Health Assessment : Final Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:55 PM on 12/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
infant vs
HR: 100-160
RR: 30-53
BP: 72-104/ 37-56
RR: 30-53
BP: 72-104/ 37-56
2
New cards
toddler vs
HR: 98-140
RR: 22-37
BP: 86-106/ 42-63
RR: 22-37
BP: 86-106/ 42-63
3
New cards
school age vs
HR: 75-118
RR: 18-25
BP: 97-115/ 57-76
RR: 18-25
BP: 97-115/ 57-76
4
New cards
adolescent vs
HR: 60-100
RR: 12-20
BP: 110-131/ 64-83
RR: 12-20
BP: 110-131/ 64-83
5
New cards
adult vs
HR: 60-100
RR: 12-20
BP: 120/80
RR: 12-20
BP: 120/80
6
New cards
objective data
data that can be observed with senses (these are facts)
7
New cards
subjective data
what the patient tells you is happening
8
New cards
signs
what you can observe about the patient (objective)
9
New cards
symptoms
what the patient is telling you they feel (subjective)
10
New cards
When does the general inspection begin and what are the criteria?
Occurs the moment you meet the patient
Observing physical appearance and hygiene, body structure, body movement, emotional status, disposition, and behavior
Observing physical appearance and hygiene, body structure, body movement, emotional status, disposition, and behavior
11
New cards
What is the nursing process?
Assess
Diagnose
Plan
Intervention
Evaluate
Diagnose
Plan
Intervention
Evaluate
12
New cards
skin assessment
Inspect skin
Palpate skin
Inspect + palpate the scalp + hair
Inspect facial + body hair
Inspect + palpate the nails
Palpate skin
Inspect + palpate the scalp + hair
Inspect facial + body hair
Inspect + palpate the nails
13
New cards
cyanosis in light skin
Grayish-blue tone, especially in the nail beds, earlobes, lips, mucous membranes, palms and soles of feet
14
New cards
cyanosis in dark skin
Ashen-gray color most easily seen in the conjunctiva of the eye, oral mucous membranes, and nail beds
15
New cards
jaundice in light skin
Yellowish color of skin, sclera of eyes, fingernails, palms of hands, and oral mucosa
16
New cards
jaundice in dark skin
Yellowish-green color most obviously seen in the sclera of the eye, palms of hands, and soles of feet
17
New cards
pallor in light skin
Pale skin color that may appear white
18
New cards
pallor in dark skin
Skin tone appears light than normal, may have yellowish-brown skin, may have ashen skin, loss of underlying healthy red tones of the skin
19
New cards
stage 1 pressure ulcer
Intact skin with Non blanchable redness, usually over a bony prominence
May be painful, firm, soft, warmer/cooler compared to adjacent tissue
May be difficult to detect in individuals with dark skin tones
May be painful, firm, soft, warmer/cooler compared to adjacent tissue
May be difficult to detect in individuals with dark skin tones
20
New cards
stage 2 pressure ulcer
Partial thickness loss of dermis
Presents as a shiny/dry shallow open ulcer with pink wound bed without slough or bruising
May also present as an intact or open/ruptured serum-filled blister
Presents as a shiny/dry shallow open ulcer with pink wound bed without slough or bruising
May also present as an intact or open/ruptured serum-filled blister
21
New cards
stage 3 pressure ulcer
Full thickness skin loss involving damage/necrosis of subcutaneous tissue
Subcutaneous mau be visible, but bone, tendon, or muscle are not exposed
Slough may be present, wound may include undermining and tunneling
Subcutaneous mau be visible, but bone, tendon, or muscle are not exposed
Slough may be present, wound may include undermining and tunneling
22
New cards
stage 4 pressure ulcer
Full-thickness tissue loss with exposed bone, tendon, or muscle
Slough or eschar may be present within the wound bed
Undermining and tunneling present
Slough or eschar may be present within the wound bed
Undermining and tunneling present
23
New cards
who is at risk for pressure ulcers
People in the hospital → immobilized patients
24
New cards
What scale do we use to evaluate suspicious nevi and what does it stand for?
Asymmetry
Boarder
Color
Diameter
Evolving
Boarder
Color
Diameter
Evolving
25
New cards
What measurement tool is a national standard for pressure ulcers
braden scale
26
New cards
cardio assessment
General Appearance
Inspect for general appearance, skin color, and breathing effort
Heart
Inspect the anterior chest wall
Palpate the apical pulse
Auscultate the apical pulse
Auscultate the heart (listen for S1, S2, and, Murmurs)
Palpate temporal and carotid pulses
Inspect the jugular veins
Measure the blood pressure
Inspect the upper and lower extremities
Palpate the upper and lower extremities
Palpate the upper and lower extremity pulses
Check capillary refill on fingers and toes
Assess for edema in lower extremities
Inspect for general appearance, skin color, and breathing effort
Heart
Inspect the anterior chest wall
Palpate the apical pulse
Auscultate the apical pulse
Auscultate the heart (listen for S1, S2, and, Murmurs)
Palpate temporal and carotid pulses
Inspect the jugular veins
Measure the blood pressure
Inspect the upper and lower extremities
Palpate the upper and lower extremities
Palpate the upper and lower extremity pulses
Check capillary refill on fingers and toes
Assess for edema in lower extremities
27
New cards
What do I need to document regarding the pulse to provide all the information?
Rate, rhythm, amplitude, and contour
28
New cards
Why do we check Capillary Refill, how is it recorded in the EMR? What is an expected finding?
Indicates the level of perfusion
Cap refill < 3 seconds
Should be less than 3 seconds
Cap refill < 3 seconds
Should be less than 3 seconds
29
New cards
How is edema assessed?
Firm press on upper and lower extremities to make an indentation → skin should not make an indent
\
__**Grades 1-4 (0-4+)**__
*Grade 0:* No clinical edema
*Grade 1:* Immediate rebound, with 2mm pit
*Grade 2:* Less than 15 seconds rebound with 3-4mm pit
*Grade 3:* Rebound greater than 15 seconds but less than 60 seconds with 5-6mm pit
*Grade 4:* Rebound between 2 to 3 minutes with 8mm pit
\
__**Grades 1-4 (0-4+)**__
*Grade 0:* No clinical edema
*Grade 1:* Immediate rebound, with 2mm pit
*Grade 2:* Less than 15 seconds rebound with 3-4mm pit
*Grade 3:* Rebound greater than 15 seconds but less than 60 seconds with 5-6mm pit
*Grade 4:* Rebound between 2 to 3 minutes with 8mm pit
30
New cards
S1
Systole
Ventricle CONTRACT
Lubb
mitral/tricuspid (atrioventricular)
31
New cards
S2
Diastole
Ventricles RELAX & FILL
Dubb
aortic/pulmonic valves (semilunar)
Ventricles RELAX & FILL
Dubb
aortic/pulmonic valves (semilunar)
32
New cards
Why do we listen to all the heart tones?
Could indicate what valves are working properly and correctly → could reveal a murmur in certain locations
33
New cards
What are we listening for when using the bell?
Murmurs
34
New cards
What is heart failure often a result of?
High blood pressure/hypertension
35
New cards
What are the symptoms of heart failure?
Left sided: Fatigue, shortness of breath, orthopnea, dyspnea on exertion, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
May reveal displaced apical pulse and palpable thrill
S3 heart sound heard → systolic murmur at apex
Crackles bilaterally
Right sided: Dependent peripheral edema
S3 heart sound heard at LLSB
Systolic murmur
Weight gain
May reveal displaced apical pulse and palpable thrill
S3 heart sound heard → systolic murmur at apex
Crackles bilaterally
Right sided: Dependent peripheral edema
S3 heart sound heard at LLSB
Systolic murmur
Weight gain
36
New cards
What are the symptoms of MI?
Worst chest pain ever
Pain that lasts longer than 5 minutes
Radiate to left shoulder, jaw, arm, or other areas of the chest that is not relieved by rest or nitroglycerin
Dysrhythmias are common
Heart sounds may be distant with a thready pulse
Pain that lasts longer than 5 minutes
Radiate to left shoulder, jaw, arm, or other areas of the chest that is not relieved by rest or nitroglycerin
Dysrhythmias are common
Heart sounds may be distant with a thready pulse
37
New cards
respiratory assessment
Inspect patient’s appearance, posture, and breathing effort
Count respirations and observe breathing patterns and chest expansion
Inspect patient’s nails, skin, and lips
Inspect posterior and anterior thorax
Auscultate posterior, lateral, and anterior thorax
Count respirations and observe breathing patterns and chest expansion
Inspect patient’s nails, skin, and lips
Inspect posterior and anterior thorax
Auscultate posterior, lateral, and anterior thorax
38
New cards
What do we do for a patient that has secretions in the upper airway?
Treat with medication
39
New cards
What muscles are used to breathe?
Diaphragm and intercostals
40
New cards
How do you document expected lung sounds? What do they sound like?
Breath sounds clear, with vesicular breath sounds heard over most lung fields
41
New cards
What does asthma sound like?
Audible wheeze and occasionally diminished breath sounds
42
New cards
What sounds are heard when there is fluid or consolidation in thelungs?
Crackles or wheezes
43
New cards
What is a pneumothorax? What can cause one?
Air in the pleural space
Three types:
Closed: May be spontaneous, traumatic, or iatrogenic (caused by illness or medical treatment)
Open: Following penetration of the chest
Tension: Develops when air leaks into the pleura and cannot escape (resp. emergency)
Three types:
Closed: May be spontaneous, traumatic, or iatrogenic (caused by illness or medical treatment)
Open: Following penetration of the chest
Tension: Develops when air leaks into the pleura and cannot escape (resp. emergency)
44
New cards
pulmonary edema
Condition caused by too much fluid in the lungs → collects in the air sacs of the lungs and make it difficult to breathe
45
New cards
COPD
Something that is blocking the airway
Breathing difficulty, cough, mucous productions, frequent respiratory infections
Swelling in ankles, feet, or legs
Coarse crackles
46
New cards
emphysema
Destruction of the alveolar walls that causes permanent enlargement of the air spaces
Underweight individual with barrel chest that becomes SOB with little exertion
Pursed-lip breathing and tripod position
Diminished breath sounds, possible wheeze and crackles
47
New cards
chronic bronchitis
Hypersecretion of mucous by the goblet cells of the trachea and bronchi → results in productive cough for 3 months in each of 2 successive years
Productive cough, increased mucous production, and dyspnea
Rhonchi, sometimes cleared by coughing
Cyanosis and clubbing
48
New cards
asthma
Hyperreactive airway that is characterized by bronchoconstriction, airway obstruction, and inflammation
Dyspnea and tightness of chest
Tachycardia, tachypnea with prolonged expiration, audible wheeze, use of accessory muscles, and cough
Inspiratory wheeze and diminished breath sounds
49
New cards
What is a common complication for elderly, immobile adults in the hospital?
DVT
50
New cards
abdominal assessment
Observe patient’s general appearance, behavior, and position
Inspect the abdomen
Auscultate the abdomen
Palpate the abdomen lightly
Palpate the abdomen deeply
Inspect the abdomen
Auscultate the abdomen
Palpate the abdomen lightly
Palpate the abdomen deeply
51
New cards
What are the main functions of digestive system?
Digestion/Ingestion
Secretion
Absorption
Excretion
Secretion
Absorption
Excretion
52
New cards
Ulcerative Colitis
Unpredictable periods of remission with relapses
Severe, constant abdominal pain
Fever during acute attacks and rectal bleeding
Profuse watery diarrhea with blood, mucous, and pus
Severe, constant abdominal pain
Fever during acute attacks and rectal bleeding
Profuse watery diarrhea with blood, mucous, and pus
53
New cards
UTI
Dysuria, frequency (more than every 2 hours), urgency, and suprapubic pain
Urine may contain blood or sediment
Older adults → nonlocalized abdominal discomfort and may have cognitive impairment
Urine may contain blood or sediment
Older adults → nonlocalized abdominal discomfort and may have cognitive impairment
54
New cards
Diverticulitis
Complain of pain in the LLQ
Nausea, vomiting, and altered bowel habits (constipation)
Fever, decreased bowel sounds with LLQ pain on palpation
Nausea, vomiting, and altered bowel habits (constipation)
Fever, decreased bowel sounds with LLQ pain on palpation
55
New cards
What is the dysfunction in pancreatitis? What are the causes? Clinical presentations?
Dysfunction: Inflammation of the pancreas
Causes: Alcoholism and cholelithiasis
Clinical Presentation:
-Sudden onset of severe pain, describes as steady, boring, dull, or sharp, that radiates to the back
-Becomes worse with food
-Preferred position is knee-chest
-Nausea, vomiting
-Fever, tachycardia, hypotension
-Ascites, jaundice, decreased/absent bowel sounds, abdominal tenderness
Causes: Alcoholism and cholelithiasis
Clinical Presentation:
-Sudden onset of severe pain, describes as steady, boring, dull, or sharp, that radiates to the back
-Becomes worse with food
-Preferred position is knee-chest
-Nausea, vomiting
-Fever, tachycardia, hypotension
-Ascites, jaundice, decreased/absent bowel sounds, abdominal tenderness
56
New cards
GERD
Gastric secretions that become chronic and go back up into the esophagus
57
New cards
Peptic Ulcers
Break in the duodenal mucosa lining that heals and scars to create ulcers
58
New cards
What are some modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors with Colon Cancer?
Modifiable:
\-Diet
\-Physical activity
\-Weight
\-Smoking
\-Alcohol use
Non-modifiable:
\-Age
\-Family history
\-Inherited
\-Diet
\-Physical activity
\-Weight
\-Smoking
\-Alcohol use
Non-modifiable:
\-Age
\-Family history
\-Inherited
59
New cards
musculoskeletal assessment
Inspect skeleton and extremities
Palpate the muscles
Palpate bones and joints
Assess range of motion of each joint
Assess muscle tone
Assess muscle strength and compare sides
Palpate the muscles
Palpate bones and joints
Assess range of motion of each joint
Assess muscle tone
Assess muscle strength and compare sides
60
New cards
What are the presenting symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Bilateral joint involvement
Pain, edema, and stiffness of the fingers, wrists, ankles, feet, and knees
Pain and stiffness after awakening in the morning that lasts more than 30 minutes
Causes by autoimmune response → fever and fatigue
Pain, edema, and stiffness of the fingers, wrists, ankles, feet, and knees
Pain and stiffness after awakening in the morning that lasts more than 30 minutes
Causes by autoimmune response → fever and fatigue
61
New cards
risk factors for osteoporosis
Age > 50 years old
Women
Caucasian and Asian
Small-boned thin women
Long-term asteroid users
Women
Caucasian and Asian
Small-boned thin women
Long-term asteroid users
62
New cards
risk factors for osteoarthritis
An increased risk with age
Women > 50
Obesity
Joint injury in their history
Genetics
Women > 50
Obesity
Joint injury in their history
Genetics
63
New cards
How do we grade and document muscle strengths?
No evidence of contractility: 0
Evidence of contractility: 1
Complete ROM with gravity eliminated: 2
Complete ROM with gravity: 3
Complete ROM against gravity with some resistance: 4
Complete ROM against gravity with full resistance: 5
64
New cards
Define Substance dependence.
When a person uses alcohol or other drugs despite extreme negative consequences such as impairment to their daily lives
65
New cards
What differentiates delirium and dementia?
Delirium:
-Altered level of consciousness
-Usually comes from infection
-Temporary
-Impaired memory
-Manifestations
Dementia:
-Onset occurs slowly over years
-Irreversible memory, judgment, and calculation are impaired
-Flat affect, speech is slow and incoherent
-Altered level of consciousness
-Usually comes from infection
-Temporary
-Impaired memory
-Manifestations
Dementia:
-Onset occurs slowly over years
-Irreversible memory, judgment, and calculation are impaired
-Flat affect, speech is slow and incoherent
66
New cards
How is PTSD diagnosed?
At least one re-experiencing symptom: Flashbacks, bad dreams, or frightening thoughts
At least one avoidance symptom: Staying away from places, events, or objects that are reminders of the experience or avoiding thoughts or feelings related to the traumatic event
At least two arousal and reactivity symptoms: Being easily startled, feeling tense or “on edge,” having difficulty sleeping, and/or having angry outbursts
At least two cognitive and mood symptoms: Trouble remembering key features of the traumatic event, negative thoughts about oneself or the world, distorted feelings such as guilt or blame; loss of interest in enjoyable activities
At least one avoidance symptom: Staying away from places, events, or objects that are reminders of the experience or avoiding thoughts or feelings related to the traumatic event
At least two arousal and reactivity symptoms: Being easily startled, feeling tense or “on edge,” having difficulty sleeping, and/or having angry outbursts
At least two cognitive and mood symptoms: Trouble remembering key features of the traumatic event, negative thoughts about oneself or the world, distorted feelings such as guilt or blame; loss of interest in enjoyable activities
67
New cards
What are the symptoms of major depressive illness?
Loss of interest or pleasure for at least 2 weeks and have at least 5 of the following:
-Depressed mood most of the day
-Markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all or almost all activities of the day
-Significant weight loss when not dieting or weight gain or decrease or increase in appetite
-Psychomotor agitation or retardation
-Fatigue or loss of energy
-Feelings of worthlessness or excessive or inappropriate guilt
-Diminished ability to think or concentrate or indecisiveness
-Recurrent thoughts of death, recurrent suicidal ideation without a specific plan
-Suicide attempt or a specific plan for committing suicide
-Depressed mood most of the day
-Markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all or almost all activities of the day
-Significant weight loss when not dieting or weight gain or decrease or increase in appetite
-Psychomotor agitation or retardation
-Fatigue or loss of energy
-Feelings of worthlessness or excessive or inappropriate guilt
-Diminished ability to think or concentrate or indecisiveness
-Recurrent thoughts of death, recurrent suicidal ideation without a specific plan
-Suicide attempt or a specific plan for committing suicide
68
New cards
HEENT assessment
Head:
-Inspect head
-Inspect facial features
Eyes:
-Test visual acuity
-Assess visual fields for peripheral vision
-Inspect ocular structures
-Inspect the corneal light reflex
-Inspect each sclera
-Inspect each cornea transparency and surface characteristics of each eye
-Inspect each iris
-Inspect the pupils
Ears:
-Assess hearing
-Inspect the external ears
-Inspect each external auditory meatus
Nose:
-Inspect the external nose
Mouth:
-Inspect the lips
-Inspect the teeth and gums
-Inspect the tongue
-Inspect the buccal mucosa and anterior and posterior pillars
-Inspect the palate, uvula, posterior pharynx, and tonsils
Neck:
-Inspect the neck
-Assess the range of motion
-Assess neck muscle strength
-Inspect head
-Inspect facial features
Eyes:
-Test visual acuity
-Assess visual fields for peripheral vision
-Inspect ocular structures
-Inspect the corneal light reflex
-Inspect each sclera
-Inspect each cornea transparency and surface characteristics of each eye
-Inspect each iris
-Inspect the pupils
Ears:
-Assess hearing
-Inspect the external ears
-Inspect each external auditory meatus
Nose:
-Inspect the external nose
Mouth:
-Inspect the lips
-Inspect the teeth and gums
-Inspect the tongue
-Inspect the buccal mucosa and anterior and posterior pillars
-Inspect the palate, uvula, posterior pharynx, and tonsils
Neck:
-Inspect the neck
-Assess the range of motion
-Assess neck muscle strength
69
New cards
What are the characteristics of down’s syndrome?
Low-set ears or ears that are misaligned are abnormal
Enlargement of the tongue or hypothyroidism
Enlargement of the tongue or hypothyroidism
70
New cards
When checking for drainage from the nose and ears following a head injury, what are we looking for and why?
Look for the description of discharge (color, consistency, odor)
thick/purulent green-yellow, malodorous discharge → bacterial infection
Foul-smelling discharge (unilateral) → foreign body or chronic sinus
Bloody discharge → neoplasm, trauma, or opportunistic infection (fungal disease)
Epistaxis → occurs secondary to trauma, chronic sinusitis, malignancy, or a bleeding disorder (also from cocaine use)
Look for other symptoms
Related symptoms may be consistent with allergic rhinitis → itching, swelling, discharge from eyes, postnasal drip, and cough
Symptoms related to infection → fatigue, fever, and pain
Asking what they have done to treat the discharge/bleeding
If the patient used nasal spray other than normal saline → should only be used for 3-5 days to avoid causing rebound congestion
thick/purulent green-yellow, malodorous discharge → bacterial infection
Foul-smelling discharge (unilateral) → foreign body or chronic sinus
Bloody discharge → neoplasm, trauma, or opportunistic infection (fungal disease)
Epistaxis → occurs secondary to trauma, chronic sinusitis, malignancy, or a bleeding disorder (also from cocaine use)
Look for other symptoms
Related symptoms may be consistent with allergic rhinitis → itching, swelling, discharge from eyes, postnasal drip, and cough
Symptoms related to infection → fatigue, fever, and pain
Asking what they have done to treat the discharge/bleeding
If the patient used nasal spray other than normal saline → should only be used for 3-5 days to avoid causing rebound congestion
71
New cards
What can cause a foul odor in the nares or ears?
Obstruction in the ear/nose
72
New cards
Dizziness
Symptom used by many patients to describe a wide range of sensations, including fairness, light-headedness, feeling as if their head is spinning, or the inability to maintain a normal balance in standing/seated position
73
New cards
Vertigo
The sensation of movement or spinning, the cardinal symptom of the inner ear system → controls balance identifies spatial orientation)
74
New cards
Light-headed
A vague description of dizziness that does not fit specific classifications
75
New cards
Pre-syncope
The feeling of faintness and the impending loss of consciousness → often a cardiovascular problem
Ex: patient falls postpartum on the way to the bathroom (BP probably dropped on her way)
Ex: patient falls postpartum on the way to the bathroom (BP probably dropped on her way)
76
New cards
What are the different types of hearing loss?
Conductive:
-Sudden, onset
-If there is a mechanical blockage or damage
Sensorineural:
-Permanent, nonreversible, progressive
-Causes deafness
-Occurs with age
-Caused by consistent, loud noises
-Sudden, onset
-If there is a mechanical blockage or damage
Sensorineural:
-Permanent, nonreversible, progressive
-Causes deafness
-Occurs with age
-Caused by consistent, loud noises
77
New cards
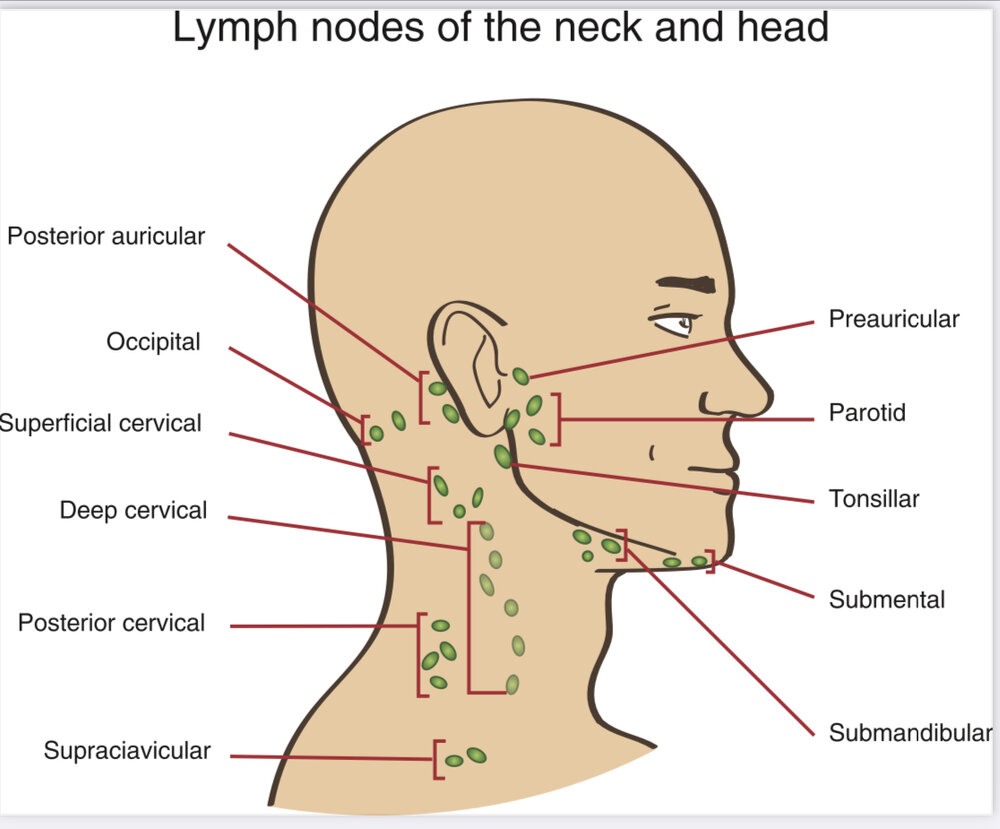
When checking lymph nodes in the head, what are we checking for?
Palpable, soft, mobile, non-tender, and bilaterally equal in size
78
New cards
What does it mean if lymph nodes are swollen, tender, or movable? What if they are painless and fixed?
Could be an infection in the head if swollen, tender, or movable
If they are painless and fixed could mean malignancy
If they are painless and fixed could mean malignancy
79
New cards
Know the lymph nodes we went over in class and their locations.
Preauricular
Postauricular
Occipital
Parotid
Tonsillar
Submandibular
Submental
Postauricular
Occipital
Parotid
Tonsillar
Submandibular
Submental
80
New cards
Who is at the greatest risk for oral cancer? How is this assessed?
Tobacco use (M)
Alcohol use (M)
Older than 55 → increased risk between ages 64 and 74
2:1 male to female incidence
HPV in mouth
Exposure to UV → increased risk for lip cancers (M)
Immunosuppression
Alcohol use (M)
Older than 55 → increased risk between ages 64 and 74
2:1 male to female incidence
HPV in mouth
Exposure to UV → increased risk for lip cancers (M)
Immunosuppression
81
New cards
Upon assessment of a patient with seasonal allergies, what would the nurse expect?
Sneezing, nasal congestion, and nasal drainage
Itchy eyes, cough, and fatigue → turbinate's are often enlarged and may appear pale or darker red
Itchy eyes, cough, and fatigue → turbinate's are often enlarged and may appear pale or darker red
82
New cards
Define an eye emergency
Sudden onset of visual symptoms → could indicate detached retina (requires emergency referral)
83
New cards
Ptosis
Drooping of the eye, seen in older adults, dry eye, drainage when waking up
84
New cards
Exophthalmos
Graves' disease symptom → can see the sclera all the way around
85
New cards
Strabismus
Cross eyes (fix by the age of 8)
86
New cards
Glaucoma (inner eye)
Pressure behind the eyes, treatable with eye drops, incurable
87
New cards
Cataracts (inner eye)
Film on the lens, gets worse, can be treated (but not entirely)
88
New cards
Diabetic retinopathy (inner eye)
Uncontrolled hypercalcemia
89
New cards
Conjunctivitis (external eye)
Conjunctiva is inflamed or infected
90
New cards
Corneal abrasion or ulcer (external eye)
Caused by a foreign body in the eye, wearing contacts for long periods of time (not changed, sleeping in them), heals pretty quickly with drops
91
New cards
What can cause a perforated septum?
The most common cause is cocaine use
92
New cards
Why is it concerning if a patients tonsils are swollen and almost meet in the middle?
Means that they are obstructing the airway and do not have a good passageway
93
New cards
neuro assessment
Assess mental status and level of consciousness
Assess speech
Notice cranial nerve functions
Observe gait
Assess extremities for muscle strength and tone
Assess speech
Notice cranial nerve functions
Observe gait
Assess extremities for muscle strength and tone
94
New cards
What are the presenting symptoms of meningitis?
Headache, fever, nuchal rigidity → diagnosis through a spinal tap
95
New cards
What are the presenting symptoms of Encephalitis?
Confusion, fever, vomiting
96
New cards
frontal lobe
responsible for personality, controls emotions, sense of self (space), Broca’s area
Primary motor cortex → voluntary motor activity
Primary motor cortex → voluntary motor activity
97
New cards
temporal lobe
auditory, receive messages, Wernicke’s area
Comprehension of spoken and written language
Thought and memory
Comprehension of spoken and written language
Thought and memory
98
New cards
occipital lobe
sensory (position, sense, touch, shape, and texture of objects)
99
New cards
parietal lobe
vision
Receiving and interpreting visual information
Receiving and interpreting visual information
100
New cards
What is the earliest and most sensitive way neurological functioning is assessed?
Determining how alert and oriented the patient is based on admission