5.2 - Troubleshooting Storage Devices
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Storage Failure Symptoms
Read/write failure - “Cannot read from the source disk”.
Slow performance - Constant LED activity - Retry…retry…retry.
Loud clicking noise
The click of death.
May also include grinding and scraping.
Troubleshooting Disk Failures
Get a backup - First thing - a bad drive is bad.
Check for loose or damaged cables.
Check for overheating - especially if problem occurs after startup.
Check power supply - especially if new devices were added.
Run hard drive diagnostics.
From the drive or computer manufacturer.
Preferably on a known-good computer.
Boot Failure Symptoms
Drive not recognized, Boot device not found.
Lights (or no lights), beeps, error messages.
OS not found.
The drive is there, Windows is not.
Grinding Noises
Hard drives are mechanical devices - Spinning drives (often 5,400 RPM and higher), moving actuator arms.
Very high tolerances - one small problem can cause the drive to fail.
Metal on metal - Clicking or grinding - poor performance, or no access at all.
Difficult to recover from this issue
Time to get your well managed and very recent backup.
Troubleshooting Disk Failures
Get a backup (if possible) - First thing - a bad drive is bad.
Check for loose or damaged cables.
Check for overheating - Especially if problems occur after startup.
Check power supply - Especially if new devices were added.
Run hard drive diagnostics
From the drive or computer manufacturer.
Preferably on a known-good computer.
Boot Failure Symptoms
Drive not recognized, Boot Device not Found.
Lights (or no lights), beeps, error messages.
OS not found - The drive is there, Windows is not.
Troubleshooting Boot Failures
Check your cables - Physical problem.
Check boot sequence in BIOS.
Check for removable disks (especially USB).
Check for disabled storage interfaces.
For new installation, check hardware configuration.
Data and power cables.
Try different SATA interfaces.
Try the drive in a different computer.
Data loss/corruption
Hard drives are mechanical devices - They will eventually fail.
Repairs are difficult and expensive - Dust free environment, not always successful.
An SSD may simply stop working - Sometimes can read but not write.
Data becomes unavailable or corrupted - Can be impossible to recover.
ALWAYS have a backup!
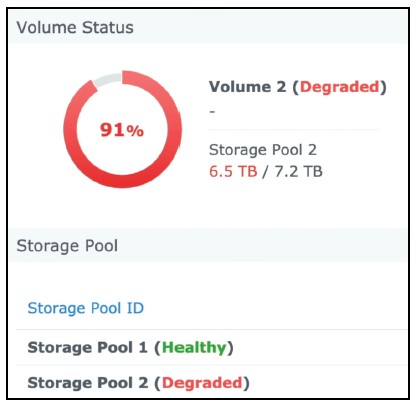
RAID Failure
A drive in a RAID array has failed.
Hardware failure, power issue, communication issue.
Almost always very obvious - Error messages, email notifications, audible alarms.
A careful analysis is required - Many drives, different volumes.
Each RAID is different - Don’t start pulling drives until you check the console!
SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology)
System that uses third party utilities to monitor disk health.
Avoid hardware failure - Look for warning signs.
Schedule disk checks - Built-in to most drive arrays.
Warning signs - Replace a drive.
SMART Analysis
Monitoring SMART metric over time.
Watch for changes or incrementing values.
May be part of a NAS or third-party software.
Automated notifications - Email, text messages, console notifications.
Resolve the issue before it’s a problem.
Get a good backup, replace the bad drive.
Extended Read/Write Times
A lot happens when reading or writing data.
Memory access, communication across the bus, spinning drive access, writing or reading the data to the storage device, etc.
Delays can occur anywhere along the way.
Need a way to measure storage device access.
Input/output operations per second (IOPS)
A broad metric of maximum performance.
Useful for comparing storage devices.
Hard drive: 200 IOPS
SSD: 1000000 IOPS
RAID 0 Failure Condition
RAID that requires two or more drives to function.
A single drive failure breaks the array.
RAID 1 Failure Condition
RAID requiring 2 or more disks to function.
Array will work as long as one drive is operational.
RAID 5 Failure Condition
RAID that requires 3 or more disks to function.
Need all drives operational but one.
RAID 6 Failure Condition
RAID requiring 4 or more disks to function.
Deed all drives operational but two.
RAID 10 (1+) Failure Condition
RAID requiring 4 or more disks to function.
Can lose all but one from each set of mirrors.