bio 191 lab midterm
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
labs 1-5 (taxonomy to invertebrates II) - definitions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
binomial nomenclature
naming organisms using two names
specific epithet
second part of a specimen’s name
dichotomous key
tool used by biologists to help them identify all kinds of organisms
morphological characteristics
physical appearance/traits
systematics
identifying and differentiating between species
phylogeny
evolutionary history of diversity on earth
parts of a phylogenetic tree
root, branch, node, tip
cladogram
depicts relationships between taxa
phylogram
depicts both the relationship between taxa scaled to represent the amount of evolutionary change along a branch
chronogram
branch lengths scaled to actual time
pleisomorphic
characters shared between taxa because the common ancestor of all of those taxa had that character
synapomorphic
shared derived characters
apomorphic
derived characters (with respect to ancestral condition)
monophyletic
group includes ancestor and all of its descendants
paraphyletic
consists of an ancestor and some, but not all descendants
polyphyletic
group of organisms that does not include a common ancestor
saprotrophic
send out digestive enzymes into the environment and pick up resulting nutrients
cellular slime mold
individual amoebas retain their cell membranes, creating a community of slime molds
acellular slime mold
individual cell membranes break down, creating the entire plasmodium one large, multinucleated cell
gram positive
purple stain, high peptidoglycan, penicillin effective
gram negative
pink stain, low peptidoglycan, penicillin ineffective
algae, slime molds, protozoa
3 broad groups of protozoa
unicellular, colonial, filamentous
3 structural arrangements of protists
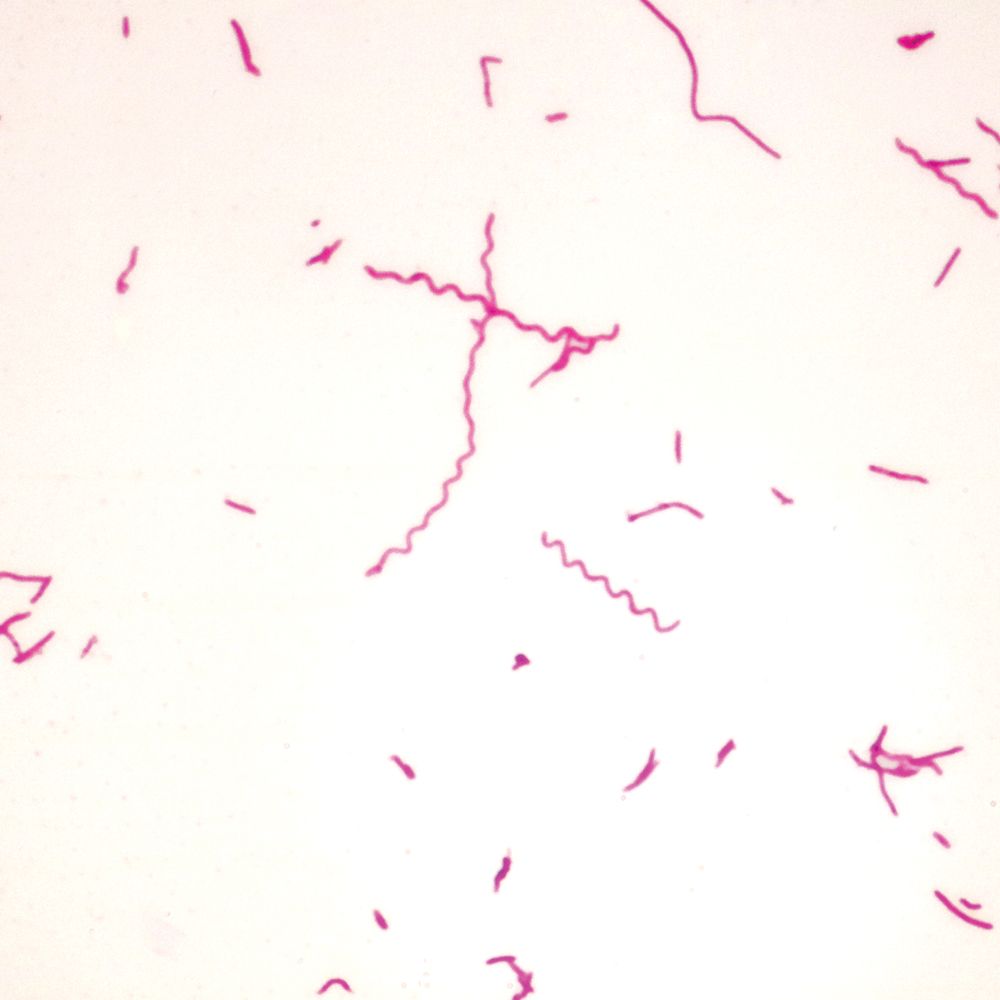
Bacteria, Bacillus megaterium, rod shape, gram positive/purple
Domain, Genus + Species, shape, gram stain of this image
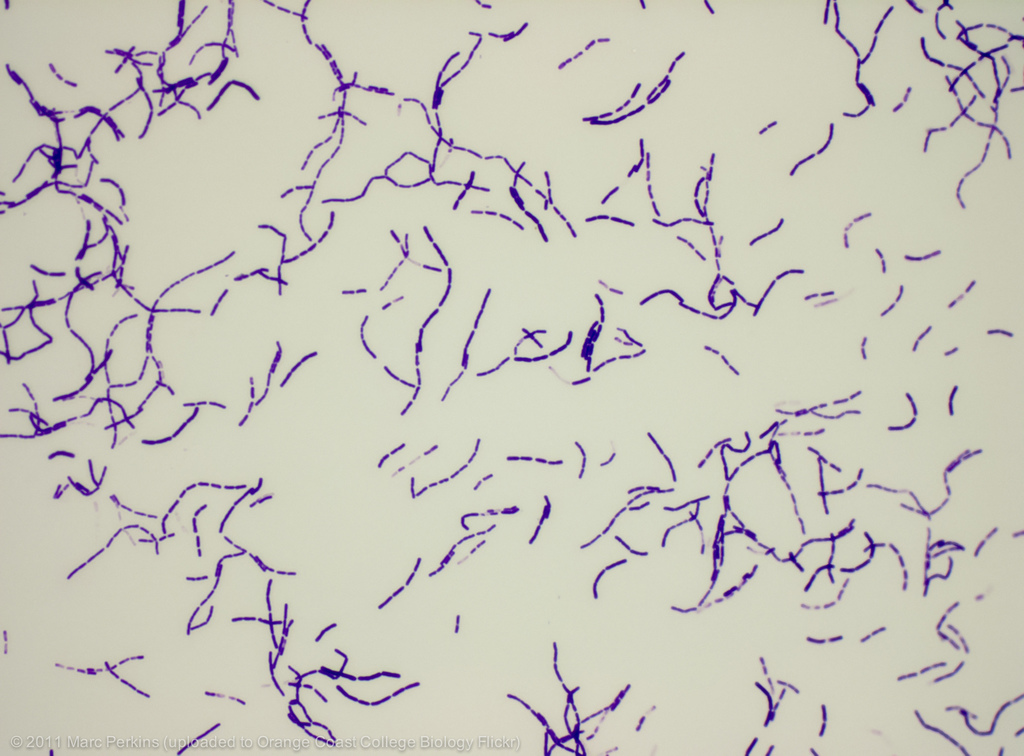
Bacteria, Rhodospirillum rubrum, spirilla/spirillum, gram negative/pink
Domain, Genus + Species, shape, gram stain of this image
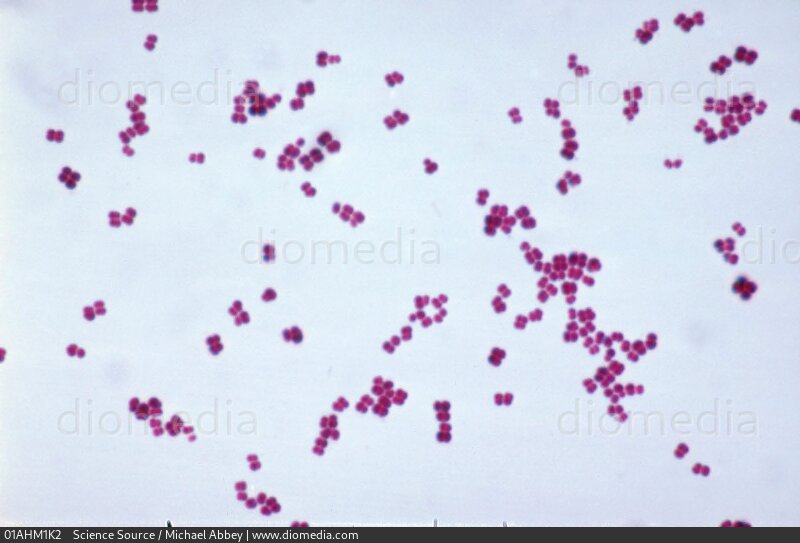
Bacteria, Micrococcus luteus, coccus, gram positive/purple
Domain, Genus + Species, shape, gram stain of this image
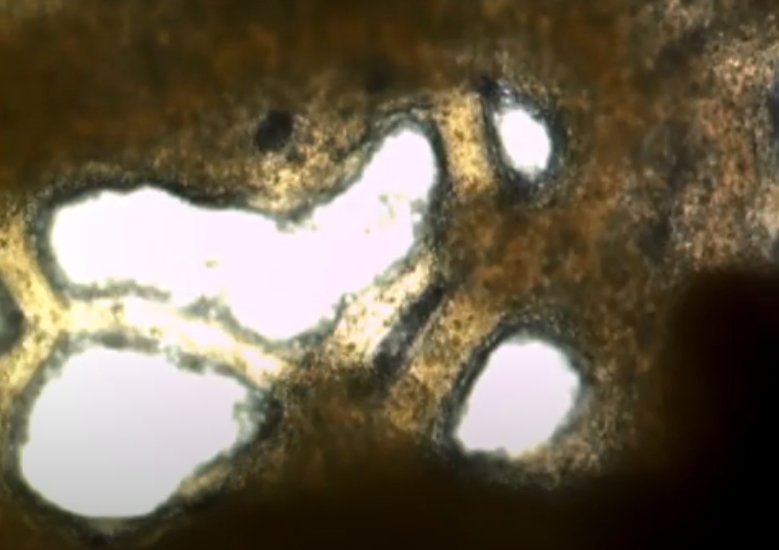
Eukarya, Protista, Physarum, cytoplasmic steaming, slime mold
Domain, Kingdom, Genus, important structure(s), general protist group of this image
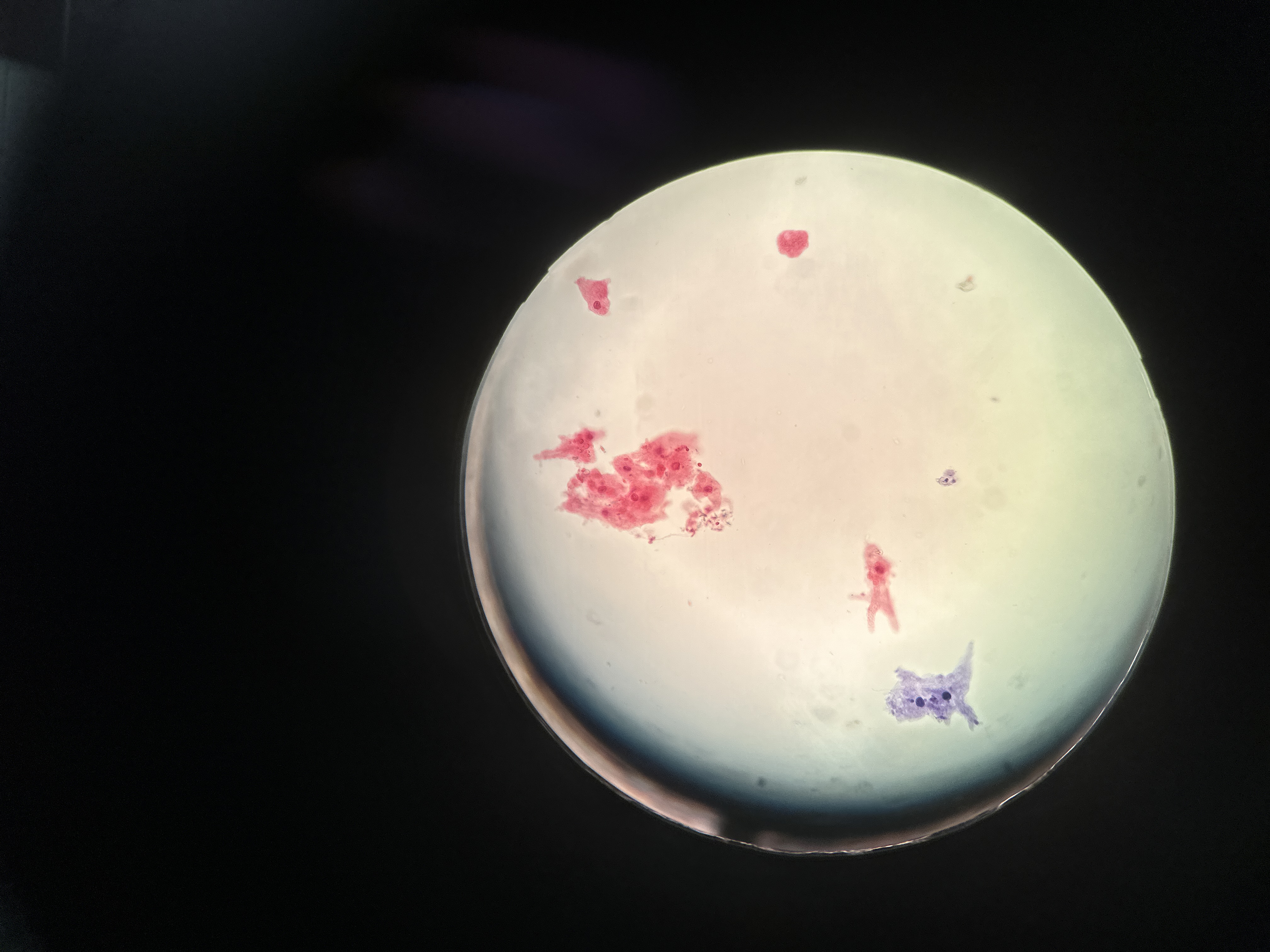
Eukarya, Protista, Amoeba, pseudopodia, protozoa
Domain, Kingdom, Genus, important structure(s), general protist group of this image
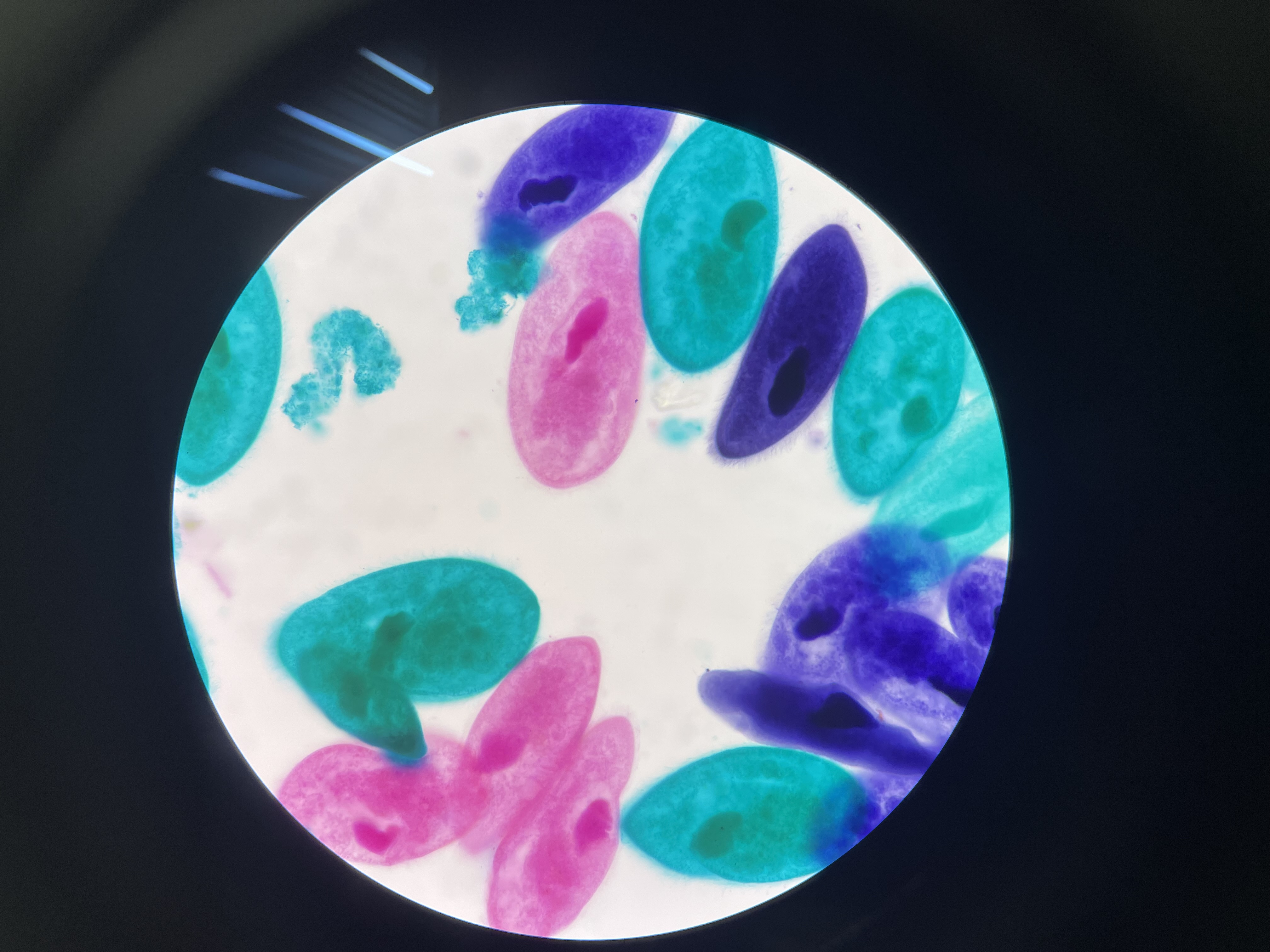
Eukarya, Protista, Paramecium, (alveoli, pellicle, trichocysts, 2 nuclei (micro/macro nuclei)), protozoa
Domain, Kingdom, Genus, important structure(s), general protist group of this image
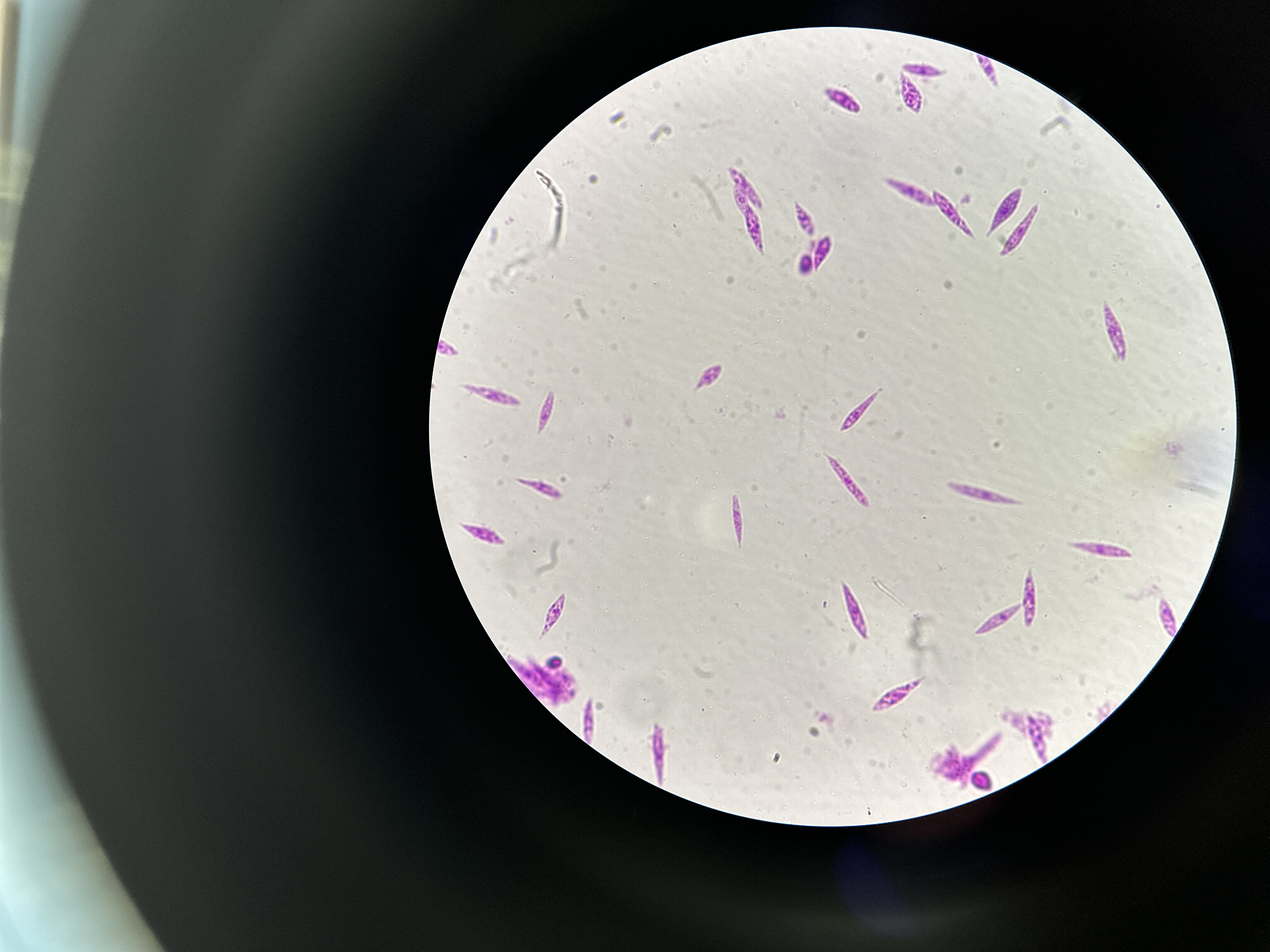
Eukarya, Protista, Euglena, (mixotrophic, eyespot, pellicle, flagella), protozoa
Domain, Kingdom, Genus, important structure(s), general protist group of this image
isogamy, heterogamy, oogamy
3 sexual reproductive strategies in algae
isogamy
motile male & female gametes look exactly alike
heterogamy
motile male and female gametes that look alike except egg is larger
oogamy
male gamete is small and motile, female gamete is large and non-motile
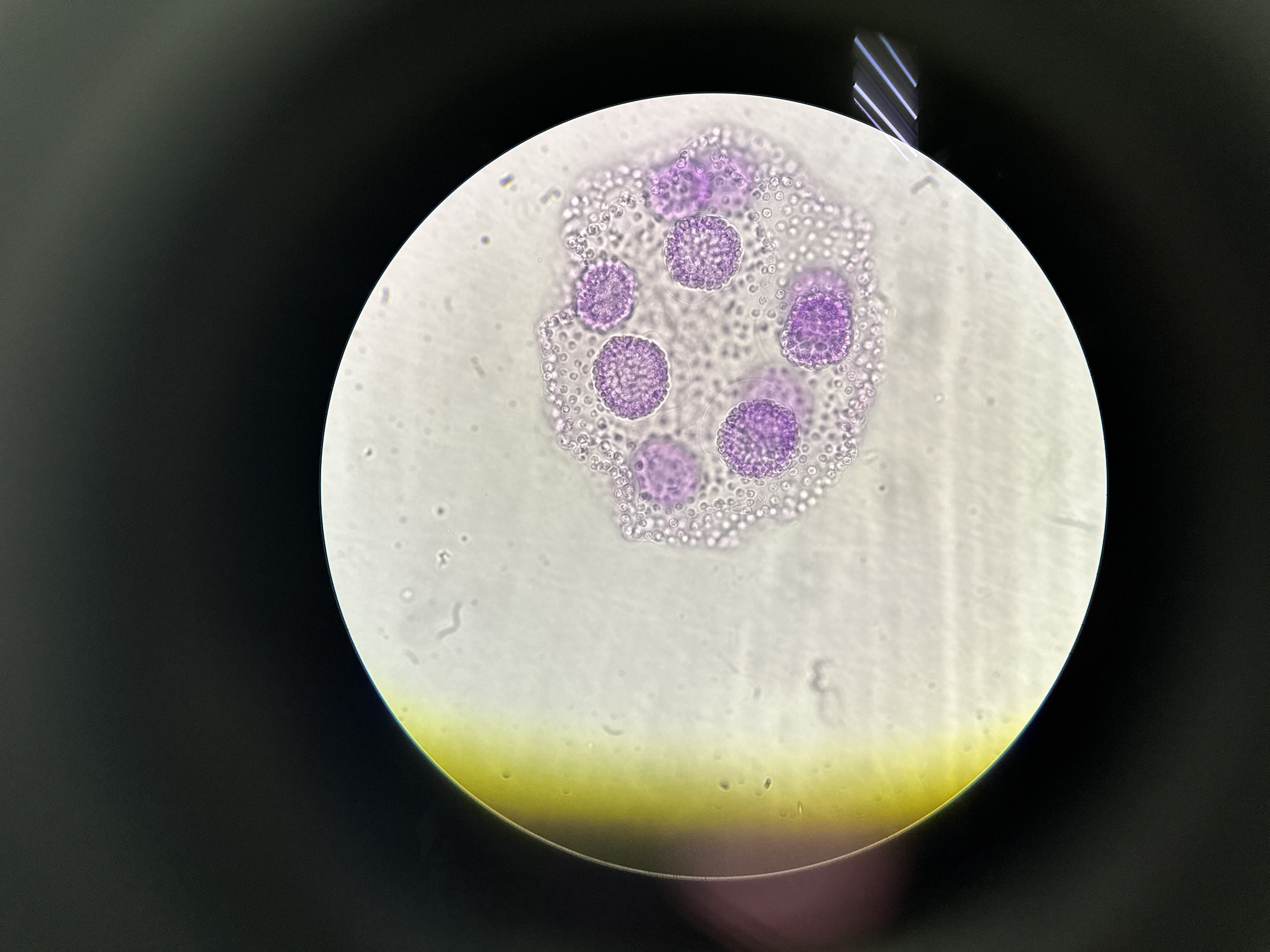
Eukarya, Protista, Volvox, (oogamous, daughter colony retained until broken down), algae
Domain, Kingdom, Genus, important structure(s), general protist group of this image
Eukarya, Protista, Spirogyra, (spiral chloroplasts, isogamous via conjugation), algae
Domain, Kingdom, Genus, important structure(s), general protist group of this image
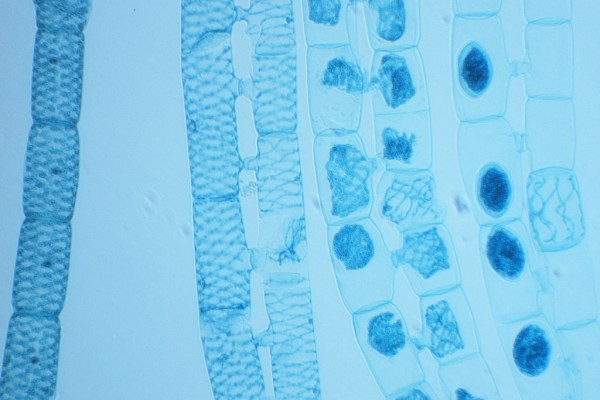
septate hyphae
hyphae with cross walls
coenocytic/aseptate
lacking septa (cross walls)
Eukarya, Fungi, Chytridiomycota, Allomyces, chytridiomycosis, Chytrids
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Genus, important structure(s), disease that made 200 amphibians extinct, common name
mating strains
use + or - instead of male or female Plas
Plasmogamy
plasma membranes fuse into one from 2 cells, nuclei still separate
dikaryotic
(n + n)
karyogamy
two nuclei fuse to form single cell (2N)
Eukarya, Fungi, Zygomycota, Rhizopus, (sporangium, sporangiophore, zygosporangium, sporangia, zygospore), Bread mold
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Genus, important structure(s), common name
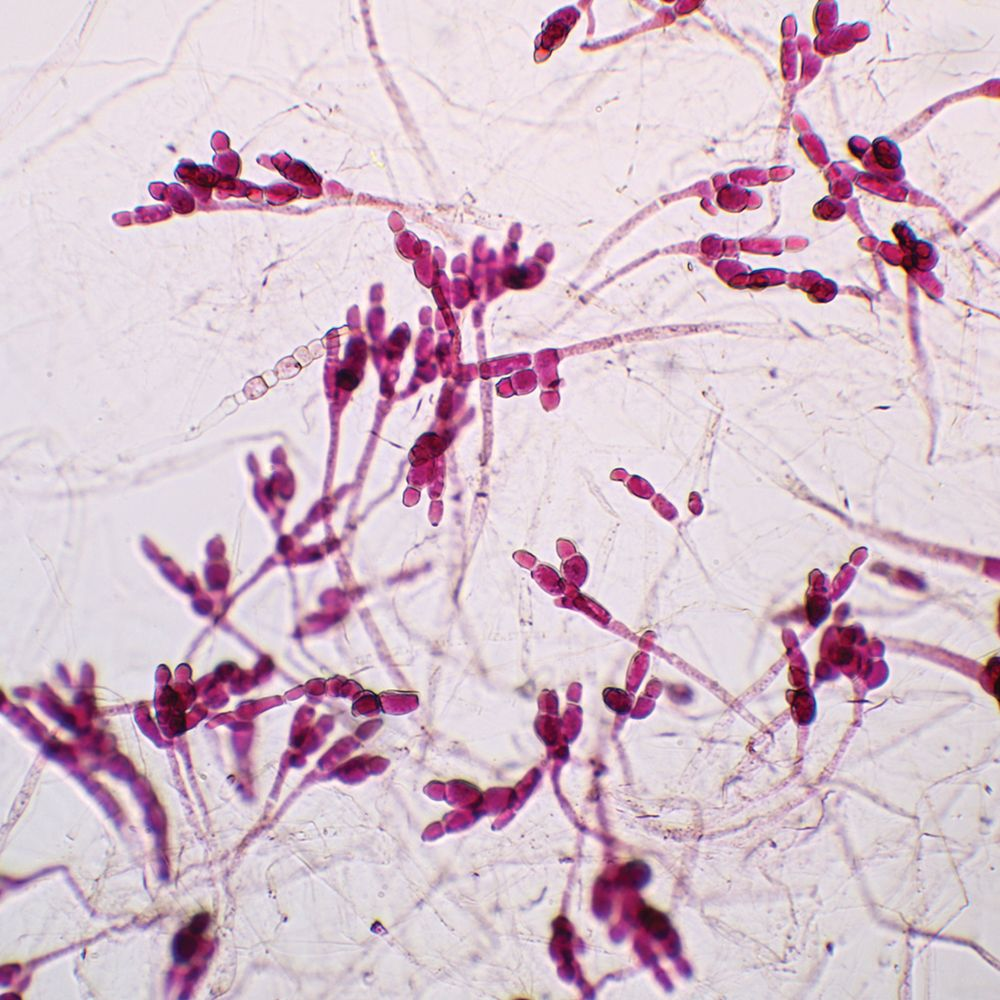
conidia
asexual spores of Phylum Ascomycota
ascospores
sexual spores from Phylum Ascomycota
Eukarya, Fungi, Ascomycota, Aspergillus, sac-like ascus, Black mold
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Genus, important structure(s), common name
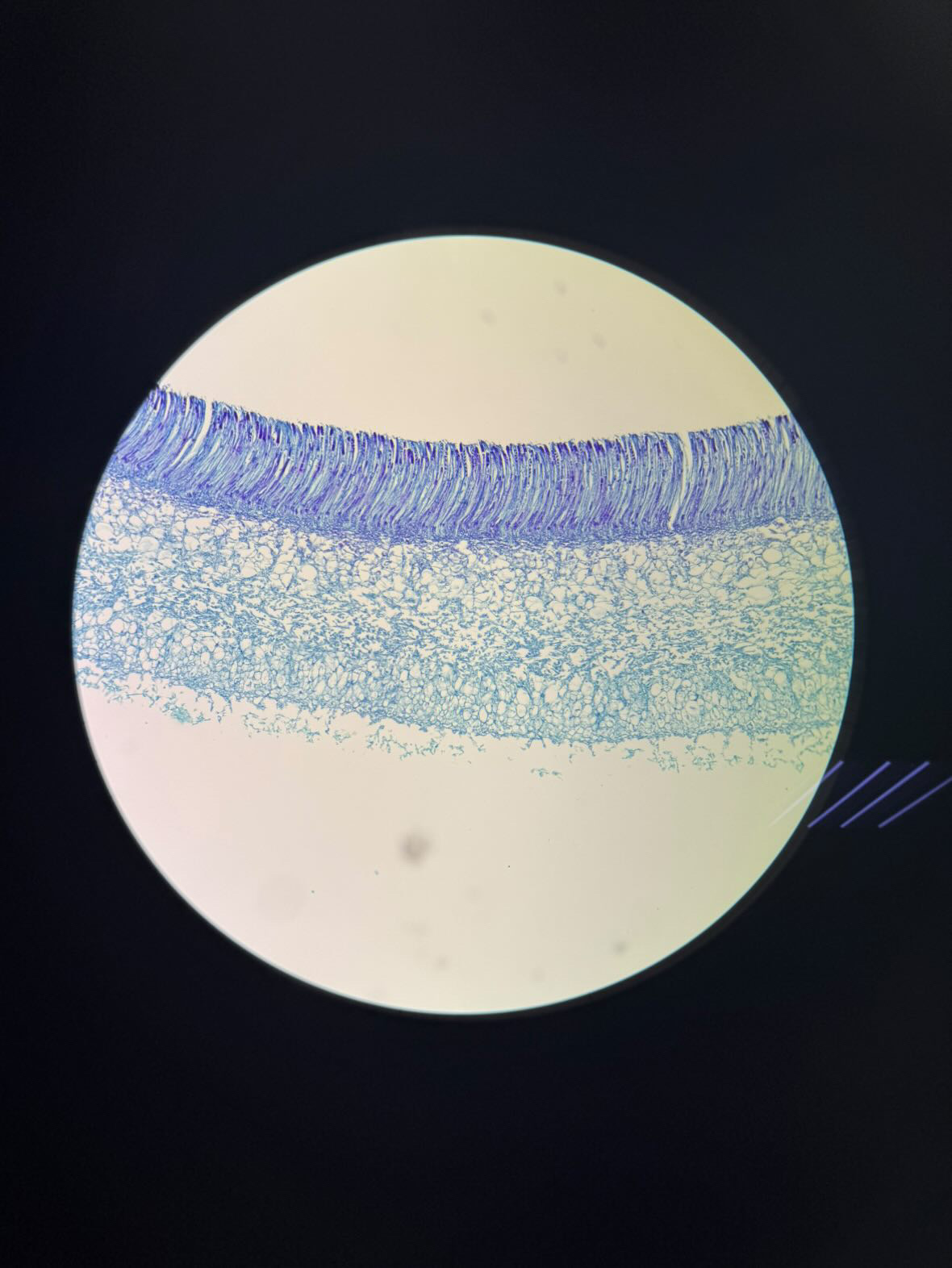
Eukarya, Fungi, Ascomycota, Peziza, sac-like ascus, Cup fungus
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Genus, important structure(s), common name
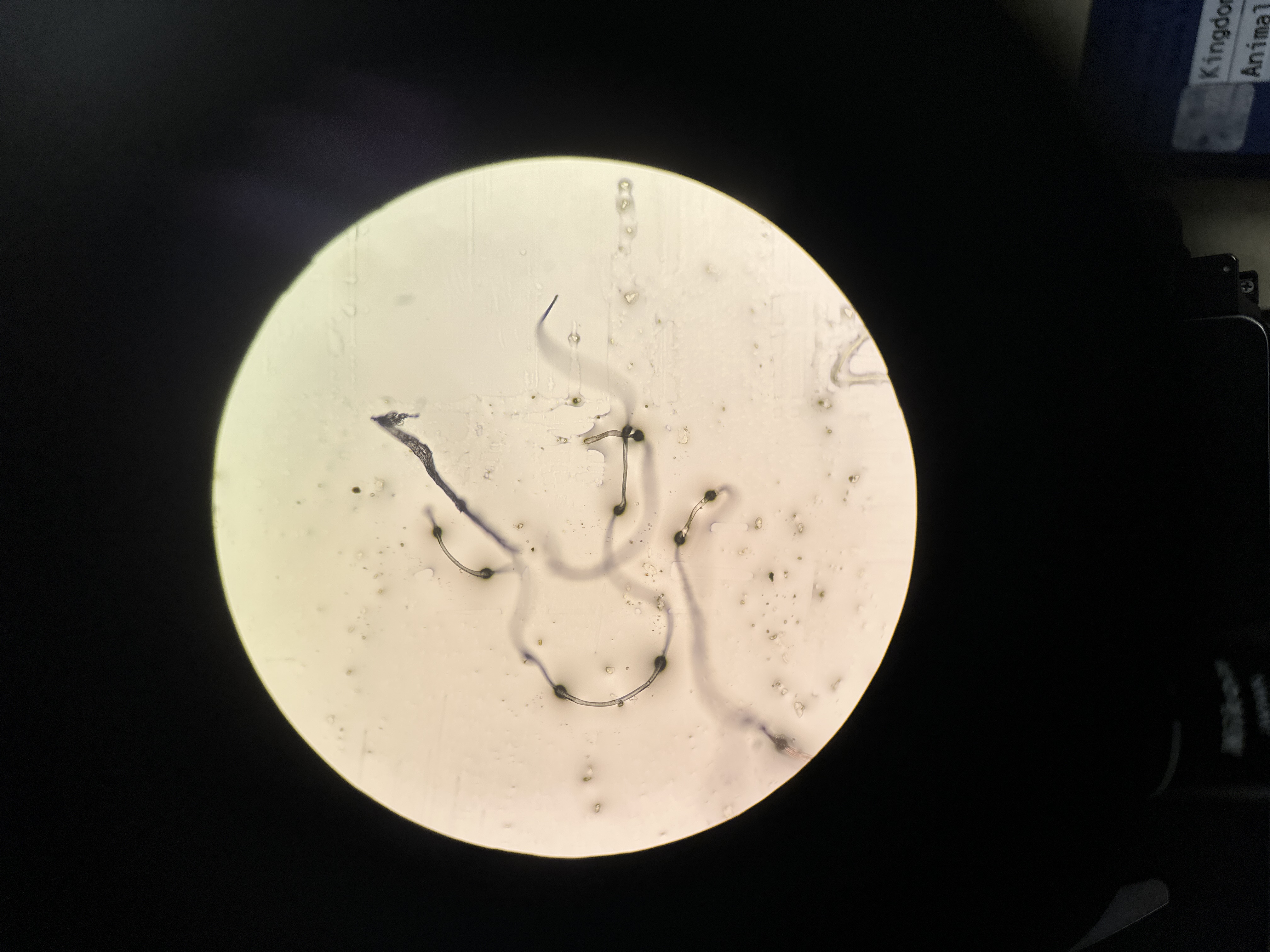
Eukarya, Fungi, Ascomycota, Penicillium, sac-like ascus, Blue/green mold
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Genus, important structure(s), common name
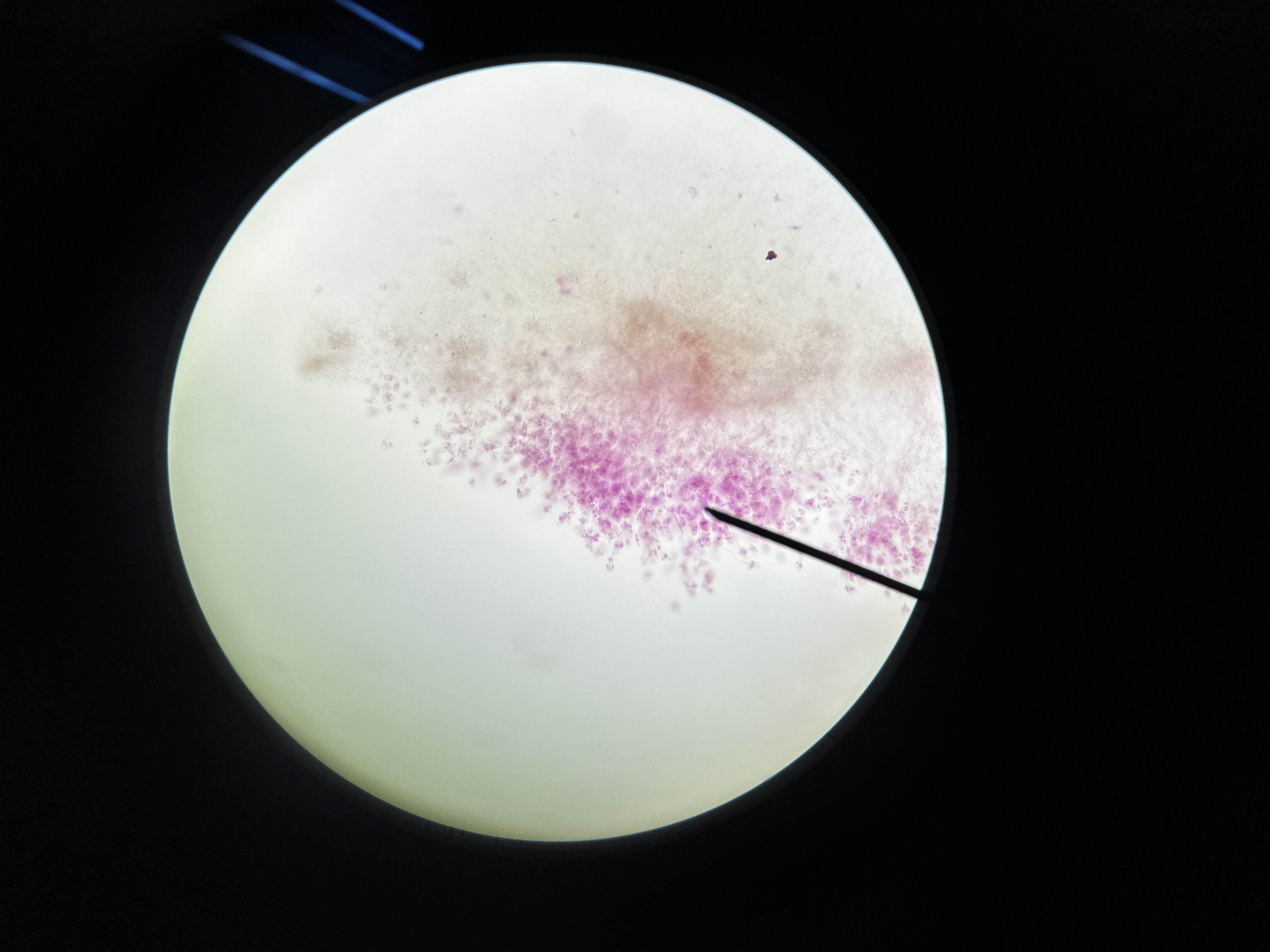
Eukarya, Fungi, Ascomycota, Saccharomyces, (asexually reproduce by budding, single non-motile cells, sac-like), Yeast
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Genus, important structure(s), common name
basidiocarp
fruiting body of Phylum Basidiomycota
basidiospore
sexual spores for Basidiomycota
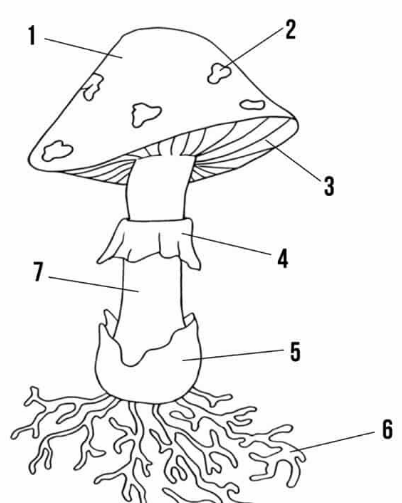
cap
umbrella shaped top (#1 on the picture)
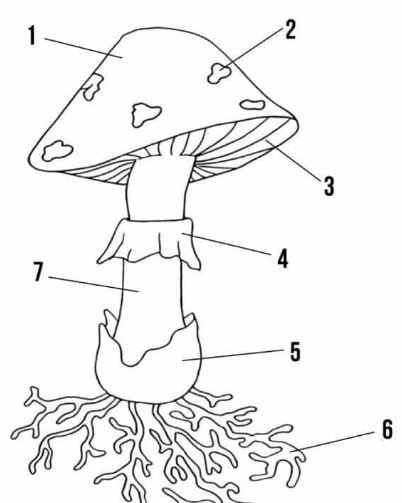
gills
strips of tissue that radiate outwards on the underside of the cap (#3 on the picture)
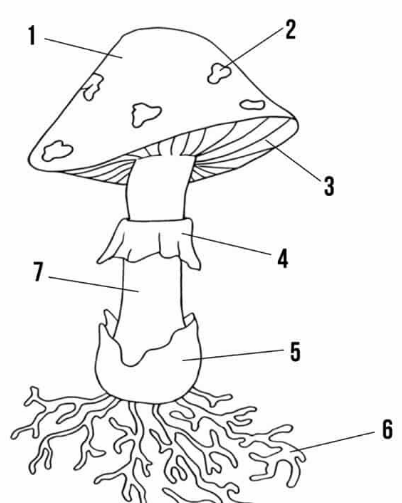
basidia
small club-shaped structures long the surface of each gill to make basidiospores

stalk (stipe)
upright portion of basidiocarp that supports the cap; formed by intertwining hyphae (#7 on picture)
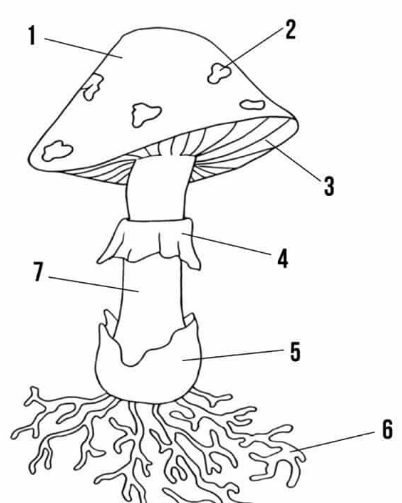
annulus
membrane around stalk where the cap was attached to the stalk before it opened up (#4 on picture)
Eukarya, Fungi, Basidiomycota, Agaricus, white mushroom
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Genus, common name
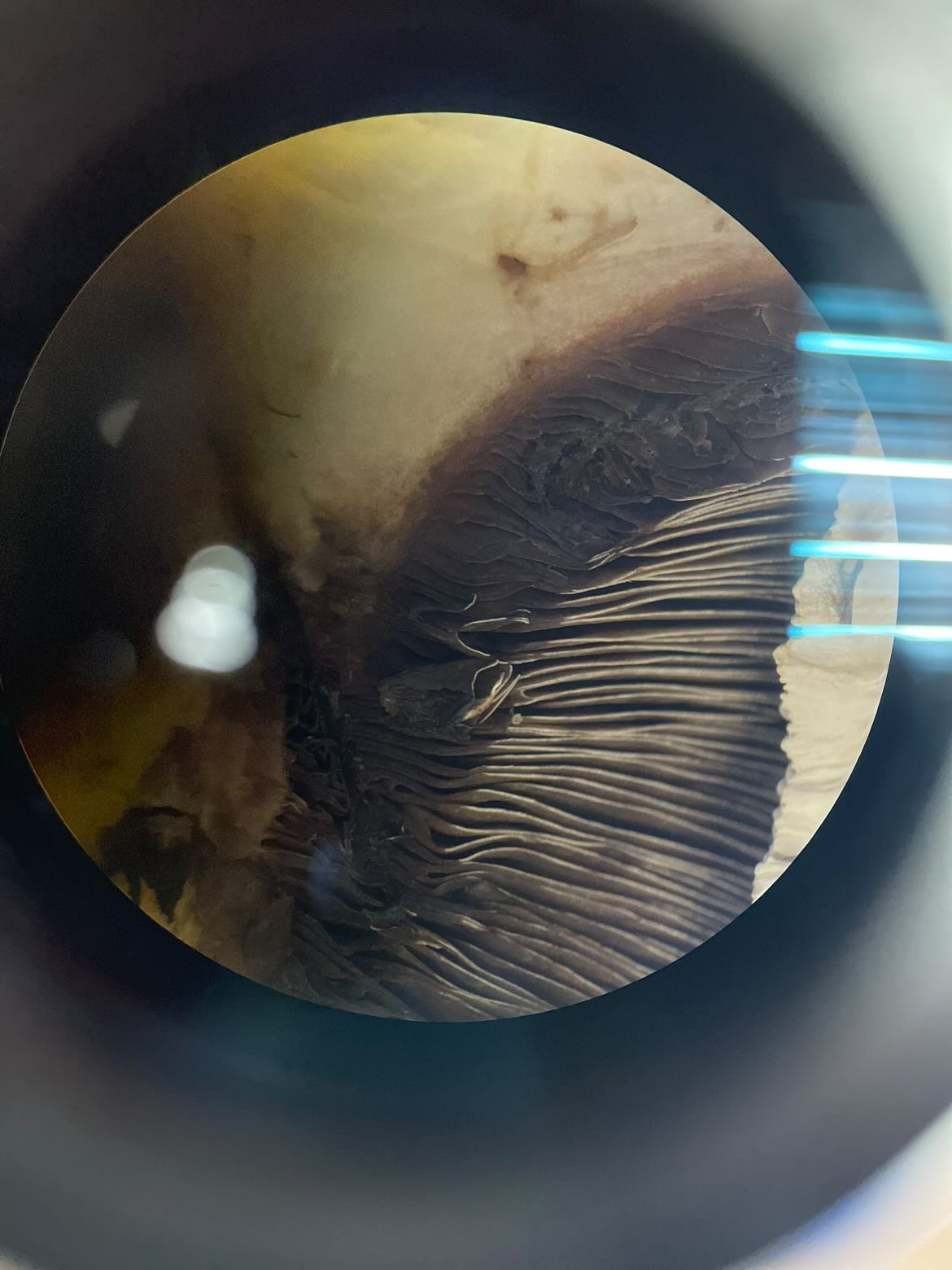
Eukarya, Fungi, Basidiomycota, Coprinus, Common grey mushroom
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Genus, common name
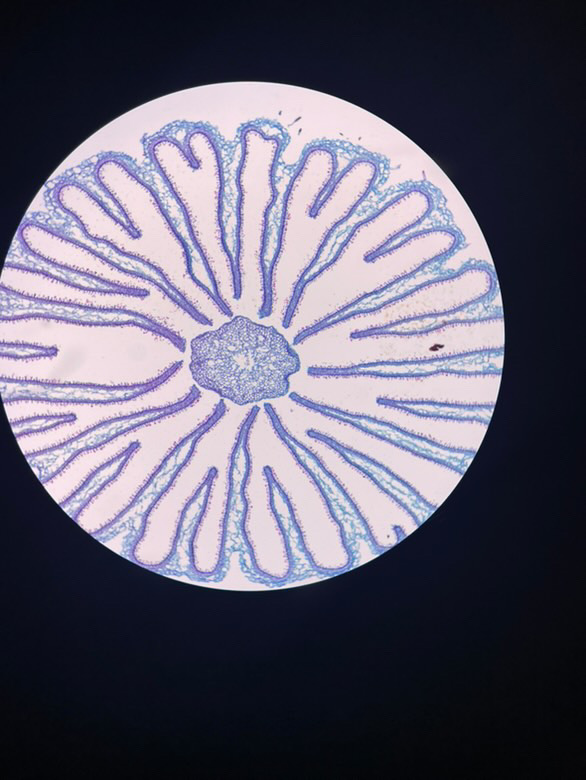
fruticose, crustose, foliose,
3 forms of lichen
soredia
asexual reproduction of lichen by fragmentation using lichen and algae
crustose
name the form of lichen from the image

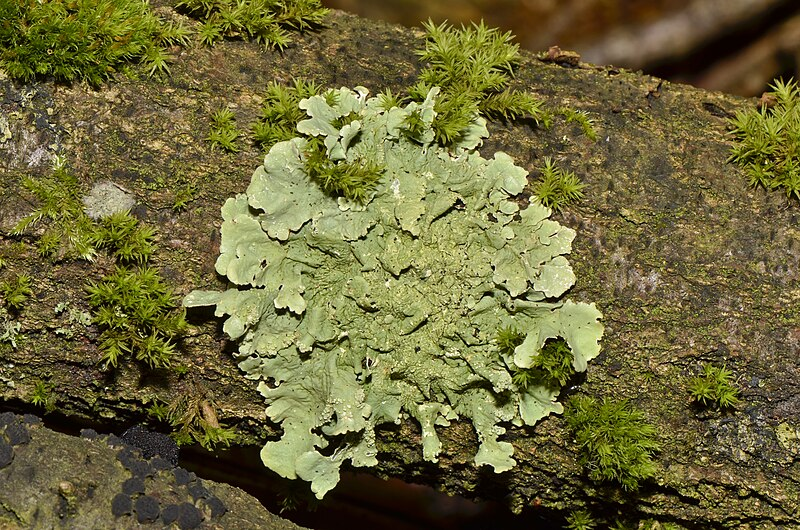
foliose
name the form of lichen from the image

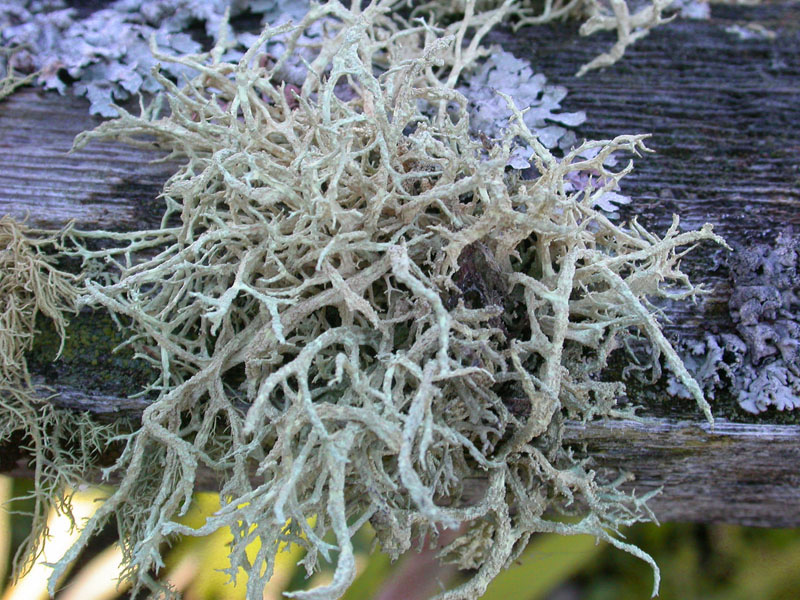
fruticose
name the form of lichen from the image

Mycorrhizae
symbiotic relationship of fungi and plant root
ectomycorrhizal
fungi grows between plant cells en
endomycorrhizal
grow and penetrate into plant cells
choanocytes
specialized cells used to create water flow in sponges
spicules
tiny rod-like elements that can be tough and fibrous or sharp and skeletal
Eukarya, Animalia, Porifera, (choanocytes, amoebocytes, asexual reprod via budding/fragmentation, spicules), sponge
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, important structures, common name

spicules
name this structure
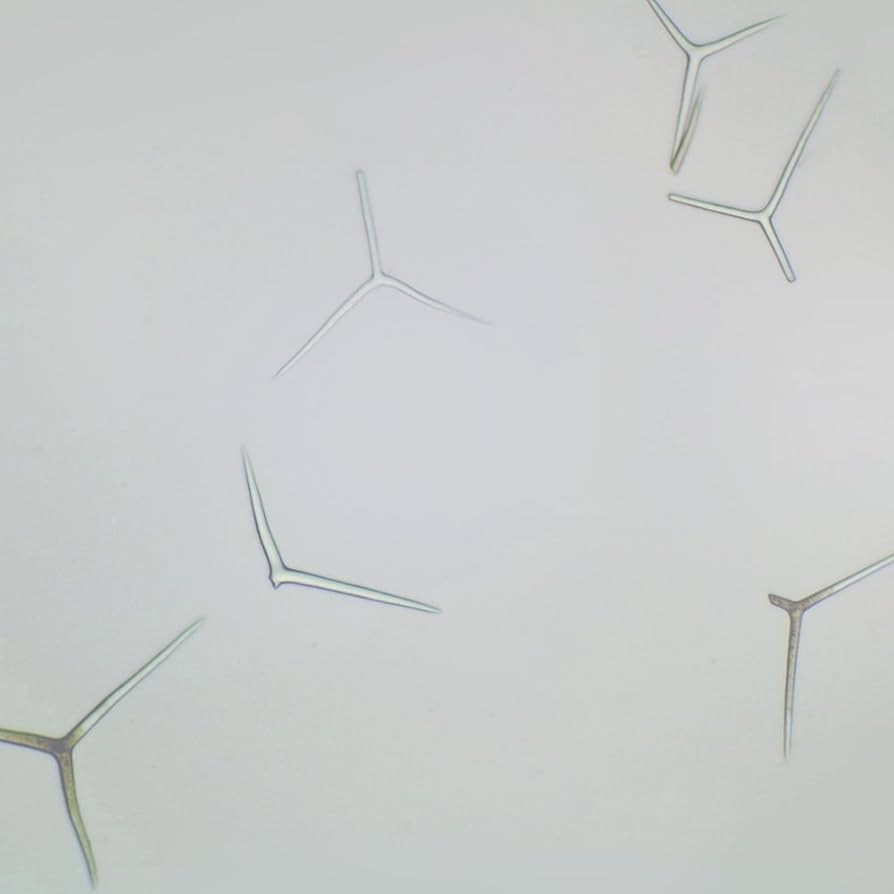
tentacles
Cnidarians use this to capture food and prey
nematocysts
specialized cells within tentacles that discharge encapsulated stinging organelles
Eukarya, Animalia, Cnidaria, Hydrozoa, Hydra, radial, dipoblastic, protostome
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Genus, symmetry, tissue organization, embryonic development of this organism
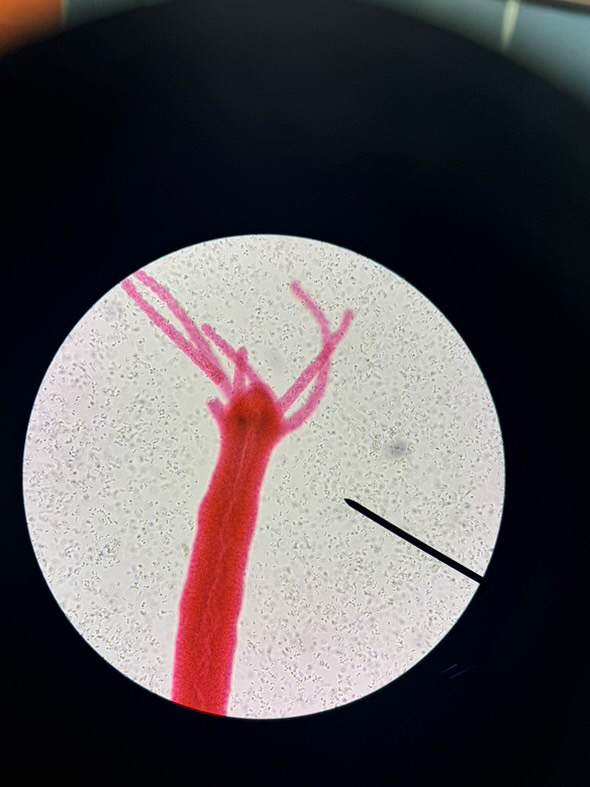
Eukarya, Animalia, Cnidaria, Scyphozoa, Aurelia, radial, dipoblastic, protostome, moon jellies
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Genus, symmetry, tissue organization, embryonic development, and common name of this organism

Eukarya, Animalia, Cnidaria, Anthozoa, Metridium, radial, dipoblastic, protostome, sea anemone
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Genus, symmetry, tissue organization, embryonic development of this organism
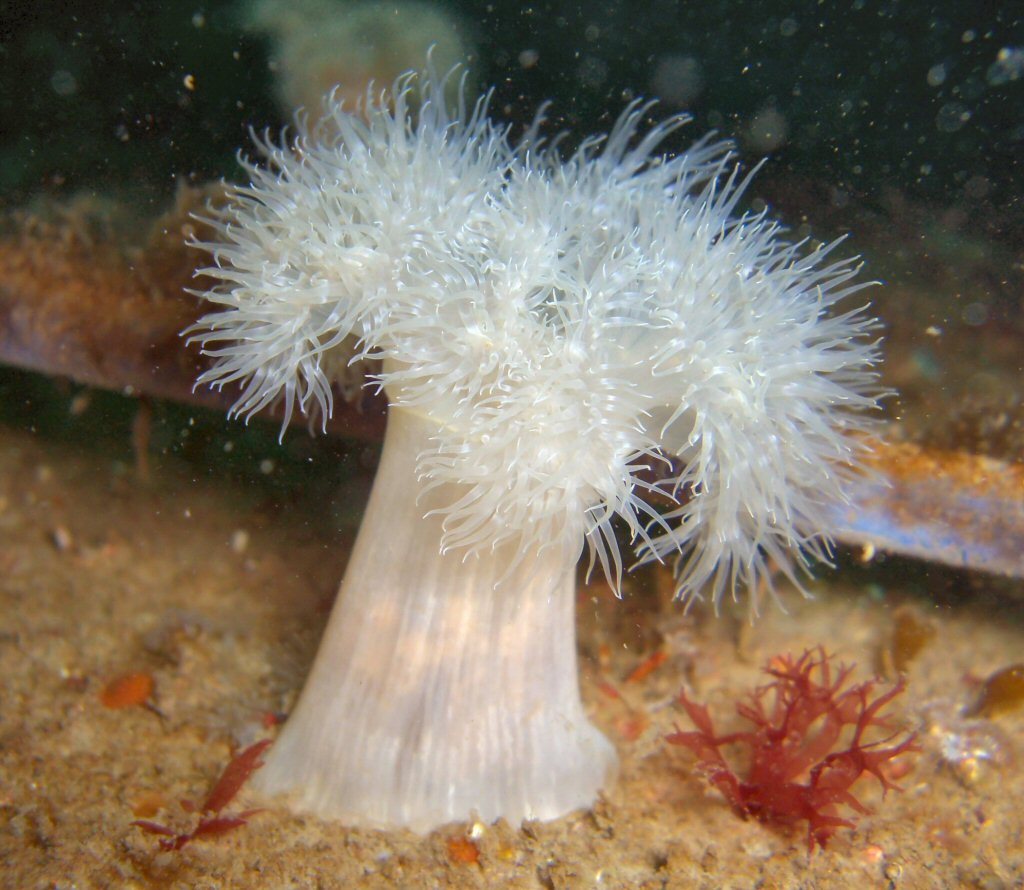

Eukarya, Animalia, Cnidaria, Anthozoa, radial, dipoblastic, protostome, coral
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, symmetry, tissue organization, embryonic development of this organism

eyespots
on the heads of Phylum Platyhelminthes that detect like, but cannot see images
Auricles
on the side of the head of Phylum Platyhelminthes, with tactile and chemical sensory cells
gastrovascular cavity
sac, mouth only, no anus
Eukarya, Animalia, Platyhelminthes, Dugesia, bilateral, trpoblastic, acoelomates, protostome, flatworm/planarian
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Genus, symmetry, tissue organization, embryonic development, common name of this organism
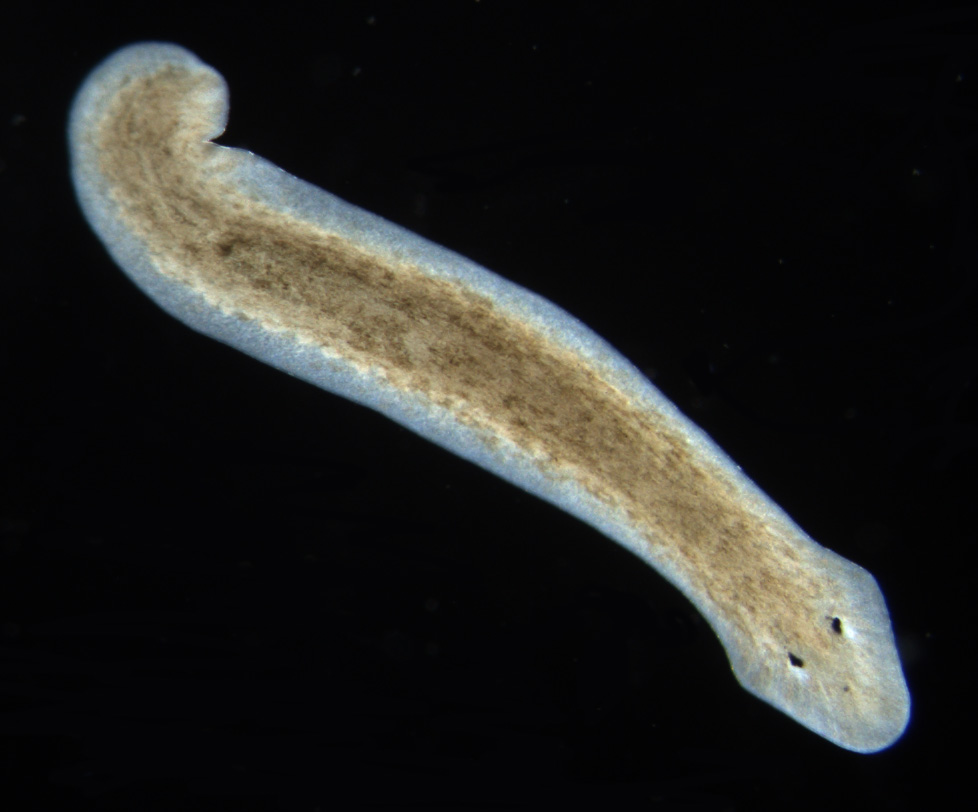
Eukarya, Animalia, Platyhelminthes, Cestoda, Dipylidium, bilateral, tripoblastic, acoelomate, tapeworm
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Genus, symmetry, tissue organization, common name of this organism
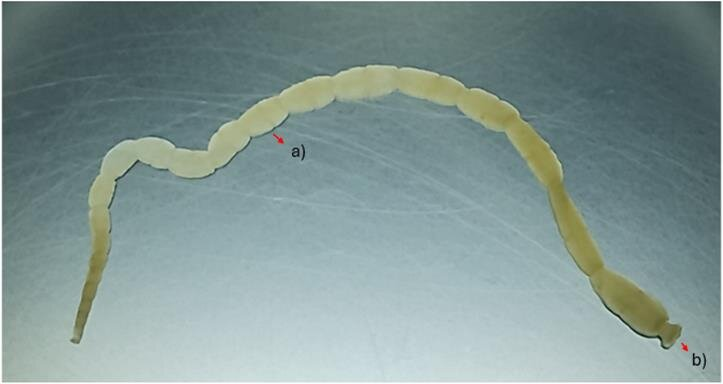
Eukarya, Animalia, Nematoda, Ascaris, bilateral, tripoblastic, pseudocoelomate, Small intestinal roundworm
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Genus, symmetry, tissue organization, common name of this organism
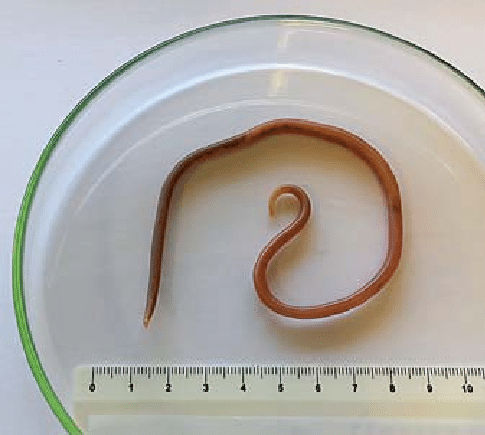

Eukarya, Animalia, Nematoda, Trichinella, bilateral, tripoblastic, pseudocoelomate, Human round worm
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Genus, symmetry, tissue organization, common name of this organism
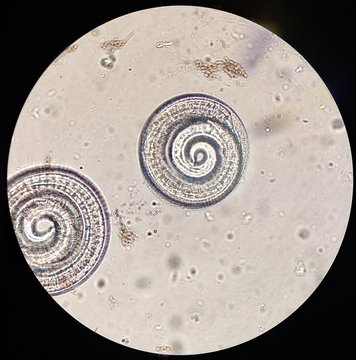
Trichinella (encysted larvae)
What form of Trichinella is this?
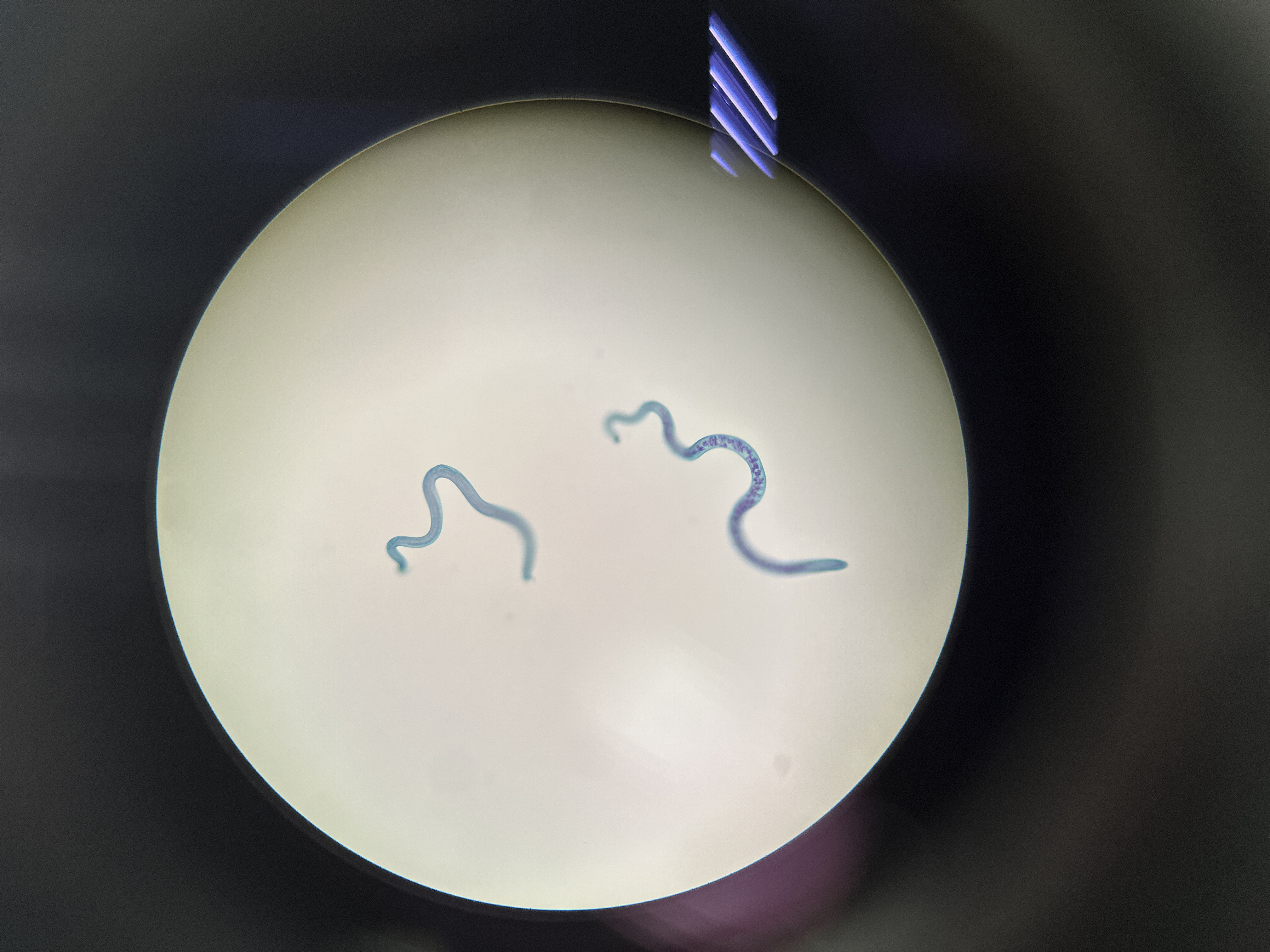
Trichinella (male/female)
What form of Trichinella is this?
visceral mass, muscular foot, mantle
common morphological traits of Phylum Mollusca
Eukarya, Animalia, Mollusca, Gastropoda, bilateral, tripoblastic, coelomate, protostomes, snails/slugs
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Genus, symmetry, tissue organization, embryonic development, common name of this organism

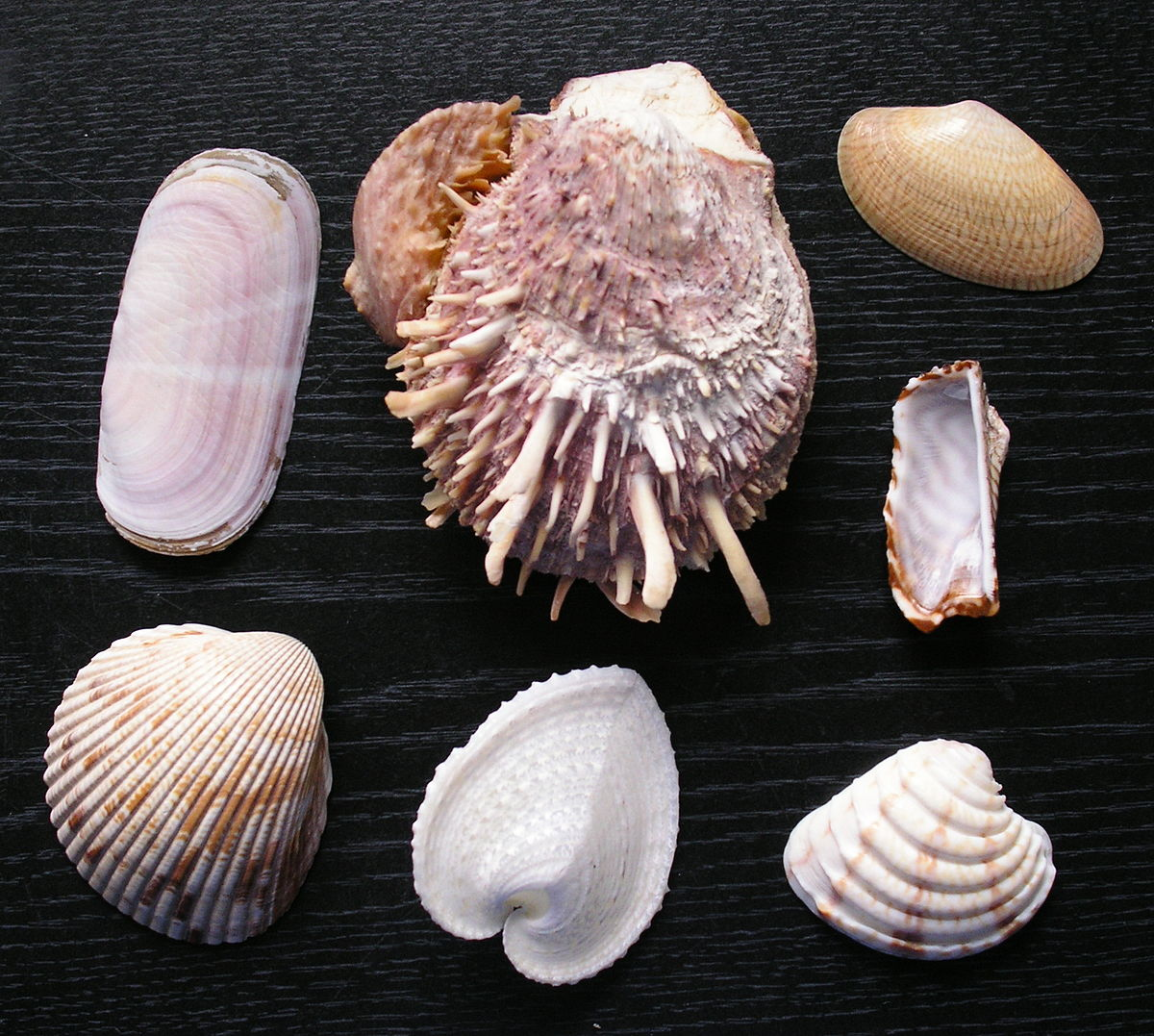
Eukarya, Animalia, Mollusca, Bivalvia, tripoblastic, coelomate, protostomes, (oysters/clams/scallops/mussels)
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, symmetry, tissue organization, embryonic development, common name of this organism

Eukarya, Animalia, Mollusca, Cephalopoda, bilateral, tripoblastic, coelomates, protostomes, (octopus/squid/nautilus)
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, symmetry, tissue organization, embryonic development, common name of this organism

Eukarya, Animalia, Annelida, Oligochaeta, bilateral, tripoblastic, coelomate, protostome, Earthworm
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, symmetry, tissue organization, embryonic development, common name of this organism

Eukarya, Animalia, Arthropoda, Chelicerata, Merostomata, Limulus, Horseshoe Crab, bilateral, tripoblastic, coelomate, protostome
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, Class, Genus, symmetry, tissue organization, embryonic development, common name of this organism

Eukarya, Animalia, Arthropoda, Chelicerata, Arachnida, (pedipalps, four pairs of walking legs, chelicerae), spiders/ticks/scorpions
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, Class, characteristics, common name of this organism

Eukarya, Animalia, Arthropoda, Crustacea, bilateral, tripoblastic, coelomate, protostome, Crayfish
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, symmetry, tissue organization, embryonic development, common name of this organism

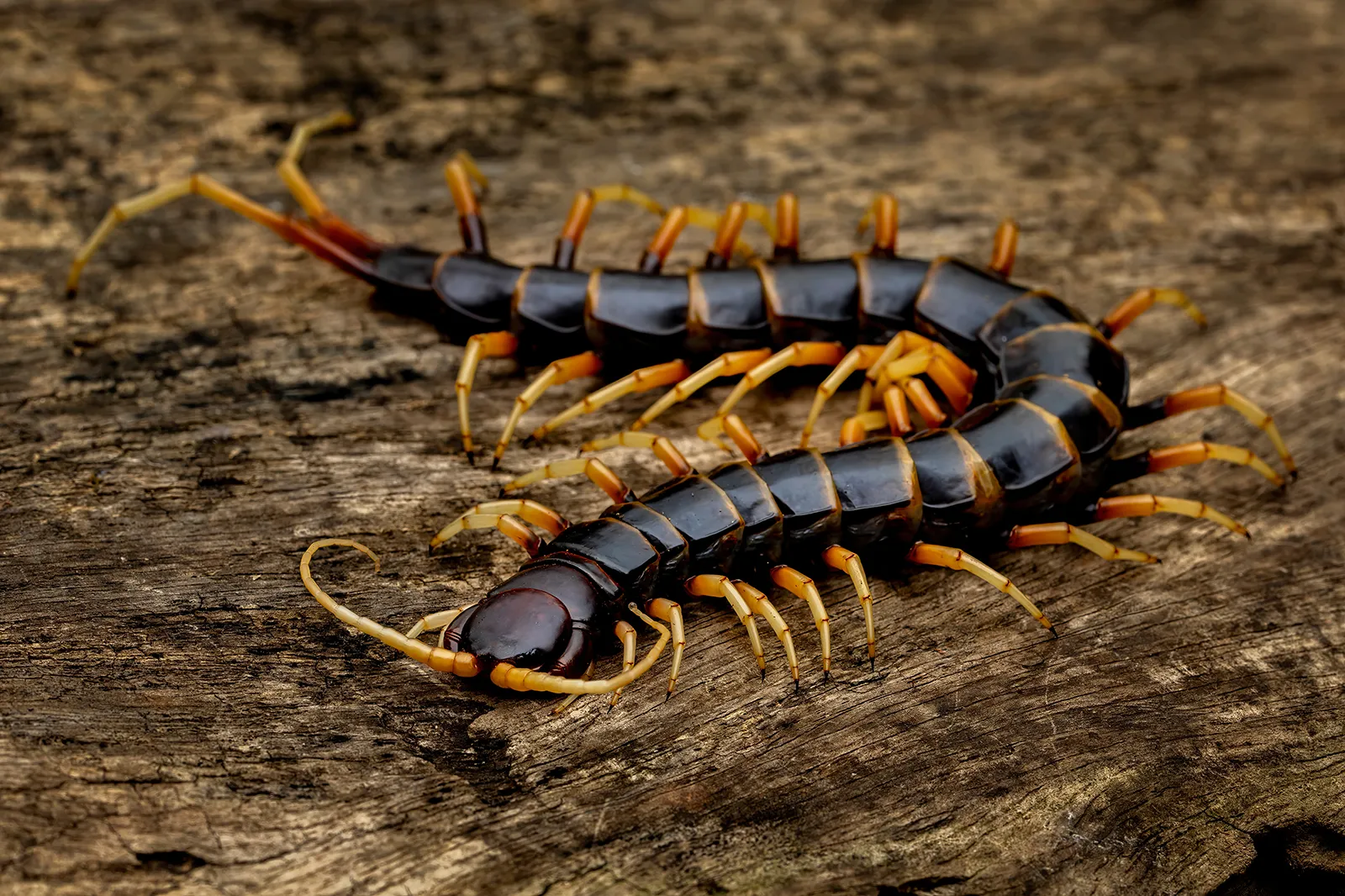
Eukarya, Animalia, Arthropoda, Myriapoda, Chilopoda, bilateral, tripoblastic, coelom, protostome, centipede
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, Class, symmetry, tissue organization, embryonic development, common name of this organism

Eukarya, Animalia, Arthropoda, Myriapoda, Diplopoda, bilateral, tripoblastic, coelom, protostome, millipede
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, Class, symmetry, tissue organization, embryonic development, common name of this organism

Eukarya, Animalia, Echinodermata, Ophiuroidea, Brittle Stars
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, common name of this organism

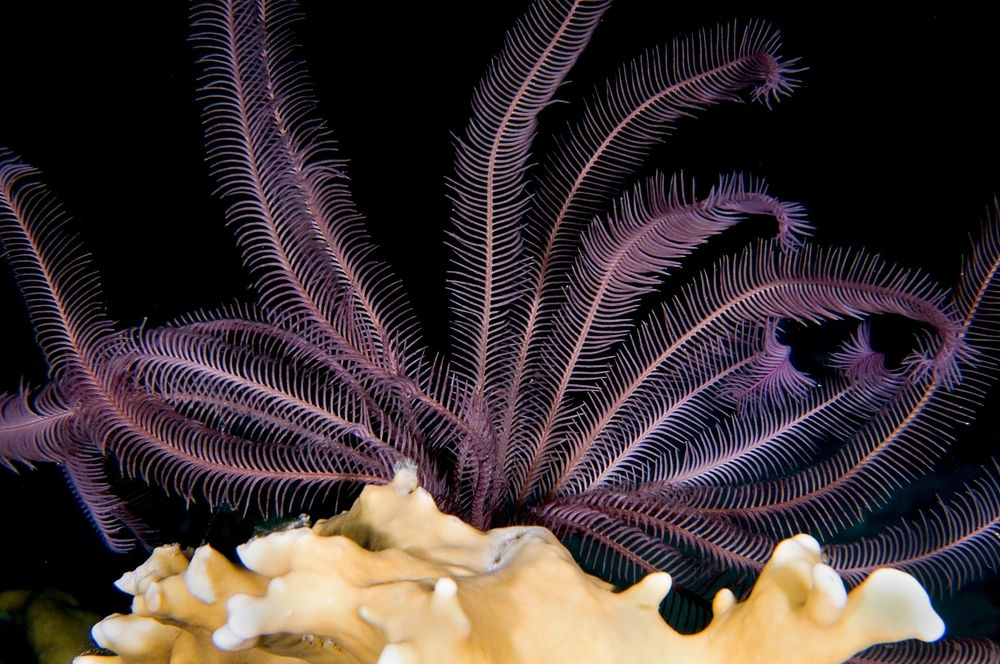
Eukarya, Animalia, Echinodermata, Crinoidea, Sea Lilies/Feather Stars
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, common name of this organism

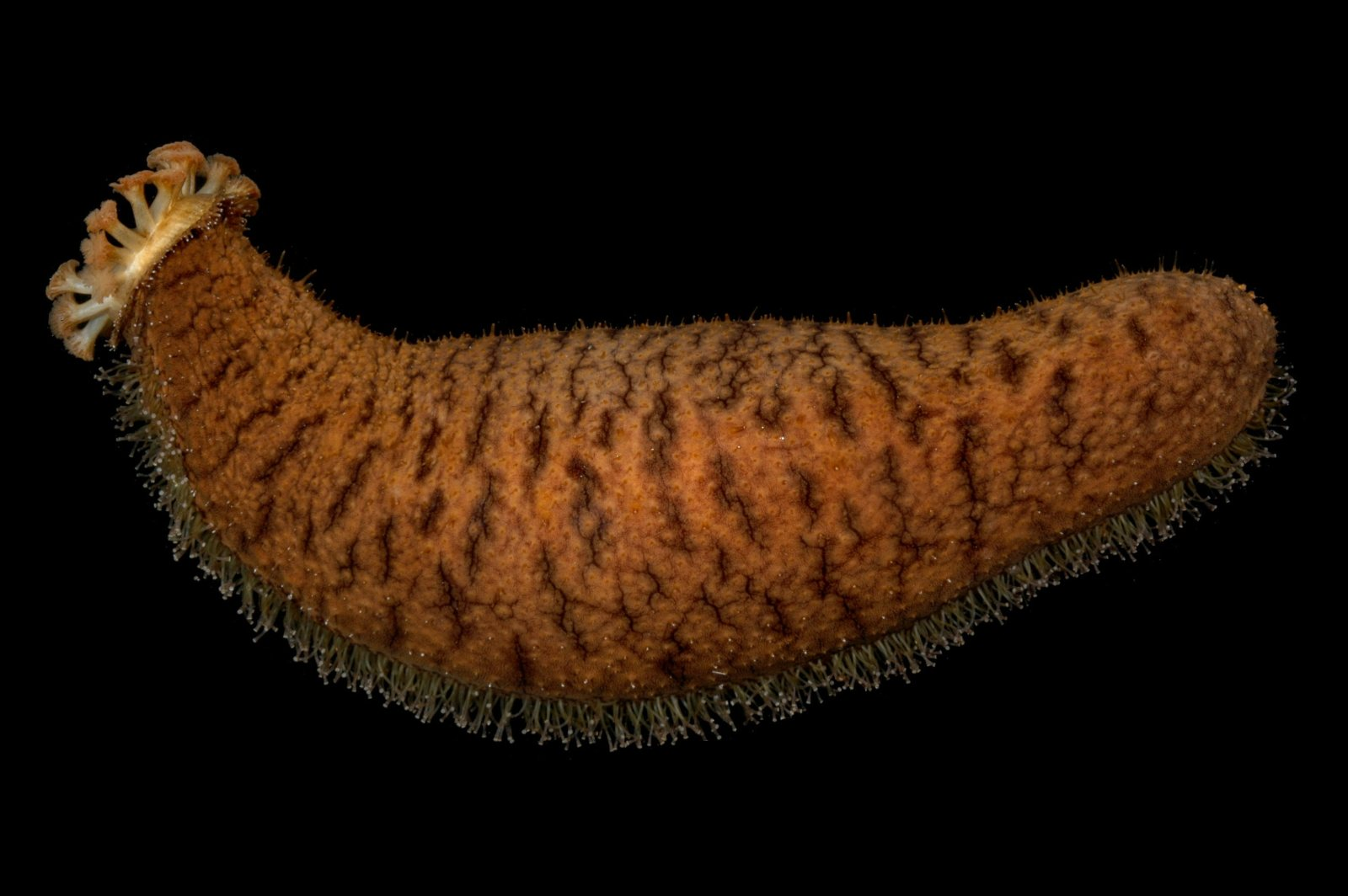
Eukarya, Animalia, Echinodermata, Holothuroidea, Sea Cucumbers
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, common name of this organism

Eukarya, Animalia, Echinodermata, Asteroidea, radial (adult), bilateral (larvae), tripoblastic, coelomate, deuterstomes, Sea Stars
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, symmetry, tissue organization, body cavity, embryonic development, common name of this organism
