Session 1: Sources of Health Data
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Who might want to measure disease in a population?
- Researchers
- Public health campaigners
- Doctors
- Medical students
How do we assess health & disease in populations.
Name two ways
1) Routine surveillance
2) Ad-hoc samples (e.g., local health surveys by CCGs)
Three examples of routine data
1) Demographic data e.g., census
2) Health events data e.g., morbidity/mortality
3) Population-based health info e.g., health surveys

What members of the population might be excluded from routine data surveillance?
- Homeless
- People in war-torn countries
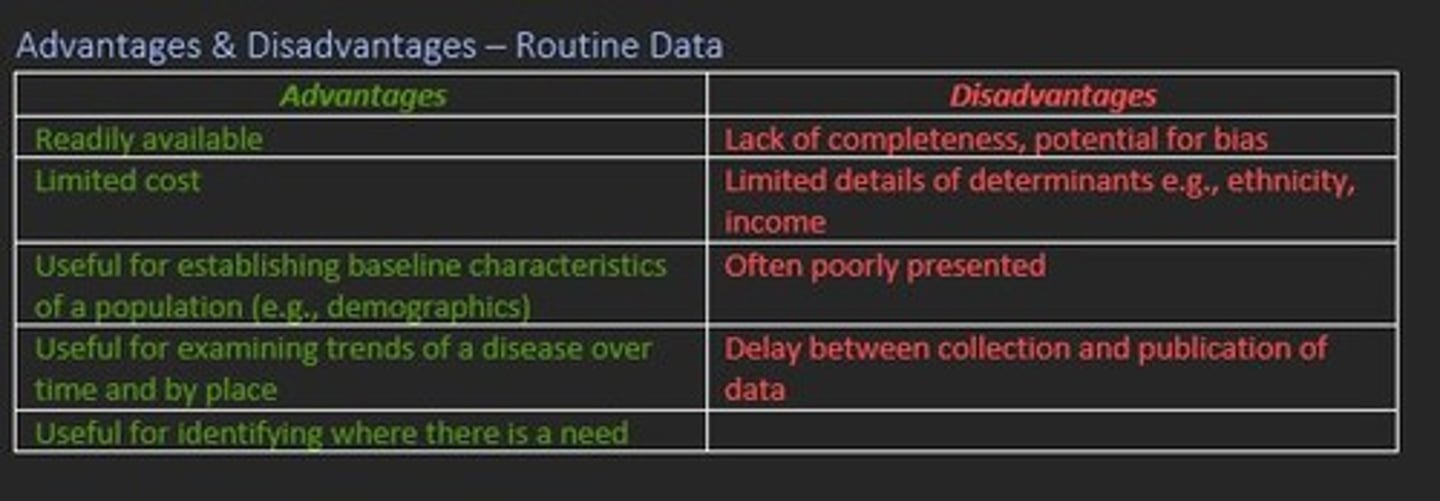
Advantages of routine data surveillance
Advantages
- Readily available
- Limited cost
- Useful for finding baseline characteristics
- Useful for examining trends of disease over time
- Useful for identifying where there is a NEED
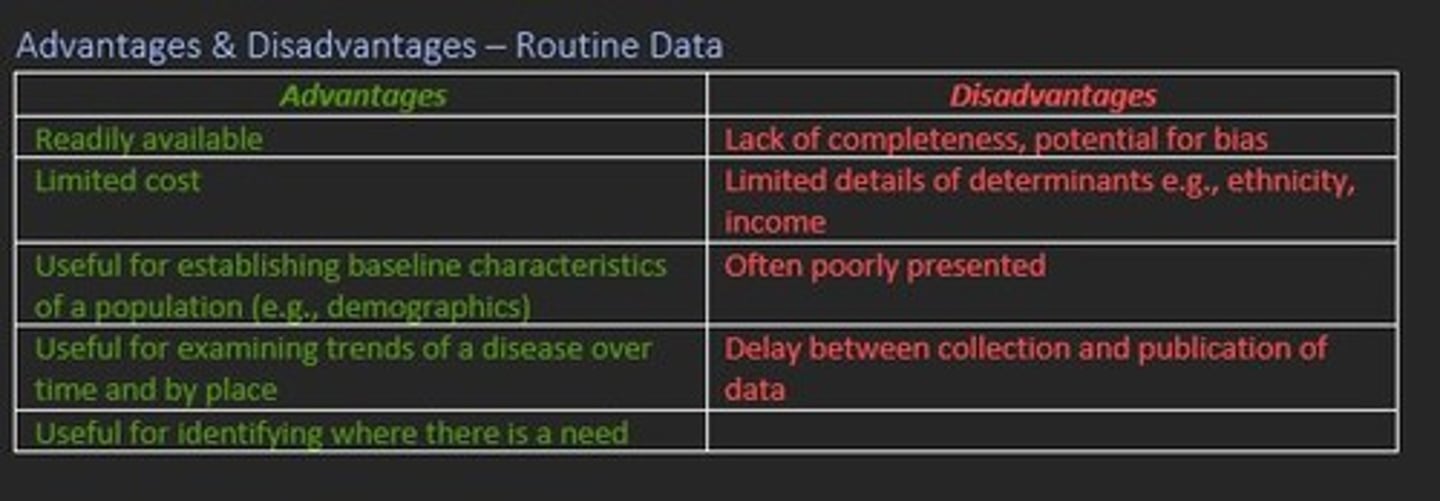
Disadvantages of routine data surveillance
Disadvantages
- Lack of completeness
- Potential for bias
- Limited detail of determinants e.g., ethnicity
- Often poorly presented
- Delay between collection of data and publication
Four examples of demographic data
1) Age
2) Sex
3) Ethnicity
4) Religion
An example of a measure in the UK which collects demographic data
Population census
Features of a Census
- Run by the government
- Covers defined area
- Personal enumeration of data
- Simultaneous through each area
- Universal coverage
- Occurs at regular intervals
In the UK, how often is the Census taken?
Census taken every 10 years in the UK
Issues with personal enumeration in Census data
- Language barriers
- Inability to write or read
What information is recorded in the Census?
- Population size = calculate rates
- Population structure = service needs
- Population characteristics = measures of deprivation
What measures of deprivation are registered in the Census (population characteristics)?
- Unemployment
- Overcrowding
- Lone pensioners
- Single parents
- Lack of basic amenities
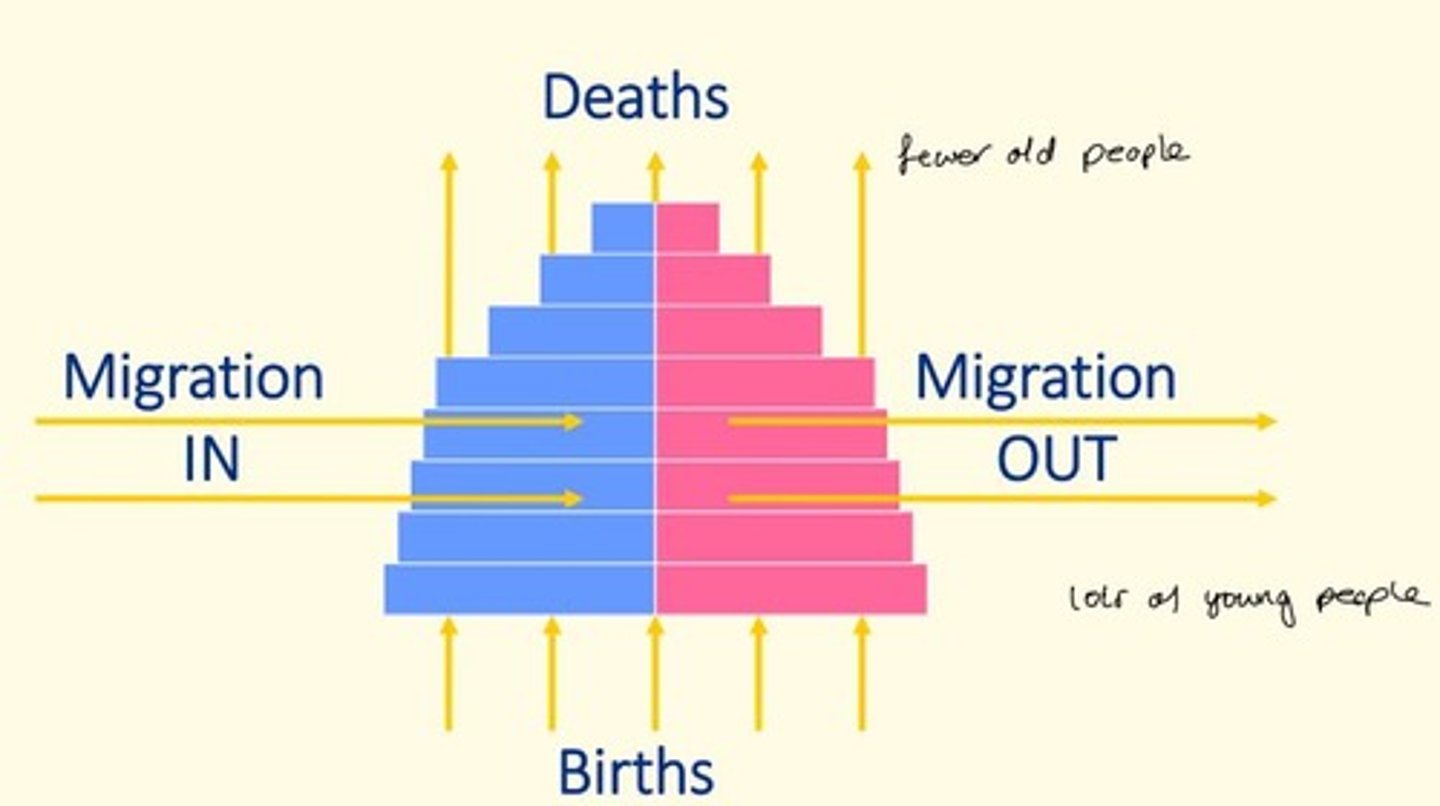
What is this a diagram an example of?
Population structure pyramid
Population estimates and population projections
1) Population estimates
- Apply what is known about births, deaths, migration to the PRESENT
2) Population projections
- Apply what is known about births, deaths, migration to the FUTURE
Fecundity
Ability to produce offspring
Fertility
Production of live offspring
Two sources of births data
1) Birth Notification
Completed by attendant at birth (e.g., midwife) within 36 hours. Sent to the local Child Health Register.
Important for relevant services e.g., immunisations.
2) Birth Registration
Completed by parent within 42 days and submitted to local Registrar for Births.
Important for statistical purposes.
Sources of health activity data
1) Primary care e.g., GP
2) Secondary care e.g., hospital admissions
3) Hospital episode statistics
Sources of disease registries and data on chronic conditions
Public Health England
- Public health profiles
- Infectious disease surveillance
- National cancer registration and analysis service
Three causes of dramatic changes in epidemiological data trends...
1) Chance (random variation)
2) Artefactual systematic errors
3) Real phenomenon = epidemiological (natural) or the effect of medical care
Two sources of death (mortality) data
1) Death certification
- Statutory obligation for an attending doctor to complete
- Legally required to include likely cause of death
- If unsure, must contact Coroner's office
2) Death registration
- Completed by qualified informant e.g., relative
- Within 5 days to local Registrar for Deaths
- Requires death certificate from doctor
Why is it important to collect mortality data?
1) Classify causes of death
2) Analyse patterns in mortality rates
3) Identify health problems
4) Inform service needs
What is a verbal autopsy?
Family of the deceased is surveyed/interviewed about the symptoms/circumstances of the deceased person prior to death - info given to doctors to interpret and come up with probable cause of death
Crude Death Rates
Measured as deaths per 1,000 per year
Takes account of population size, but NOT population structure
Sources of sample-based health information
Surveys
Surveys
Investigations in which information is systematically collected in variety of methods (F2F, self-completed questionnaire, telephone, post, online)
Generalisability of results depend on extent to which survey population is representative
Example of sample-based health information (survey in the UK)
Health Survey of England
- Collated information on health and related behaviours of 8,000 adults and 2,000 children. Combined a questionnaire with recording of some physical measurements and blood tests.
Life expectancy at birth
Predicted average length of life at birth (if current mortality rates continue to apply).
This varies widely among different countries.
Census data describes...
Population size and population structure
Population estimates depend on what factor?
Migration
Population projections depend on what factors?
- Projected migration
- Fertility rates