Toes and Foot
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
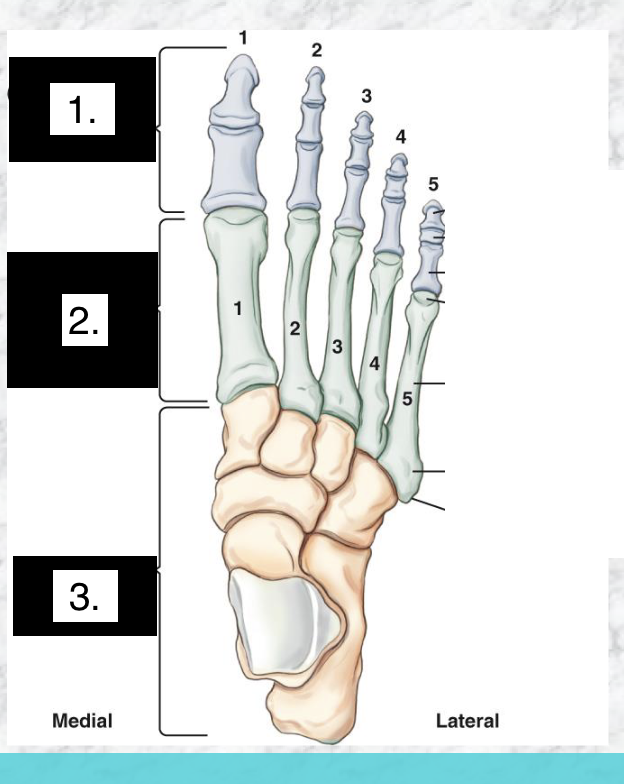
LABEL
Phalanges (14)
Metatarsals (5)
Tarsals (7)
Big toe = digit 1
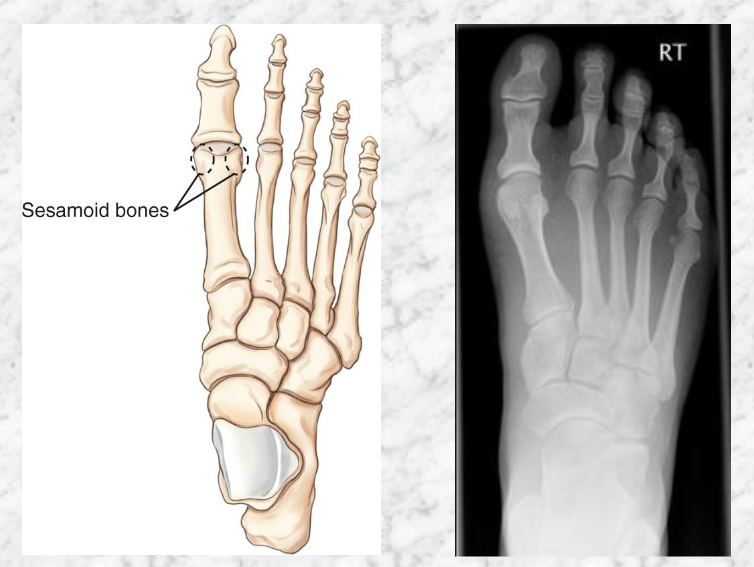
Sesamoid bones
Where are they?
Embedded in tendons
Present near joints
Plantar surface of foot
Naming the tarsals & alternate names
Come To Colorado (the) Next 3 Christmases
Calcaneus/Os Calcis
Talus/Astrangulus
Cuboid
Navicular/Scaphoid
3 Cuneiforms (1,2,3 or medial, intermediate, lateral)
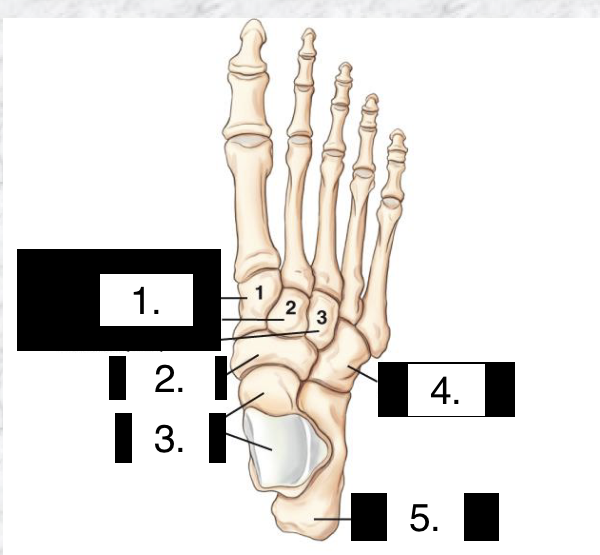
LABEL
Cuneiforms, 1-medial 2- intermediate 3-lateral
Navicular
Talus
Cuboid
Calcaneus
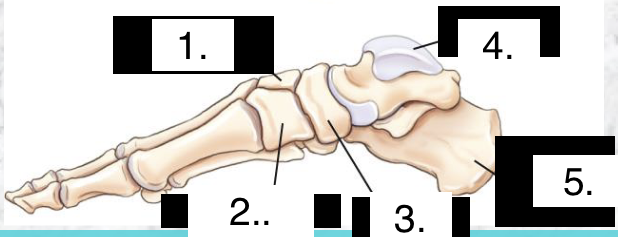
LABEL
Intermediate Cuneiform
Medial Cuneiform
Navicular
Talus
Calcaneus
Arches of the foot
-2 Longitudinal arch : medial and lateral
-Transverse arch
Determine movements
Dorsiflexion
Plantar flexion
Inversion (varus)
Eversion (valgus)
Interphalangeal (IP, DIP, PIP)
Hinge
Metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint
Condyloid
Intertarsal
Gliding
Technical factors for lower extremity
Low to medium KV (50-80)
Small focal spot
Grids for anatomy that measures over 10 cm (knee)
Always wear gloves
Shoes & socks off, pants legs rolled up or pants removed
AP Foot- dorsoplantar
plantar surface on IR
Angle tube 10 degrees posteriorly/towards heel - because of arches
CR = base of 3rd metatarsal
MTP joints open
Metatarsals seperated
Symmetrical concavity on phalanges & metatarsals
Medial aspect well visualized (1st and 2nd cuneiform)
Calcaneus and Talus superimposed
AP Oblique Foot
30 degree medial rotation
CR = base of 3rd metatarsal
No tube angle
Plantar surface on IR with knee bent
Lateral aspect of foot best visualized
Cuboid, lateral cuneiform
Tuberosity/base of 5th metatarsal in profile
3rd-5th metatarsals free from superimposition
Asymmetrical concavity
Mediolateral foot
True lateral may need to roll patient *best for foreign body
Dorsiflex foot
CR = to medial cuneiform (level base of 3rd metatarsal)
Tibiotalar joint demonstrated
Metatarsals & phalanges superimposed
Calcaneous in profile
Cubiod and base of fifth more inferior
AP Weight bearing feet
CR = 10 to 15 posterior/towards the heel
CR = base of metatarsals
ARCHES
Usually bilateral
Lateral Weight bearing feet
Horizontal beam
Evaluate arches
CR= to point above 3rd metatarsals
Usually lateromedial projection
Weight bearing oblique foot
2 options
Oblique pts foot
Angle tube
AP Toes
CR = perpendicular with angle sponge or axial 10 degrees posterior to metatarsophalangeal joint
Digits and minimus of distal ½ of metatarsal demonstrated
No overlap of soft tissues
IP and MTP joints appear open
Symmetrical concavity
AP Oblique toes
try to get a 30 degree rotation
Digits 1-2 → medial rotation
Digits 3-5 → lateral rotation
CR= perpendicular to MTP
No tube angle
IP and MTP joints open
Increased concavity on one side of shaft-asymmetric concavity
Head of metacarpals not overlapped
Lateral toes 1st-2nd digit
Lateromedial
CR= Interphalangeal joint
Asymmetric concavity
Metatarsals superimposed
IP and MTP joints appear open
Mediolateral 3rd-5th digits
CR = Proximal interphalangeal joint
Asymmetric concavity
Metatarsals superimposed
IP and MTP joints appear open