Diagnostic Imaging: Exam 1
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
X-rays are an example of a gamma ray. Do gamma rays have a long or short wavelength?
Short
cathode filaments are made of
thoriated tungsten
What causes the anode heel effect?
angle of the anode
_____________ filters can be placed between the glass enclosure and tube head to absorb weak x-rays
aluminum
What information is included when labeling films?
Patient and client name, date, and number of views taken
cathode
Negatively charged electrode that releases electrons. This structure has a focusing cup containing filaments made of tungsten
anode
Two types: stationary or rotating. A anode is a positively charged electrode that attracts the negative electrons released from the cathode.
Milliamperage (mA)
Setting used to control the quantity of electrons produced. The mA has a "toaster" effect when adjusted- increase causes density/degree of blackness to rise, decrease of mA causes lightening of density with a less black film
Kilovoltage (kVp)
Energy of electrons when they reach the anode. Higher kV value= more penetrating power for the x-ray beam. When dealing with thicker tissue, the kV should be increased.
The kilovoltage is usually associated with the ____________ of the image
contrast
The greater the number of shades of grey present, the ___________ quality of the image
higher
a higher kV and lower mA setting is used for imaging:
soft tissue (abdomen/thoracic)
a lower kV and a higher mA setting is used for imaging:
limbs
Flouroscopy
Radiographic technique that involves viewing an area in motion in real time
What do intensifying screens do?
convert x-ray energy into visible light
What is the function of the grid?
decrease scatter radiation while increasing contrast of the radiograph
What happens to cells during radiation exposure?
Intracellular water becomes ionized and causes toxic products to be released that can damage DNA
Should any part of your body be in the primary beam view?
No. A hand in a lead glove under a direct beam will still receive 25% of the radiation dose.
Where should you wear your dosimetry badge during radiation exposure?
at thyroid level clipped onto the outside of the lead gown
Radiation exposure is measured in:
Roentgen, RAD, and REM
What three methods will limit radiation exposure?
Distance, shielding, and time
What is the minimum thickness of lead used in shielding equipment?
0.5 mm
Gloves should be radiographed every _____ months to check for holes
6
Scatter radiation
Radiation that hits a target and bounces off of it
collimator
plate with a diaphragm that controls the size and shape of the x-ray beam
The cloud of electrons released from the cathode are called
thermionic emission
What controls the heat of cathode filaments?
the mAs value
X-ray machines containing a stationary type anode are most commonly used for:
Dental x-ray machines and for portable large animal machines
Where are x-rays created?
in the focal spot on the anode
A major advantage of rotating anodes is that they:
disperse heat and prevent overheating
To take advantage of the anode heel effect, put the patients _______________ side on the cathode side of the x-ray machine
thickest
Why is tungsten the best metal for the x-ray source?
It has a high melting point. X-ray machines generate a lot of heat.
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine)
Universal messenger used in medical imaging software & can be easily incorporated into the medical record. Images require special software to be viewed
a increased mA results in:
a darker image (more electrons released)
a decreased mA results in:
a lighter image (less electrons released)
Radiopaque
Term used to describe an object that is light in color. Means the structure cannot be easily penetrated by x-rays
Radiolucent
Term used to describe an object that is dark/black in color. Means the structure can be easily passed through by x-rays
What kind of kVp value (high/low) is associated with a short greyscale and higher contrast?
Low
Which kVp value (high/low) is associated with a long greyscale and lower contrast
High
A short greyscale is utilized when imaging:
areas with less tissue (limbs)
A long greyscale is utilized when imaging:
the abdominal or thoracic area (tissues/organs)
A higher contrast means there are ________ shades of grey in an image
less
A lower contrast means there are ________ shades of grey in an image
more
What is the main purpose of utilizing intensifying screens?
Intensifying screens develop film faster, preventing excess radiation exposure
casette
A light-resistant container that protects the film from exposure to daylight. The cassette holds the film between two intensifying screens and allows the passage of X-rays through the cover and onto the film
What is the function of grids?
Decrease radiation scatter and increase the contrast of the image
Parallel grids
This grid is made of lead and interspaced strips running parallel to one another. The lead markers block part of the captured image and cause grid cutoff
Focused grids
Grids that have their lead strips angled to allow the entire x-ray beam to pass
A caliper is used to measure:
the area of the body to be radiographed
What information is required on a film label?
The vet practice, exposure date, name of the patient, and the owners first and last name.
During which trimester of pregnancy is a fetus most sensitive to radiation?
the first trimester
What is the max permissible annual dose of radiation?
50 msv or 5 REM
ALARA stands for
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
Where does radiation exposure come from?
primary beam, scatter radiation, x-ray tube head, & fluoroscopy
inverse square law
States that a beam of radiation loses its intensity the farther away it moves from the source.
Math version: The intensity of the radiation is inversely proportional to the square of the distance
inverse square law formula
(previous mAs value x (new distance)^2)/(old distance)^2
What is the best option for restraint for diagnostic imaging?
Non-manual (aka drugs)
Film emulsion is composed of mainly:
silver halide crystals and gelatin
What type of radiation exposure is most likely to use single sided emulsion film?
Computed tomography
Anodes produce ______% heat and ____% x-rays
99%, 1%
The Roentgen is a measure of
radiation and x-ray machine production
A RAD is a unit of
the absorbed dose of ionizing radiation
The REM value takes the ___________ of radiation into consideration
quality
What x-ray setting is used to evaluate the quality of PPE equipment?
5 mAs and 80 kVp
The density of the image refers to the degree of ______________ of the image
blackness
Contrast
opacity or density difference between two areas or structures in a radiograph
an increase in kVp will increase the energy level of the x-rays produced, causing a ____________ image
darker/denser
Which factor has the greatest effect on contrast?
Kilovoltage
Sante's rule
States the kVp value is Two times the thickness of the area + distance from the tube head to the tabletop (40 inches on most machines) + the grid allowance (8 to 10 kvp)
Densities of substances (least to most dense)
gas, fat, water, bone, and metal
When reviewing a radiograph, you can't appreciate anatomical structures because the image is too dark and over penetrated. What value should you reduce when retaking the radiograph?
decrease the kVp value by 15% (higher kVp=greater penetration)
When reviewing a radiograph, you can't appreciate anatomical structures because the image is too light and under penetrated. What value should you increase when retaking the radiograph?
increase the kVp value by 15%
What value should you adjust when anatomical structures are visible but have little density in a radiograph?
increase the mAs value by 30-50%
What value should you adjust when anatomical structures are visible but the image is too dark?
decrease the mAs value by 30-50%
Which substance visible on a radiograph (gas, fat, water, bone, or metal) absorbs the most x-rays?
Gas (gas is black in color on radiographs)
What kind of kVp value (high/low) is preferred for thoracic images?
Higher
What kind of kVp value (high/low) is preferred for skeletal images?
Lower
The primary difference between computed radiography (CR) and digital radiography (DRI) is
related to how the latent image is produced and processed in viewing
Computed radiography (CR) systems and standard film based systems both utilize a cassette with an intensifying screen. What makes CR system cassettes unique?
they have an intensifying screen containing light stimulated phosphors. This screen is referred to as the imaging plate (IP) or PSP & has to be processed immediately after exposure
Digital radiography (DR) machines have their image receptor built into the:
x-ray table
Direct Detector systems
DR systems that use a thin film transistor to detect and display the image. The imaging plate contains selenium and releases electrons when acted on by the x-ray beam
Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS)
computer assisted programs that allow the electronic storage, management, distribution, and viewing of medical images
Why are open gloves or hand shields not recommended for optimal protection?
They don't protect fingers from scatter radiation
What is the primary concern with long-term radiation exposure?
Long-term damage that is not readily apparent (cancer, birth defects, etc)
Bucky tray
the tray within the tabletop used to hold the cassette
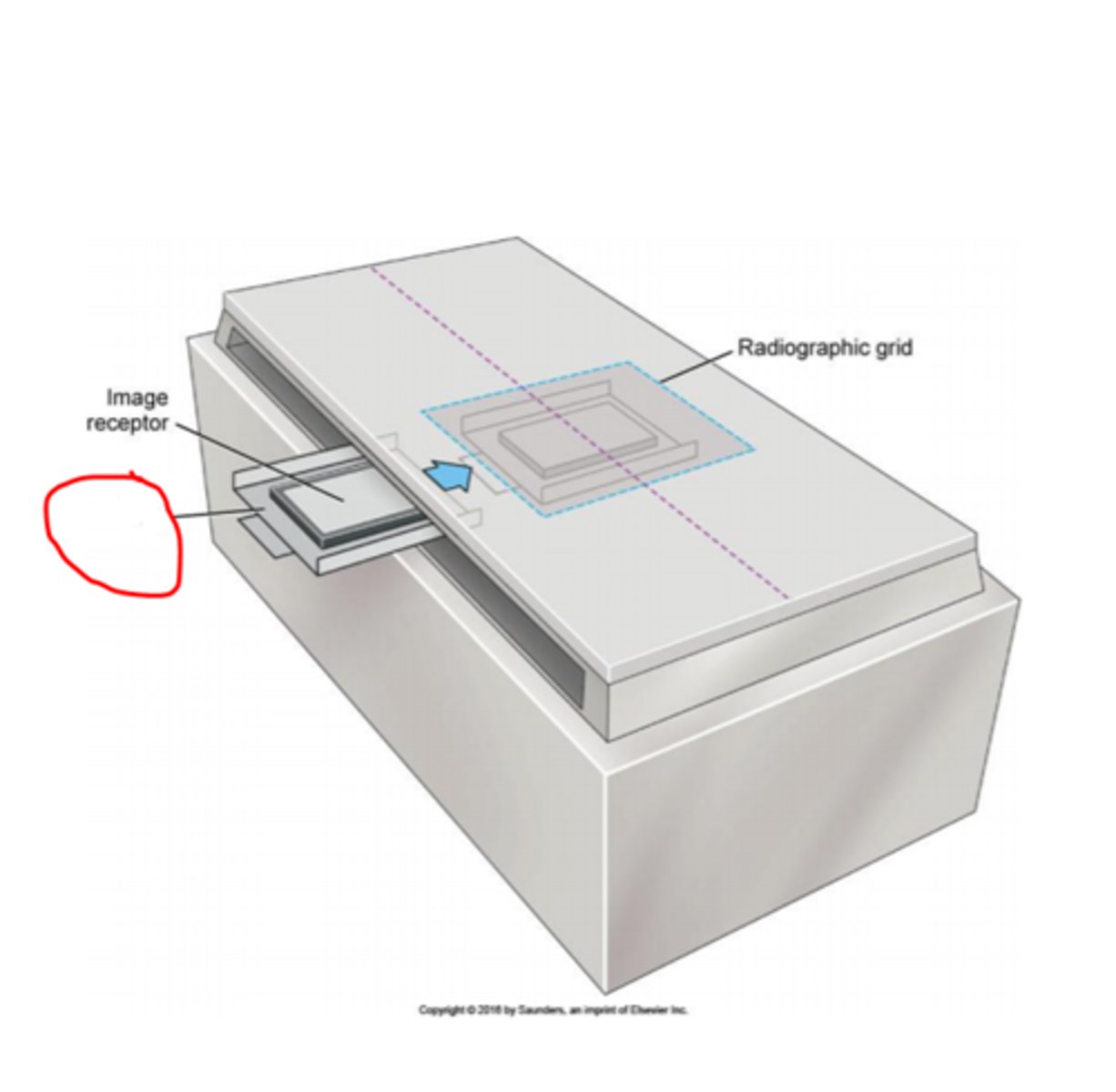
X-rays travel in _________ lines
straight (diverging from a central focus)
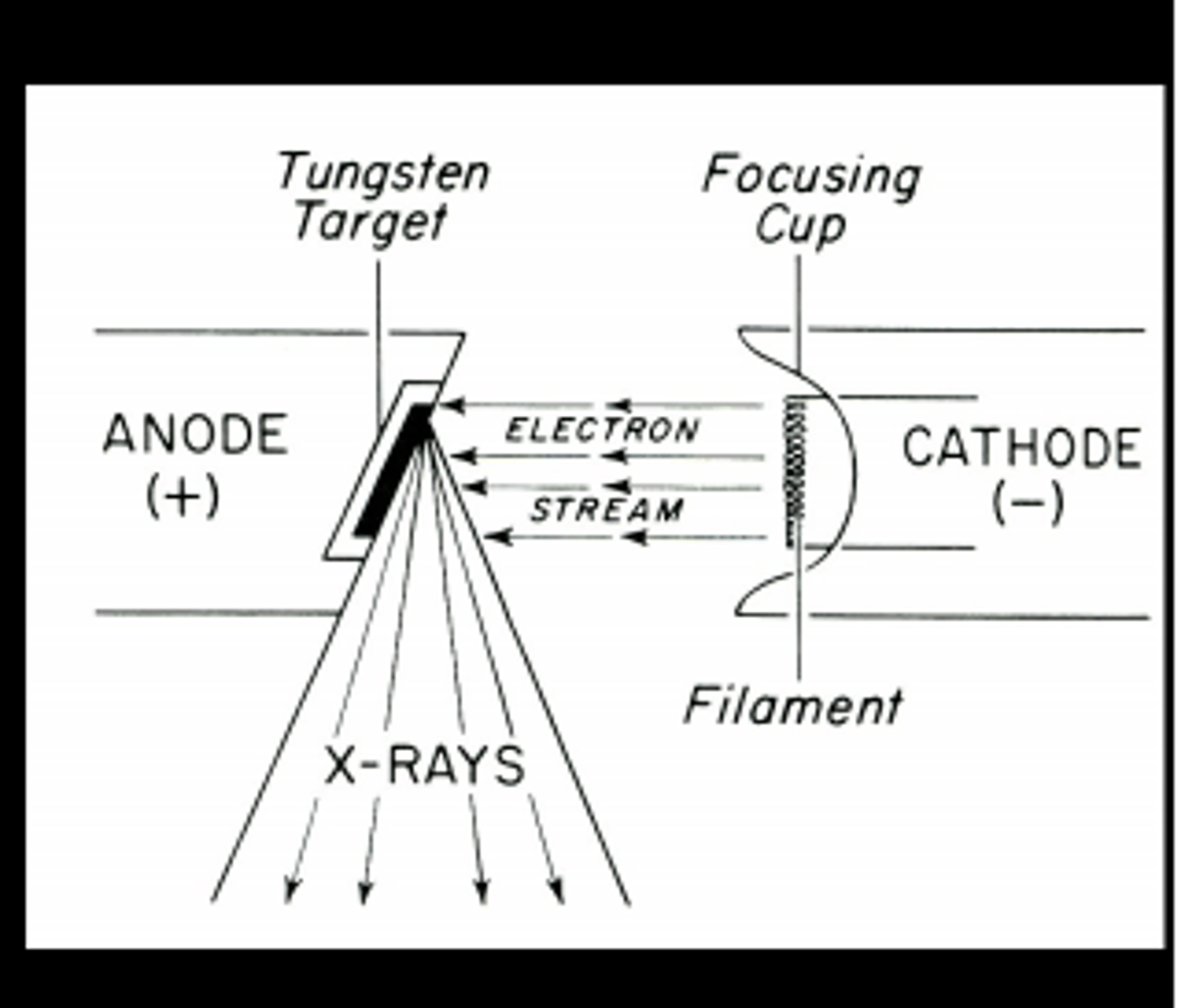
What factor can easily be adjusted to increase the amount of exposure without affecting contrast?
Milliamperage (mA)
What is the biggest factor affecting image detail on a radiograph?
Focal film distance (FFD)
Can DICOM images be viewed on any photo viewer?
No. DICOM based images require a special software to open to deter altering in photoshop, capcut, etc
What component of a digital radiography unit has the biggest influence on image quality?
The monitor
Fogging of the final digital image is caused by
background or scatter radiation
A CR cassette must be processed:
Immediately. Electrons begin to fade away within a few hours- after 8 hrs 25% of the image is lost
What gasses are radiolucent?
air, nitrous oxide, & carbon dioxide
Negative contrast study
Uses radiolucent gases that appear black on the radiograph. Agents of choice are carbon dioxide or nitrous oxide. Using room air as an agent could cause an air embolism
Barium is contraindicated when:
the patient has a chance of GI perforation
Angiography
a radiographic study of the blood vessels after the injection of a contrast medium. Used to dentify cardiac abnormalities, vessel occlusions, lesions, and tumor locations
Arthrography
taking x-ray images after injection of contrast material into a joint. Used to identify ruptured joint capsule, cartilaginous flaps, and meniscal tears
Celiography
Used for examining the abdominal cavity and structure of the diaphragm. Water soluble organic iodide is used as the medium
Pyelogram
x-ray record of the renal pelvis after injection of a contrast medium. Used to identify anatomical issues
Upper GI morphology evaluations should be completed using a ___________ agent
Barium