Biology Unit 5- Cellular Respiration
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
part of an enzyme where the substrate binds is called the
active site.
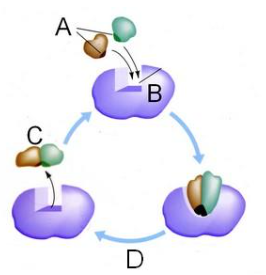
Which letter represents the enzyme?
B
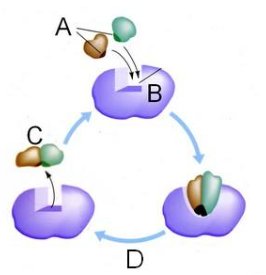
Which letter represents the substrate?
A
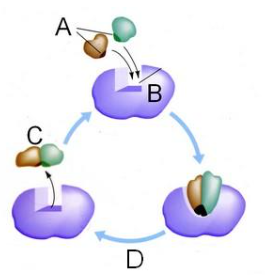
Which letter represents the product of the reaction?
C
The energy required to destabilize existing chemical bonds and to orient reactants is called the _____ energy.
activation
Why can a small amount of enzyme catalyze hundreds to thousands of reactions?
A. Because enzymes duplicate as they catalyze a reaction
B. Because enzymes are not used up as they catalyze a reaction
C. Because enzymes contain multiple sites where substrates can bind during a reaction
D. Because enzymes grow bigger as they catalyze a reaction
B
How does inhibition of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction by a competitive inhibitor differ from inhibition by a noncompetitive inhibitor?
A. competitive inhibitors interfere with the enzyme; noncompetitive interfere with the reactants
B. Competitive bind to the enzyme reversibly; noncompetitive bind to it irreversibly
C. Competitive bind to the active site; noncompetitive bind to a different site
D. Competitive are inorganic substances such as metal ions; noncompetitive are vitamins
C
One of the characteristics of life is the use of energy to create order within the organism. How does this relate to the second law of thermodynamics?
A. Living organisms do not have to obey the second law of thermodynamic thermodynamics which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed
B. Living organisms do not have to obey the second law of Thermodynamics which states that with every energy transfer there is an increase in entropy in the system
C. Life obeys the second law of Thermodynamics because the decrease in entropy as the organism grows decreases entropy in the universe
D. Life obeys the second law of Thermodynamics because the organisms create more disorder in their environment than the decrease in entropy that is associated with their growth
D
Universal energy currency for all cells is
ATP
Oxidation is the _____ of electrons, and reduction is the ______ of electrons.
loss; gain
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between photosynthesis and respiration?
A. ATP molecules are produced in photosynthesis and used up in respiration
B. Respiration is the exact step by step reversal of the biochemical pathways of photosynthesis
C. photosynthesis occurs only in plants and respiration occurs only in animals
D. Photosynthesis stores energy in complex organic molecules, while respiration releases it.
D
Generation of proton gradients across membranes occurs during:
A. glycolysis
B. pyruvate processing
C. Krebs Cycle
D. Electron Transport Chain
D
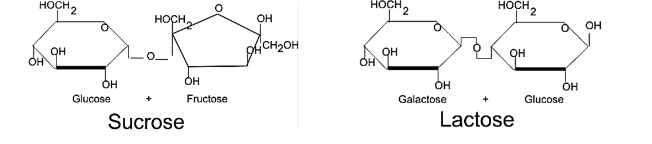
Which of the following would be a true statement about the enzyme lactase as it relates to the disaccharides sucrose and lactose?
A. Though the shape of the sucrose disaccharide is close to the shape of the lactose disaccharide it is still not specific enough for the active site on the enzyme lactase to recognize it and break it down.
B. The shape of the sucrose disaccharide is close enough to the lactose disaccharide that it can fit into the allosteric site on the lactase enzyme and be broken down into galactose and glucose.
C. The enzyme lactase does not catalyse the breakdown of either sucrose or lactose
D. If you increase the temperature of the reaction to above the boiling point of water the enzyme lactase will recognize the shape of the sucrose molecule and break it down.
A
How many electrons get transferred during the redox reactions associated with cellular respiration?
A. 2
B. 12
C. 24
D. 48
C
Generation of proton gradients across membranes occurs during:
A. Glycolysis
B. pyruvate processing
C. Krebs cycle
D. Electron transport chain
D
Carbon dioxide is a product of cellular respiration. During which step(s) in the process is it created?
A. Krebs cycle only
B. Pyruvate processing and the Krebs cycle
C. Oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis
D. Pyruvate processing and glycolysis
B.
In addition to ATP, what are the end products of glycolysis?
A. NADH and pyruvate
B. H2O, FADH2 and citrate
C. CO2 and NADH
D. CO2 and pyruvate
A
Which of the following occurs in the cytosol of a eukaryotic cell?
A. fermentation and chemiosmosis
B. glycolysis and fermentation
C. citric acid cycle
D. oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
B
Energy (in the form of ATP) is a product of cellular respiration. Which step in the process creates the most ATP?
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that functions in aerobic oxidative phosphorylation is:
oxygen
Which of the following options lists the stages of cellular respiration in the correct order?
A. the citric acid cycle, pyruvate processing, oxidative phosphorylation, and glycolysis
B. oxidative phosphorylation, pyruvate processing, glycolysis, and the citric acid cycle
C. glycolysis, pyruvate processing, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation
D. glycolysis, pyruvate processing, oxidative phosphorylation, and the citric acid cycle
C
Each FADH2 yields a maximum of ________ ATP, and each NADH yields a maximum of ________ ATP as a result of transferring pairs of electrons to the electron transport chain.
2, 3
The end products of the citric acid cycle include all of the following except:
A. pyruvate.
B. CO2.
C. ATP.
D. FADH2.
A
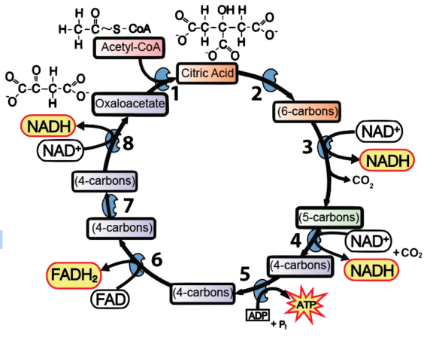
What stage in cellular respiration is depicted?
citric acid cycle
As energy released by the electron transport chain is used to pump H+ ions (protons) from the mitochondrial matrix across the inner membrane and into the intermembrane space, the result is the:
A. reduction of NAD+.
B. formation of ADP.
C. creation of a proton gradient.
D. lowering of pH in the mitochondrial matrix.
C
In the best case scenario, the complete breakdown of glucose via aerobic cellular respiration would result in what range of ATP?
35-38
Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether oxygen (O2) is present or absent?
glycolysis
One function of both alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation is to__________ so that glycolysis can continue.
A. Convert NADH to NAD+.
B. Convert FADH2 to FAD.
C. Convert FAD to FADH2.
D. Convert NAD+ to NADH.
A
Finish the sentence: the ATP synthase makes ATP from:
A. Directly from the splitting of H2O at the ATP synthase
B. ADP + Pi and energy from the reflection of light
C. ADP + Pi and energy from the proton gradient
D. From NADH going to NAD+
C
Which of the following statements is false?
A. The energy from the movement of electrons through the electron transport change powers protein pumps that actively transfer protons across the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
B. The electrons associated with FADH2 are at a higher energy state than the electrons associated with NADH.
C. A total of 24 electrons are removed from glucose during cellular respirations.
D. The flow of hydrogen ions from the inner membrane space back into the matrix of the mitochondria through the ATP synthase provides the energy necessary to convert ADP and inorganic phosphate to ATP.
B
Which of the following is false about the electron transport systems?
A. It may be found in mitochondria in animal cells.
B. It may be found in the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells but not prokaryotic cells.
C. It is composed of 4 complexes, three of which are proton pumps.
D. It involves a series of redox reactions with oxygen as the final electron acceptor.
B
Which of the following is a correct path that some electrons can take during cellular respiration?
A. Glucose → pyruvate → Acetyl CoA → Carbon Dioxide
B. Glucose → pyruvate → Citric Acid → ATP
C. Glucose → NADH → FADH2 → Acetyl CoA → ATP → Oxygen
D. Glucose → pyruvate → Acetyl CoA → FADH2 → Oxygen
D
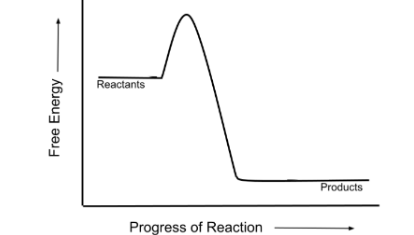
Is this graph showing an exergonic or endergonic reaction?
exergonic
What is the name of the reaction that involves adding water to release the energy stored in ATP as it breaks apart into ADP and inorganic phosphate?
hydrolysis
What is the balanced equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
In the cellular respiration equation, what two molecules are oxidized?
Glucose and Carbon Dioxide
In the cellular respiration equation, what two molecules are reduced?
Oxygen and Water
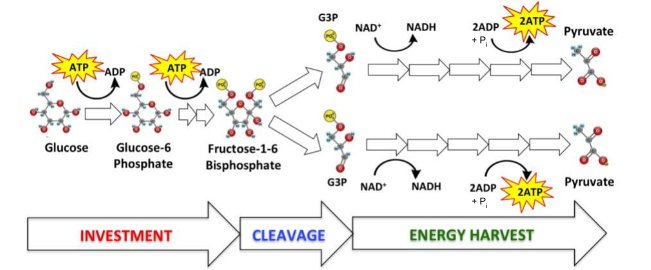
What is the name of the process represented by the diagram?
glycolysis
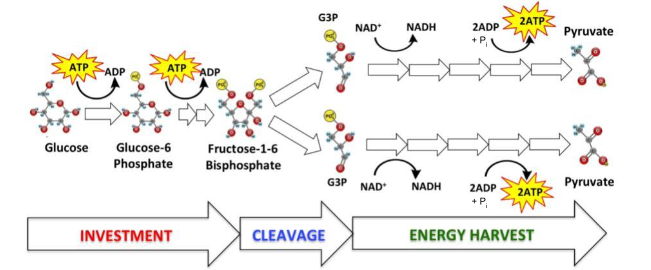
What are the reactants in this process?
Hint: ________, ____________, ___________ + __________
2 NAD+, Glucose, 4 ADP + Pi
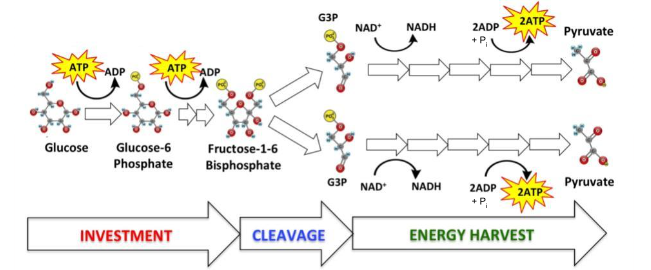
Which of the reactants in this process are oxidized? reduced?
Glucose, NAD+
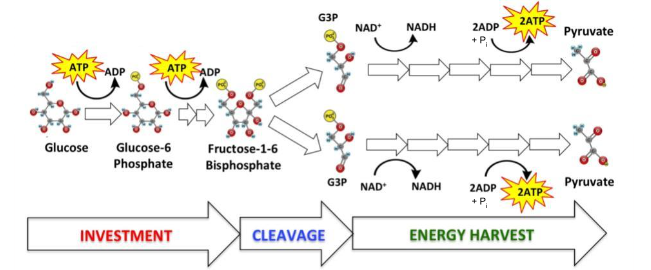
In this reaction, how many electrons were transferred to an electron carrier?
4
In the presence of oxygen where in the cell will the products (pyruvate and NADH) go? For both include the step in cellular respiration they will travel to next and the location in the cell.
A. Pyruvate will next go to the __________________
B. NADH will next go to the ___________________
A. pyruvate processing B. ETC
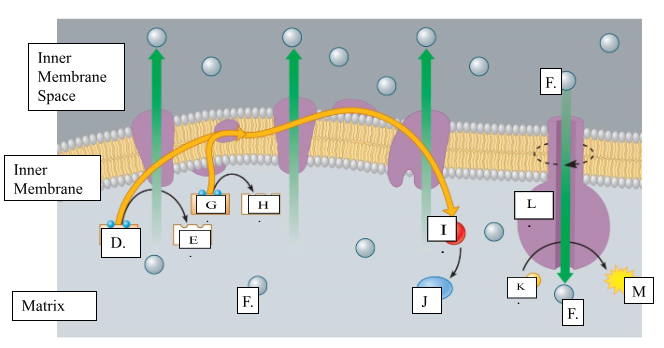
What is the name for molecule “D”?
NADH
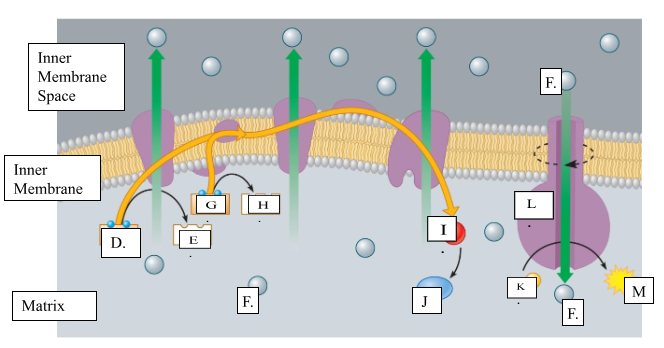
When molecule “G” loses 2 electrons to form molecule to form molecule “H”, is it oxidized or reduced?
oxidized
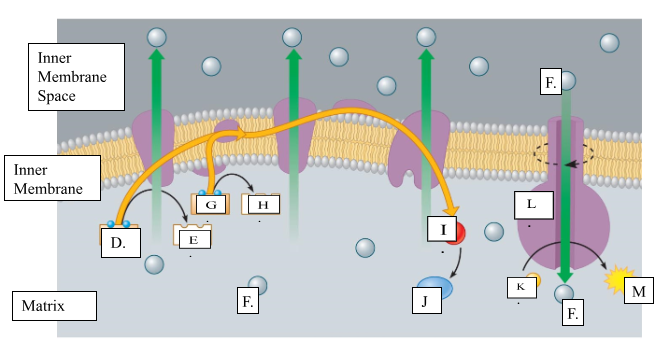
Name molecule “I”
oxygen
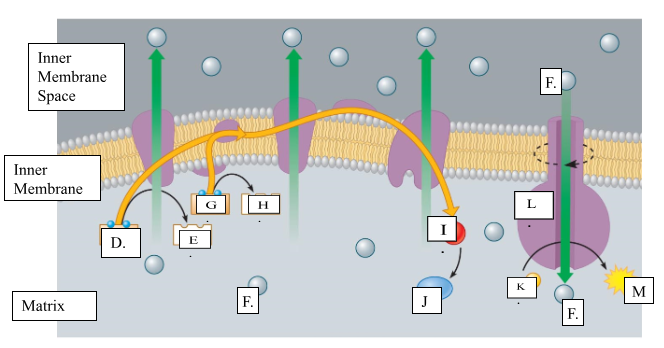
When molecule “I” combines with 2H+ ions, it forms molecule “J.” Name molecule “J”:
water
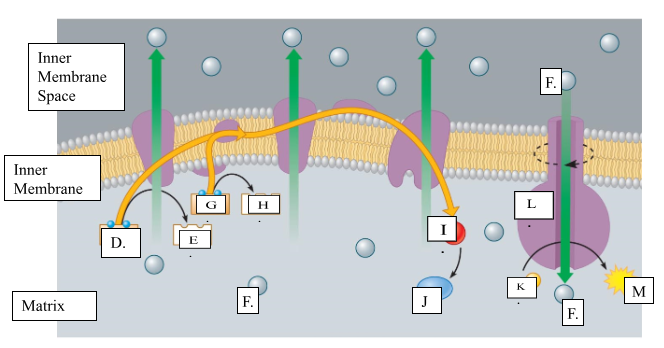
What is the name for the protein labeled L?
ATP synthase
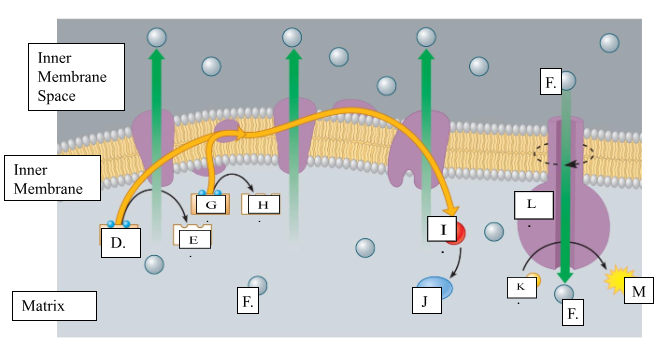
What does protein L synthesize?
ATP
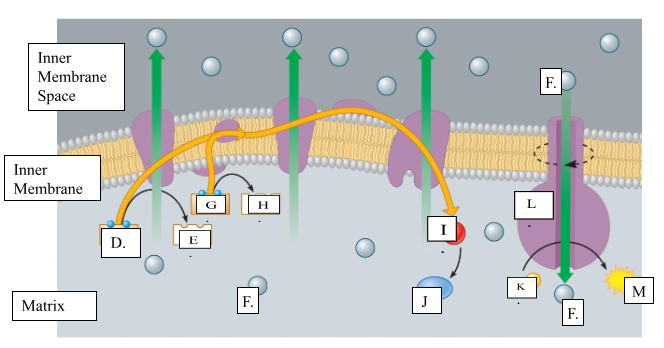
Name molecule “F”
H+
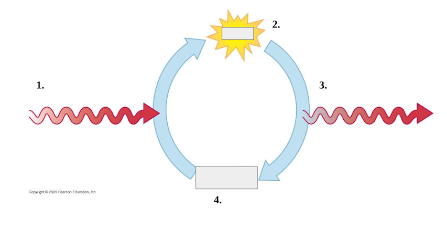
Fill in for 1, 2, 3, 4
Energy from exergonic
ATP
ADP + Pi
Energy for endergonic