B2 NERVES
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What does the nervous system involve?
detection of stimuli by receptors
transmission of nerve impulses by neurones
response by effectors
Describe the nervous systems responses
very rapid response
transmission of electrical impulses along neurones
chemical transmission along synapses
What are the 2 major divisions in the central nervous system?
central nervous system (the brain and the spinal chord)
peripheral nervous system (nerves that originate from brain or spinal chord)
What can the nervous system be divided into?
voluntary nervous system (under voluntary control)
autonomic nervous system (involuntary or subconscious)
What’re neurones?
specialised cells
carry electrical impulses from one part of the body to another
What’re the different types of neurone?
sensory (conduct impulses from receptors to the CNS)
relay (found in spinal chord, conduct impulses from sensory to motor to bypass the brain)
motor (conduct impulses from relay to effectors)
Draw the structure of the motor neurone
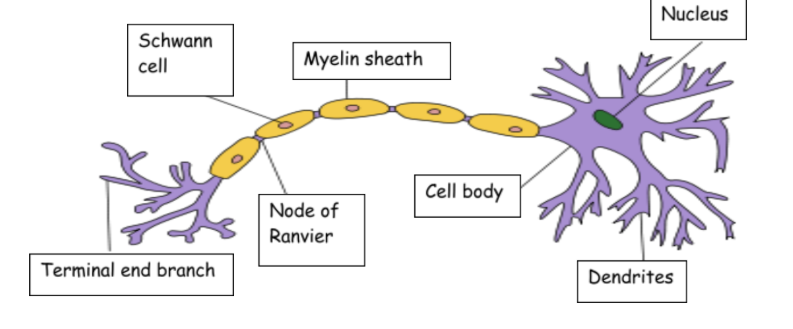
What does the cell body do?
contains the nucleus and cytoplasm
produces proteins and neurotransmitters
What do dendrites do?
carry nerve impulses towards cell body
What does the axon do?
carries nerve impulse away from cell body
What do schwann cells do?
produce myelin
What does the myelin sheath do?
insulates axon which increases the speed of transmission of nerve impulse
What do the nodes of ranvier do?
gap between schwann cells where myelin sheath is absent
What does the terminal end branch do?
connects neurone to effector
Describe reflex responses
automatic
rapid response
don’t involve the brain
avoid danger and harm
What is the order of events in a simple reflex arc?
stimulus is detected by the receptor
impulse is conducted along the sensory neurone to the relay neurone
the impulse is transmitted to the motor neurone and to the effector
What is the resting potential value of a nerve impulse?
-70mV
What occurs during the resting potential?
there is a pd of -70mV across the membrane
membrane is polarised which maintains a potential difference between the 2 sides
How is a resting potential established?
difference is maintained by a sodium potassium pump which moves 3 sodium ions out of the cell for every 2 potassium ions into the cell
sodium gates are closed while some potassium gates are open so potassium ions can diffuse back out
What is an action potential?
when the membrane becomes depolarised
What occurs during depolarisation?
stimulus causes the membrane becomes more permeable to sodium ions (sodium gates open) so there is an influx of sodium ions due to diffusion down their electrochemical gradient
the inside of the membrane becomes positive in relation to the outside
if the potential difference reaches the threshold more voltage gated sodium ion channels open increasing the influx of sodium ions
What occurs during repolarisation?
at 30mV the sodium gates close and the potassium channels open
potassium ions diffuse out of the cell
What occurs during hyperpolarisation?
potassium gates remain open for longer than needed to reach the resting potential which makes the inside of the cell even more negative
potassium gates are closed and the sodium potassium pump works rapidly to restore the resting potential
What is the all or nothing principle?
below the threshold no action potential will occur
above the threshold a full size action potential will occur
more intense stimuli are sensed by an increased frequency of action potentials
What is the refractory period?
the time following an action potential during which another action potential cannot take place, regardless of the strength of the stimulus
Why does the refractory period occur?
when the sodium channels are closed during repolarisation no action potential can be generated
its hard to generate a new action potential when the neurone is in hyperpolarisation as more sodium needs to enter to make the inside of the membrane positive
What does the refractory period ensure?
impulses are always discrete
no overlap
ensures impulses aren’t interpreted as the same impulse
ensures action potential travels in one direction
limits the frequency of impulses
How are action potentials transmitted along the axon?
action potentials act as a stimulus to adjacent polarised areas of the membrane
the action potential is passed along in a wave of depolarisation
the impulse propogates along the neurone
What’re factors affecting the speed of impulse transmission?
presence of the myelin sheath
temperature
axon diameter
How does the presence of the myelin sheath increase the speed of impulse transmission?
impulse travels by saltatory conduction (jumping from one node of ranvier to the next)
myelin sheath insulates the axon and depolarisation can only occur at the nodes
How does the temperature increase the speed of impulse transmission?
higher temperature increases the rate of diffusion of ions so increases the rate of conduction
How does the axon diameter increase the speed of impulse transmission?
the larger the axon diameter the greater the speed of conductance as the surface area to volume ratio of the cytoplasm is greater so the cytoplasm contains more ions. this means ions move down the axon quicker and the impulse can be transmitted easier
How does the synapse work?
when an impulse arrives at the synaptic knob the gated calcium ion channels in the membrane open
calcium ions move into the synaptic knob by facilitated diffusion
calcium activates enzymes which causes the synaptic vesicles to move towards the synaptic cleft
the vesicles fuse with the membrane and release the neurotransmitters by exocytosis
neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the cleft and bind to receptors on the post synaptic membrane
this opens sodium ion channels allowing sodium ions to diffuse in so the membrane is depolarised
if the membrane reaches the threshold potential an action potential occurs
the neurotransmitter is then broken down and diffuses back across the synaptic cleft into the presynaptic neurone
What neurotransmitter is used in a cholinergic synapse?
acetylcholinesterase
What do synapses do?
delay the impulse slightly
prevent the impulse from going in the wrong direction
vesicles containing neurotransmitters are only found in the presynaptic neurone
receptors for neurotransmitters are on post synaptic neurones only
What is the neuromuscular junction?
a synapse between a motor neurone and a muscle cell
What type of neurotransmitter do neuromuscular junctions use?
acetylcholine which bind to nicotinic cholinergic receptors
What’re the differences between neuromuscular junctions and cholinergic synapses?
neuromuscular post synaptic membrane has lots of folds which store the enzyme which breaks down acetylcholine
neuromuscular junction’s post synaptic membrane has more receptors so the threshold is reached easily
neuromuscular junction is always excitatory
What does summation involve?
the build up of neurotransmitters in the synapse so increase the chance of the threshold value being reached in the post synaptic membrane
What’re the 2 types of summation?
spatial
temporal
What is spatial summation?
different neurones converging so the impulse arrives from a number of neurones at the synapse
causes the release of enough neurotransmitters to cause an action potential in the next neurone
What is temporal summation?
only one presynaptic neurone where the impulse arrives in quick succession
cumulative effect which is sufficient to depolarise the post synaptic neurone
What is synaptic fatigue?
where the rate of transmitter release is higher than the rate at which it is formed
pre synaptic neurone cannot release enough neurotransmitters to generate an action potential in the post synaptic neurone until the transmitter is regenerated
What is an exitatory neurotransmitter?
causes an action potential in the post synaptic neurone
What is an inhibitory neurotransmitter?
neurotransmitters which affect different receptors on the post synaptic neurone, meaning the resting potential falls to a lower level and the post synaptic membrane is less likely to reach the threshold value and generate an action potential
Why is inhibition important?
prevents random impulses happening all over the body
How can drugs act on a synapse?
they can stimulate the nervous system by creating more action potentials in the post synaptic neurone, which has an exitatory effect
they can create fewer action potentials in the post synaptic neurone, which has an inhibitory effect
How can drugs stimulate more action potentials?
drug may has a similar shape to neurotransmitters and bind to receptors on post synaptic membrane, mimicking the effect of the neurotransmitter
increase in the release of the neurotransmitter or inhibit enzymes that break down the neurotransmitter
How can drugs inhibit action potentials?
inhibit the release of neurotransmitters
block the receptors on the post synaptic membrane
How does cocaine affect synapses?
prevents the breakdown of the neurotransmitters involved in the synapathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system
How do codeine and heroin affect synapses?
they bind to receptors for endorphins which are neurotransmitters used in sensory nerve pathways
How does valium affect synapses?
increases the effect of GABA an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the brain
How does caffeine affect synapses?
reduces the threshold value for excitation of neurones
How does botulinum affect synapses?
inhibits the release of acetylecholine