Geology
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
When looking at meteorites, what do you see?
Fusion crust - dull black to dark brown, oftens oft, can be weathered to red (but can flake off).
Generally dense.
Condrules are specifically meteoric.
Never porous, but can be dimpled with surface depressions.
99% of meteorites are magnetic.
Usually high in Fe or Ni.
What is the best place for collecting meteorites?
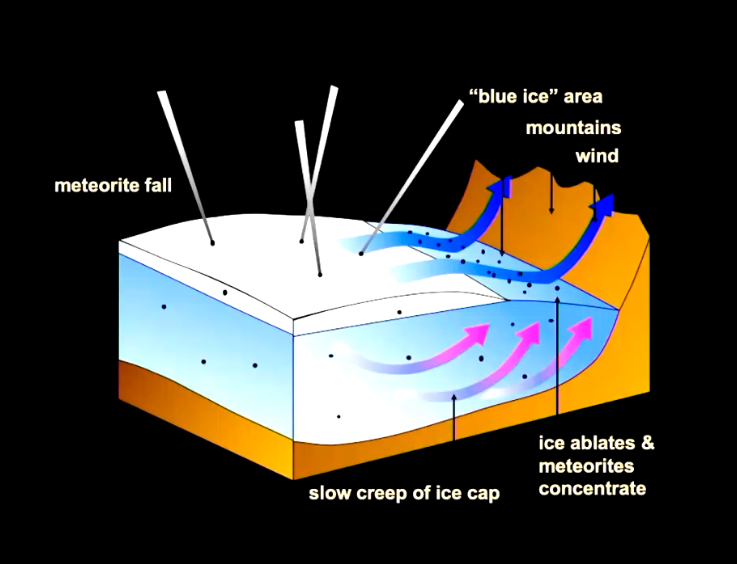
Antartica.
Easy to spot in the snow.
Glaciers flow towards the ocean, but may hit a natural barrier like a mountain, forcing the ice upward and exposing it to the surface.
As the ice sublimates (turns from ice to vapor due to wind a nd sun), meteorites are left on the surface.
Why have many meteorites been found in desert?
The heat and dryness keeps them from rusting away.
When meteorites are discovered, they are called finds.
What is a mineral?
A naturally occurring inorganic crystalline compound.
May be composed of one element, but more commonly has two or more elements.
What is a rock?
AA mixture of minerals.
What are the three main categories of meteorites?
Stony: like terrestrial rocks and may be difficult to distinguish fro terrestrial rock, unless the fall is witnessed.
Iron: nearly pure nickel-iron, and high density.
Stony-iron: mixture of stone and metallic iron.
Where do the different types of meteorites come from?
Iron meteorites: core of differentiated planetesimals.
As early planetesimals melted, dense metals like iron and nickle sank to form a metallic core.
Stony-iron: core-mantle boundary.
Stony (chondrites): material that never melted or differentiaed.
Stony (achondrites): crust or mantles
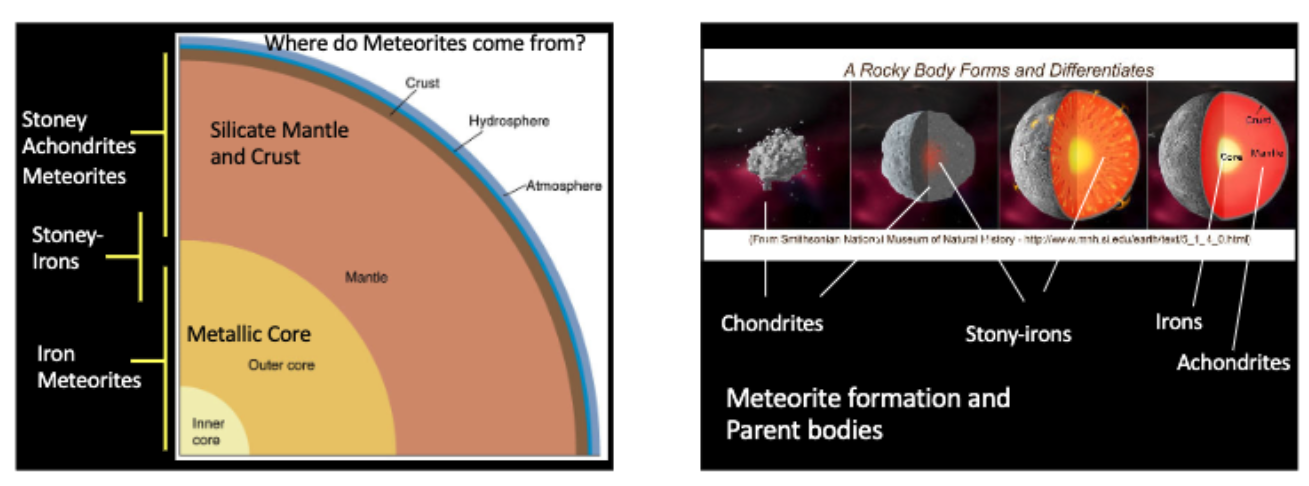
What are chondrites? Why are they spherical?
A form of meteorites composed of chondrules.
Parent bodies were small-medium asteroids, not planetoids.
Chondrules are formed from molten droplets in space.
What are the different types of chondrites?
Ordinary: make up 80% of the meteorites, and 90% of chondritic meteorites, abundant chondrules, variable Fe-Ni contents.
Carbonaceous chondrites: less than 5% of chondritic meteorites, few chondrules, more lithophile elements )Ca, mg, K, Cr), high levels of water and organic compounds (older than ordinary chondrites).
WHat does the crystal texture of chondrules indicate?
Indicates rapid cooling of chondrules in zero gravity.
What is interplanetary dust?
Interplanetary dust particles are minute pieces of space dust which rain down on the earth as it orbits the sun.
Interstellar in origin, dust grains of the origin primordial nebula.
What martian meteorites point to life on mars?
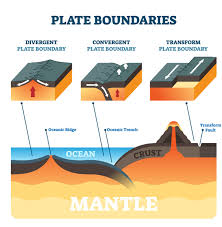
What are the different types of plate tectonic boundaries?
Convergent (moving together), leading to crust getting destroyed or thickened. Creates trenches, volcanic arcs, and mountains.
Divergent (moving apart), crust created. Produces mid-ocean ridge, rift valleys and shallow earthquakkes.
Transform (sliding past), crust unchanged, causes shallow but powerful earthquakes.
What are basalts?
Type of volcanic rock which makes up most of the oceanic crust.
It forms when mantle material melts and erupts at the seafloor, creating new crust.
What is seafloor spreading?
At a divergent plate boundary, molten rock rises from the mantle at a mid-ocean ridge
The magma cools and solidifies forming new basaltic crust.
As more magma rises and cooles, it pushes the older crust outwards.
This process adds a new ocean floor over time, moving tectonic plates apart.
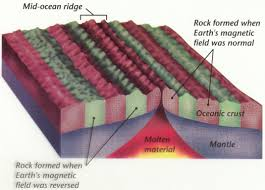
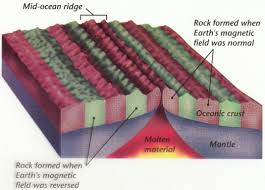
What is the age of the ocean floor relative to the map?
Youngest in the middle of mid-ocean ridges and older the further away.
As new oceanic crust forms at a mid-ocean ridge, molten basalt rises and cools quickly, where these iron rich minerals in basalt align with the direction of Earth’s magnetic field at that time.
This creates a record of Earth’s magnetic polarity, creating a strip.
Sometimes the magnetic field reverses, where this new strip of basalt records a new magnetic direction.
By comparing this signature to known history of magnetic reversals, scientists can determine the age of the ocean floor.
What are the four inner planets? What are they primarily composed of?
The four inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are primarily composed of rocks.
These rocks are principally silicate minerals and metallic iron, which have a melting point >700ºC.
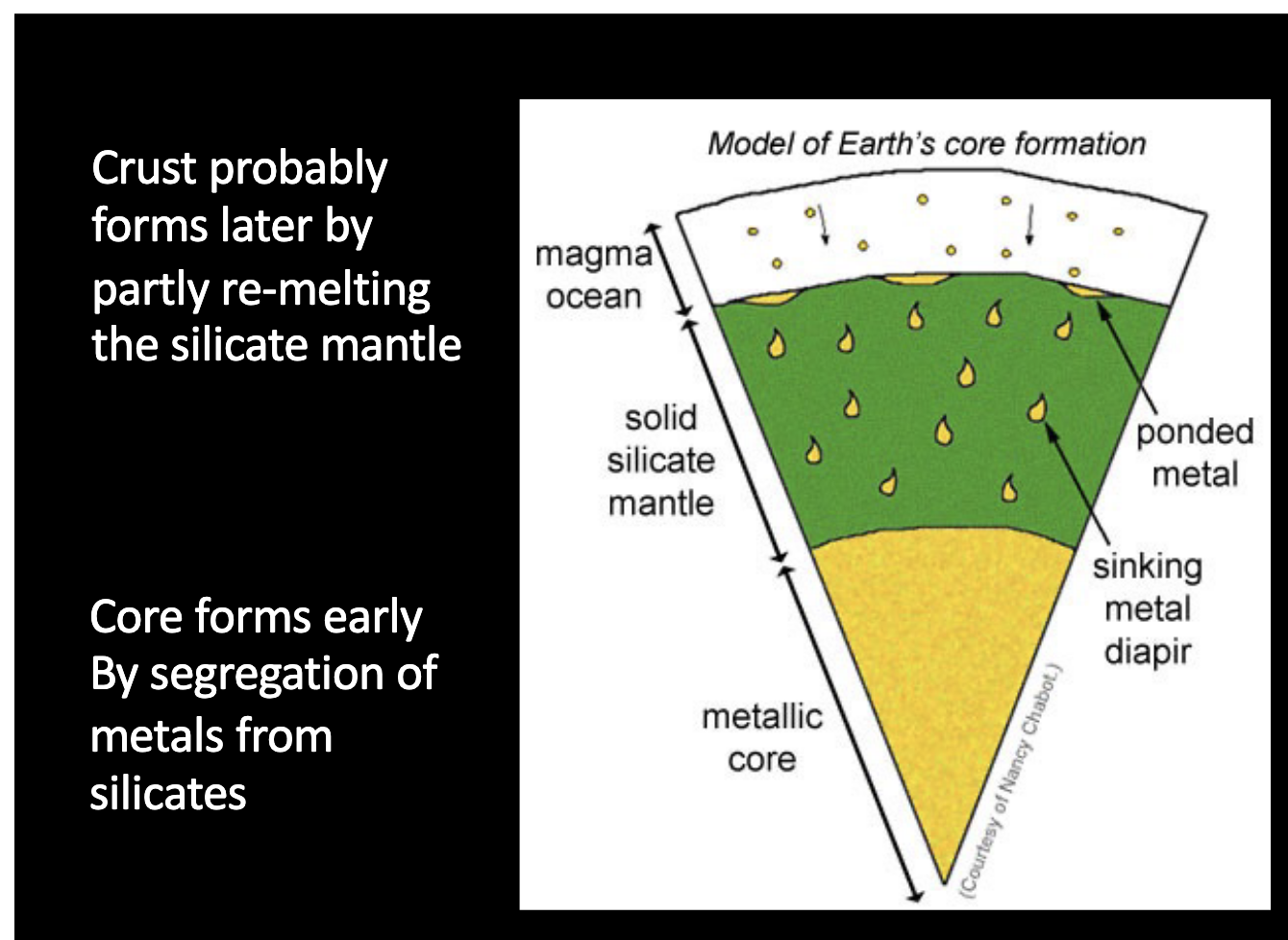
Describe planets core.
Liquid core convects - source of magnetic field.
Iron. Nickel and other iron-loving elements (platinum, gold, sulfur).
Melting chondrite material and separating iron.
Describe the mantle.
Minerals like olivine and pyroxene.
Magnesium and iron rich silicates.
Melting chondrite material and separating iron.
What is basalt?
Formed by partially melting mantle.
Forms most of crust on rocky planets.
Contains minerals like feldspar, pyroxene, olivine.
-more silica than mantle.
Describe Earth’s core formation.
What are planetary surfaces?
Volcanism eruption of molten material on surface.
Meteorite impacts.
Tectonism disruption of a planet’s surface by interal stress.
Sedimentation and erosion.
Surface changes made by wind water of ice life.
Describe lava and molvanoes on the Moon, MArs, and Earth
What is Io?

What is Europa?

What is Triton?

What happens during a meteorite impact?
Impact event: if the meteor survives atmospheric entry and hits the surface, releasing lots of energy.
This generates intense shock waves that travel through the ground and air.
Crater formation: material is ejected outward and upward. The surrounding rock melts, forming glassy material.
Bedrock fractures and deforms into a cone-shaped pattern (shatter cones).
The meteor and some rock are vaporised.
How did Lunar Maria form?

What is geological destiny?
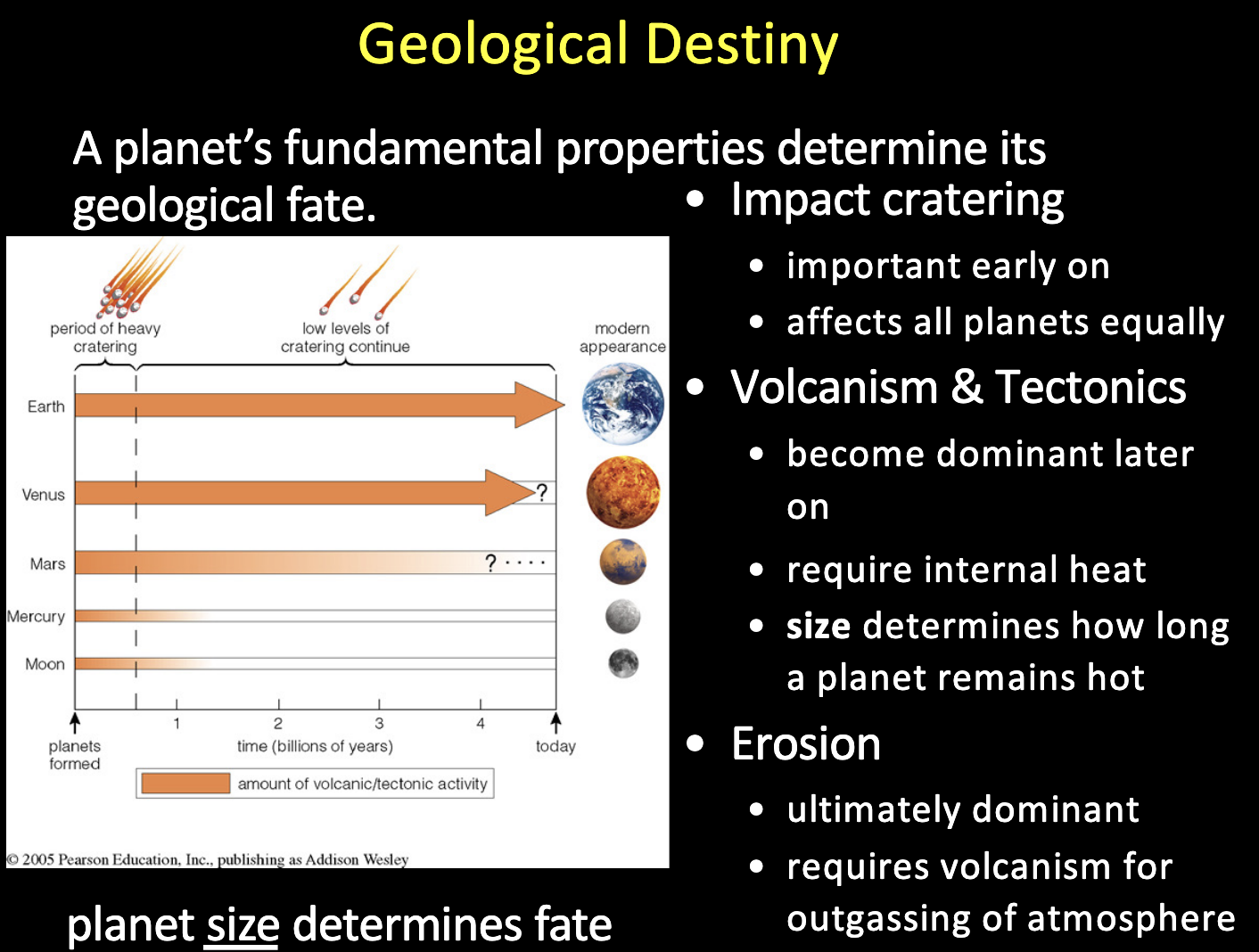
What other planets other than earth display tectonic processes?
Mars and Venus.
What did the martian surface contain a lot of?
Impact ejecta from comets and wind blown dust.
What is the relationship between grain size and energy level?
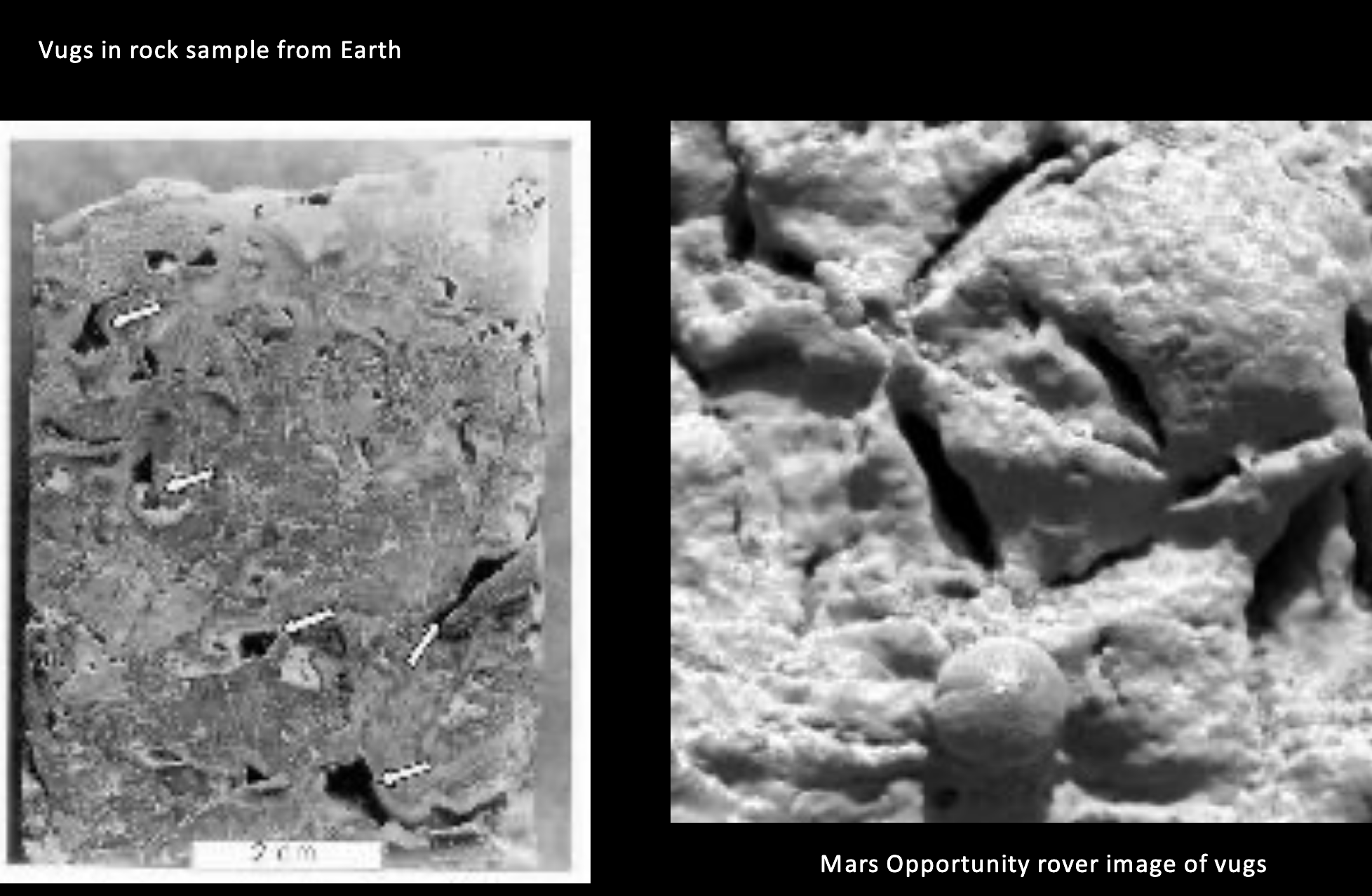


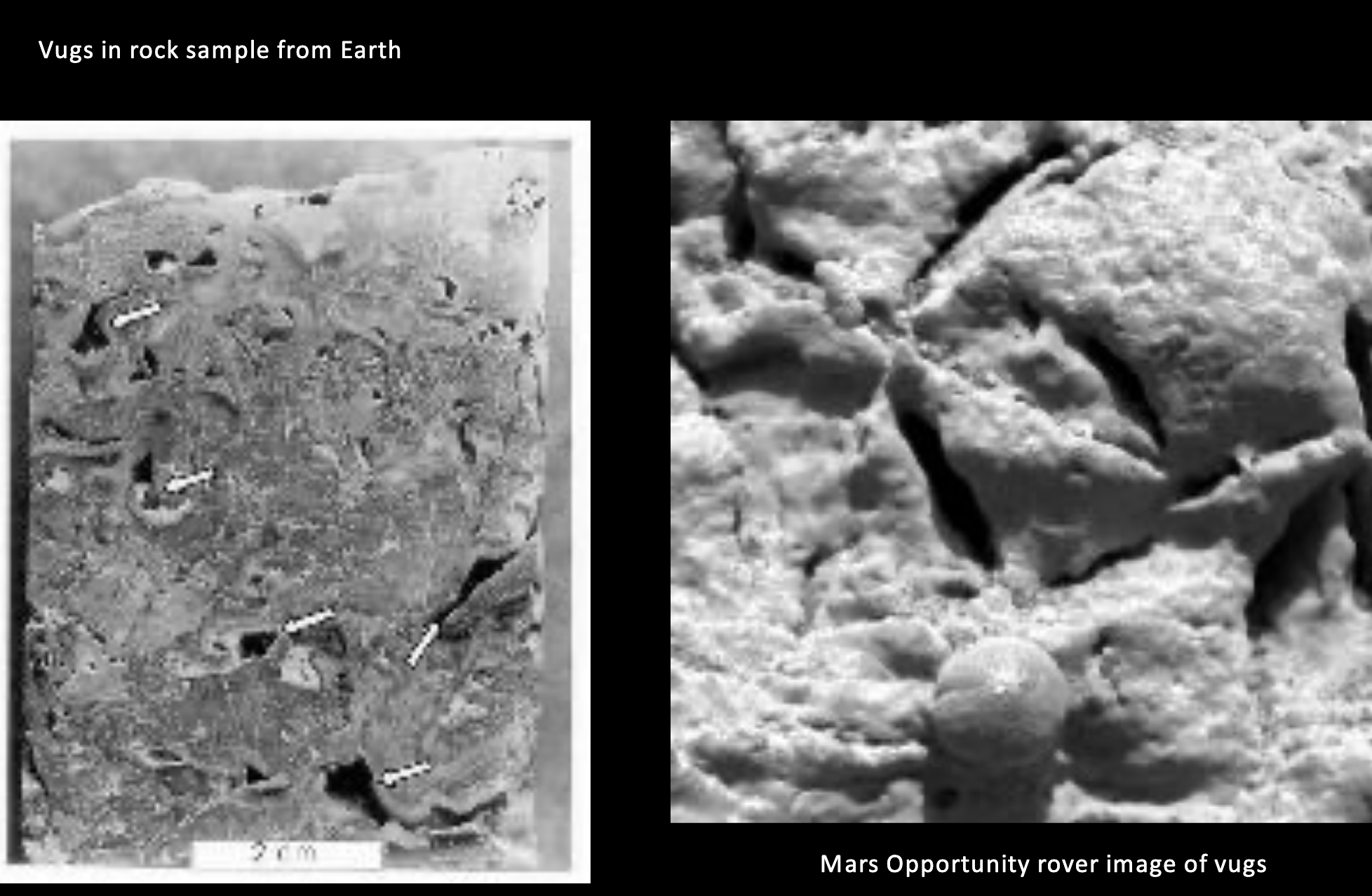
Why do vugs have holes?
Dissolved minerals: Water dissolves minerals, leaving holes.
Crystals may have grown inside of a vug, but not completely developed.

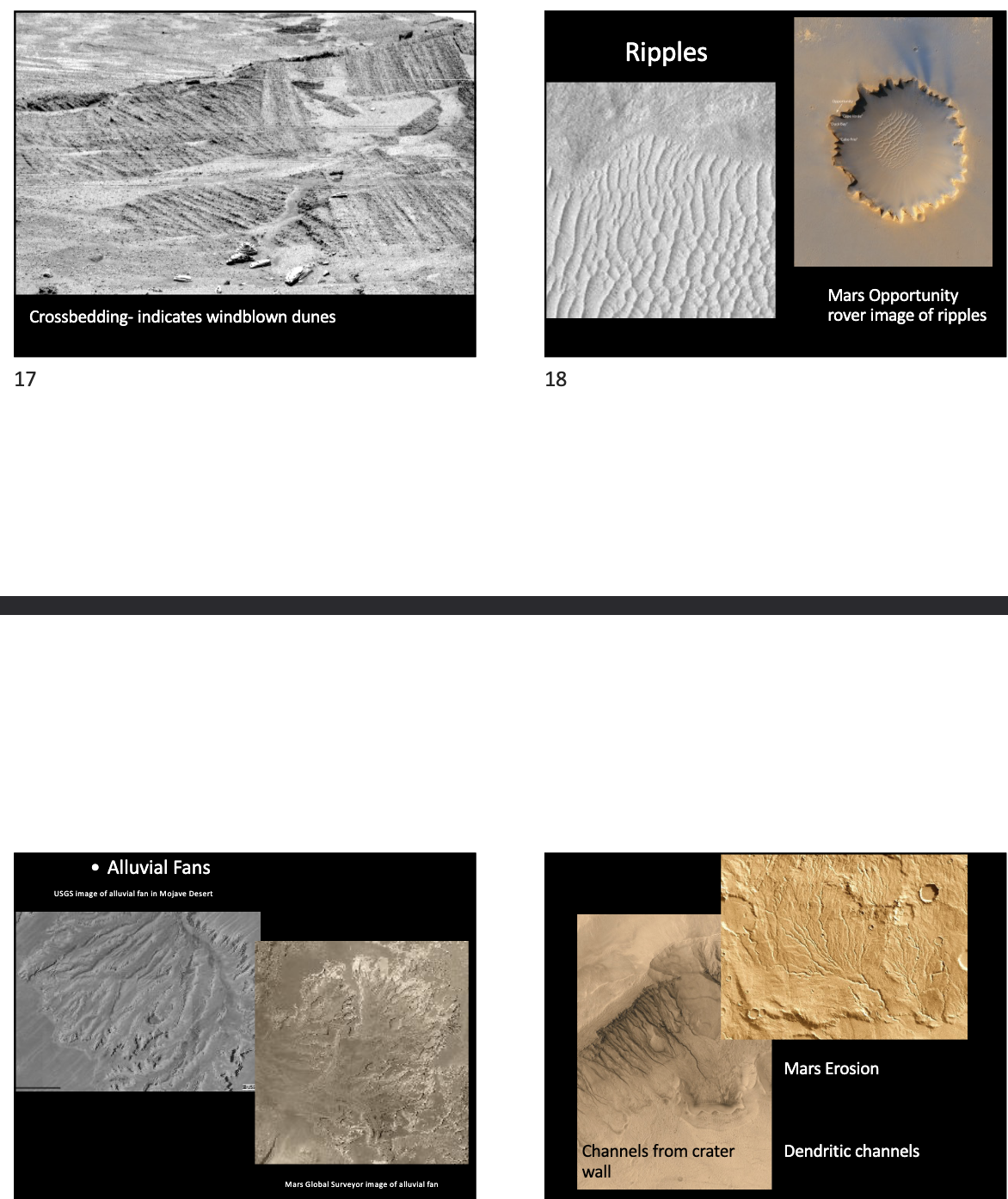
What evidence exists that Mars had liquid water?
Vugs.
Mars has layered sedimentary rocks that form from water-driven deposition.
Examples: cross-bedding, ripple marks, and mud cracks found by rovers
Hematites: Iron oxide material which can only form with water.
Ice caps on mars
What types of bonding is observed in minerals?
From weakest to strongest: Metallic bonds → ionic bonds → covalent bonds.
How does light look in minerals?
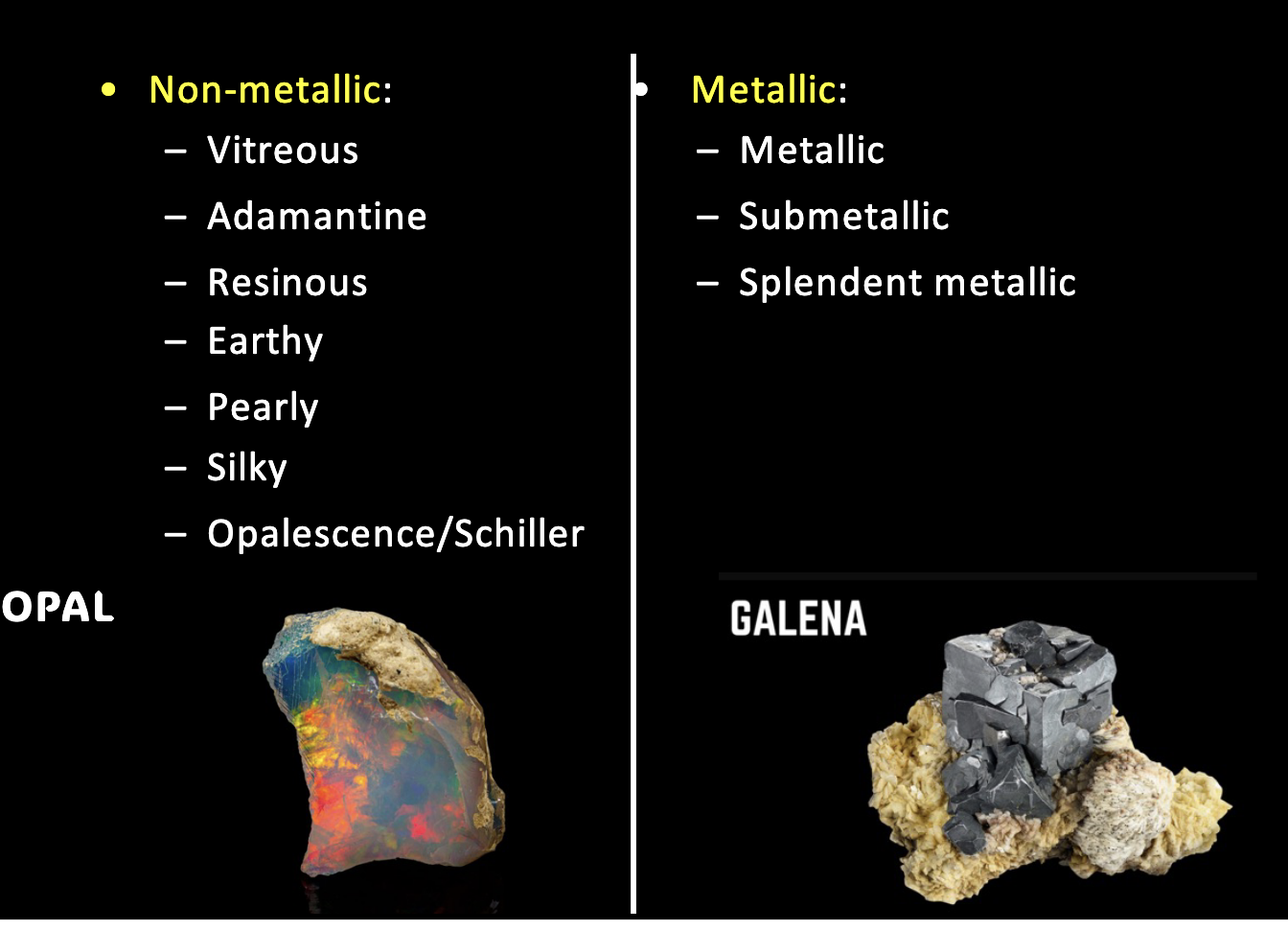
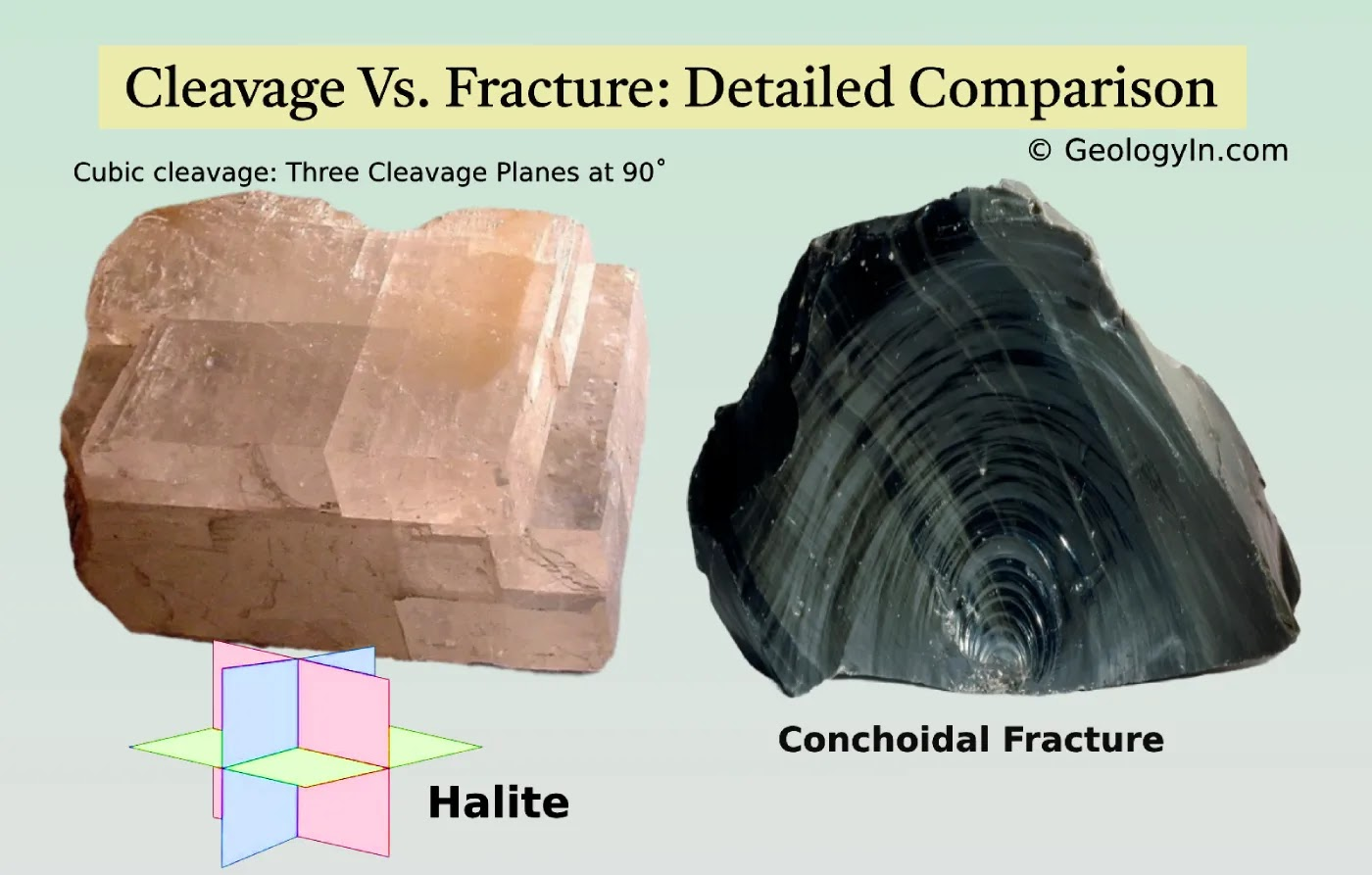
What is mineral fracture?
How a mineral breaks when it has no weak planes in its structure.
What is mineral cleavage?
Tendency for a mineral to split along a particular plane, where bonds are weakest.
Cleavage is repeatable and predictable, unlike fracture.
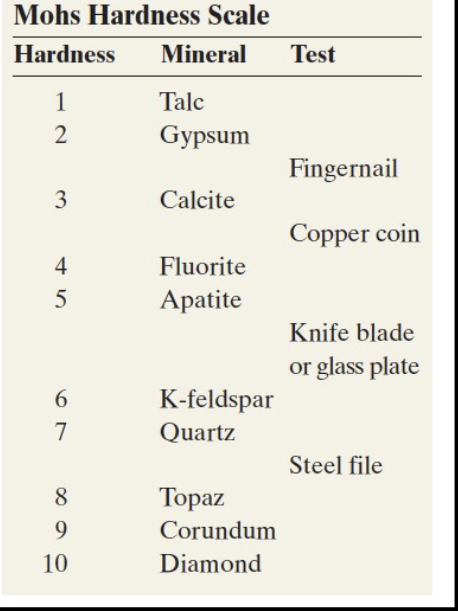
What is Mohs scale?
Hardness scale of minerals.
Draw the structure of earth.
Solid inner core, liquid outer core.
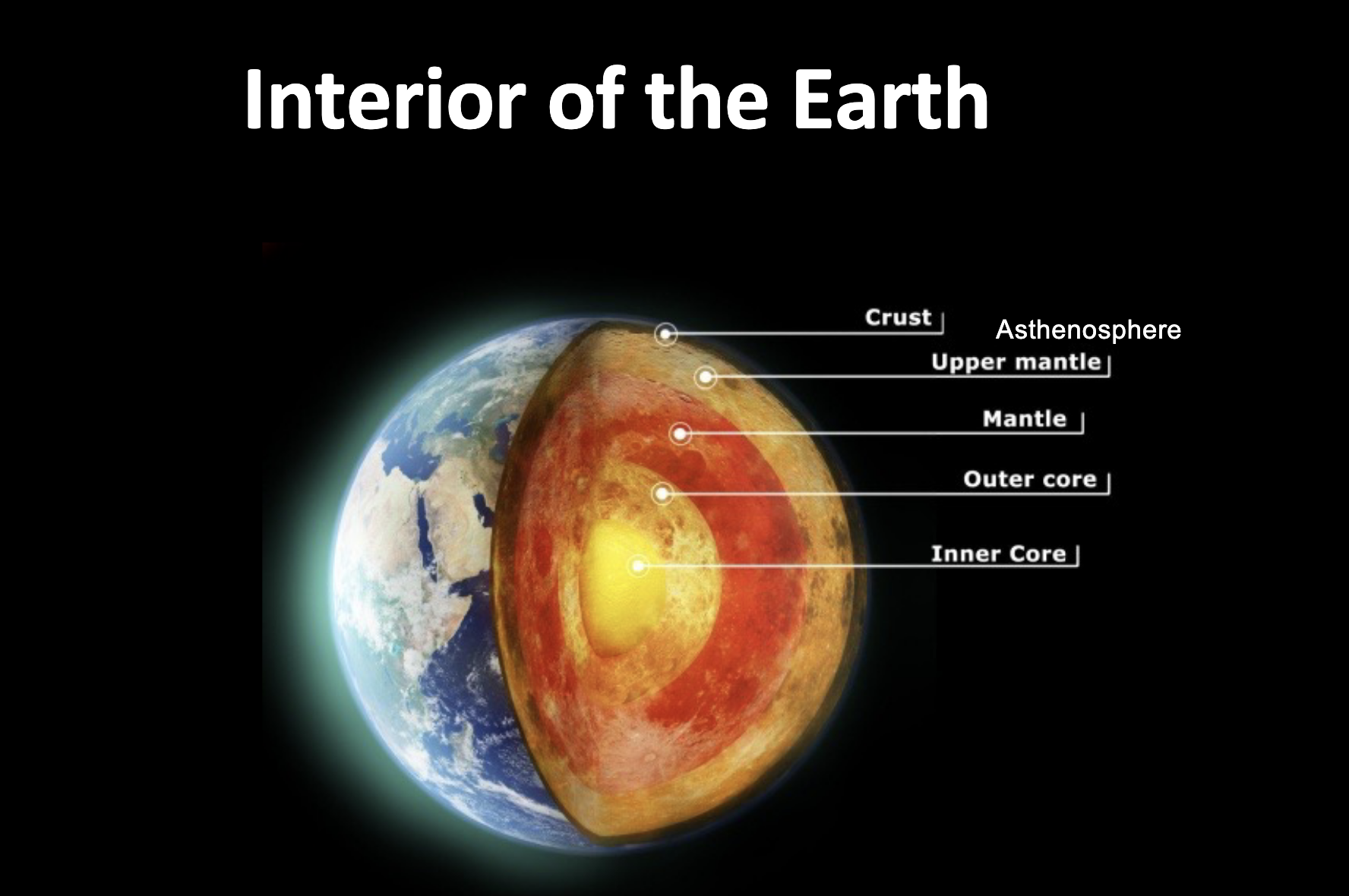
How do we know the structure of earth?
Using seismic waves.
How did we know that all the continents were once connected?
Something about volcanoes.
What type of movement can form volcanoes?
Convergent (destructive), divergent (constructive), and transform (strike slip).
What is evidence for plate tectonics?
*

What is the principle of uniformitarianism?
The processes that operate today (like erosion, sedimentation, and volcanic activity) have operated in much the same way throughout Earth’s history.
What is the principle of superposition?
Younger rocks over older rocks.
What is erosion?
Erosion is the process by which soil, rock, or other surface materials are worn away and transported from one place to another by natural forces.
What is the principle of original horizontality?
Layers of sediment are originally deposited in horizontal or nearly horizontal layers.
This means that when sedimentary rocks are formed, they typically settle in flat, level beds under the influence of gravity. If rock layers are found tilted or folded, it suggests that tectonic forces or other geological events occurred after the layers were originally deposited.
What is unconformity?
A time gap in the rock record.

What methods are used to determine the relative age of rocks?
Principle of superposition.
Cross-cutting relations.
Inclusions.
Faunal succession,
What are cross-cutting relations?
If you have a rock that cuts through another rock, it must be the younger rock.
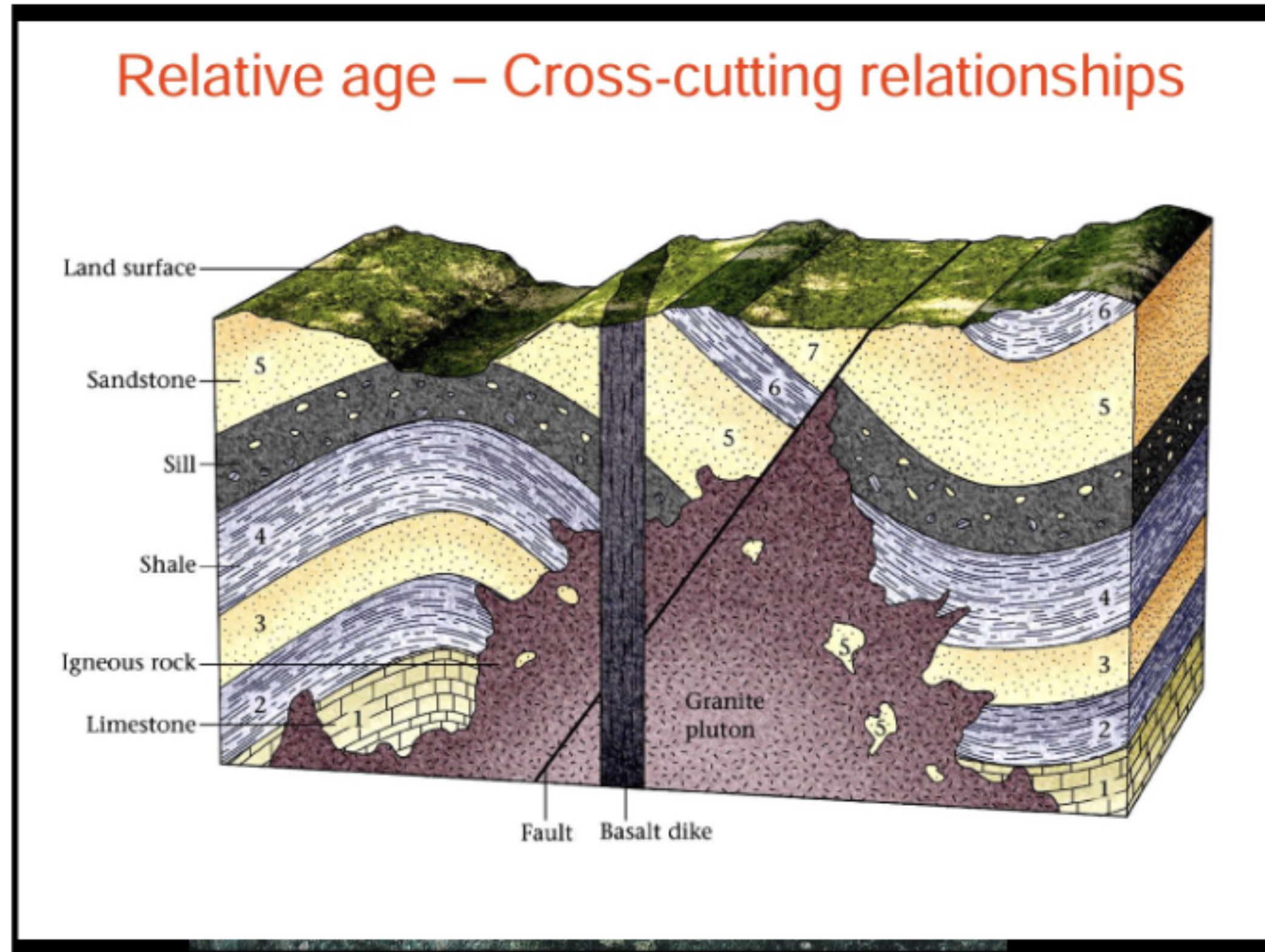
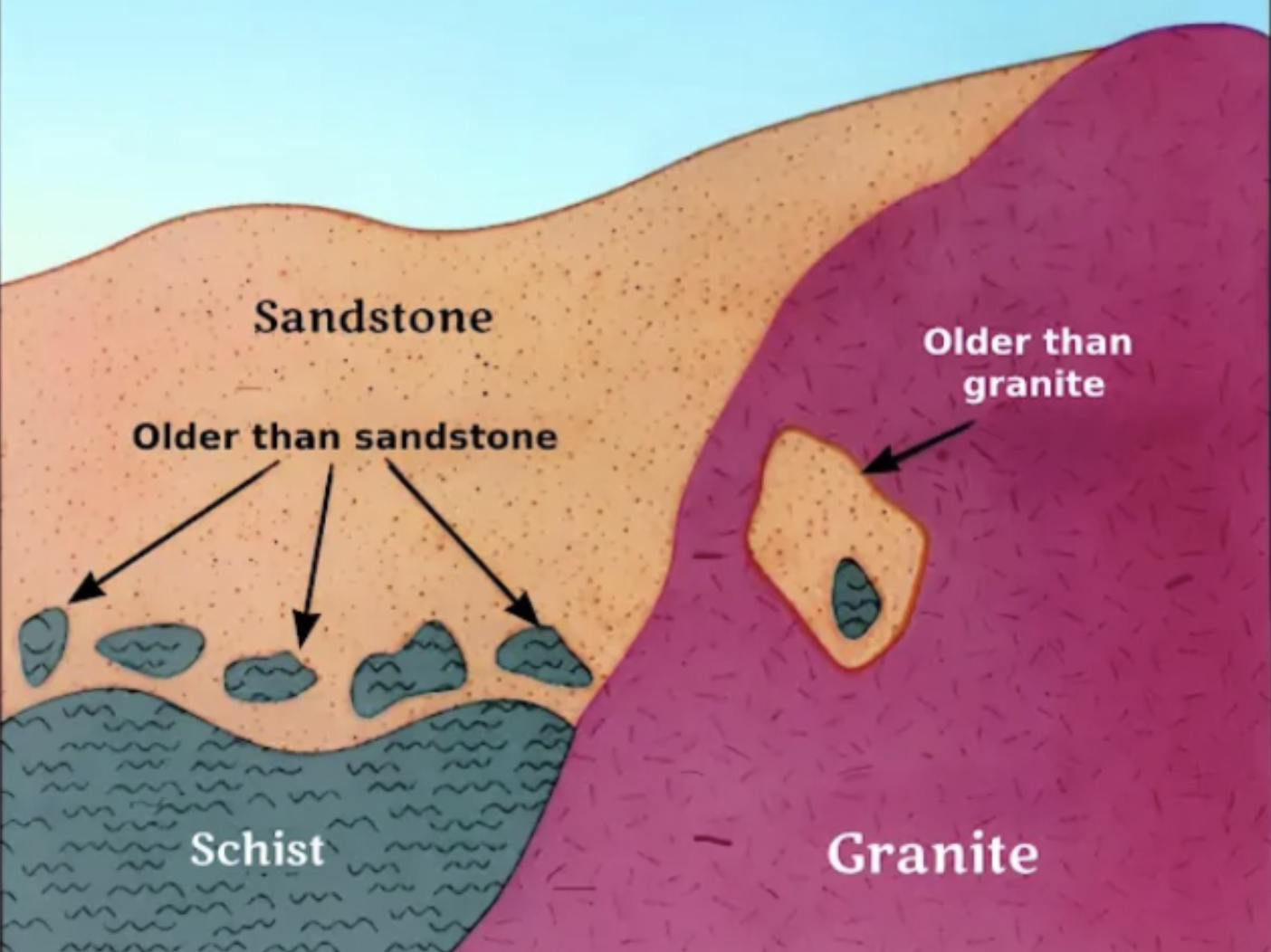
What is inclusion?
A fragment of a rock incorporated in another rock must be older than the rock in which they are enclosed.
Schist, sandstone and granite (oldest to youngest).
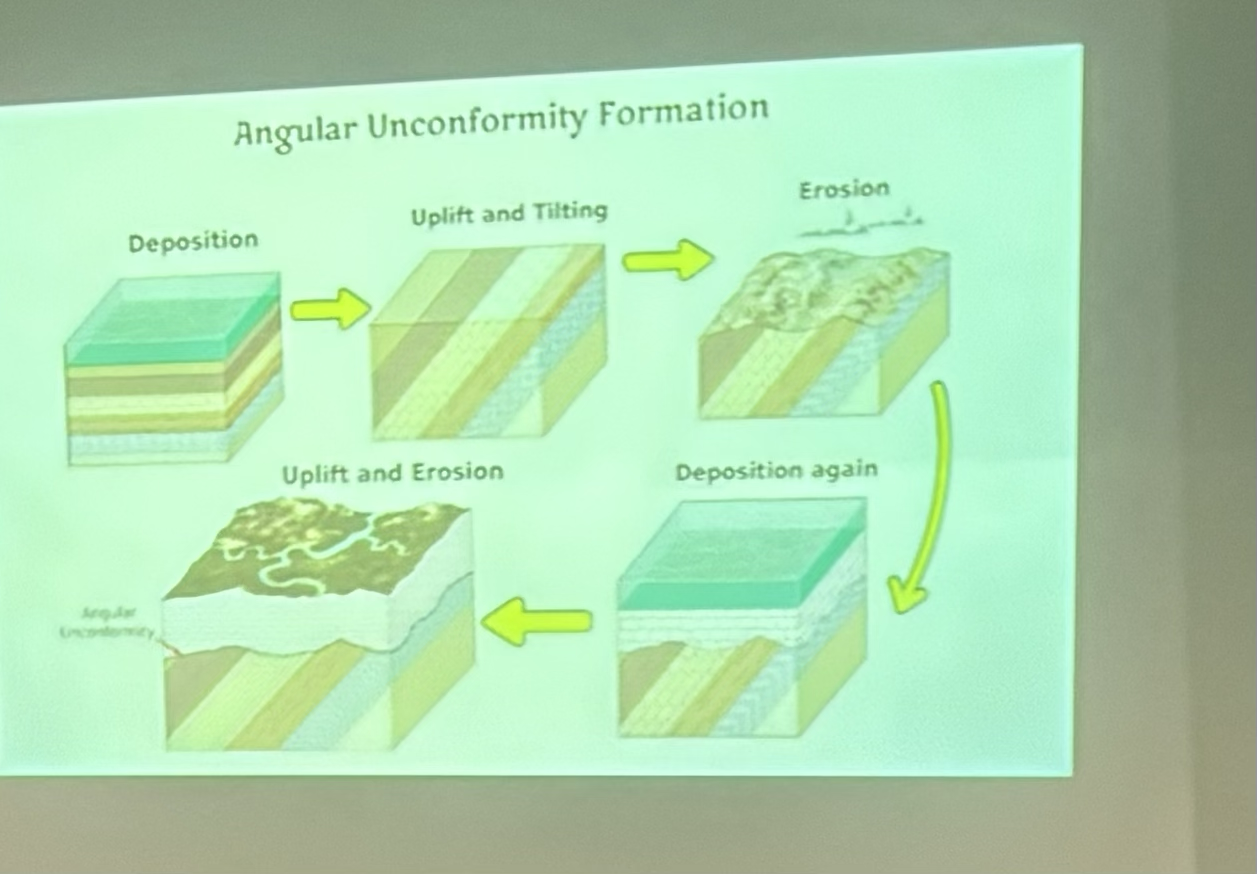
How does angular unconformity form?
What is the principle of faunal succession?
Group of fossil animals and plants occur in the geologic record in a chronological order.
Consequently, a period of geologic time can be recognized by its characteristic fossils.
Thus, in addition to superposition, a sequence of sedimentary rocks has another independent element that can be used to establish the chronologic order of events.
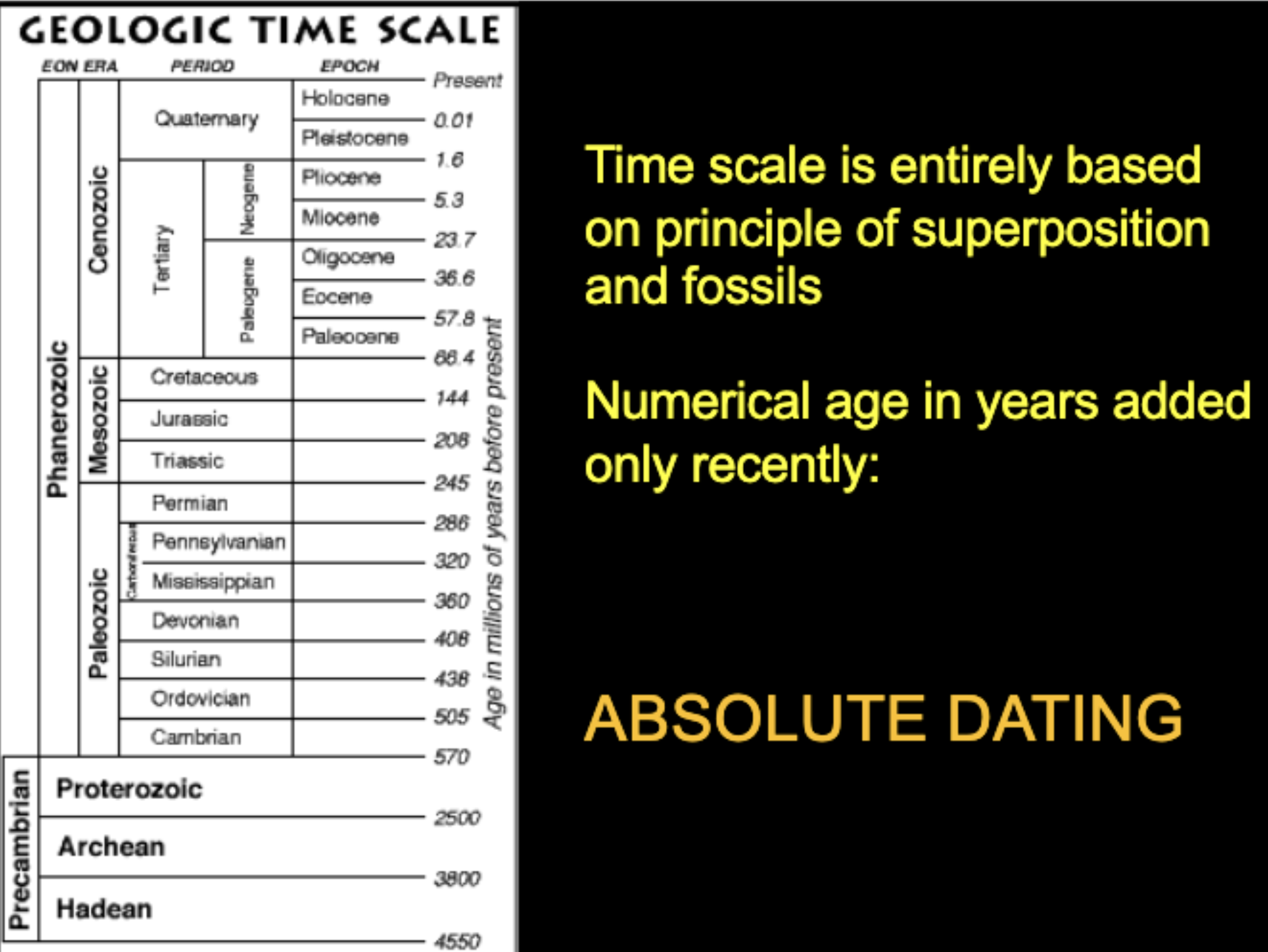
What is the geological time scale?
Need to know the major things on the scale.
Describe the different types of radiactive isotope decay.
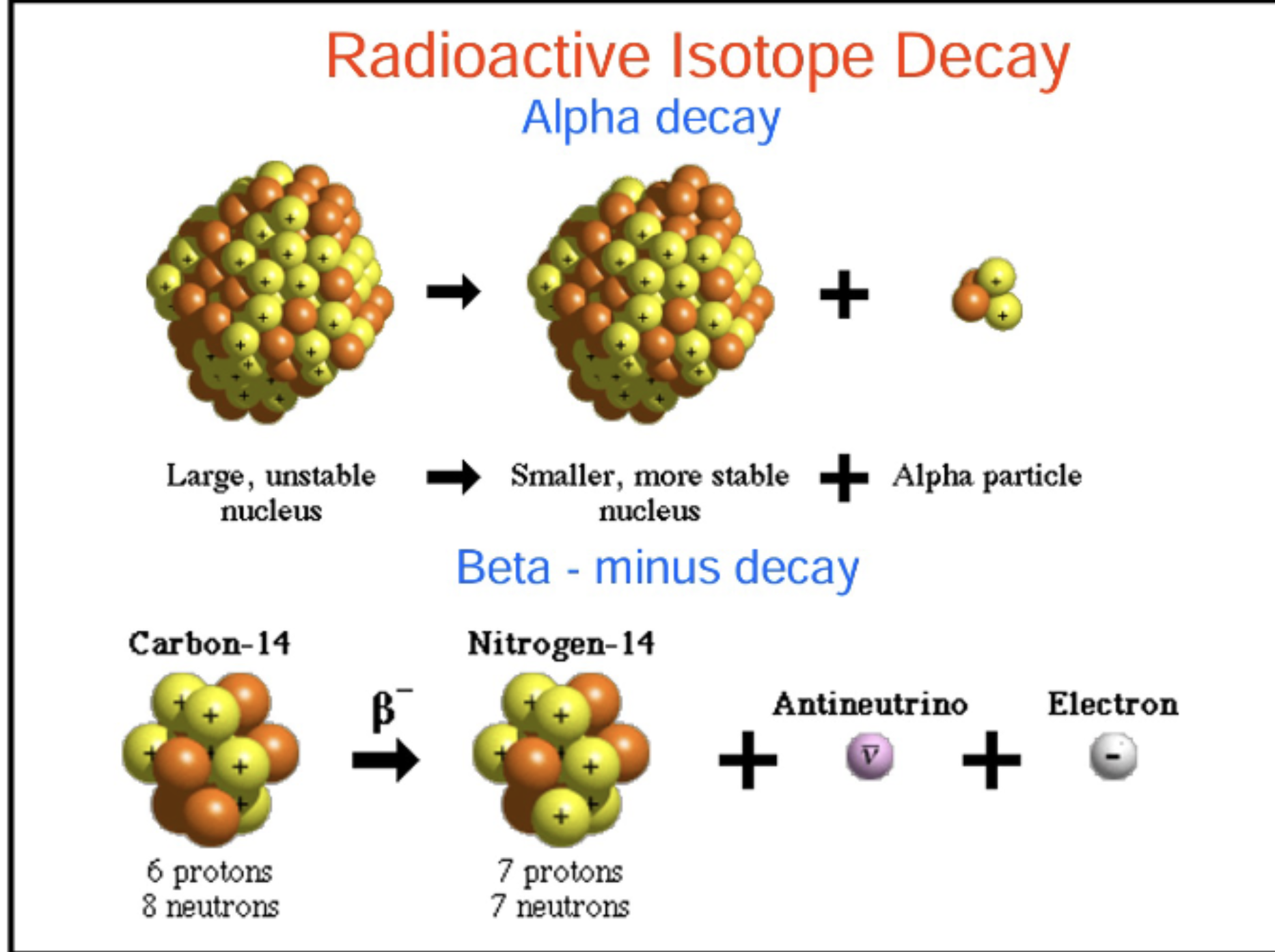
What is half-life?
Time it takes for half of the parent isotope to decay into its daughter isotope.
Describe tree rings?
A tree grows one tree ring for every year that it is alive.