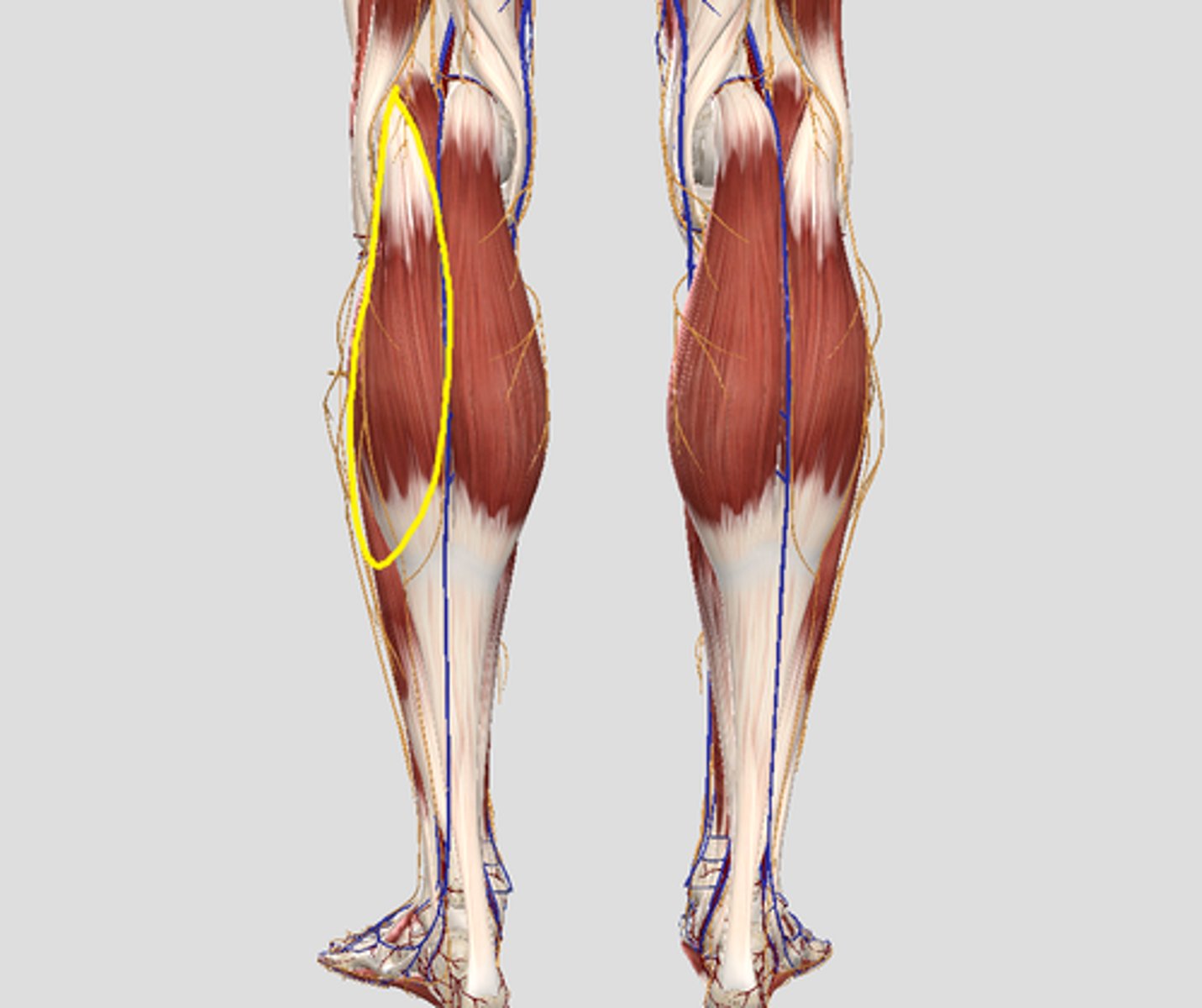
lateral head of gastrocnemius
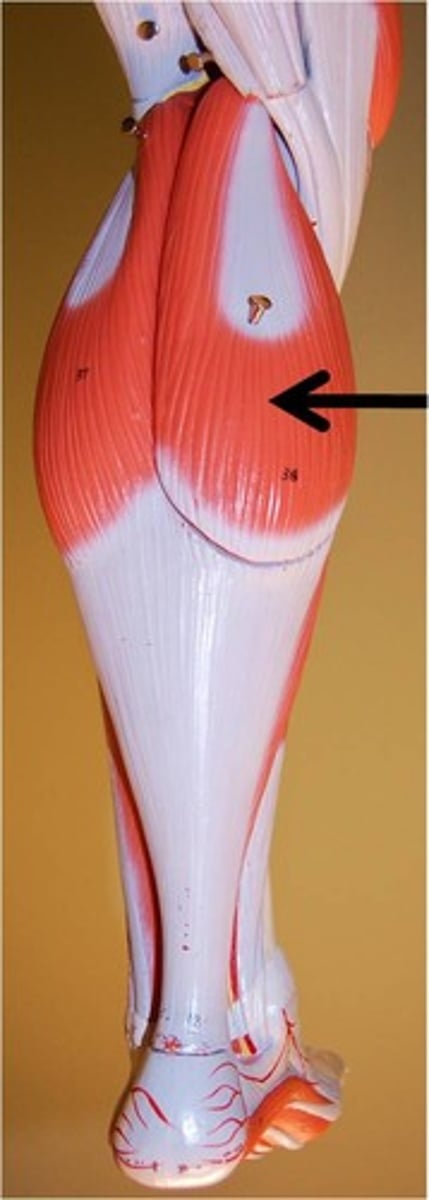
medial head of gastrocenemius
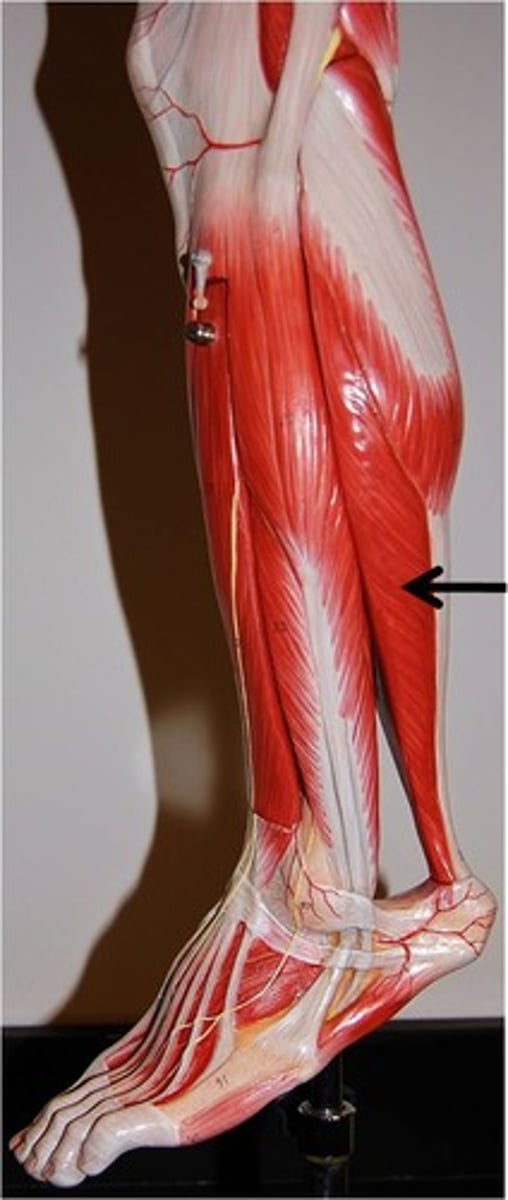
soleus
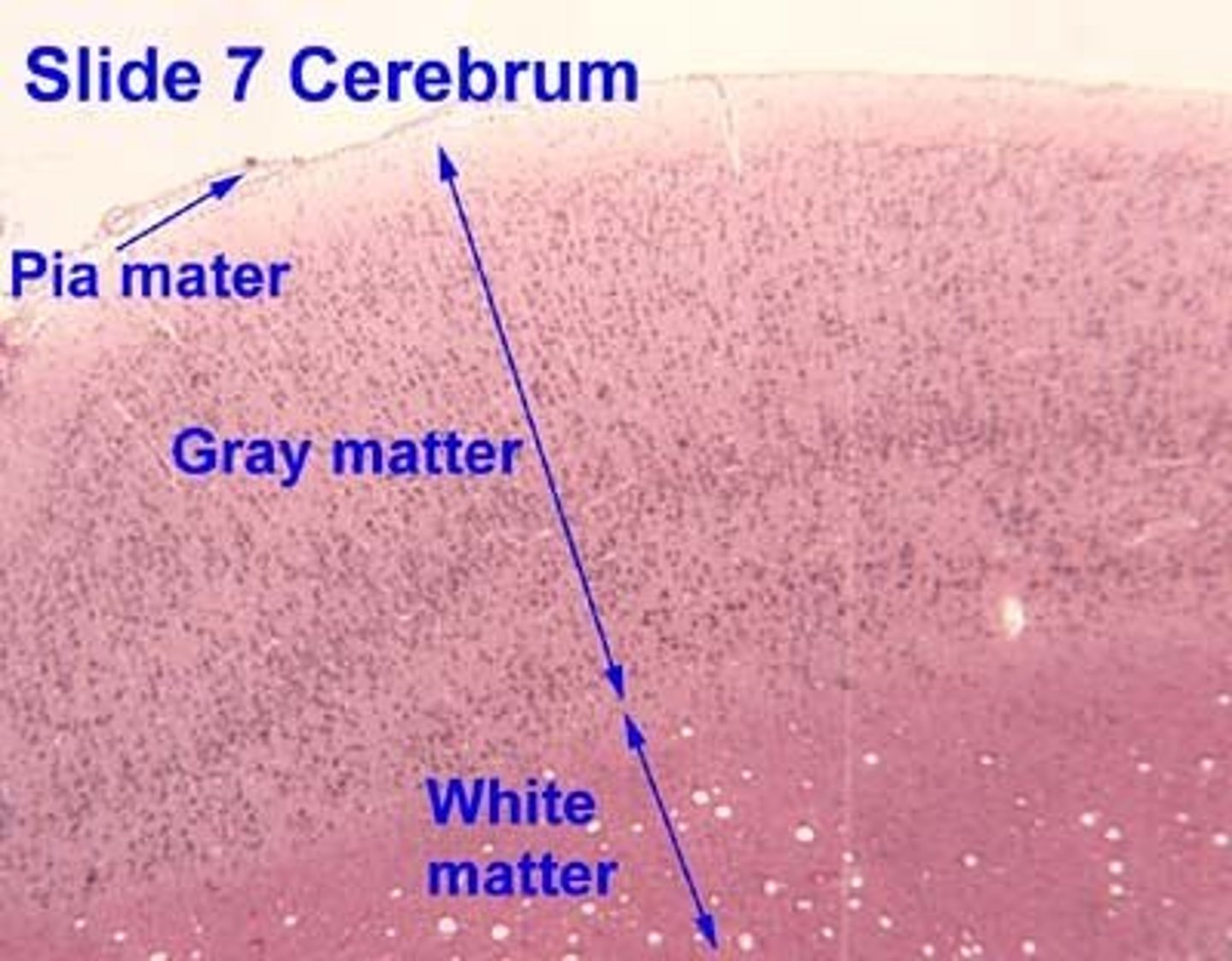
cerebral cortex
be able to identify gray & white matter and pyramidal cells will be in gray matter
white is deep