Physics
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Electrons
Tiny little electrons have a negative charge.
Protons
Much bigger protons have a positive charge.
Neutrons
Neutrons have a neutral charge.
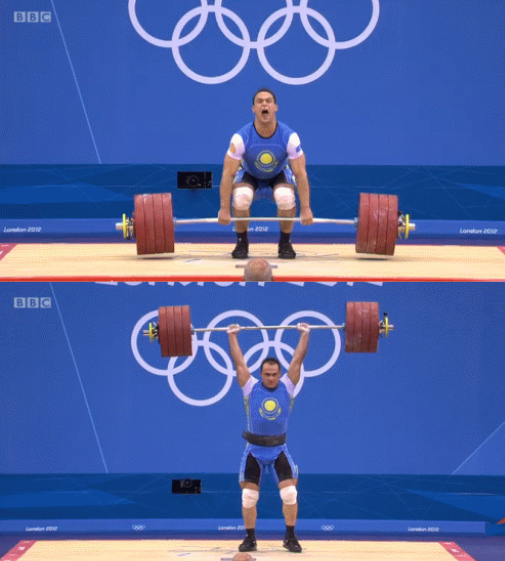
Potential Energy
Energy stored in an object relative (in comparison to) to another thing.
Relative is another way of saying…
In the first image, the weight has low potential energy in comparison to the distance from the ground.
“in comparison to”
In the second image, the potential energy is higher because the weight is lifted higher above the ground.
Electrical Potential Energy
Determined by the relative difference in strength of positive and negative charges, as well as the distance between the charges.
Static Electricity
A build of unbalanced charge in one area.
Circuit
A closed loop where current can flow, containing a power supply, a closed loop, and a load.
Power Supply
Provides energy to the circuit by separating charges.
Load
Consumes energy in a circuit, such as a light bulb.
Short Circuit
A circuit with only a power supply and a conductor, lacking a load, leading to rapid battery drain or overheating.
Voltage (V)
The potential difference in a circuit, measured in volts.
Current (A)
The number of electrons flowing through a circuit at a particular point per second, measured in amperes (amps).
Resistance
Measured in Ohms.
Ammeter
A tool used to measure the current in an electrical circuit and is placed in series.
Voltmeter
A tool used to measure potential difference (voltage) between two points in a circuit; it's positioned in parallel.
Potential Difference
The difference in electrical potential between two points (positive and negative ends) in a circuit, driving electron flow.
Resistance
Friction encountered by electrons in a circuit.
Conductors
Materials allowing free movement of electrons.
Insulators
Materials preventing electron flow, like rubber.
Delocalised Electrons
Electrons free to move in metals.
Ohm's Law
V = I x R; relates voltage, current, resistance.
Series Circuit
Components connected in a single path.
Parallel Circuit
Components connected across multiple paths.
Total Resistance (Series)
Sum of individual resistances in series.
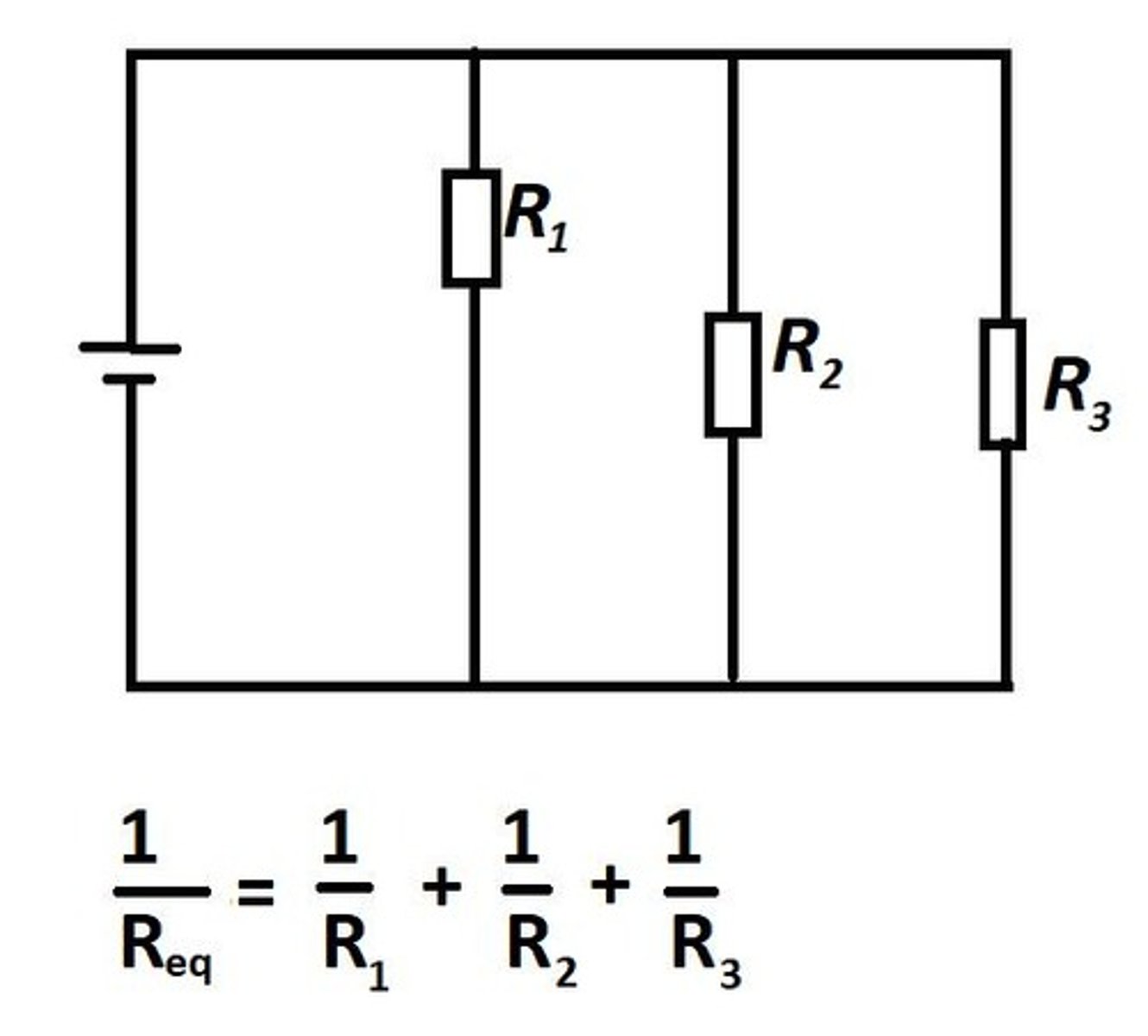
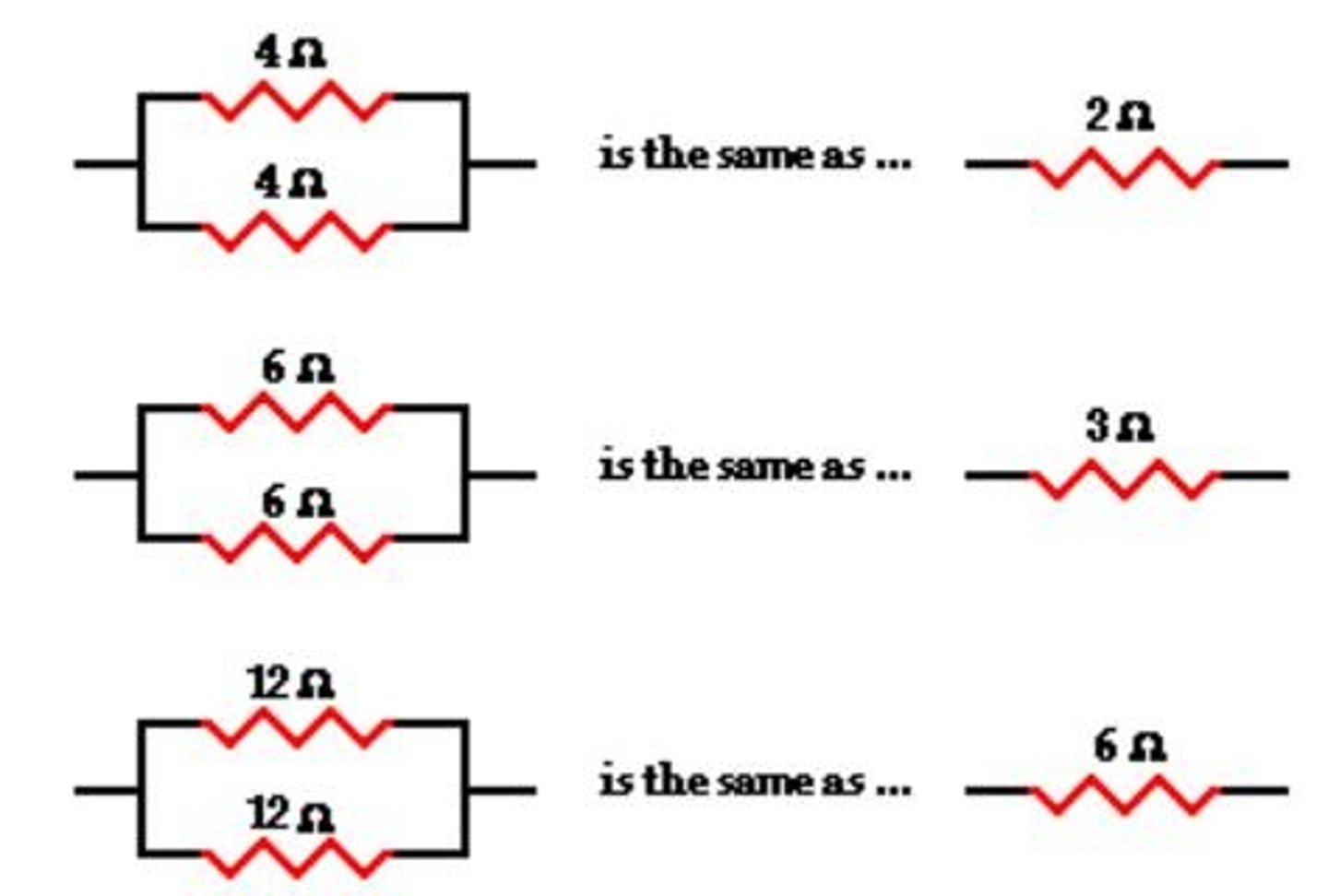
Total Resistance (Parallel)
Calculated using reciprocal formula for resistors.
Thin Wire Resistance
Higher resistance due to less space for electrons.
Thick Wire Current
Higher current due to lower resistance.
Energy Loss Prevention
Insulators prevent energy loss in circuits.
Power Surge Protection
Insulators protect from damage during surges.
Circuit Load
Devices like bulbs that add resistance.
Resistance Calculation
Total resistance = R1 + R2 + R3.
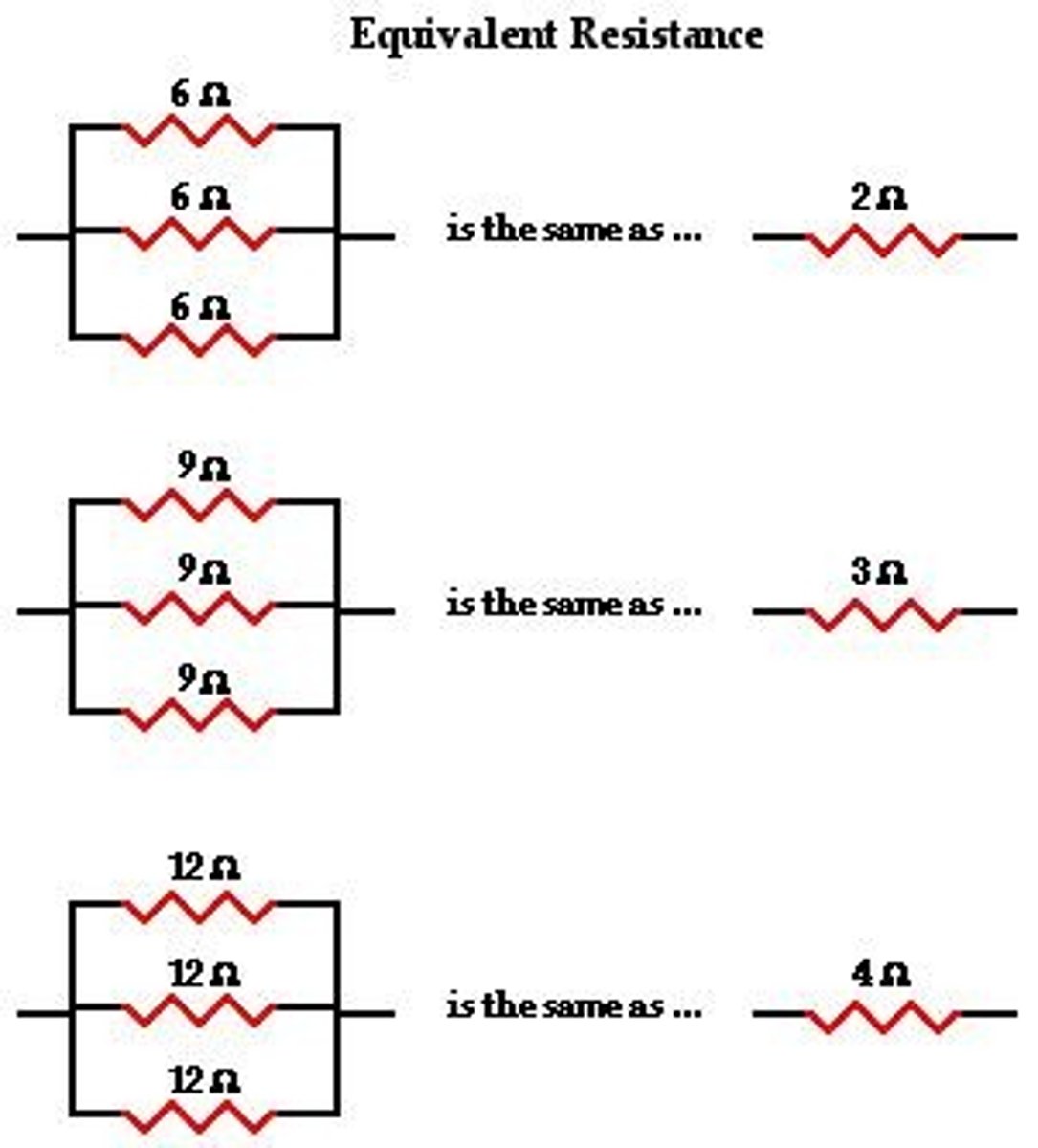
Equivalent Resistance
Resistance of combined resistors in a circuit.
Current Rule (Series)
Same current flows through all components.
Voltage Rule (Series)
Total voltage equals sum across components.
Current Rule (Parallel)
Total current equals sum of branch currents.
Voltage Rule (Parallel)
Same voltage across all parallel components.
Resistor Values
Expressed in Ohms, affecting circuit behavior.
Magnetism
Phenomenon of attracting metals from a distance.
Lodestones
Natural magnets that attract metals.
North Pole
End of a magnet pointing towards Polaris.
South Pole
Opposite end of a magnet from North.
Magnetic Field
Area around a magnet where magnetic forces exist.
Magnetisable Materials
Metals that align with magnetic fields.
Hans Christian Oerstad
Discovered electric currents produce magnetic fields.
Electromagnet
Magnet created by electric current in wire.
Current Strength
Higher voltage increases magnetic field strength.
Wire Wrapping
More turns of wire enhance magnetic field.
Solenoid
Wire coiled around a support generating magnetic field.
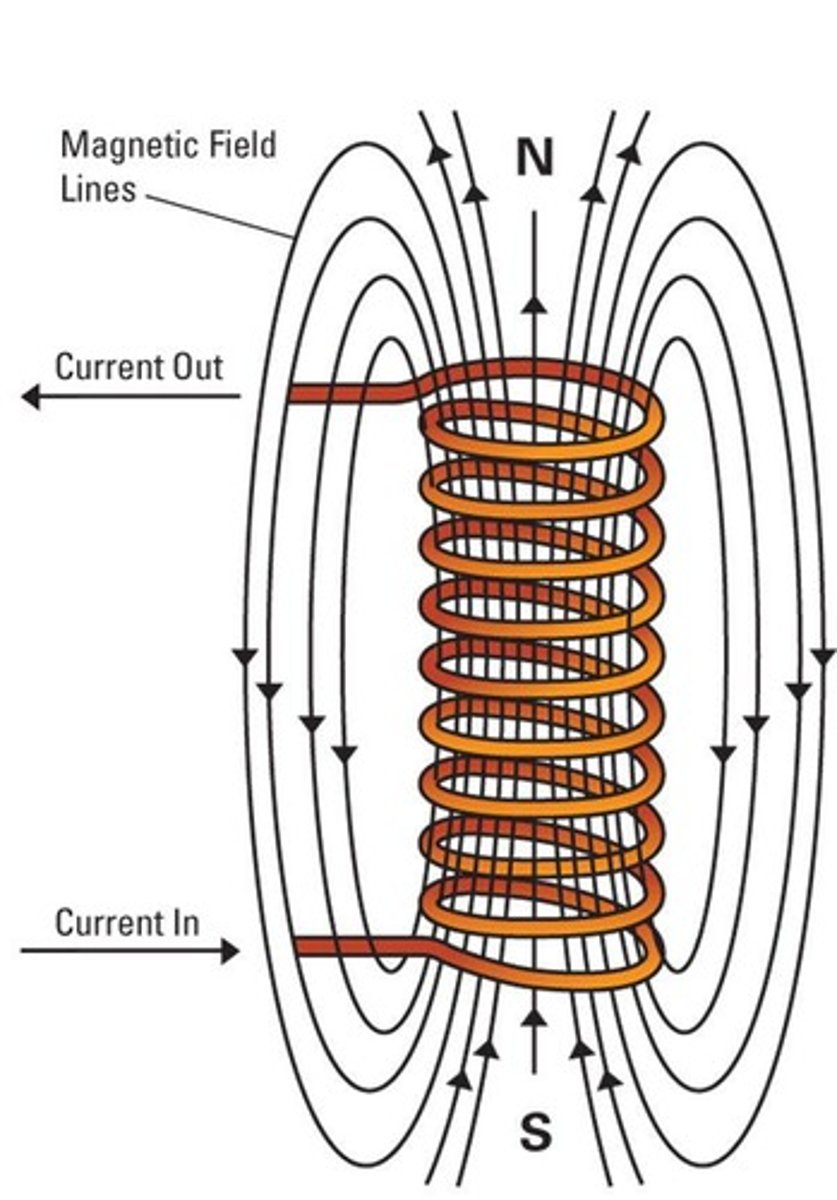
Mechanical Energy
Energy converted from electrical energy in solenoids.
Applications of Solenoids
Used in cars, locks, MRI machines, and speakers.

Electromagnetism
Phenomenon where electric currents mimic magnets.
Magnetic Force
Force experienced by current in a magnetic field.
Magnetic Interaction
Current interacts with magnetic field forces.
Voltage Supply
Power source for increasing current strength.
Magnetic Field Direction
Conventional flow from North to South pole.