Hematology Instrumentation SOLO 1
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
0 degrees angle scatter
axial light loss
measures cell size
7 degrees angle scatter
intermediate angle scatter
measures cell complexity
90 degrees angle scatter
polarized side scatter
measures lobularity
90D degrees angle scatter
depolarized side scatter
measured granularity
Beckman Coulter IRIS
consists of two smaller instruments joined together
IRIS iChem velocity
IRIS iQ-200 sprint
can perform fully automated urinalysis for a more streamlined lab and minimal intervention from the tech
IRIS iChem velocity
performs biochemical, specific gravity, color, and clarity analysis
IRIS iQ-200
measured urine sediment similar to a flow cytometer
measures size, shape, contrast, and texture
uses Auto Particle Recognition to classify particles
takes up to 500 pictures/second
RBC/platelet histogram
counted by optical light scatter
measured for MCV/MPV using optical technology
RDW/PDW calculated
WBC differential scatterplot
plots ALL(cell size) against IAS(cell complexity)
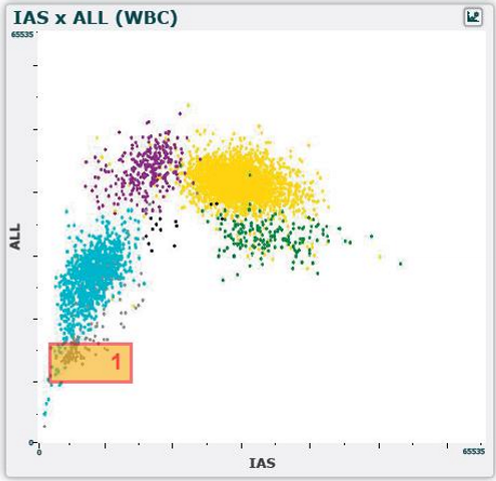
WBC differential scatterplot region 1
normal blood
few events in the region
abnormal blood
lyse resistant RBCs
sickle cells
fetal cells
nRBCs
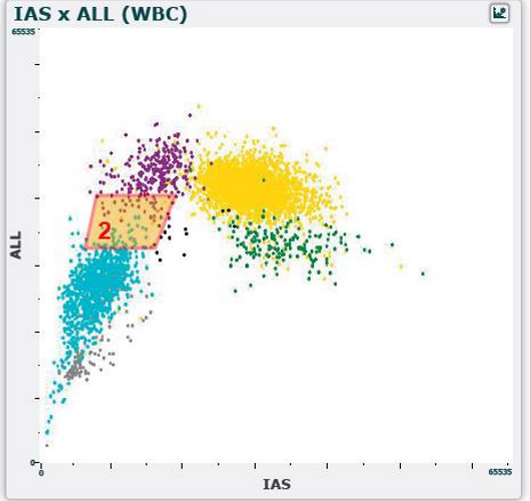
WBC differential scatterplot region 2
normal blood
lymphs and monos
abnormal blood
atypical lymphs
blasts
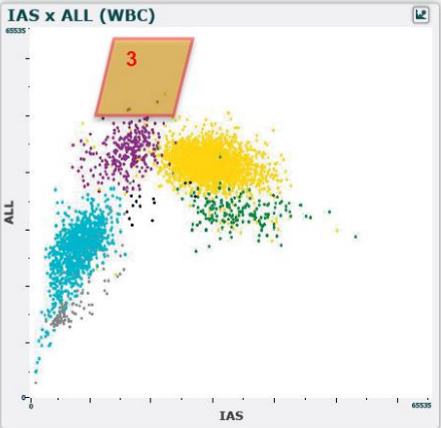
WBC differential scatterplot region 3
normal blood
few to no cells
abnormal blood
atypical monocytes
blasts
plasma cells
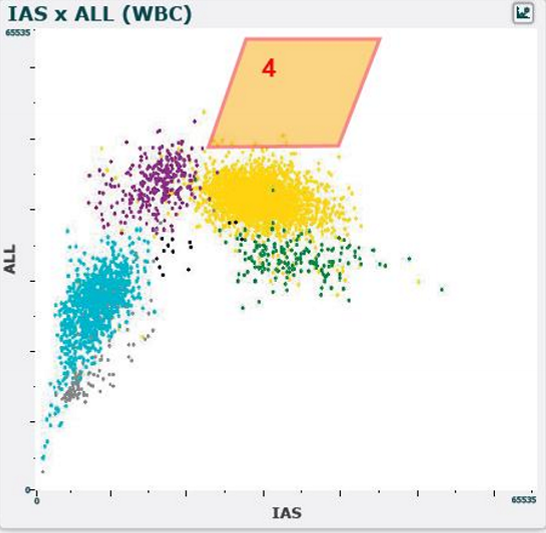
WBC differential scatterplot region 4
normal blood
few to no cells
abnormal blood
immature granulocytes
neutrophil aggregates
platelet sattelitism
Low-Hi Fl scatterplot
relative amount of intact membranes
plots ALL (cell size) against fluorescence (FL1)
mono poly 1 scatterplot
specializes in platelet aggregates
plots PSS (lobularity) versus ALL (cell size)
reticulocyte scatterplot
relative ratio of retics to mature RBCs
indirectly measures erythropoietic and megakarypoietic activity
What are falsely increased in aged blood?
MCV and HCT
What is falsely increased in lipemia?
MCHC and HGB parameters
What are CBC characteristics of cold agglutinin?
invalid data and elevated MCHC; decreased RBC and HCT
What characteristics are affected by thalassemia?
low MCV and HGB
What are the characteristics of sickle cell?
low RBC, HGB, HCT, MCV
increased RDW and RBC frag flag
What are the characteristics of AML?
high white count
invalid data, left shift, var lym, and blast flags
impedance counting
a cell suspension is created using an electrically conductive system
requires a conductive liquid
a cathode and anode are placed in opposite sides of the imped chamber
a decrease in current indiciates a cellular event is counted
the amount of current decrease is inversely proportional to the approximate size
Alinity H uses what methods to count blood
photometry/absorbance (HGB)
optical light scatter (WBC, RBC, PLT, NRBC counting; WBC class and diff)
fluorescence (detection of WBC, nRBC, RETC, and REC PLT)
absorbance spectrophotometry
a cells suspension of RBCs are mixed with a lysing agent
released hemoglobin from inside RBCs reacts with the reagent to form a colored complex that absorbs 540nm light
the amount of light absorbed is proportional to the amount of hemoglobin present
Light functions in what three ways that is useful for analysis?
diffraction
refraction
change in speed
reflection
AlinityH achieves accurate optical light scatter analysis with:
advanced MAPSS
advanced multi-angle polarized scatter separation
detects scattered light at 4 angles using a blue diode laser
counts RBCS, WBCs, PLTs,nRBCs, and RETCs
detects fluorescence from WBCs, nRBCS, and RETCs
ccharacterizes WBCs for diff
IAS1
measures hemoglobin concentration
size of PLTs
IAS2
measures size of RBCs
MCV from average of IAS2
IAS3
distinguishes PLT from RBC
distinguishes PLT from noise
fluorescence detection
fluorochromes are added to different dilutions and attach to specific cellular components
530nm light signal labeled as FL1
Reticulocyte fluorescence detection
dye binds to RNS
helps detemine compensatory ability of bone marrow
nRBC fluorescence detection
dye binds to DNA
WBC vaibility/differential fluorescence detection
dye binds to DNA
as WBCs age, cell membrane degrades and fluorochrome enters cells and attaches to DNA
h
hydrodynamic focusing
ensures orderly passage of cells through a sensing zone
moves with laminar flow which prevents mixing
prevents clogging
alinity requires what anticoagulant?
K2-EDTA
Alinity minimum volume
340 microliters whole blood
Alinity h system consists of what major components?
analyzer
reagents
data station/computer
printer
Alinity hq reagents
diluent/sheath reagent (diluting/rinsing)
hemoglobin reagent
WBC reagent
reticulocyte reagent
water from WPS
autoclean reagent
cyanide free hemoglobin reagent
primes HGB reagent tubing
rinses HGB system
lysing agent
reduces interference from leukocytes by detroying
converts HGB to a single chromagen (540nm)
alinity hs reagents/supplies
smear fix
wright-giemsa stain
phosphate buffer
glass slides
smear tape cartridge
slide label cartridge
What qualities does the iQ-200 use to analyze microscopic urine sediment?
texture
shape
size
contrast
What analyses does the iChemi velocity perform?
biochemical
clarity
specific gravity
color
list the tests present on a urine reagent strip
glucose
blood
nitrite
protein
ketone
pH
specific gravity
urobilinogen
bilirubin
leukocyte esterase
Three major systems of flow cytometers
fluidics
optics
electronics
FACS stands for
fluorescence activated cell sorting
What part of the microscope functions to focus and center the light beam with a desired numerical aperture and field size through the specimen?
condenser
parts of the microscope are divided into what categories?
magnification and illumination