C2.2 Neural Signalling
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What are neurons?
Neurons are cells in the nervous system that carries electrical impulses and makes up the nervous system. they make up nerves
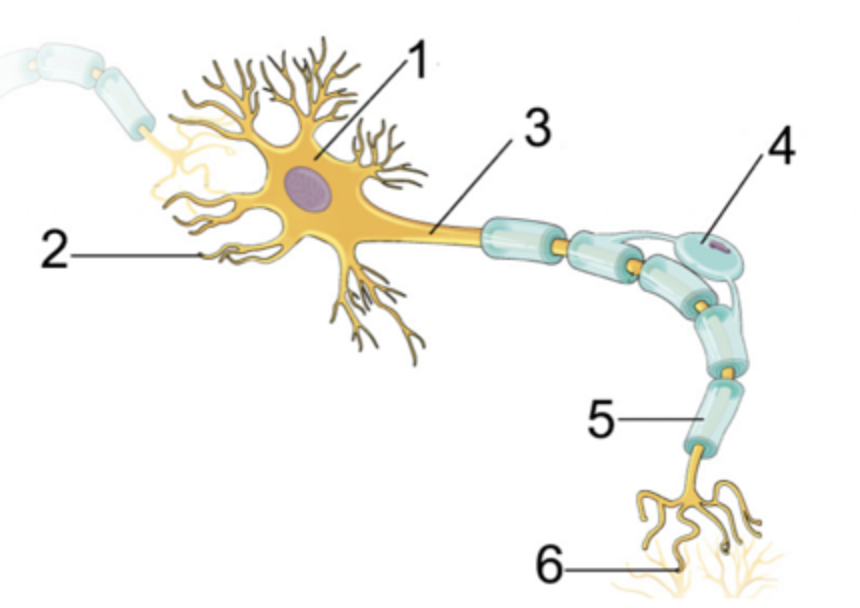
Parts of the neuron
cell body
dendrites - short branched fibres tha convert chemical infomration from other nuerons or receptors cells into electircal signals
axons - an elongated fibre that transmits electical signals to terminal regfions for communication with other neurons or effectors
soma - containing the nucleus cytoplasm and organelles, where essential metabolic processes occur to mantain cell survival
mylein sheath - form of insulation for the axons and make the electron signal faster
axon terminals
What is a resting potential
Resting potential is in all the cells and its the voltage difference between the inside and outside environment when not in use. Usually a neuron has the resting potential of -70mv, being more negative inside it is mantained at all times unless it’s being used for an electrical impulse
What are the 3 factors that affect resting potential
Na+/k+ pumps - helps mantain the resting potential by moving sodium ions out of the neuron whilst transferring potassium ions in. This is conducted through ATP, making it an active transport and can carry 2 different types of ions. For every 3 sodium ions pumped out, 2 potassium ions are pumped in.
Sodium Channels
Potassium Channels
Why is maintaining the resting potential so important?
so you can create an action potential which is the signal that can get sent to the next neuron
what is a nerve impulse
an action potential that starts at the dendrites of a neuron and is then propagated along the axon to the synapse/axon terminal of the neuron. this is how signals are sent through!
what is the action potential
rapid change in membrane potential and it has 2 phases
depolarisation
depolarisation (positive feedback because we’re continuing the positive change throughout the neuron)
a change from negative to positive
sodium channels in our membrane is passive transport so sodium ions flood into our neuron and fuse inside and it causes our inside to be more positive than negative
re-polarisation
(negative feedback because it wants to get it back to -70mv)
changing back from positive to negative
sodium channels close and the pottasium channel open up and pottasiums now leave so it causes the inside of the neuron to be negative again
potassium pump stays open until it falls back again to -80 mV and thats when the body is trying to bring it back up.
refractory period
sodium and potasium pumps are working to restore resting potential because the concentration gradient of sodium and potasium ion have not been re-established again
what does it mean when its an all for nothing process
if u cant get the threshold, than the process of depolarisation wont open up so sodium channels will fail to open. so it’s either complete depolarisation or no depolarisation
What’s a threshold?
A threshold is the amount of voltage an electrical impulse needs to start the depolarisation process and is usually at around 55mV
steps of a nerve impulse
resting potential is -70mv
sodium potasium pumps maintain the resting potential when more sodium ions are outside and more potassium ion are inside
when a neuron is stimulated, sodium ion channels open
sodium ions diffuse in causing depolarisation (thats the signal)
a nerve impulse is sent as a wave of depolarisation along the membrane
potassium ion channels open
potassium ions diffuse out causing repolarisation
sodium potassium pumps re-establish the resting potential
Myelination
it is a form of insulation surrounding the axons which is made of fatty acids (phospholipid bilayers) made by the Schwann cells. The myelin and insulation can be generated much faster, improving reaction time; from 1 meter per second to 100 meter per second, however a disadvantage to this is that they take up a lot of space
Variation in the speed of nerve impulses
in humans the diameter is usually 1 micrometer with a speed of approximated 1 meter per second
in squid the diameter is typically 500 micrometer and has a speed of 25 meters per second
and the reasons why they have giant axons is so there’s a rapid response to danger but the downside is that they take more space and resources