Diueretics, CCB, BB, ACEi, ARBs
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
diuretics are classified according to their
site of action
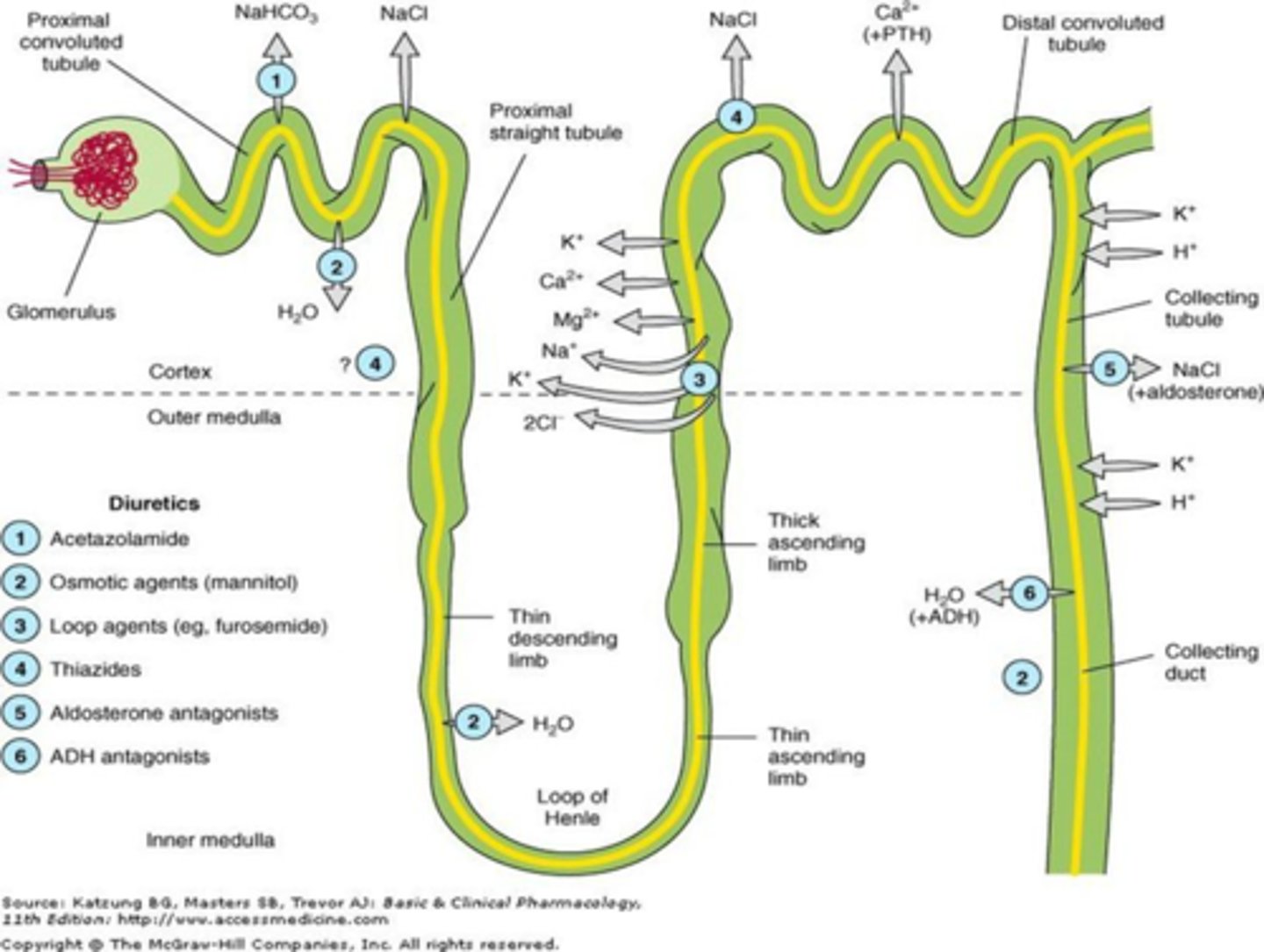
osmotic diuertic
mannitol
MOA of mannitol
Filtered at the glomerulus but poorly
reabsorbed; water is held in the lumen by
the osmotic effect producing diuresis
primary site of action of mannitol
proximal convoluted tubule
main therapeutic use of mannitol
-head trauma
-Rapid (emergent) treatment of increased intracranial pressure
carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Acetazolamide
other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors used for glaucoma
•Dorzolamide (Trusopt ®)-topical eye drop
•Brinzolamide (Azopt ®)-topical eye drop
•Methazolamide (Neptazane®) –oral
Key to diuretic action in the PCT is inhibition of reabsorption of
•NaCl
•NaHCO3
MOA of CA inhibitors (acetazolamide)
inhibits carbonic anhydrase in the proximal convoluted tubule resulting in excretion of sodium bicarbonate
-decreases bicarb and sodium reabsorption
CA inhibitors makes the urine
alkalinized
acetazolamide is not a
good option for a diuretic
most potent diuretics
loop diuretics
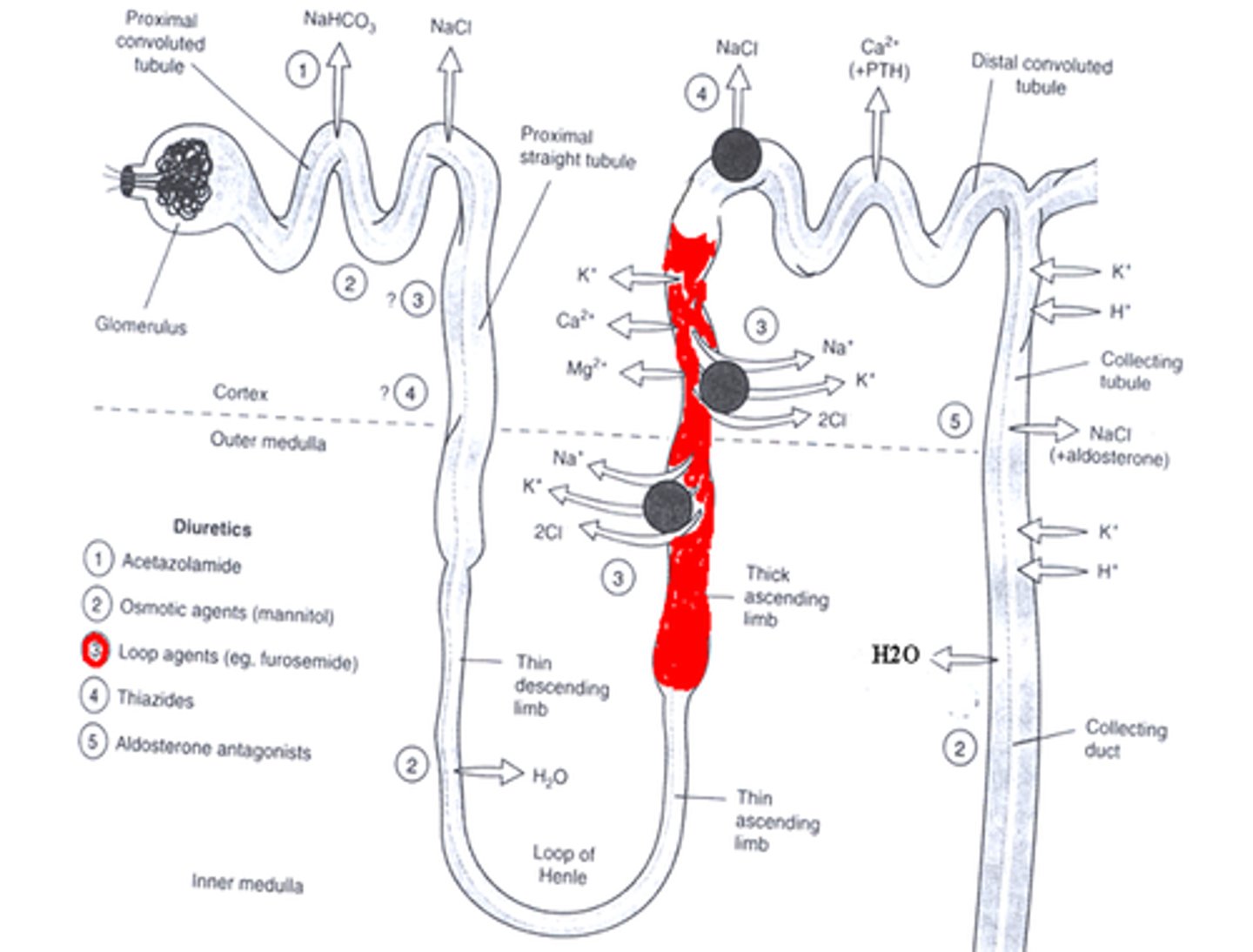
key therapeutic uses of loop diuretics
-CHF
-edema
-kidney disease
site of action of loop diuretics
ascending limb of loop of henle (big site of reabsorption of many electrolytes)
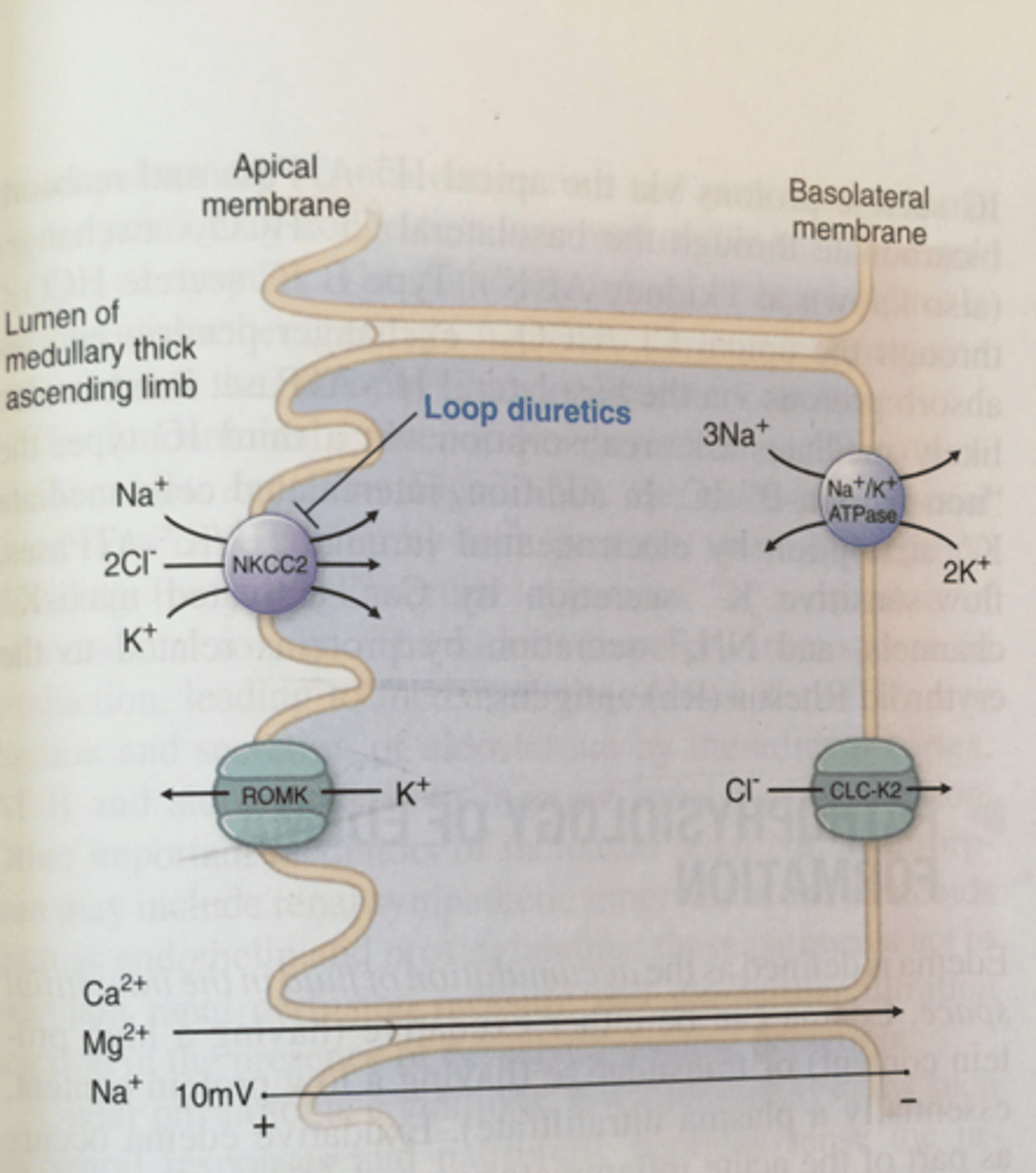
MOA of loop diuertics
inhibits the sodium-potassium- chloride transporter and reducing Na reabsorption in the ascending loop of Henle
uIncreased loss of: Na, Cl, H2O, K, Mg, Ca
what do you lose when you use a loop diuretic
potassium
name the loop diuertics
uFurosemide (Lasix®)
uBumetanide (Bumex)
uTorsemide (Demedex)
uEthacrynic acid (Edecrin)
is about 40 times more potent than furosemide
bumetanide
may be used in patients allergic to other loop diuretics (not a sulfonamide)
Ethacrynic acid
Greater ototoxic potential than other loop diuretics
Ethacrynic acid
All loop diuretics are
ototoxic
-limit infusion rate of furosemide to 4mg/min
electrolyte imbalances of loop diuertics
Hypokalemia(arrythmias), hypochloremia, hypomagnesemia
alkalosis
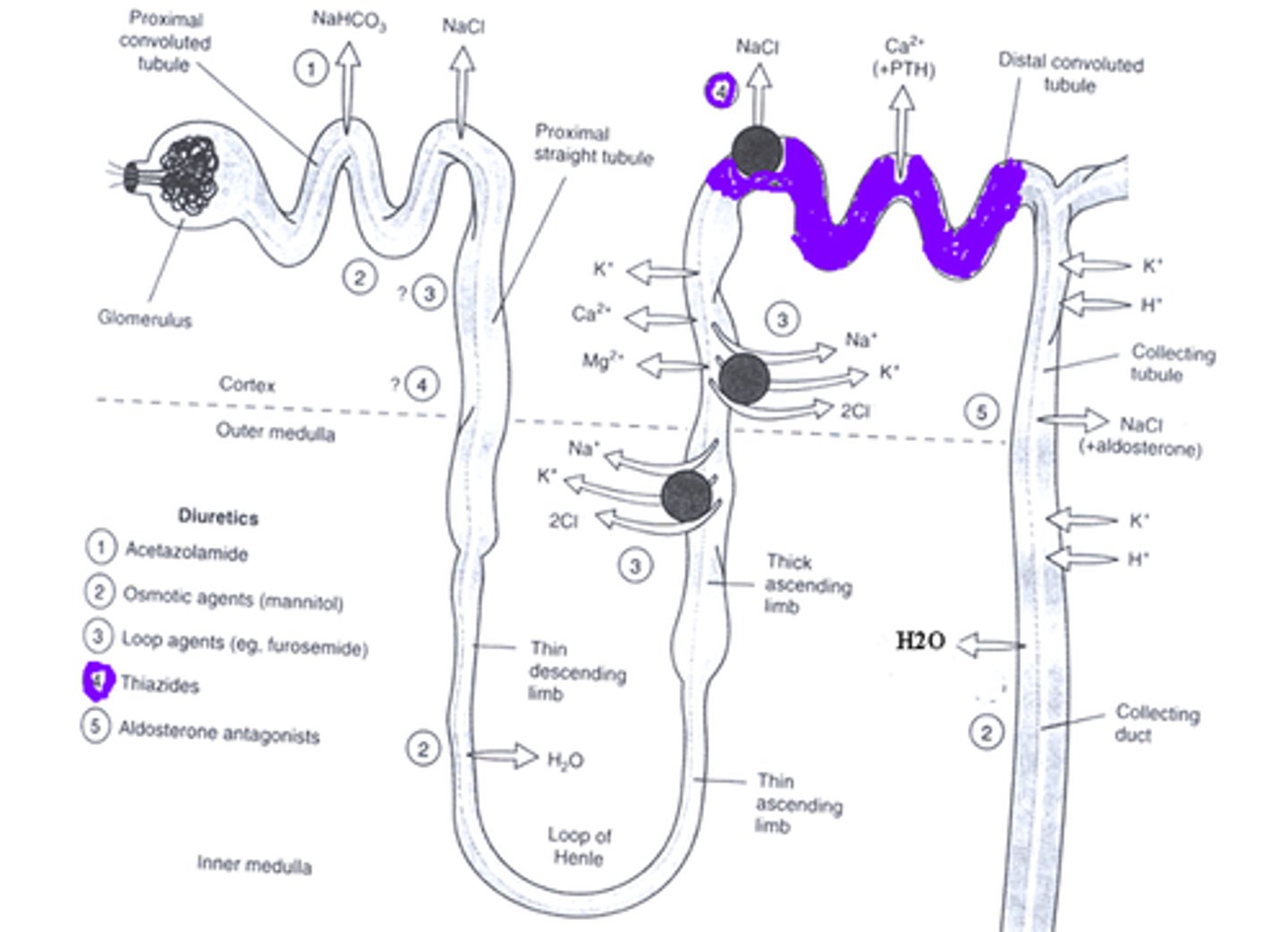
moa of thiazide diuretics
Inhibit the reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions in the distal convoluted tubules by blocking the Na-Cl transporter
site of action of thiazide diuertics
distal convoluted tubule
name the thiazie diuretics
Chlorothiazide (Diuril©) - iv & po
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) - po
Metolazone (Zaroxolyn©) po
Chlorthalidone - po
Indapamide (Lozol ©) po
PTH is affiliated in the area of the
distal convoluted tubule and regulates calcium
which thiazide diuretic has a long half life (47 hours)
chlorthalidone
therapeutic use of thiazide diuertic
-HTN
-prevention hypercalcemic kidney stones
electrolyte imbalances of thiazide diuertics
Hypokalemia
Hypochloremia
Hypomagnesemia
decrease calcium excretion in the kidney and increase calcium in the blood.
thiazide diuertics can exacerbate
gout (hyperuricemia)
may be used together to optimize the diuretic efficacy by interfering with sodium reabsorption at the thick ascending loop and the distal convoluted tubule
Loop and thiazide
Treatment option for diuretic resistance
Loop and thiazide
which do you give first?
thiazide before loop
long term use of loop can cause
diuretic resistance: hypertrophy of distal nephron segments resulting in increased reabsorption of sodium at distal sites
loops decrease ____ and thiazides inc ____
calcium
potassium sparing diuretics site of action
last distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct
MOA of spirnolactone
synthetic hormone that competes with aldosterone in the collecting duct and late DCT for the mineralocorticoid site to reduce the synthesis of sodium channels resulting in loss of Na and retention of K (↓ Na, ↑ K)
SE of spirnolactone
gynecomastia
Spironolactone analog
More selective than spironolactone; less active on androgen site
Eplerenone
potassium sparing diuertics that block sodium channel activity in the collecting tubule
Amiloride
Triameterene
frequently combined with HCTZ to prevent hypokalemia
Triameterene
SE of potassium sparing diuertics
hyperkalemia especially when used alone
action of the calcium channel
Increased concentration of cytosolic Ca+2 causes contraction in vascular smooth muscle and cardiac cells
MOA of calcium channel blockers
Blocks the flow of calcium into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle resulting in decreased intracellular calcium
dihydropyridine CCB
Amlodipine
Nifedipine
Clevidipine
Felodipine
Nondihydropyridines CCB
Diliriazem
Verapamil
most negative ionotropic CCB
verapamil
decreasing contraction and conduction
verapamil
dilitazem
vasodilates the most (CCB)
amlodipine
all CCB cause
vasodilitation
_____ CCB best for HTN
dihydropyridine
____ CCB best for arrythmias
nondihydropyridine
ADE of verapamil
constipation
ALL CCBs ADE
Peripheral edema
Headache
Gingival hyperplasia
SE specific to DHP CCBs
Reflex tachycardia
Flushing
SE specific to nDHP CCBs
Bradycardia
Heart block
be cautious using a nDHP with a
beta blocker
action of BB in the heart
Block action of norepinephrine and epinephrine at β1 receptors on cardiac muscles
-Reduce HR and contractility → decreased cardiac output
BB action on the kidneys
Decrease renin release from juxtaglomerular cells → decreased total peripheral resistance (TPR)
uMixed α- and β- Blockers
Block action of norepinephrine at α-1 receptors -> vasodilation with no reflex tachycardia
Chronic use of BB results in upregulation of Beta receptors resulting in super-sensitivity to
β agonists (always taper a beta blocker)
cardioselective BB
B1 > B2
name the cardioselective BB
•Metoprolol succinate (Toprol XL)
•Metoprolol tartrate (Lopressor)
•Atenolol (Tenormin)
•Esmolol (Brevibloc)
•Acebutolol (Sectral)**
•Betaxolol (Kerlone)
•Bisoprolol (Zebeta)
•Nebivolol (Bystolic)
dont use ____ BB with asthmatic pts
non selective (because they also block B2)
name the mixed a and b
carvedilol
labetalol
name the nonselective BB
•Nadolol (Corgard)
•Propranolol (Inderal)
•Sotalol* (Betapace)
•Pindolol (Visken)**
•Timolol (Blocadren)
always used as an antiarythmic
Sotalol
have intrinsic sympathomimetic activity
Pindolol
Acebutolol
partial agonist activity providing beta stimulation at rest but acts as a typical beta-blocker when sympathetic activity is high.
Pindolol
Acebutolol
is a racemic mixture
sotalol
ADE of BB
-mask the signs of hypoglycemia
-bradycardia
-heart block
-erectile dysfunction
-depression
SE of nonselective BB
bronchoconstriction
is a naturally occurring peptide hormone of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) that causes increased vasoconstriction and increase in blood pressure
angiotensin II
MOA of ACEi
Inhibit ACE to block conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II
how do ACEi affect bradykinin
Inhibition of bradykinin metabolism increased PG = vasodilation & decreased BP
ADE of ACEi
Dry cough
angioedema
hyperkalemia
ACEi contraindicted in
pregnancy
do not use ACEi in patients with
bilateral renal artery stenosis
name some ACE inhibitors
Captopril
Enalapril
Lisinopril
Ramipril
MOA of arbs
selective, competitive angiotensin II receptor blockade
Blocks the vasoconstriction and aldosterone - secreting effects of angiotensin II
SE of ARBs
Less incidence of cough and angioedema than with ACE inhibitors
Hyperkalemia (monitor K)
Contraindicated for use in pregnancy
Acute kidney injury (Monitor Scr)
Do not use in bilateral renal artery stenosis
name some ARBs
Candesartan
Losartan
Olmesartan
Valsartan
ARBS act on the
AT1 receptor (not AT2 receptor)