Environmental Biology Final Study Guide 👩🏽🔬
1/138
Earn XP
Description and Tags
i use a lot of acronyms so this might not work for you but it worked for me but follow me 😛 (I got an A btw)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
What is science?
A philosophy used to answer questions about the natural world through observation and experimentation
Scientific Method
Way of collecting evidence that supports or rejects a prediction
Controlled Experimentation
Trying to answer a question by changing one variable at a time; one thing must be changed; one thing must be measured
Independent/Manipulated Variable
Variable being changed, on the x axis
Dependent/Responding Variable
The variable you measure, on the y axis
Steps of Scientific Method
Make an observation
Ask a question
Research
Make a Hypothesis
Develop a controlled experiment
Conduct the experiment; measure and record data
Analyze data
Draw Conclusion
Share your results and try again
(marm dcads)
What are the three things that conclusions can do?
Support hypothesis, reject hypothesis, or leave the hypothesis inconclusive
Levels of Organization
Subatomic particles, atoms, molecules, macromolecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ system, organisms, populations, community, ecosystem, biomes, biospheric, solar system, galaxy, universe (sam moc tooop cebbsgu)
Subatomic Particles
Protons, neutrons, electrons
Atoms
Hydrogen, oxygen, carbon
Molecules
Two or more atoms chemically combined
H2O, CO2
Macromolecules
Smaller molecules combined
ex: proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids
Organelles
Organs of the cell
ex: mitochondria, nucleus, lysosomes
Cells
Plant vs animal
Prokaryotic (no nucleus) and Eukaryotic (nucleus)
Populations
Group of similar organisms living in the same region
ex: school of fish, humans, murder of crows
Community
A bunch of populations in the same area
ex: Masters Campus
Ecosystem
Community + non living things (abiotic)
ex: forest
Biomes
Ecosystems that have similar populations as well as environmental conditions
ex: desert, tundra, rain forest
Biospheric
All the biomes
ex: earth
Solar System
Galaxy
Universe
Characteristics of Living Organisms
They are made of cells
They reproduce
They are based on a universal genetic code
They grow and develop
They use materials and energy
They respond to the environment
They maintain an internal balance (homeostasis)
They change over time
(mr bgurm c)
What is the goal of most atoms?
To have 8 valence electrons, hydrogen is an exception
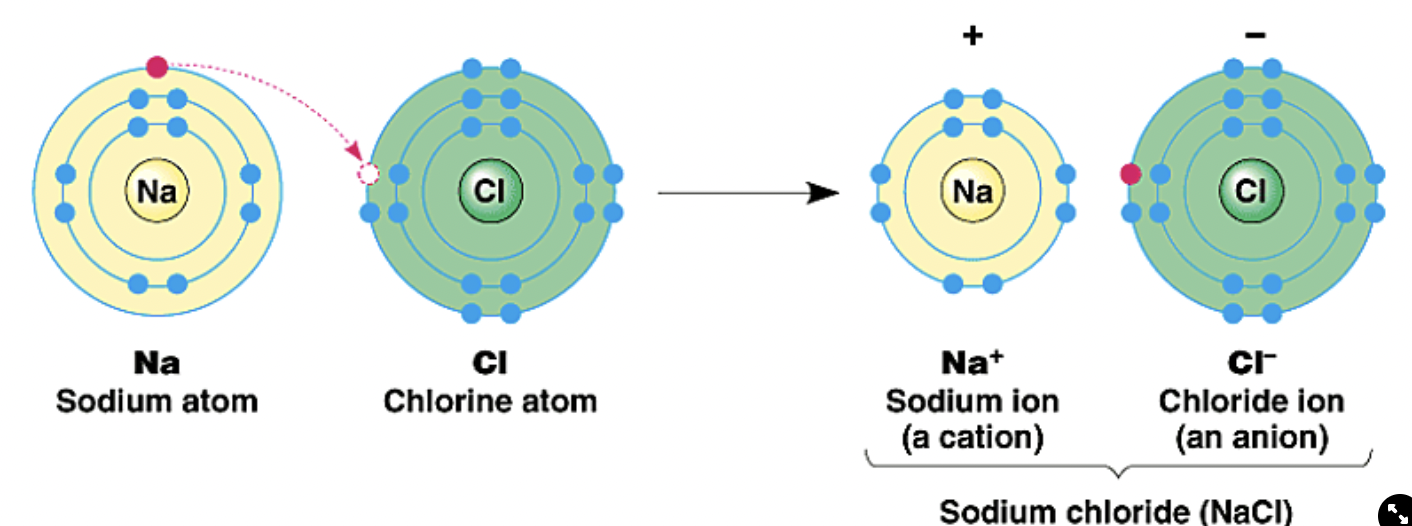
Ionic Bonds
Form when atoms transfer electrons
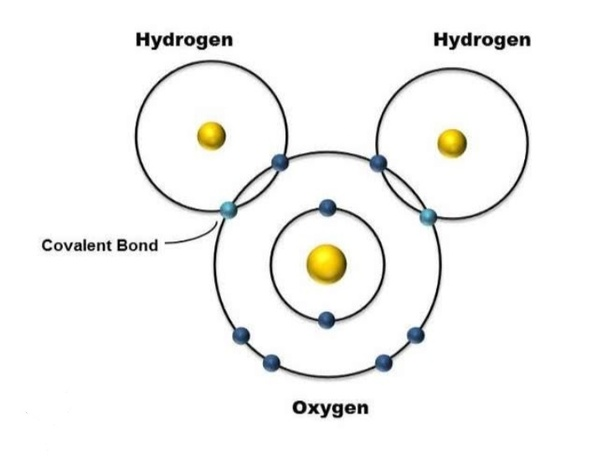
Covalent Bonds
Form when atoms share electrons (hydrogen is positive, oxygen is negative)
What are the seven properties of water?
Cohesive, adhesive, high heat capacity, surface tension, polar, universal solvent, capillary action
Cohesive
Water molecules “stick” to other water molecules
ex: water on a penny
Adhesive
Water molecules “stick” to other substances
ex: The smaller tube having the most water
High Heat Capacity
Slow to heat and its slow to cool
ex: On a humid day, the sand gets hot but the ocean remains cold
Surface Tension
The molecules on the top of the water are attracted to the molecules beneath which creates a thin “net” holding the water together
Polar
Has a positive and negative side
Universal Solvent
Can dissolve a wide variety of solutes
ex: Salt dissolving in water
Capillary Action
The ability of a liquid to flow in narrow spaces without the assistance of external forces like gravity.
ex: Water getting from roots to plants
Ionic Bonds
Form when atoms transfer electrons
Enzymes
Biological catalyst, reusable, each enzyme is unique to a specific substrate
How can an enzyme be denatured?
Change in temperature and change in pH
Catalysts
Speeds up chemical reactions at a lower temperature, reusable, aren’t consumed
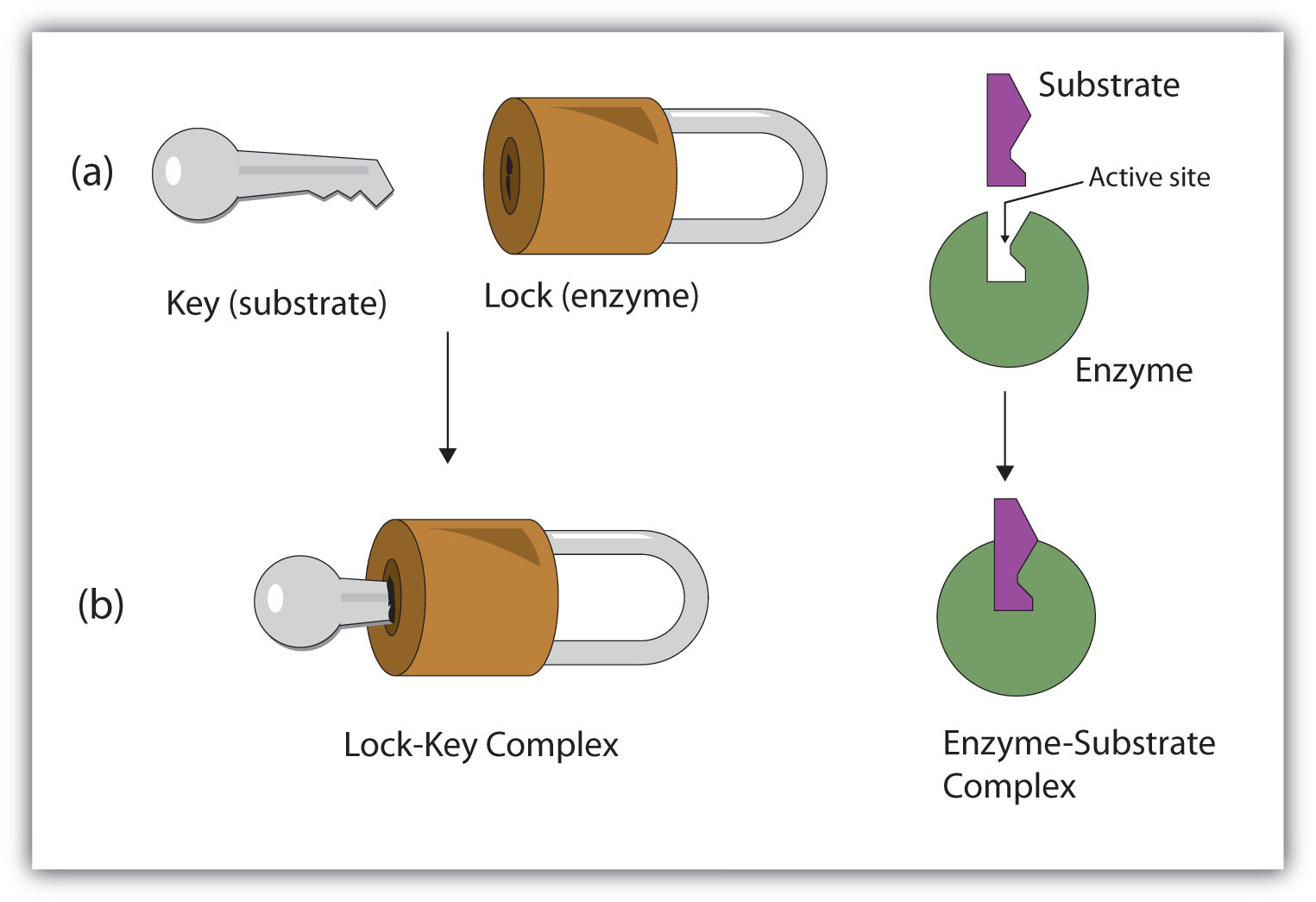
What is the metaphor for enzymes and substrates?
Lock (enzyme) and Key (substrate)
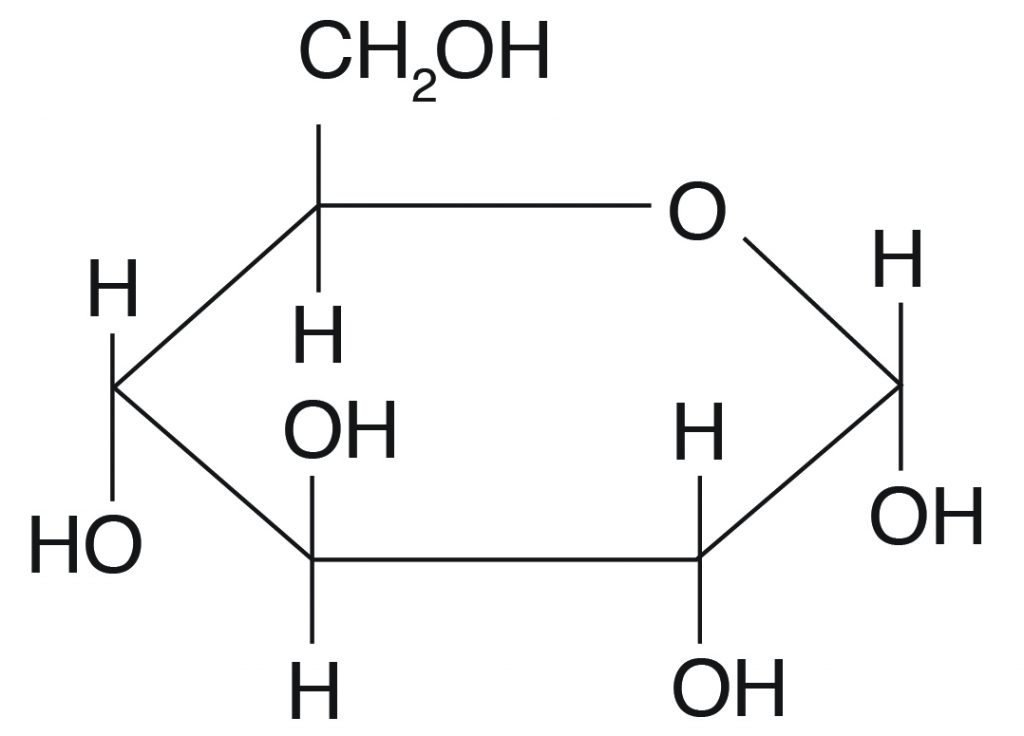
What are carbohydrates composed of?
Hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon
What are the monomers of carbohydrates?
monosaccharides: glucose, fructose, and galactose
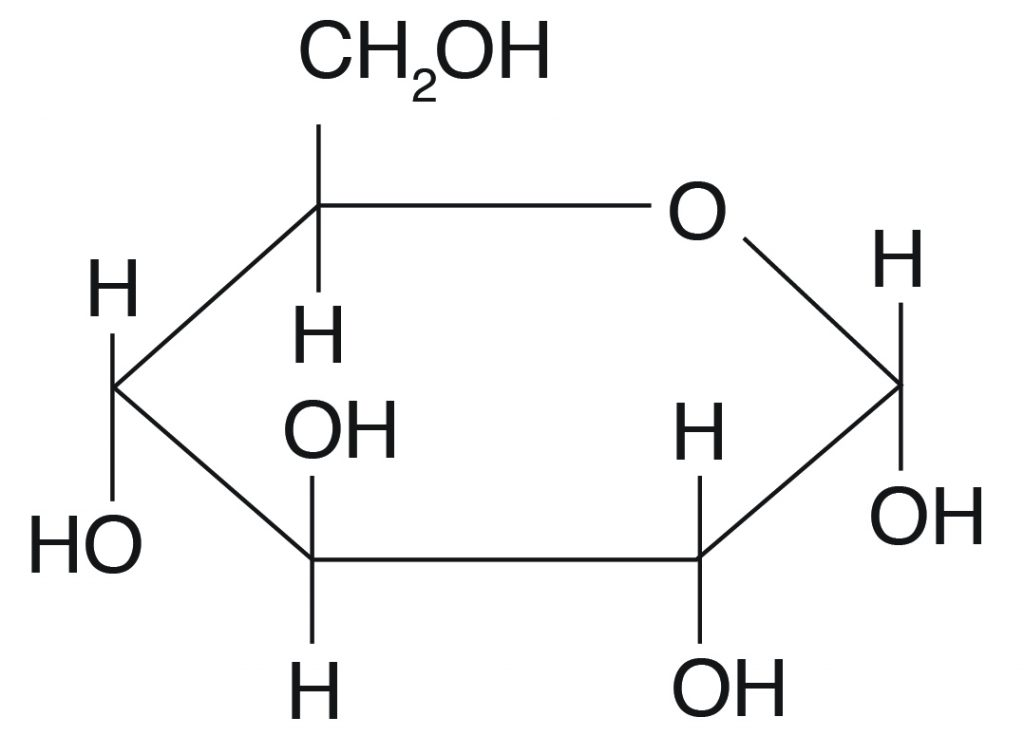
What are examples of carbohydrates?
Sugar, starch, cellulose
What are the functions of carbohydrates?
Short-term energy
What are lipids composed of?
Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen
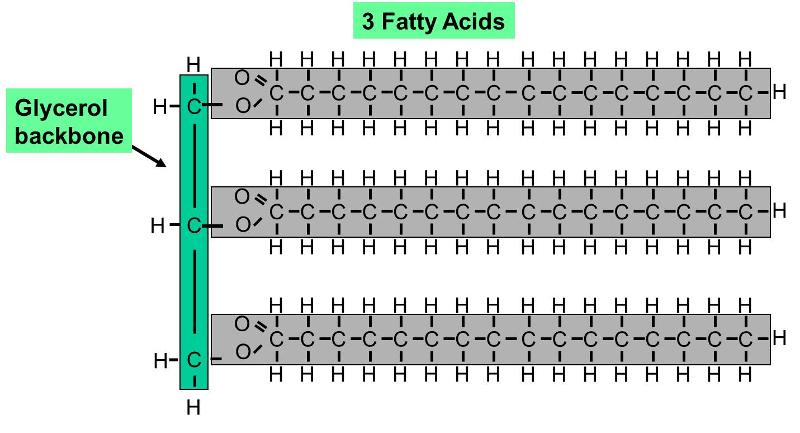
What are the monomers of lipids?
Glycerol and Fatty Acids
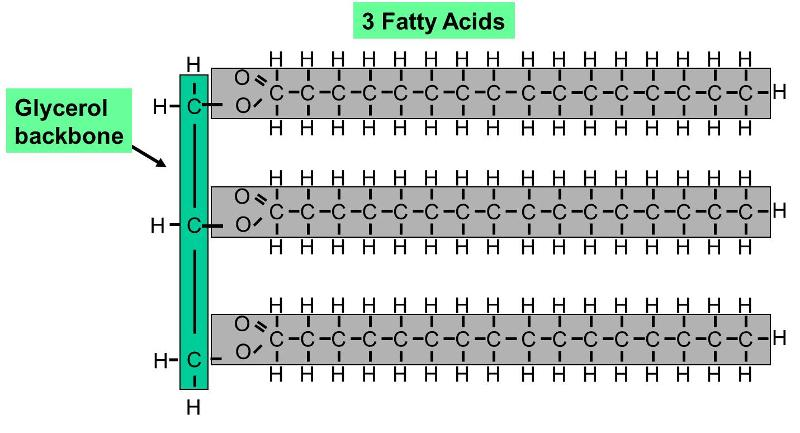
What are examples of lipids?
Oil, wax, glyceride
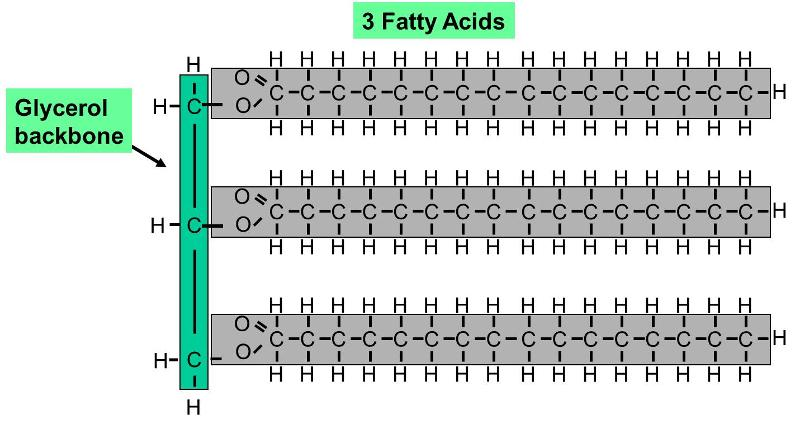
What are the functions of lipids?
Insulation, long term energy
What are proteins composed of?
Nitrogen, sulfur, hydrogen, oxygen, carbon
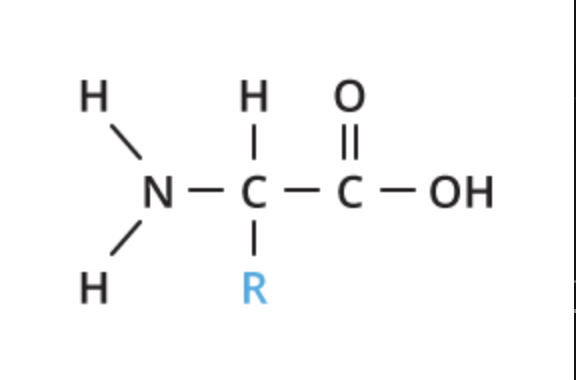
What are the monomers of proteins?
Amino acids
What are examples of proteins?
Enzymes, hormones
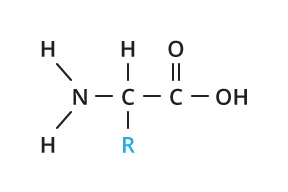
What are the functions of proteins?
Control rate of reactions and regulates cell processes, transports substances in and out of cells
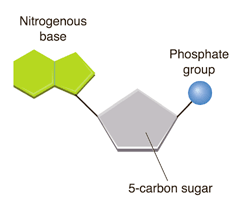
What are nucleic acids composed of?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphates
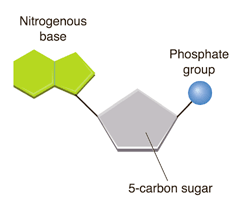
What are the monomers of nucleic acids?
Nucleotides
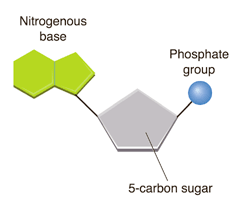
What are examples of nucleic acids?
DNA and RNA
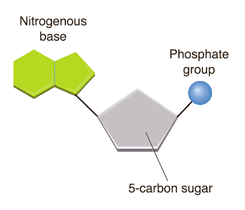
What are the functions of nucleic acids?
Store and transfer genetic and hereditary information
Nucleus
Contains genetic material (DNA) and controls cellular processes
Ribosome
Responsible for manufacturing proteins
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Location of protein and liquid synthesis, located near the nucleus
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for transport within and outside of the cell
Lysosomes
Contains digestive enzymes to breakdown waste materials within the cell
Vacuoles
Stores materials and water
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, produces ATP through cellular respiration
Chloroplasts
Where photosynthesis takes place
Cell Membrane
Regulates the passage of substances in and out of the cell
Cell Wall
Rigid structure that is outside of the cell membrane that protects and provides structural support to the cell
Cytoplasm
Watery fluid inside of the cell membrane that contains organelles and other materials necessary for cellular functions
Prokaryotes
No nucleus, no membrane-bound organelles, and simple compared to eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotes
Has a nucleus, has membrane-bound organelles, and more complex compared to prokaryotic cells
Cell Concepts
Membranes are fluid and flexible
Membranes can self-repair
Eukaryotic cells feature membrane bound organelles
Membrane proteins perform special functions
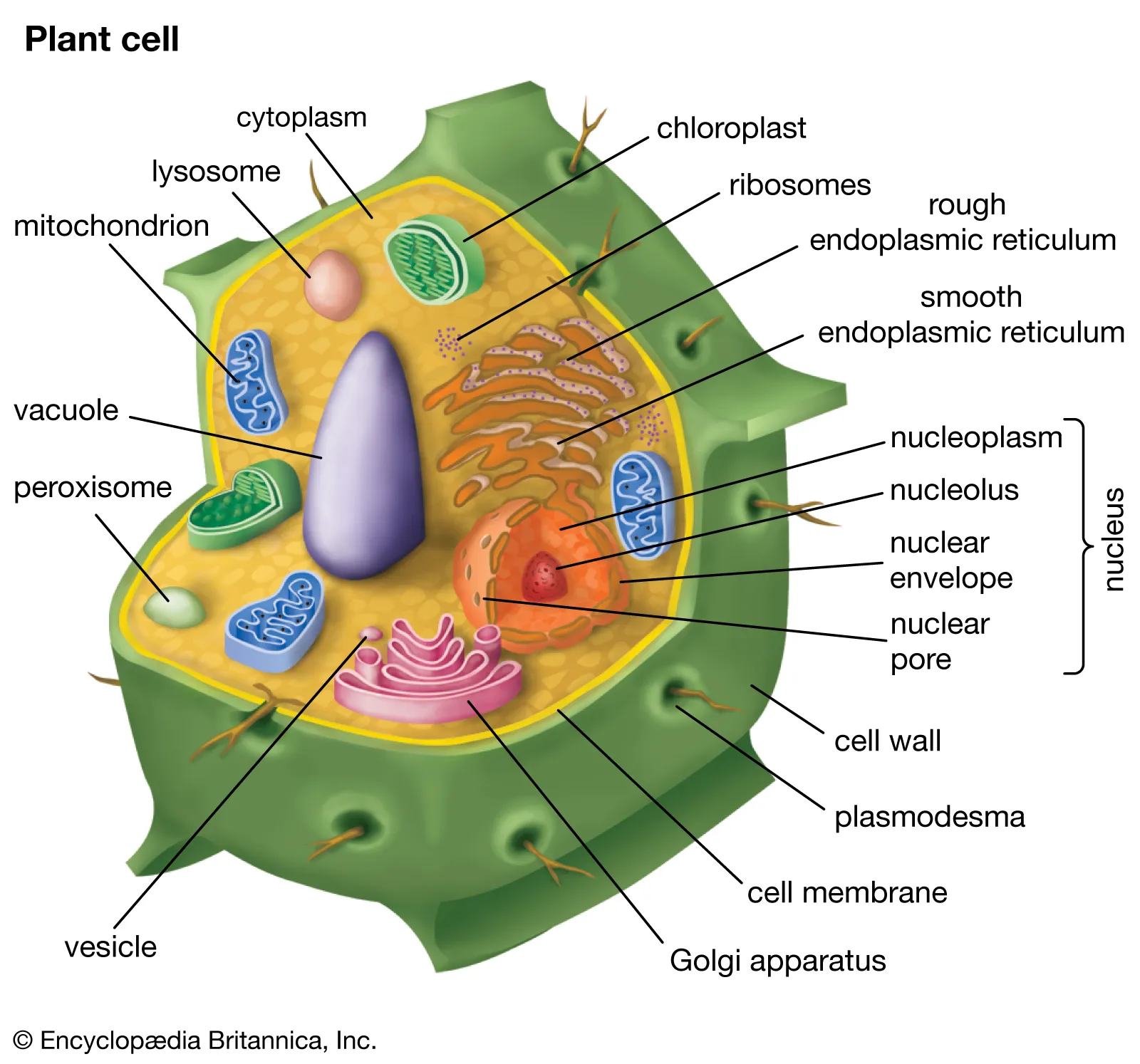
Plant Cell
Cell Wall, cytoplasm, cell membrane, chloroplasts, golgi Apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleus, mitochondria, vacuole, ribosome
ccccgenmvr
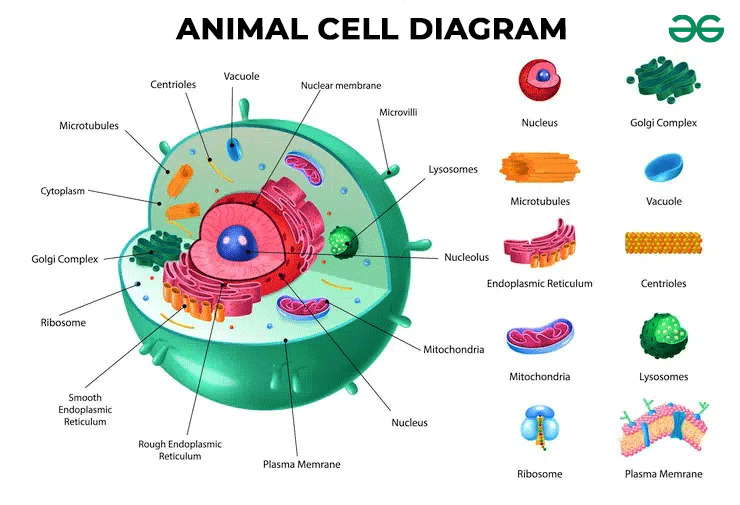
Animal Cell
Cell membrane, cytoplasm, lysosomes, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, nucleus
cclmergn
Passive Transport
Requires no energy, substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
Diffusion
Molecules move directly through the lipid bilayer of the membrane
Ex: the smell of hand lotion travelling
Facilitated Diffusion
Molecules move across the membrane using protein channels
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane, moves through aquaporins, goal is equilibrium
Active Transport
Requires energy, moves from low to high concentration, uses protein pumps
Exocytosis
Process used to move substances out of the cell
Endocytosis
Process where the cell takes in materials from the outside environment
Vesicle
Contain the substances that are being moved in endocytosis and exocytosis
Cell Theory
All living organisms are made from cells
Cell are the basic unit of life
All cells come from other cells
Protein Pumps
Helps move molecules across the membrane across the concentration gradient
Hypotonic
When comparing two solutions, the solution with the lower amount of solute in the cell. Cells swell, then lead to potential bursting
Hypertonic
When comparing two solutions, the solution with the higher amount of solute in the cell. Cells shrink
Isotonic
A solution that has the same concentration of solutes as another solution, water can move in and out of cells at the same rate
What is true about solutions?
Water will always move from a hypotonic solution to a hypertonic solution
Cytolysis
When a cell swells and bursts due to too much water in a hypotonic solution. Can be prevented by the cell wall (in plant cells) by providing structural support
Plasmolysis
Occurs when a plant cell loses water and shrinks away from its cell wall due to being placed in a hypertonic solution
Pigments
Light-absorbing compounds
Chloroplasts
Organelle where photosynthesis takes place
Electron Carriers
A compound that can accept a pair of high energy electrons and transfer them a long with most of their energy.
Photosynthesis Chemical Equation (symbols)
6CO2 + 6H20 → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Photosynthesis Chemical Equation (words)
Carbon dioxide + water + light energy → glucose + oxygen
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis uses the energy of sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide (low energy reactants) into high energy oxygen and glucose (products)
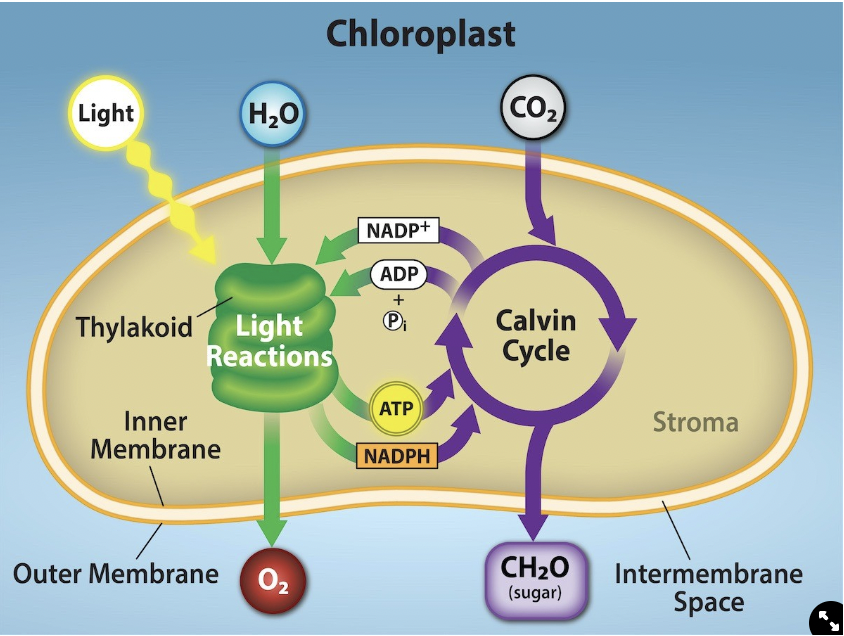
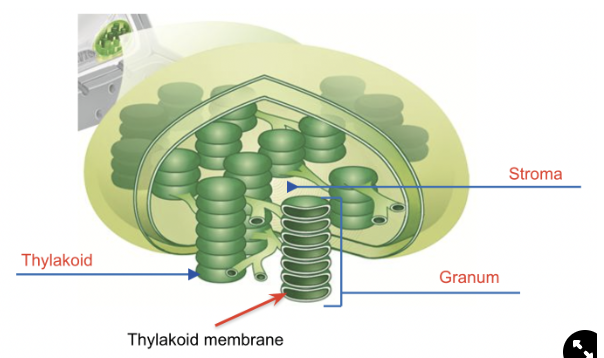
Light Dependent Reactions
Occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts
Inputs: H20, Light, ADP, NADP+
Outputs: O2, ATP, NADPH
Light Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
Occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast
Inputs: CO2, ATP, NADPH
Outputs: Glucose (C6H12O6), ADP, NADP+
Cellular Respiration
A process of energy conversion that releases energy from food in the presence of oxygen
Cellular Respiration Chemical Equation (symbols)
6O2 + C6H12O6 → 6CO2 + 6H20 + ATP
Cellular Respiration Chemical Equation (words)
Oxygen + Glucose → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
Where does glycolysis occur?
Cytoplasm
What are the inputs of glycolysis?
2 ATP, 1 Glucose, NAD+, ADP