HPEX 301 exam 2 review
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What is muscular strength?
ability of a muscle to generate max force
What is muscular endurance?
ability to generate force over and over again
What are muscle fibers?
Long, thin cells that make up skeletal muscle
What is a fascia?
Dense layer of connective tissue that surrounds fibers
What are tendons?
Connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. Muscle action causes the tendons to pull on the bones rather than push them
What is muscle action?
Shortening of skeletal muscle (causing movement) or the lengthening of a skeletal muscle (resisting movement)
What is a motor unit?
A motor nerve and all the muscle fibers it controls
What’s the process of a muscle action?
A message (nerve impulse) reaches the neuromuscular junction
The impulse triggers the action process by allowing interaction of contractile proteins in muscle
When the signal is removed, the nerve stopes sending signals, making the muscle action stop
What are the 3 main categories of skeletal muscle exercise?
Isotonic
Isometric
Isokinetic
What is isotonic (dynamic) exercise?
Movement of a body part at a joint
Ex. bicep curls or a lot of exercise activities or sports
What is isometric (static) exercise?
No movement of body parts
Ex. pressing the palms of the hand together or holding a plank
Great way to develop strength during early stages of injury rehab
What is isokinetic exercise?
Speed of muscle shortening or lengthening is regulated at a controlled rate
Ex. machine that provides accommodating resistance throughout full ROM
What is concentric muscle action (positive work)?
Movement of body part AGAINST resistance or gravity, usually when the muscle shortens
Can happen during isotonic or isokinetic exercise
Ex. upward movement of a bicep curl
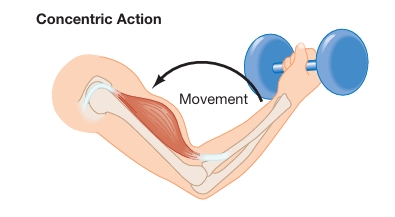
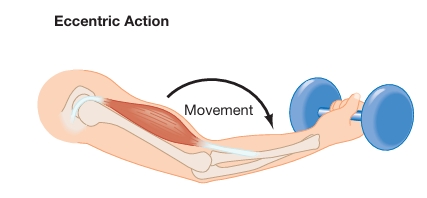
What is eccentric muscle action (negative work)?
Movement of body part WITH resistance or gravity, usually when the muscle lengthens
Ex. downward movement of a bicep curl
What are slow-twitch muscle fibers?
Type I
Slow contraction, low force, highest resistance to fatgiue
Predominately in aerobic exercise since they generate high ATP
Red or dark in color
Used more for endurance events
What are fast-twitch fibers?
Type IIA
Fast contraction, high foce, high resistance to fatigue
Seen in both aerobic and anaerobic exercise
White/pink in color
Used more for middle distance
Type IIX
Fastest contraction, highest force, low resistance to faituge
Seen in anerobic exercise like sprinting, jumping, heavy lifting
White in color
Used more for short distance events
How does fiber recruitment work?
There is a steady increase in muscle fibers recruited when the muscular force produced increases.
The fibers go from slow-twitch to intermediate fibers and finally to fast-twitch fibers as intensity increases
So, high-intensity exercise like weightlifting recruits large numbers of fast-twitch fibers
What 2 factors determine muscle force?
Size of the muscle
Number of fibers recruited during the contraction
What is the one-repetition max (1 RM) test?
Measures the max amount of weight that can be lifted at one time
It’s been criticized as an unsuitable for use by older people or highly deconditioned people
What’s one test to assess muscular strength?
1 RM test
What are two tests to assess muscular endurance?
Push-up test
Sit-up test or curl-up test
How do you achieve increased muscular strength and increased muscular endurance?
Increased muscular strength= high resistance + low repetitions
Increased muscular endurance= low resistance + high repetitions
What’s the difference between hypertrophy and hyperplasia?
Hypertrophy: Increase in muscle size d/t increase in fiber size (increase in SIZE)
Hyperplasia: Formation of new muscle fibers (increase in NUMBER)
What are the recommendations to improve muscle strength and endurance?
Strength: 3 sets of 6 reps each exercise
Endurance: 4-6 sets of 15-18 reps
What is the resting metabolic rate?
Amount of energy expending during all sedentary activity
Usually increased with strength training
What is a neuromuscular junction?
It’s where a motor nerve and individual muscle fiber make contact
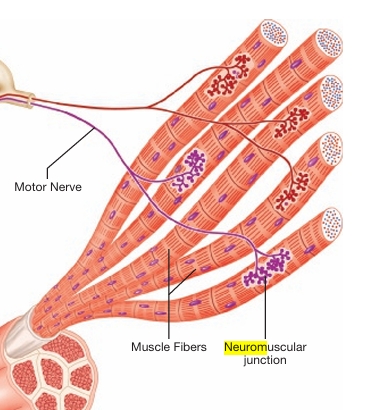
What are the 5 structural limitations of movement?
Shape of bones
Stiff muscle
Connective tissue
Tendons
Tight skin
What is a stretch reflex?
It’s a reflex caused by rapid stretching of muscle spindles
Activating this reflex is counterproductive to flexibility since the muscles shorten rather than stretch
What are proprioceptors?
specialized receptors in muscles and tendons that provide feedback to the brain about the position of the body parts
What are muscle spinders?
Type of proprioceptors within MUSCLE that provide feedback to the brain about the position of body parts
What are Golgi tendon organs?
Type of proprioceptors within TENDONS that provide feedback to the brain about the position of body parts
What is hypokinetic disease?
Also known as lower back pain and is associated with a lack of exercise
Causes
Weak abdominal muscles from sedentary individuals
Lack of flexibility in hip flexor muscles
Can also be caused by hamstrings and lower back muscles that aren’t properly stretched
What are two tests that assess flexibility?
Sit-and-reach test (measures trunk flexion)
Shoulder flexibility test (measures shoulder’s full ROM)
What are the 3 types of stretches?
Dynamic
Effective for sports and exercise program
Fluid, exaggerated movements that mimic movements of exercises
Ballistic
Effective for athletes involved in quick movements
Rapid and forceful bouncing movements
Static
Effective to improve flexibility
Slow lengthening of a muscle to the point of slight discomfort
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF)
Stretching with alternately contracting and relaxing muscles
CR stretching: first contact the muscle to be stretched then after it’s relaxed, its slowly stretched
CRAC stretching: came contract-relax routine but it adds contraction with the antagonist muscle
What is body composition?
Relative amounts of fat and fat-free tissues in the body
What are the major types of fat in the body?
Essential fat
Storage fat
What is essential fat?
Fat necessary for body functions like facilitating nerve impulses
Found in nerves and cell membranes
Men have 3% and women have 12% (it’s more since they have breasts, uterus, and other sex-specific sites)
What is storage fat?
Contained within adipose tissue and provides energy, insulation, and protection
It can be visceral (around internal organs) or subcutaneous (below the skin)
What are the classifications of fat based on 20-39 yrs?
Men
Body fat <8% and BMI <18.5: underweight and increased health risk
Body fat 8-19% and BMI 18.6-24.9: average, normal health risk
Body fat 20-24% and BMI 25-29.9: over-weight and increased health risk
Body fat >25% and BMI >30%: obese and high health risk
Women
Body fat <21% and BMI <18.5%: underweight and increased health risk
Body fat 21-32% and BMI 18.6-24.9: average, normal health risk
Body fat 33-38% and BMI 25-29.9: over-weight and increased health risk
Body fat >39% and DMI >30%: obese and high health risk
What are the classifications of fat based on 40-59yrs?
Men
Body fat <11% and BMI <18.5: underweight and increased health risk
Body fat 11-21% and BMI 18.6-24.9: average, normal health risk
Body fat 22-27% and BMI 25-29.9: over-weight and increased health risk
Body fat >28% and BMI >30%: obese and high health risk
Women
Body fat <23% and BMI <18.5: underweight and increased health risk
Body fat 23-33% and BMI 18.6-24.9: average, normal health risk
Body fat 34-39% and BMI 25-29.9: over-weight and increased health risk
Body fat >40% and BMI >30%: obese and high health risk
What are the classifications of fat based on 60+ yrs?
Men
Body fat <13% and BMI <18.5: underweight and increased health risk
Body fat 13-24% and BMI 18.6-24.9: average, normal health risk
Body fat 25-39% and BMI 25-29.9: over-weight and increased health risk
Body fat >30% and BMI >30%: obese and high health risk
Women
Body fat <24% and BMI <18.5: underweight and increased health risk
Body fat 24-35% and BMI 18.6-24.9: average, normal health risk
Body fat 36-41% and BMI 25-29.9: over-weight and increased health risk
Body fat >42% and BMI >30%: obese and high health risk
What is the general healthy percentage of body fat for young men and women?
Men: 8%-19%
Women: 21%-32%
What is the android pattern?
Pattern of fat distribution characterized by fat stored in the abd region. Commonly seen in men
Greater risk at developing heart disease and diabetes d/t fat being close to vital organs
What is the gynecoid pattern?
Pattern of fat distribution characterized by fat stored in the waist, hips, and thighs. Commonly seen in women
What are some diseases associated with obesity and being overweight?
Cardiovascular disease
Coronary heart disease leading to heart attacks
HTN and high cholesterol
Diabetes
Inflammatory cytokine release linked to Alzheimer’s
Menstrual abnormalities, fertility issues, and complications during pregnancy
Sleep apnea
What are some diseases associated with being underweight?
Malnutrition
loss of muscle mass and strength
Increased risk for osteoporosis
Menstrual abnormalities leading to infertility
Eating disorders linked to heart issues, digestive disorders, kidney damage, anemia, lethargy dry skin, decreased immunity
What are the field methods for assessing body composition?
Height/Weight tables
Body Mass Index
Skin Fold Assessment
Waist Measurements and Waist-Hip Ratio
What are height/weight tables?
determine whether a person is over weight
Pros
determine if a person is too fat
Cons
does not reveal how much of the body weight is fat
do not recommend their use to determine an ideal weight
What’s a BMI?
Determine whether someone is overweight or obese. Best used to obtain an initial estimate of whether one’s percentage is at a healthy level
Pros
BMI indicates that you are underweight, normal, or overweight.
simple and inexpensive method for deter mining your weight status
Cons
can over- or underestimate body fatness
NOT a perfect predictor of body fat percentage
What is a skinfold assessment?
used to estimate a person’s overall body fatness by using a skinfold caliper. The 3 sites used in men are the abd, chest, and thigh. In women, it’s the suprailium, triceps, and thigh
Pros
easy and inexpensive measure to obtain and can provide GOOD estimates of body fat
Cons
3%-4% margin of error
needs a trained technician
not a good measure to assess body composition for obese individuals
What is the Waist Measurements and Waist-Hip Ratio
used to estimate risk of disease associated with high body fat
Pros
good indicators of whether body fat distribution is unhealthy
Cons
DOES NOT provide an estimate of body fat percentage
What are the lab measures for assessing body composition?
Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA)
Hydrostatic weighing (underwater weighing)
Air displacement
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)
What is Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA)?
low-radiation X-ray scan of the body to obtain estimates of body fat percentage
Pros
provides a measure of total body fat as well as of regional fat distribution
used to assess bone density as it relates to osteoporosis and osteoporosis risk
Cons
equipment is expensive, and because it uses an X-ray, only trained professionals can perform the scan
What is Hydrostatic weighing (underwater weighing)?
Weighing the person both on land and in a tank of water to determine body volume and density
Pros
CAN estimate body fat %
Cons
very time consuming and requires special equipment
does not appeal to most individuals because it involves being completely submerged under water
What is Air displacement?
Person ins seated in a chamber (Bod Pod) and sensors are used to estimate the amount of air that is displaced when the participant is in the chamber.
Pros
body volume and then body fat can be calculated
less time consuming than under water weighing
Cons
equipment is expensive
What is Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)?
person either stands on the sensors of a scale-like piece of equipment or holds sensors between both hands. a very low-level electrical current (too low to be felt) is passed through the body between the electrodes or sensors. Body fat is estimated according to the resistance to the flow of the current
Pros
Fairly accurate, fast, portabel, reasonable cost
Cons
Reuslts vary with age, gender, body temp, diet, and hydration level
What’s a better conductor of the current in BIA?
Lean tissue since it contains more water