Class 8: Theories of Motivation
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Motivation
Is a process that account for individual’s intensity, direction, and persistence. Motivated individuals stay with a task long enough to achieve the goal
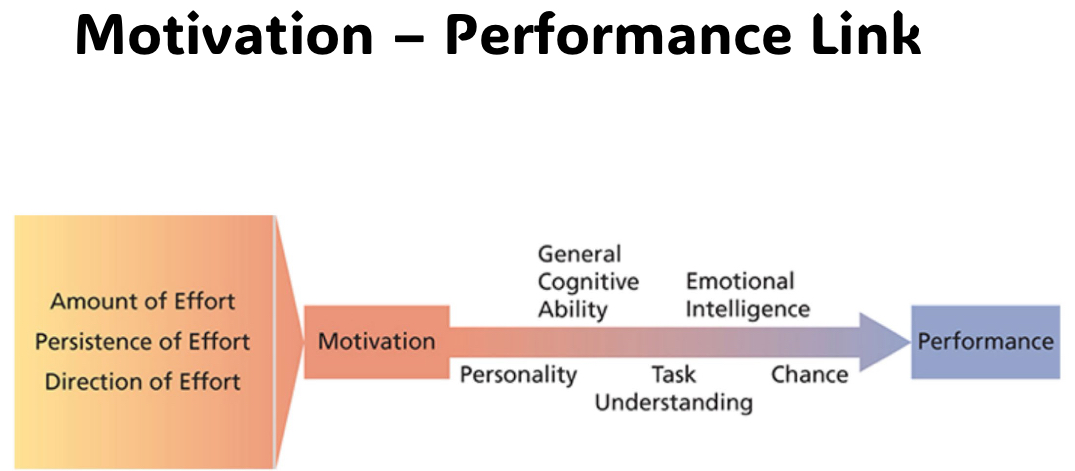
Intensity
Amount of effort put forth to meet goal
Direction
Effort channeled toward goal
Persistence
How long effort is maintained
Intrinsic motivation
Stems from direct relationship between worker and task
feelings of achievement or accomplishment
Feelings of competence drives from performing job
Enjoying the challenge
Sheer interest in job or task itself
Extrinsic motivation
Stems from work environment external to task
pay + fringe benefits
Company policies
Esteem from others
Grades
McClelland’s Needs Theory
Achievement, affiliation, power
Achievement
Desire to do challenge task well
value personal responsibility
Set difficult goals with calculated risks
Affiliation
Desire to establish positive relationships
want to be liked
Avoid conflict and competition, desire for belonging
Power
Desire to influence others; make impact
seek environments where they can be influential
Strong concern for personal prestige; self-serving, but can also serve organization
Expectancy theory
I’ll put in the work if i think it’ll get pay out. (Effort, performance, reward)
Effort
If i prepare extra for my interview, will i do well? (Expectancy)
Performace
If i do well on my interview, will i be offered the job? 9instrumentality)
Reward
If in get the job, would i take it? Do i actually want it? (Valence)
Goal setting theory
Clear and difficult goals make me work harder
Goals most motivational
when specific, challenging
When members are committed
When feedback about progress toward goal attainment is provided
Leads to:
1, greater effort
Increased and prolonged persistence
3. Improved strategiess to attain goals
SMART1 Goals
Specific: the goal is precise on what is to be accomplished
Measurable: the goal to be accomplished can be assessed objectively
Achievable: the goal is within reach yet also challenging
Results-based: the goal has clear, demonstrable outcomes (not just activities)
Time specific: the goal has a specific time by which it it to be accomplished
SMART2 goals
Significant: the goal is challenging and important
Meaningful: the goal has meaning beyond its objective value
Agreed upon: members participate in developing their own goals
Relevant: the goal is linked to important issues for a variety of stakeholders
Timely: the goal is appropriate for the present situation and the future
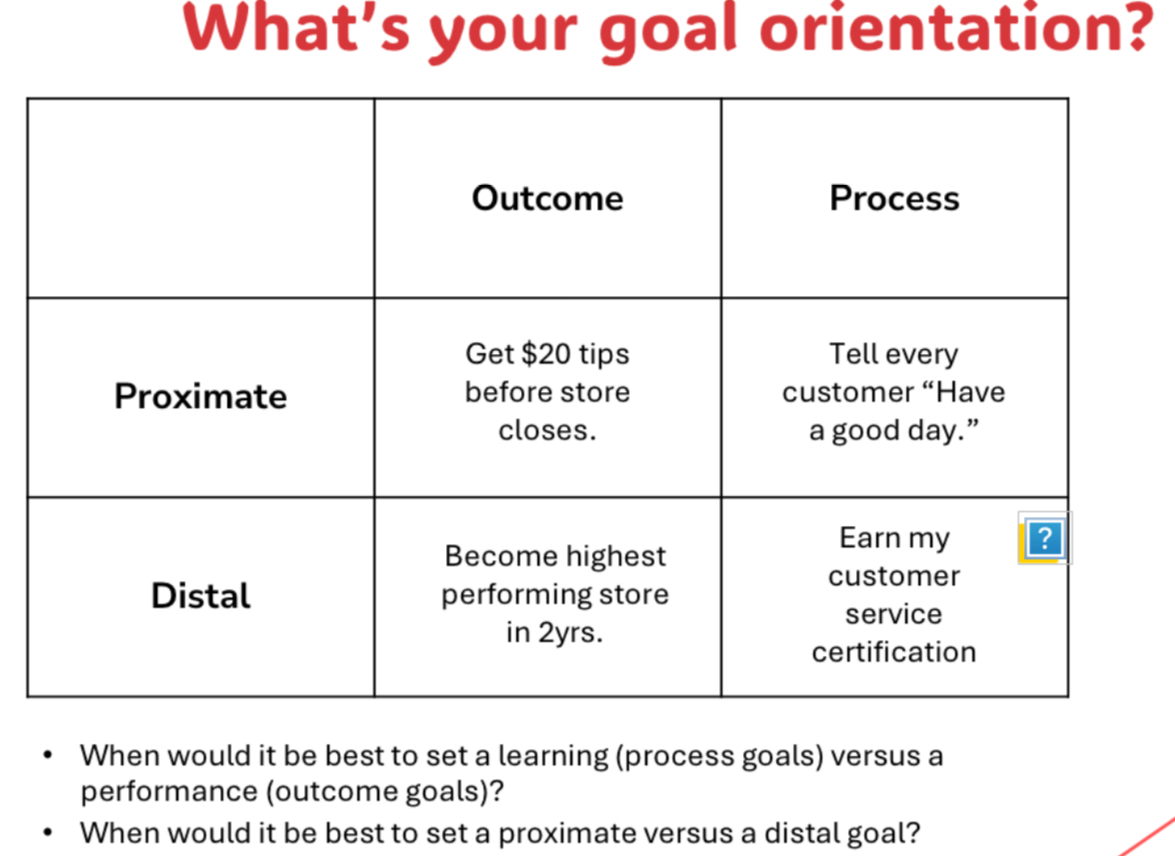
Goal orientation
refers to an individual’s goal preference in achievement situations
Proximate: near term
Distal: long term
Outcome: results
Process: behaviors
What motivates workers needing affiliation?
Desire for friendly and close interpersonal relationships
Need for affirmation and belonging
Mutually beneficial connections and reciprocal exchange