Unit 3- AMSCO
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:20 PM on 7/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
1
New cards
Neuron
\
A nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
A nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
2
New cards
Cell body
\
The part of a neuron that contains the nucleus, the cell’s life support center
The part of a neuron that contains the nucleus, the cell’s life support center
3
New cards
Dendrites
A neuron’s often bushy, branching extensions that receive and integrate messages, conducting impulses toward the cell body
4
New cards
Axon
\
The neuron extension that passess messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands
The neuron extension that passess messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands
5
New cards
Myelin sheath
A fatty tissue layer segmentally encasing the axons of some neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speeds as neural impulses hop from one node to the next
6
New cards
Glial cells
Cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons, they also play a role in learning, thinking, and memory
7
New cards
Action potential
\
A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down the axon
A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down the axon
8
New cards
Threshold
The level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
9
New cards
Refractory period
\
In neural processing, a brief resting pause that occurs after an neuron has fired; subsequent action potentials cannot occur until the axon returns to its resting state
In neural processing, a brief resting pause that occurs after an neuron has fired; subsequent action potentials cannot occur until the axon returns to its resting state
10
New cards
All-or-none response
A neuron’s reaction of either firing (with a full-strength response) or not firing
11
New cards
Synapse
The junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. The tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap or cleft
12
New cards
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons.
13
New cards
Reuptake
A neurotransmitter’s reabsorption by the sending neuron
14
New cards
Cell body
\#1
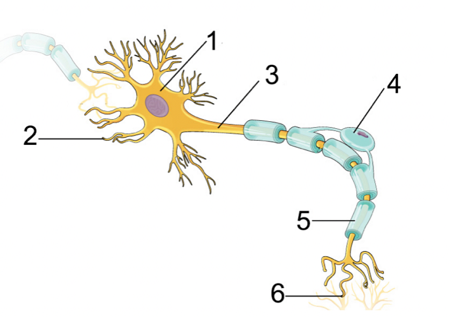
15
New cards
Dendrites
\#2
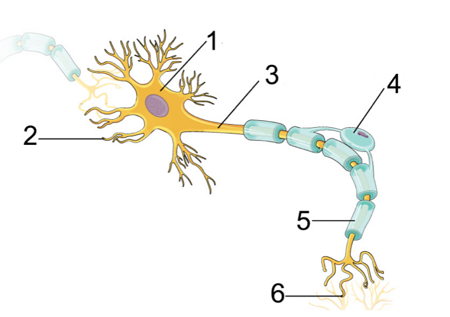
16
New cards
Axon
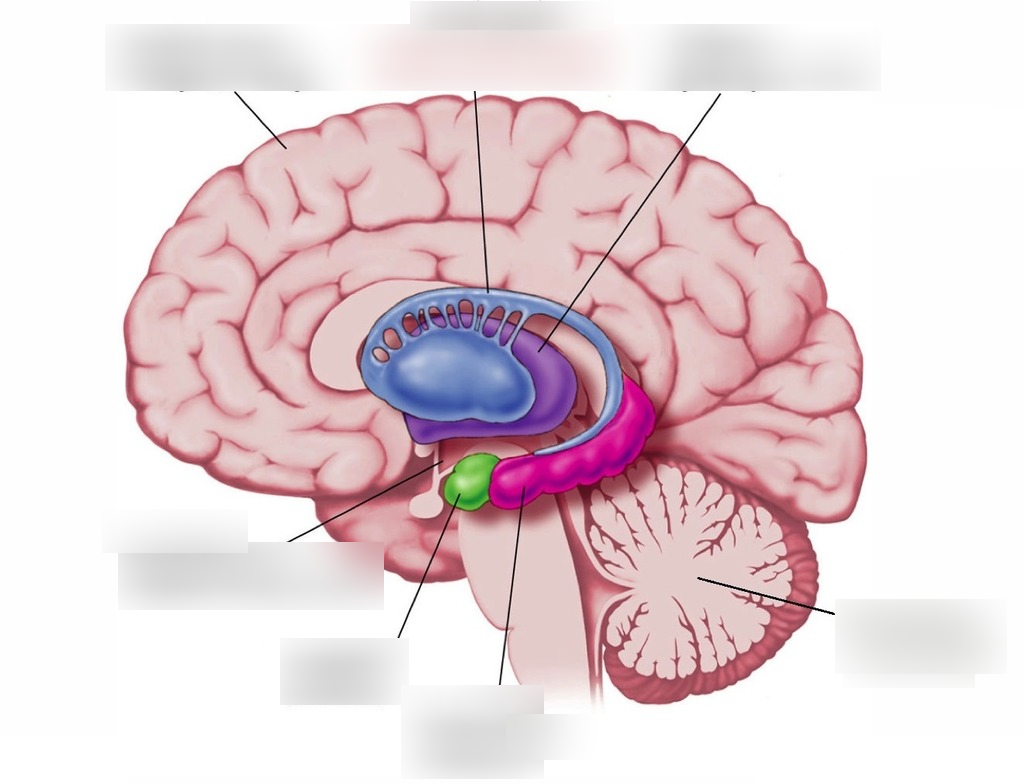
\#3
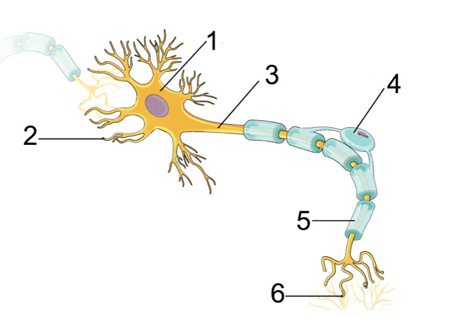
17
New cards
Myelin sheath
\#5
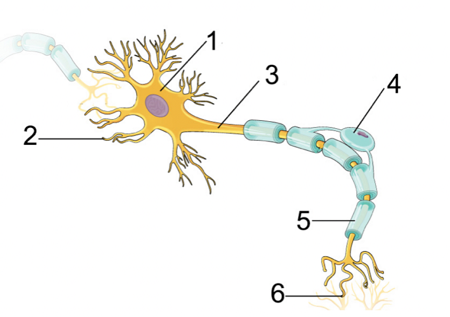
18
New cards
Terminal branches
\#6
19
New cards
Dendrites, Cell Body, Axon, Terminal Branches
Order of how impulse travels through a neuron
20
New cards
Resting potential
When a neuron is positively charged on the outside and negatively charged on the inside
21
New cards
Depolarization
When the neuron no longer has a charge difference between the inside and outside of the axon membrane
22
New cards
Excitatory signal exceeding the inhibitory signal by a mimum threshold
What triggers an action potential?
23
New cards
No
Can an action potential happen during the refractory period?
24
New cards
More neurons are triggered and fire more rapidly
How do humans sense the intensity of a stimulus?
25
New cards
Synaptic gap
What is the space between neurons called?
26
New cards
They bind to receptor sites on receiving neurotransmitters
What happens when neurotransmitters cross the synaptic gap?
27
New cards
Brake down, drift away, reabsorbed (reuptake)
What happens to excess neurotransmitters?
28
New cards
Acetylcholine (ACh)
\
* Function: Enables muscle action, learning, and memory
* Malfunction: Alzheimer’s when the neurons that produce this neurotransmitter deteriorate
* Function: Enables muscle action, learning, and memory
* Malfunction: Alzheimer’s when the neurons that produce this neurotransmitter deteriorate
29
New cards
Dopamine
\
* Function: Influence movement, learning, attention, and emotion
* Malfunction: Oversupply can cause schizophrenia and undersupply can lead to Parkinson’s
* Function: Influence movement, learning, attention, and emotion
* Malfunction: Oversupply can cause schizophrenia and undersupply can lead to Parkinson’s
30
New cards
Serotonin
\
* Function: Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
* Malfunction: Undersupply linked with depression
* Function: Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
* Malfunction: Undersupply linked with depression
31
New cards
Norepinepherine
\
* Function: Control alertness and arousal
* Malfunction: Depressed mood
* Function: Control alertness and arousal
* Malfunction: Depressed mood
32
New cards
GABA
\
* Function: Major inhibitory neurotransmitter
* Malfunction: undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia
* Function: Major inhibitory neurotransmitter
* Malfunction: undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia
33
New cards
Glutamate
\
* Function: Major excitatory neurotransmitter involved in memory
* Malfunction: Oversupply over stimulates the brain and causes migraines or seizures
* Function: Major excitatory neurotransmitter involved in memory
* Malfunction: Oversupply over stimulates the brain and causes migraines or seizures
34
New cards
Endorphins
\
* Function: Neurotransmitters that influence pain/pleasure perception
* Malfunction: Oversupply caused by opiates can suppress the body’s natural supply
* Function: Neurotransmitters that influence pain/pleasure perception
* Malfunction: Oversupply caused by opiates can suppress the body’s natural supply
35
New cards
Agonist
A molecule that increases a neurotransmitter’s action
36
New cards
Anatgonist
A molecule that inhibits or blocks a neurotransmitter’s action
37
New cards
Nervous system
The body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous system
38
New cards
Central nervous system
The brain and the spinal cord
39
New cards
Peripheral nervous system
\
The sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
The sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
40
New cards
Nerves
Bundled axons that form neural cables connecting the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs
41
New cards
Sensory (afferent) neurons
Neurons that carry incoming information from the body’s tissues and sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
42
New cards
Motor (efferent) neurons
Neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
43
New cards
Interneurons
Neurons within the brain and spinal cord; they communicate internally and process information between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
44
New cards
Somatic nervous system
\
The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles
The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles
45
New cards
Autonomic nervous systen
\
The part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic divisions arouses and the parasympathetic division calms.
The part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic divisions arouses and the parasympathetic division calms.
46
New cards
Sympathetic nervous system
The division of the ANS that arouses the body
47
New cards
Parasympathetic nervous system
\
The division of the ANS that calms the body
The division of the ANS that calms the body
48
New cards
Reflex
A simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response
49
New cards
Endocrine system
The body’s slow chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
50
New cards
Hormones
\
Chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues
Chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues
51
New cards
Adrenal glands
A pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones that help arouse the body in times of stress
52
New cards
Pituitary glands
The endocrine system’s most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, it regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands
53
New cards
Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System
2 major parts of the nervous system
54
New cards
Sensory, motor, interneurons
What are the three types of neurons
55
New cards
Somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system
Two parts of the peripheral nervous system
56
New cards
Sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system
What are the two parts of the autonomic nervous system?
57
New cards
Neural networks
The neruons in the brain that have clustered into work groups
58
New cards
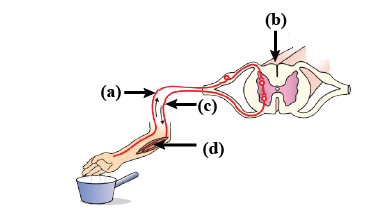
Sensory neuron
A
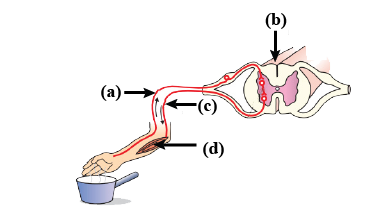
59
New cards
Interneuron
B
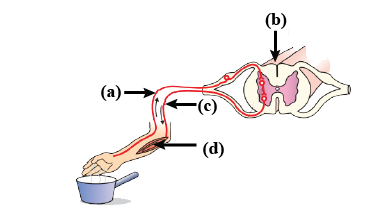
60
New cards
Motor neuron
C
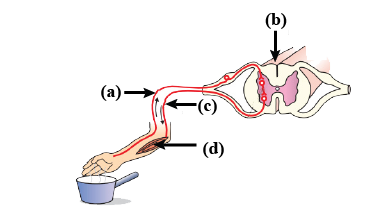
61
New cards
Muscle
D
62
New cards
Similarities between endocrine and nervous system
Hormones and neurotransmitters can be chemically similar
Both produce chemicals that act on receptors elsewhere
Both produce chemicals that act on receptors elsewhere
63
New cards
endocrine, nervous
The ______ system is slower but the effects last longer than the __ system
64
New cards
Hypothalamus
Brain region controlling pituitary gland
65
New cards
Thyroid gland
Affects metabolism
66
New cards
Adrenal gland
Inner parts help trigger the fight or flight response
67
New cards
Testis
Secrete male sex hormones
68
New cards
Pituitary gland
Secretes many different hormones, some of which affect other glands
69
New cards
Parathyroids
\
Help regulate the level of calcium in the blood
Help regulate the level of calcium in the blood
70
New cards
Pancreas
Regulates the level of sugar in the blood
71
New cards
Ovary
Secretes female sex hormones
72
New cards
Pituitary
What is the most influential gland in the endorcine system and it is controlled by the hypothalamus
73
New cards
EEG
\
Measures the electrical activity in the brain, information is collected by placing electrodes on the scalp
Measures the electrical activity in the brain, information is collected by placing electrodes on the scalp
74
New cards
MEG
Measures the magnetic fields from the brain’s natural electrical activity
75
New cards
CT/CAT scan
\
* Series of X-ray photos taken from different angles and combined into a composite representation of a slice of the brain’s structure
* Help reveal brain damage
* Series of X-ray photos taken from different angles and combined into a composite representation of a slice of the brain’s structure
* Help reveal brain damage
76
New cards
PET scan
\
* A visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose foes while the brain performs a given task
* A visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose foes while the brain performs a given task
77
New cards
MRI scan
\
* A technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue. Shows brain anatomy
* A technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue. Shows brain anatomy
78
New cards
fMRI scan
\
* A technique for revealing blood flow, and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans. fMRI scans show brain function as well as structure
* A technique for revealing blood flow, and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans. fMRI scans show brain function as well as structure
79
New cards
The brainstem
The oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull. It is responsible for automatic survival functions
80
New cards
Medulla
The base of the brainstem
Controls heart rate and breathing
Controls heart rate and breathing
81
New cards
Pons
Above the medulla
Coordinate movement and sleep
Coordinate movement and sleep
82
New cards
The Thalamus
\
* Sits atop the brainstem
* Sensory control center of the brain
* Receives all information from sense except scent and routes it to the right places in the higher regions of the brain
* Sits atop the brainstem
* Sensory control center of the brain
* Receives all information from sense except scent and routes it to the right places in the higher regions of the brain
83
New cards
The Reticular Formation
\
* Neuron network that goes from the spinal cord up through to the thalamus
* Filters incoming stimuli and relays information to other parts of the brain
* Also controls arousal
* Neuron network that goes from the spinal cord up through to the thalamus
* Filters incoming stimuli and relays information to other parts of the brain
* Also controls arousal
84
New cards
The Cerebellum
\
* Extends from the back of the brainstem
* Enables nonverbal learning and skill memory
* Judge time, modulate emotions, discriminate sounds and textures
* Coordinates voluntary movement
* Extends from the back of the brainstem
* Enables nonverbal learning and skill memory
* Judge time, modulate emotions, discriminate sounds and textures
* Coordinates voluntary movement
85
New cards
The Limbic System
\
* Neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres and is associated with emotions and drives
* Contains the amygdala, hypothalamus, and hippocampus
* Neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres and is associated with emotions and drives
* Contains the amygdala, hypothalamus, and hippocampus
86
New cards
Amygdala
\
* Linked with aggression and fear
* Linked with aggression and fear
87
New cards
The hypothalamus
\
* Just below the thalamus
* Influences hunger, thirst, body temperature, and sex drive
* Helps maintain homeostasis
* Contains reward centers
* Just below the thalamus
* Influences hunger, thirst, body temperature, and sex drive
* Helps maintain homeostasis
* Contains reward centers
88
New cards
The hippocampus
\
* Process conscious, explicit memories
* Decreases in size and function as we grow older
* Process conscious, explicit memories
* Decreases in size and function as we grow older
89
New cards
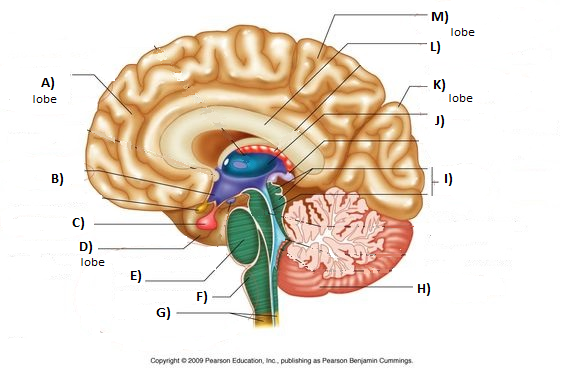
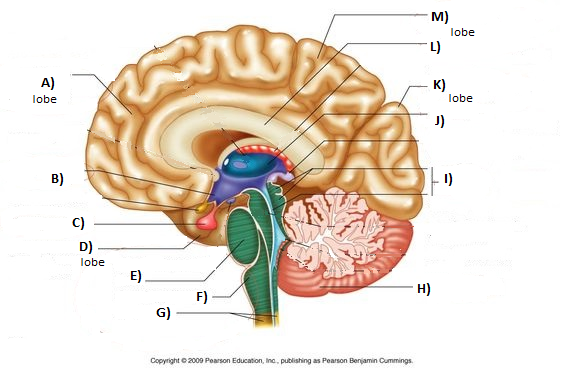
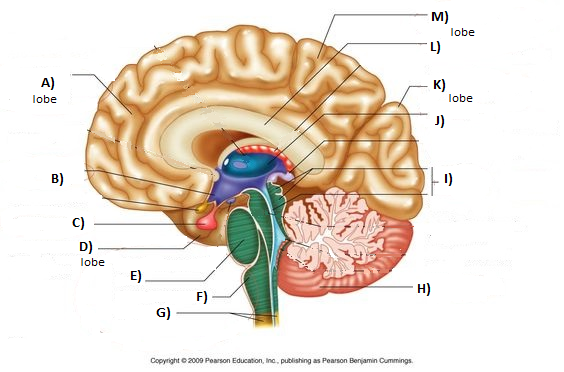
Brainstem
F, E, and reticular formation
90
New cards
Medulla
F
91
New cards
Pons
E
92
New cards
Thalamus
J
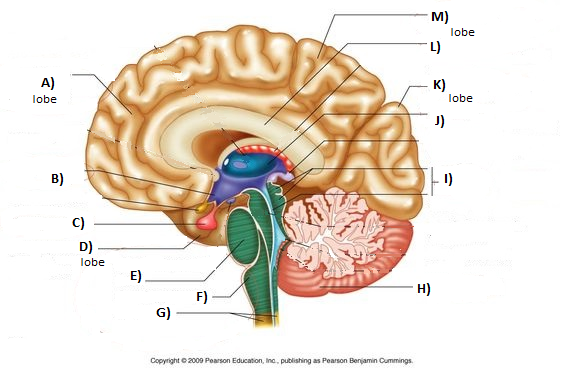
93
New cards
Cerebellum
H
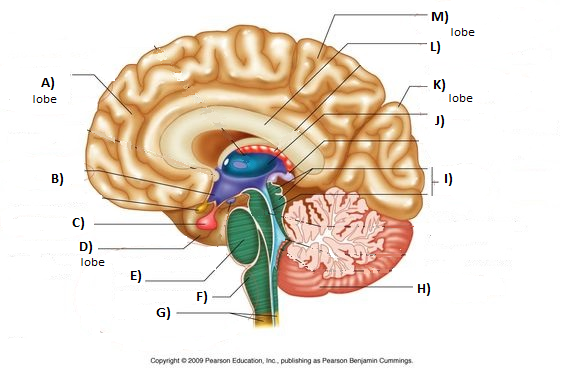
94
New cards
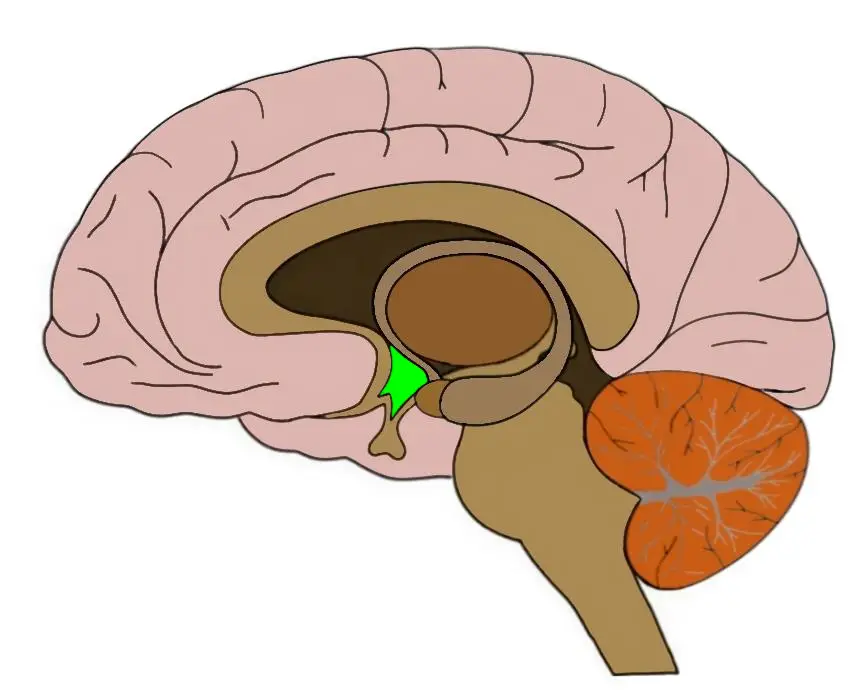
Amygdala
Green section
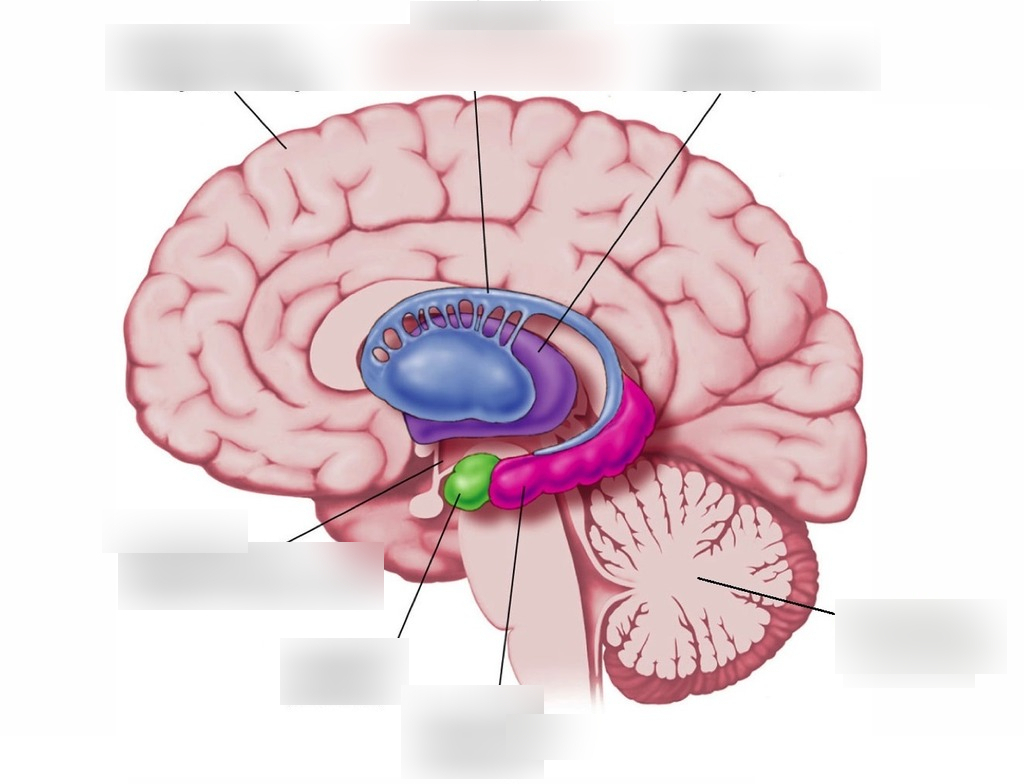
95
New cards
Hypothalamus
96
New cards
Hippocampus
Pink section
97
New cards
Cerebral cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body’s ultimate control and information-processing center
98
New cards
Frontal lobes
The portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead; involved in speaking, muscle movements, and making plans/judgments
99
New cards
Parietal lobes
\
The portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body positions
The portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body positions
100
New cards
Motor cortex
An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movement