Parasitic Platyhelminths - Cestode
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Describe Cestodes
Hermaphrodites
They include all tapeworms
They have suckers and teeth that grip the host
Their reproductive structures lie behind their short necks
They have ribbon-like structures that are beneficial for absorbing nutrients from the intestine
Pseudophyllidean Cestodes: Have Slit-like grooves
Diphyllobothrium latum (fish tape worm) is the only pseudophyllidean cestode (that I care about)
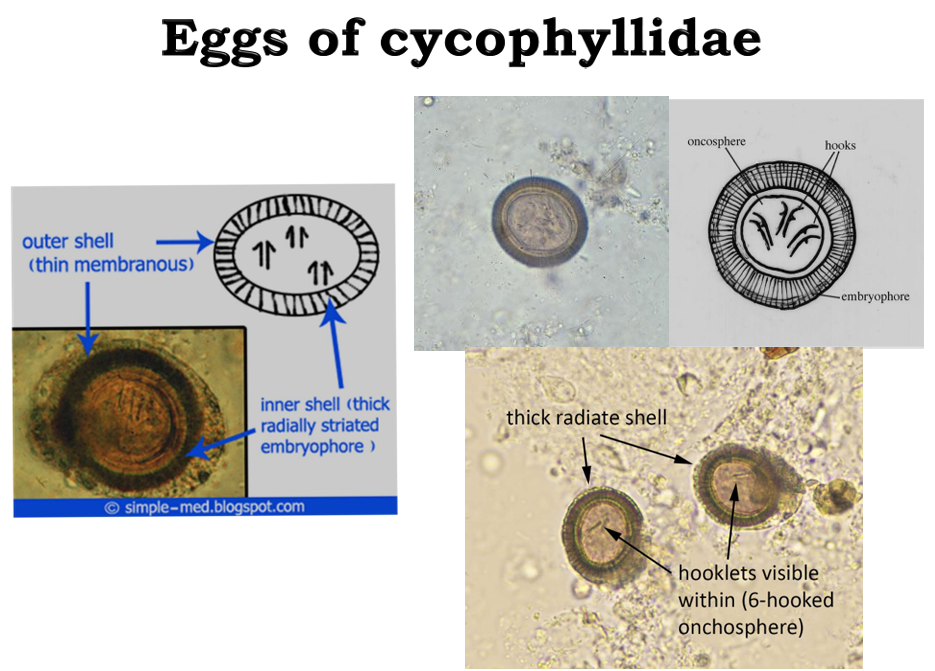
Cyclophyllidean Cestodes: Have cup-like round suckers
Their eggs have thin outer shells and thick, radially striated inner shells
They also have arrow things inside of them, these are actually hooks
Intermediate and definitive hosts of tapeworms definition
Different cause hermaphrodites:
Intermediate hosts: harbor immature forms of the parasite
*Man is intermediate for Dog and Pig tapeworm
Definitive hosts: harbors the mature forms of the parasite
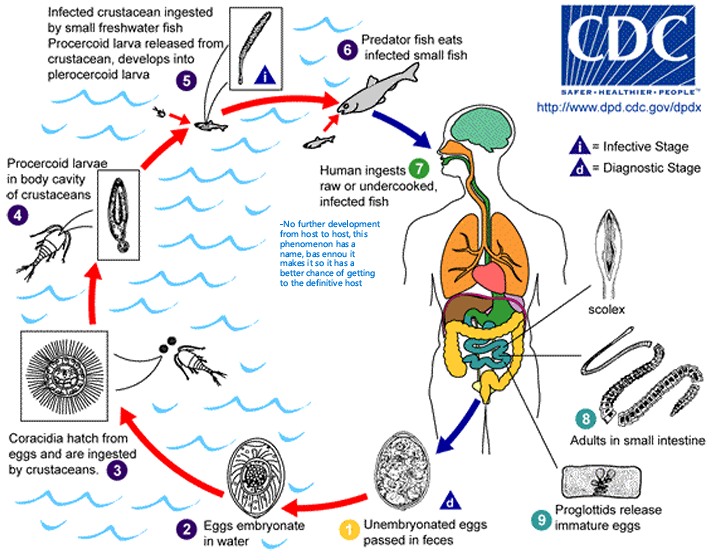
Fish tape worm causative agent and its life cycle
Caused by Diphyllobothrium latum
Cycle main points:
Unembryonated egg is shed in feces and gets embryonated in water (only)
Eggs hatch and are ingested by crustaceans
Becomes percercoid larvae in crustaceans
Crustacean eaten by fish, and inside the fish, the parasite progresses to the infectious Plerocercoid stage (Fish may be eaten by another fish with no change to the parasite before reaching humans)
Scolex stage
Adult stage in small intestine
Release of unembryonated eggs → Recycle
Fish tape worm disease presentation, diagnosis, and treatment
Symptoms:
Digestive disturbances
Vit B12 deficiency (competition) → Megaloblastic anemia
Diagnosis:
Operculated eggs in stools
Treatment:
Niclosamide/Praziquantel
Dog tape worm organism and life cycle
Echinococcus granulosus
We’re accidental hosts and that my swallow Embryonated eggs in dog or sheep feces
Describe the cysts of dog tapeworms
Hydatid cysts have an inner germinal layer that produces brood capsules and daughter cysts containing protocolizes; dogs become infected by eating these cysts
Dog tapeworm clinical presentation
Echinococcosis:
Non-specific symptoms or asymptomatic
60% right hypochondriac pain
Skin rashes
15% jaundice
Cyst can rupture → Broncho-biliary fistula
Cystic hyatid disease
Liver cysts cause swelling and right epigastric pain, nausea, and vomitting
Obstruction of bile ducts and BVs → Cholangitis / jaundice/ Cirrhosis
Dog tapeworm diagnosis
Imaging
Serology
Casoni’s intermediate test
Dog tape worm contraindication
In echinococcosis, aspiration is strongly contraindicated because it may burst the cyst, releasing their fluids into the peritoneal cavity and causing anaphylaxis
Dog tape wormtreatment
Echinococcosis drugs are not curative
Surgically remove cysts
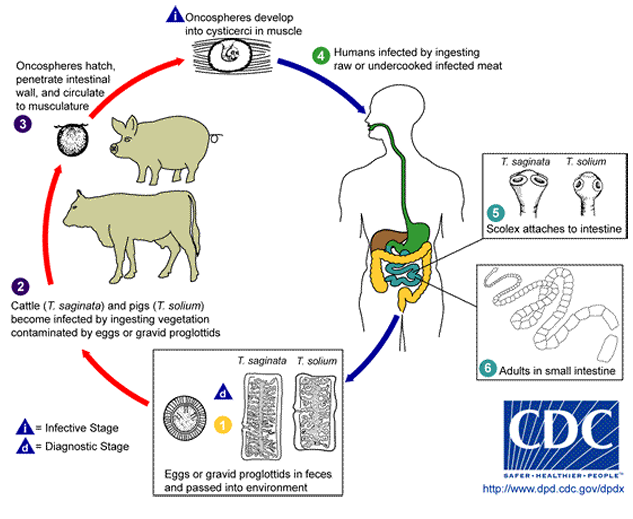
Taenia life cycle
Human definitive host
We ingest cysticerci (from undercooked meat) and shed eggs or gravid proglottids in stools
Beef tapeworm organism and epidemiology and clinical presentation
Taenia sagitana
Epi: In poor sanitation and no meat-inspection areas
Symptoms: None or mild abdominal discomfort
Pork tape worm organism (+ specific description) and epidemiology and clinical presentation
Taenia solium
→ T. solium has a scolex (A) with four suckers and a double crown of hooks, a narrow neck, and a large strobila (2-4 m) (B) consisting of several hundred proglottids. • About 2 months after ingestion, proglottids begin to detach from the distal end and are excreted in the feces. • Each segment contains 50-60,000 fertile eggs
Epi: Endemic to countries where pigs are raised as a food source
Symptoms: None or mild abdominal discomfort (Same as Saginata)
Taeniasis diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis: Eggs or segments stools
Treatment: Niclosamide/ Praziquantel
Dog vs pork tapeworm differential diagnosis
T- solium has 7-13 branche of the uterus
T. saginata has 15-20
Saginata has motile proglottids, and an irregularly-alternated Gonopore
Human cysticercosis
Only caused by T. solium
→ Cross into bloodstream and carried to other tissue → Encyst at terminal vesels → Neurocysticercosis & Ophthalmic cysticercosis
Neuroccysticercosis
T. solium in CNS
Parasite localized in the cerebral ventricles or basal cisterns
Symptoms: Epileptic seizures, intracranial hypertension, hydrocephalus, ocasionally, cyst may grow larger (giant cysts)
Cysts: Upon degeneration release fluid that becomes opaque and dense, and brain calcification occurs starting at the cephalic portion
Cysticercosis diagnosis
Serology
Neuroimaging
Cysticercosis treatment
Individualized based on cyst location and degree of inflammation
Antiepileptics, cysticidal drugs
Albendazole + Dexamethasone
Praziquantel
Note: No reason to use antiparasitic drugs to treat dead calcified cysts.
Surgery to resolve hydrocephalus + removal of giant cysts or intraventricular cysts