Economics: Opportunity Cost, Scarcity, and Factors of Production
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Opportunity Cost
Opportunity Cost is what needs to be given up to get something.

Trade-Off
Giving up 1 or more benefits to gain another.
Opportunity Cost For Consumers
Choices that Consumers Face include what product to buy and how to spend time.
Opportunity Cost For Producers
Choices that Producers Face include what to make, how to make it, and where to make it.
Economic Decision-Making Grid
A framework to evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of choices.
Marginal Cost
The additional cost of adding 1 unit.
Marginal Benefit
The additional benefit of adding 1 unit.
Marginal Analysis
Compare the marginal benefit and marginal cost to make decisions.
MB > MC
Indicates that more units should be added when marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost.
Trade-Offs & Opportunity Costs Example
You buy a $250 set of Beats Headphones.
Trade-Offs in Business
A business spends $10k on advertising.
Government Trade-Offs
The US Gov't spends $10m for extra security at airports.
Economic Decision-Making Grid Example
Part-Time Job vs. Play Basketball.
Benefits of Part-Time Job
Earn extra money and gain work experience.
Drawbacks of Part-Time Job
Diminished basketball skills and lack of extra spending money.
Benefits of Playing Basketball
Improve skills and improve opportunity to make the varsity team.
Drawbacks of Playing Basketball
Less chance to make the varsity team and no job to prepare for future employment opportunities.
Opportunity Cost of Playing Basketball
Lack of extra spending money.
Economic Decisions
Involves evaluating trade-offs and opportunity costs.
Consumer Choices
What product should I buy? How should I spend my time?
Producer Choices
What will we make? How will we make it? Where will we make it?
Importance of Opportunity Cost
Each choice comes with an opportunity cost that affects personal finance and economics.
Daily Choices Example
Picking what you ate for breakfast or what you wore to school.
Decision-Making Reflection
Think of a decision you made yesterday and what you had to give up.
Trade offs
The alternatives that must be given up when a choice is made.
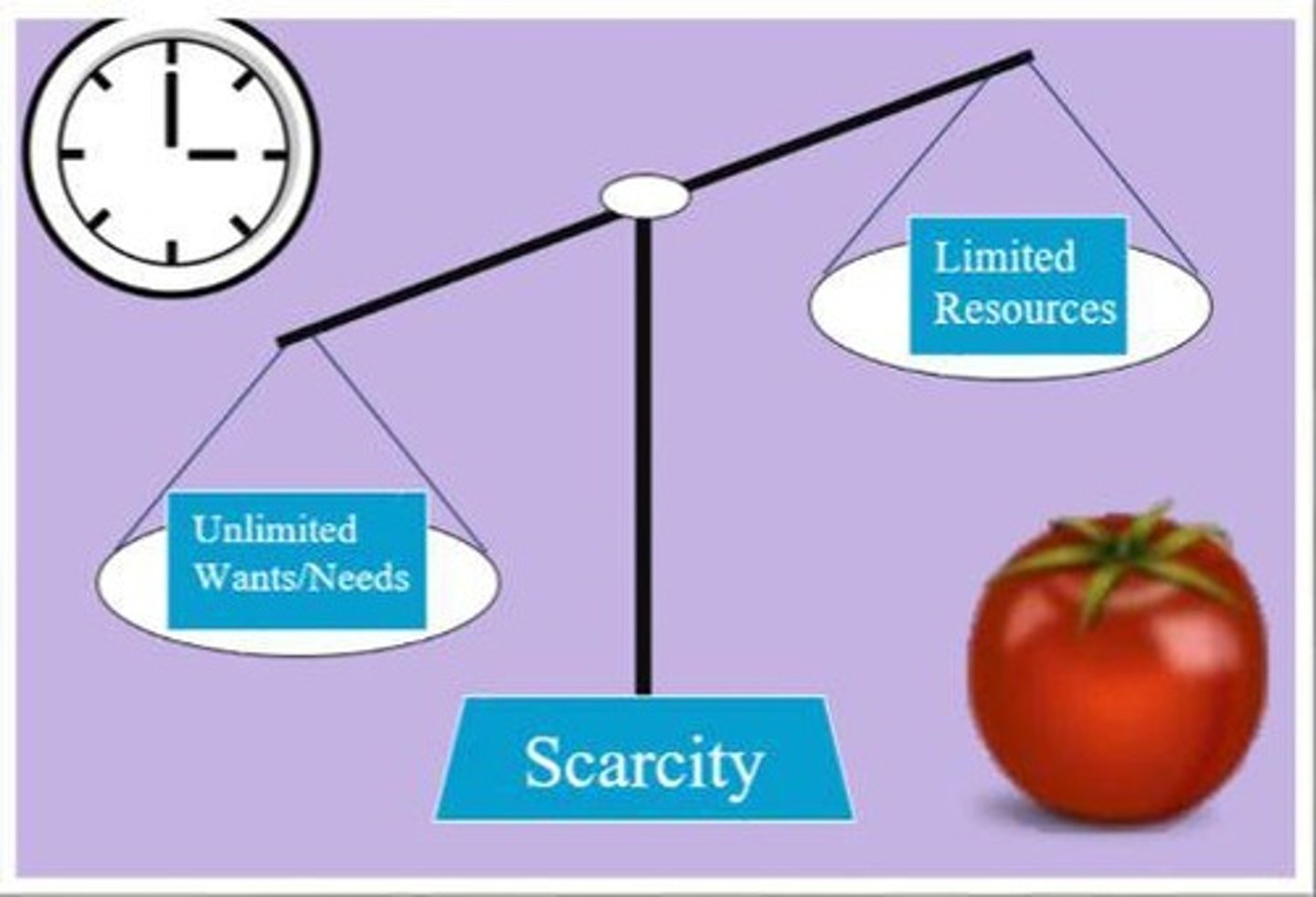
Scarcity
A basic condition that exists when unlimited wants exceed limited productive resources.
Factors of Production
The resources used to produce goods and services, including land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship.
Production Possibilities Frontier
A curve that shows the maximum feasible amount of two goods that can be produced with available resources.
High Demand and Low Supply
A situation where the demand for a product exceeds its supply, leading to increased market value.
Scarcity Problem
The fundamental economic issue of having seemingly unlimited human wants in a world of limited resources.
Abundance
A condition where resources are plentiful and can satisfy all wants.
Desirable Scarcity
Something is scarce when it is both limited and desirable.
Examples of Scarcity
Lebron James, oil, time, rest, grass in the winter.
Permanent Scarcity Problems
Issues that cannot be solved due to the nature of limited resources.
Allocation of Scarce Resources
The process of distributing limited resources in a market economic system.
Market Economic System
An economic system where resources are allocated based on supply and demand.
Professional Athlete vs. Entry Level Receptionist
A professional athlete is scarcer than an entry level receptionist due to their unique skills.
Scarce Skills
Skills that are rare and in high demand, leading to higher pay.
Elmo Craze
The phenomenon during the 1996 holiday season where the Elmo toy became extremely popular.

Elmo Toy Production
Only 400,000 units were produced, while over 1,000,000 were in demand.
Elmo Resale Price
The Elmo toy was being resold for up to $2,500 by the end of 1996.
Scarcity in 2019-2020
Examples include the Playstation 5 and toilet paper shortages during the COVID pandemic.
Simulation of Scarcity
An activity designed to demonstrate how scarcity impacts all people.
Examples of Scarcity in Life
Time, sleep, and leisure are common examples of scarcity individuals experience.
Economics
The study of choices; how individuals and groups seek to satisfy their wants and needs in light of scarcity.
Land
Natural resources not created by human effort that are used to produce goods and services.
Labor
Time and effort devoted to producing goods and services.
Capital
Human-made objects used to create other goods and services.
Physical Capital
Human-made objects used to create other goods and services such as machines, phones, and computers.
Human Capital
Skills, abilities, and specialized talents of people.
Financial Capital
Money, used by businesses to invest in their business.
Entrepreneurs
Business owners who organize the factors of production to bring goods or services to the market.
Cashier
A worker who handles cash transactions at a business.
Teacher
An individual who educates students in a school setting.
Professional Athlete
An individual who competes in sports for a living.
$65,000 per year
An example of income for a teacher.
$21.1 Million per year
An example of income for a professional athlete.
$13.25 per hour
An example of income for a cashier.
Peppers
A natural resource used to produce Tabasco hot sauce.
Glass bottles and plastic
Materials needed to package Tabasco hot sauce.
Water or vinegar
Ingredients used to mix with peppers in Tabasco hot sauce production.
Elon Musk
An example of an entrepreneur.
Automobile for DoorDash
An example of physical capital.
iPads used by employees
An example of physical capital in a communications company.
Waiters and waitresses
An example of labor in a local pizza place.
Knowledge of fixing computers
An example of human capital for a computer technician.
Lettuce, tomatoes, deli meat, and bread
Examples of land resources for a sub shop.
Power plant for a local city
An example of physical capital.
Eggs, wheat, and cornstarch for a bakery
Examples of land resources for a bakery.
Grill for a Mexican restaurant
An example of physical capital.
Cameraman for a television company
An example of labor.