Gov 312 midterm
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/165
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:42 PM on 2/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
1
New cards
The Big 4
race, socioeconoomic class, gender, and religion
2
New cards
Scientific Method Steps
1. make observations
2. develop theoretical framework
3. form **falsifiable** hypothesis
4. collect data to test hypothesis
5. draw conclusions
6. Systpublicize results
7. wait for rebuttals and revisions
3
New cards
Issues with social science
* incredibly complex systems
* ethical & practical issues with conducting experiments, making it difficult to rule out confounding variables
* ethical & practical issues with conducting experiments, making it difficult to rule out confounding variables
4
New cards
what do they do as a result?
more methodologically complicated studies that attempt to isolate effects of X and Y
5
New cards
How?
by making observations and developing theoretical framework
6
New cards
most important invention of all time?
fire? democracy? basic human rights? scientific method?
all of the above --- right answer
all of the above --- right answer
7
New cards
System level Approach
gov. system designed to make public policy
8
New cards
what makes it successful?
efficiency, natural examples (species evolution), and response to environmental factors (info processing)
9
New cards
Societies need a way to organize themselves by having what?
procedures to set rules, and being able to enforce those rules
10
New cards
Successful gov described as what?
authoritative allocations of values (ex. chore wheel)
11
New cards
Policymaking is process of what?
collecting a resource and then reallocating it to solve problem (too easy to say it’s bad cause of redistribution and there are winners + losers for most policies)
12
New cards
Constitution accomplishes what?
\-establishes “rule of law” in a society
\-basics of policymaking
\-outlines responsibilities of gov. institutions
\-who is eligible for gov positions
\-basics of policymaking
\-outlines responsibilities of gov. institutions
\-who is eligible for gov positions
13
New cards
Articles of Confederation
\-first consititution ratified in 1781, each state had one vote, no enforcement, required unanimous consent to attend
14
New cards
Origins of Constitution
\-weak national gov, states wouldn’t pay taxes or accomplish anything, couldn’t raise funds for nat. military
15
New cards
What came out of the Constitutional Convention?
bicameral legislation came out of this (except Nebraska only has one chamber)
16
New cards
Policymaking Insitutions
elected- president, congress
unelected- courts, bureaucracy, const. says almost nothing about role of courts of bureaucracy
unelected- courts, bureaucracy, const. says almost nothing about role of courts of bureaucracy
17
New cards
What level does media coverage spend most of their time on?
Federal level
18
New cards
Congress
* designed to be the most *powerful* branch (federalist papers)
* -primary lawmaking body
* -primary lawmaking body
19
New cards
What article lists powers of Congress
Article 1 Section 8- Necessary and Proper Clause
20
New cards
Bicameral (House + Senate)
\-compromise between big + small states
\-designed to provide friction + mitigate role of ppl
\-originally no direct election of senators
\-designed to provide friction + mitigate role of ppl
\-originally no direct election of senators
21
New cards
The President
powerful, yet restrained
head of state- embodies values & traditions “above” politics is unifying symbol
head of gov- highest pol. office, tension with head of state role, policymaking
head of state- embodies values & traditions “above” politics is unifying symbol
head of gov- highest pol. office, tension with head of state role, policymaking
22
New cards
What is the constitutional basis of presidential powers?
Enumerated Powers- sign bills into law, execute the law, military authority, issue pardons, diplomacy, veto legislation, appts.
23
New cards
Judicial Power
little in constitution regarding judicial checks on other branches
24
New cards
Powers for judicial branch established over time:
judicial review + supremacy of federal courts
25
New cards
Judicial Review
Judiciary Act of 1789 established lower fed courts, also allowed federal officials to ask court for a writ of mandamus
26
New cards
Marbury v. Madison (1803)
established judicial review; midnight appointments did not issue writ of mandamus, empowered court to declare a law unconstitutional
27
New cards
3 Models of Court-Decision Making
1. Legal
2. Ideological - interpreting from their perspective
3. Strategical - want to behave ideologically but is more legal
28
New cards
Bureaucracy
refers to all agencies, work for gov but are not elected (civilian + military bureaucracies)
29
New cards
Bureaucrats as Policy Makers
\-made within executive bureaucracy
\-takes place when agencies have discretion to interpret laws made by legislatures; follows a rule-making process
(ex. marijuana is illegal in TX but Austin PD does not enforce)
\-takes place when agencies have discretion to interpret laws made by legislatures; follows a rule-making process
(ex. marijuana is illegal in TX but Austin PD does not enforce)
30
New cards
Bureaucratic Drift
when policy preferences of Congress or president shift more left or right, so does the agency
31
New cards
Iron Triangle
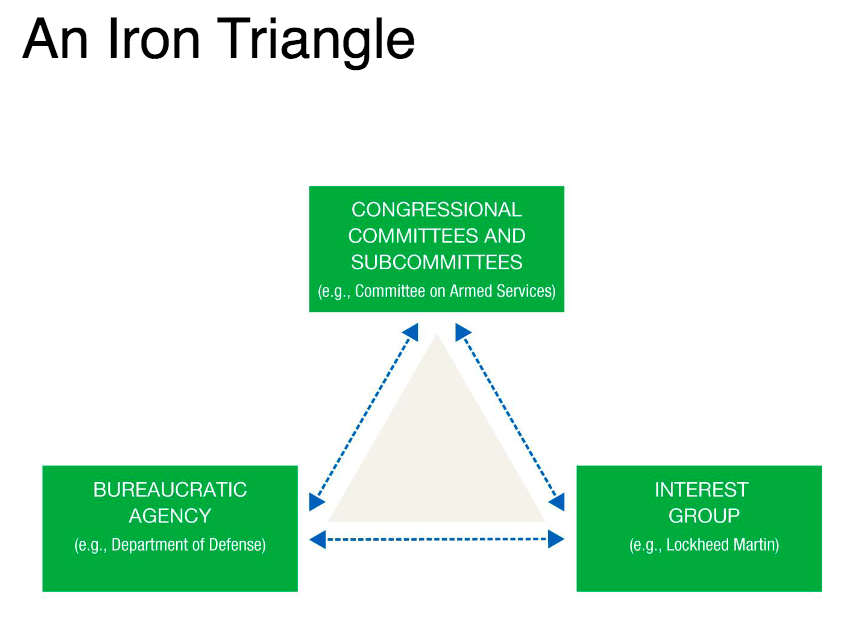
32
New cards
Public Opinion in a democratic System
\-collection of attitudes, opinions, and preferences of the general public
33
New cards
How does opinion influence public policy?
dynamic responsiveness
34
New cards
direct responsiveness
representatives actively monitor to try and figure out what constituents want + vote accordingly
35
New cards
indirect responsiveness
losing an election because constituents are unhappy (senators are most likely to do this)
36
New cards
Two big concerns
minority rule- norm in oligarchies + dictatorship
tyranny of majority- majority does nasty stuff to minority groups
tyranny of majority- majority does nasty stuff to minority groups
37
New cards
solution of minority rule
fair democratic systems, competition, one person one vote
38
New cards
solution of tyranny of majority
development of norms/ culture centered on basic human rights, checks from judicial branch
39
New cards
The founders on public opinion
laid foundations for future development of human rights, democratic norms respecting society (bill of rights)
40
New cards
Skepticism of potential dangers
concerned people are uneducated so checks on influence of public opinion
41
New cards
Minority Party Rule
party receives fewer votes but still retains power
(ex. D+R both have 50 seats in Senate but Dems represent 41 mil more Americans)
(ex. D+R both have 50 seats in Senate but Dems represent 41 mil more Americans)
42
New cards
Americans lack what?
…political knowledge
2/3rds of American adults cannot name Chief Justice of supreme court
2/3rds of American adults cannot name Chief Justice of supreme court
43
New cards
Rational ignorance-
we have busy lives and if we feel we can’t change it, we’re not too interested
44
New cards
Non-attitudes
lack of strong opinions
45
New cards
American Electorate
\-behavior of mass public suggest it is possible
\-displays some systematic tendencies
\-displays some systematic tendencies
46
New cards
Liberalism Index
higher values= liberal
lower values= conservative
(wouldn’t happen if public was informed)
lower values= conservative
(wouldn’t happen if public was informed)
47
New cards
Thermostatic Behavior
public responds to who’s president
ex. Republican in House, public means more liberal
ex. Republican in House, public means more liberal
48
New cards
Aggregation Gain
Individual level: lots of randomness, few ideological ppl
Electorate level: what appears to be some coherent movement, the public is reacting
Electorate level: what appears to be some coherent movement, the public is reacting
49
New cards
Public Organizations
Political parties- dem + repub
Interest groups- corporations + orgs
Social Movements- least organized, trying to lobby gov.
Interest groups- corporations + orgs
Social Movements- least organized, trying to lobby gov.
50
New cards
What are parties?
-groups that organize to win offices
\-ubiquitous in democracies with strong legislatures
\-organize political conflict
\-complex political organizations
\-unified ideologically
\-ubiquitous in democracies with strong legislatures
\-organize political conflict
\-complex political organizations
\-unified ideologically
51
New cards
Party Structure
party in government
\-elected officeholders
party as organizations
\-”fundraising” institutional apparatus, helps win elections
party in the electorate
\-group of ppl who identify with a particular party
\-elected officeholders
party as organizations
\-”fundraising” institutional apparatus, helps win elections
party in the electorate
\-group of ppl who identify with a particular party
52
New cards
Interest Group
any group other than a party that is organized to influence government (lobbying)
\-most represent businesses
\-another type is public interest group
\-most represent businesses
\-another type is public interest group
53
New cards
Social Movements
\-use popular participation to influence the gov.
\-not formal organizations
\-made up of many interest groups
\-develop when groups feel excluded from political process
\-not formal organizations
\-made up of many interest groups
\-develop when groups feel excluded from political process
54
New cards
Capitalism
economic system where means of production are controlled in large part by private enterprise
55
New cards
Right View of capitalism
Ayn Rand School of Thought
-market outcomes are sacrosanct
\-govt. redistribution is bad
-market outcomes are sacrosanct
\-govt. redistribution is bad
56
New cards
Left View of capitalism
\-growing skepticism with capitalism
\-wants to redistribute govt. funds
\-wants to redistribute govt. funds
57
New cards
Late capitalism
overabundance of consumer choices but foundational needs are not being met
58
New cards
Given sufficient competition (entry + exit points), has potential to:
* process wealth @ extremely high levels
* generates lots of wealth
* increase human agency (meaningful choices)
* generates lots of wealth
* increase human agency (meaningful choices)
59
New cards
Unchecked capitalism has potential to produce:
huge inequalities, monopolies, bad working conditions, pollution, etc. (corporations are prioritizing short & medium run games over long run games
60
New cards
Amartya Sen (Uses and Absuses of Adam Smith) says…
gov regulations have to be apart of capitalistic systems to break up monopolies, make working regulations, etc.
61
New cards
Is Inequality inevitable? (Bruce M. Boghesian)
yes. simulation shows that all starting on equal footing still leads to a small percentage of the world amounting all resources
62
New cards
So, what’s the solution?
gov. regulations stop this by breaking monopolies and redistributing funds
63
New cards
Dimensions of Inequality
some level is desirable as it drives competition
64
New cards
Vertical Inequality
income + wealth
65
New cards
Horizontal Inequality
differences in income + wealth observed across race, ethnicity, and gender
66
New cards
Consequences of Inequality
* economic stagnation
* social unrest
* worse health outcomes
* polarization
* lobbying
* unequal application of law
* social unrest
* worse health outcomes
* polarization
* lobbying
* unequal application of law
67
New cards
Causes of Inequality
income + wealth inequality is direct consequence of capitalism and free enterprise, necessary to sustain system
68
New cards
Increasing inequality is a function of
economic factors + political factors
69
New cards
What are those economic factors
globalization + tech that eliminate lower skills position
70
New cards
What worsens inequality?
when it finds it’s way into public policy
71
New cards
Cause of post 1980’s rise?
globalization- benefitted consumers (less expensive + higher quality)
lower taxes for wealthy
decline of unions
lower taxes for wealthy
decline of unions
72
New cards
Unequal democracy thesis
money related to political influence, meaning it could matter a lot in terms of policy
73
New cards
Policies classified as what move system in a liberal direction?
landmark legislation
ex. no child left behind, affordable care act
ex. no child left behind, affordable care act
74
New cards
Public goods benefit who?
those less well-off disproportionately (education)
75
New cards
Major set of exceptions:
tax rate changes
76
New cards
What caused initial inequality for black people?
public policy buttressed by custom + violence
ex. slavery, black codes in south, vigilante actions
ex. slavery, black codes in south, vigilante actions
77
New cards
public policies used to …
segregate; seen in home ownership
78
New cards
Economic perspective of inequality
distribution of wealth is consequence of market forces
79
New cards
Political science perspective of inequality
distribution of wealth is consequence of policy
80
New cards
Racial inequality is product of
policy + historical institutional processes that have biases that produce long-term consequences
\-unequal outcomes can occur even in absence of racist actors
\-unequal outcomes can occur even in absence of racist actors
81
New cards
Racial Formation
socio-historic process by which radical identities are created, experienced, defined, and redefined
82
New cards
Race in racial formation perspective
neither an objective fixed fact or a complete illusion that we can completely move past “element of social structure and dimension of human representation”
83
New cards
Racialization
extension of racial meaning to previously unclassified relationships/ practices/ groups
84
New cards
Race in racialization perspective
fluid, context dependent; contested from above (oppression) and below (resistance)
85
New cards
Racial Projects
how racial formation processes occur through a linkage between structure & representation; whenever race is invoked or signified, or social structures are being organized along racial lines
86
New cards
Race in that perspective
observed differences can be understood as a product of different treatment embedded in policy, rather than biology
87
New cards
Racial formation in Politics
racial hierarchy is embedded in constitution through protection of slavery
\-3/5ths clause + proportional rep. in House
\-electoral college
\-the “domestic insurrections clause”
\-equal rep. in Senate
\-veto any policy impacting slavery
\-3/5ths clause + proportional rep. in House
\-electoral college
\-the “domestic insurrections clause”
\-equal rep. in Senate
\-veto any policy impacting slavery
88
New cards
Southern veto
political power held by slave states in congress established via equal representation in senate
89
New cards
13th amendment
abolishes involuntary servitude (except convicts)
90
New cards
14th amendment
provided citizenship rights for newly freed slaves; extends rights protections to all citizens of US (equal protection clause)
91
New cards
15th amendment
prohibits curtailing access to the right to vote on basis of race
92
New cards
Jim Crow
formal, codified system of enforced racial order (ex. of racial project)
93
New cards
Slaughterhouse cases (1873)
14th amendment only protects legal rights associated with federal citizenship (ex. bill of rights doesn’t inhibit state action)
94
New cards
Plessy v. Ferguson (1896)
14th amendment doesn’t prohibit social discrimination; separate but equal is lawful
95
New cards
Black Codes in south
criminalized everyday behavior while Black-violation of which carried a sentence of hard labor via convict leasing system
96
New cards
Criminalizing black pverty in north
rates of poverty and arrests taken as statistical proof that black people were predisposed to engage in crime
97
New cards
example of racialization
reconstruction through criminalizing blackness
98
New cards
new deal policies that remade the american political landscape
emergency banking act, works progress administration, social security act
99
New cards
why are civil rights acts passed?
ongoing agitations from citizens demanding lawmakers make good on the radical promise of equality under the law- also embedded in constitution
100
New cards
Multiple traditions thesis
competing ideologies- equality & ascriptive racial hierarchy