AP Psychology: Topic 5.3 - Explaining and Classifying Psychological Disorders
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Dysfunction
a breakdown in a person's cognition, emotion, or behavior that indicates a significant issue with their psychological processes

Distress
a state of emotional suffering characterized by depression (e.g., loss of interest; unhappiness; desperateness) and anxiety (e.g., restlessness; feeling tense)

Deviation from the social norm
behavior significantly differing from societal expectations (cultures vary, so a universal set of social rules cannot be established)

Cultural/societal norms
shared beliefs, values, and behaviors that are expected of a society's members

Stigma
a negative social attitude towards a person's characteristic that is considered a physical, mental, or social deficiency
Racism
when a person or group is mistreated, disadvantaged, harassed, or degraded because of their ethnicity
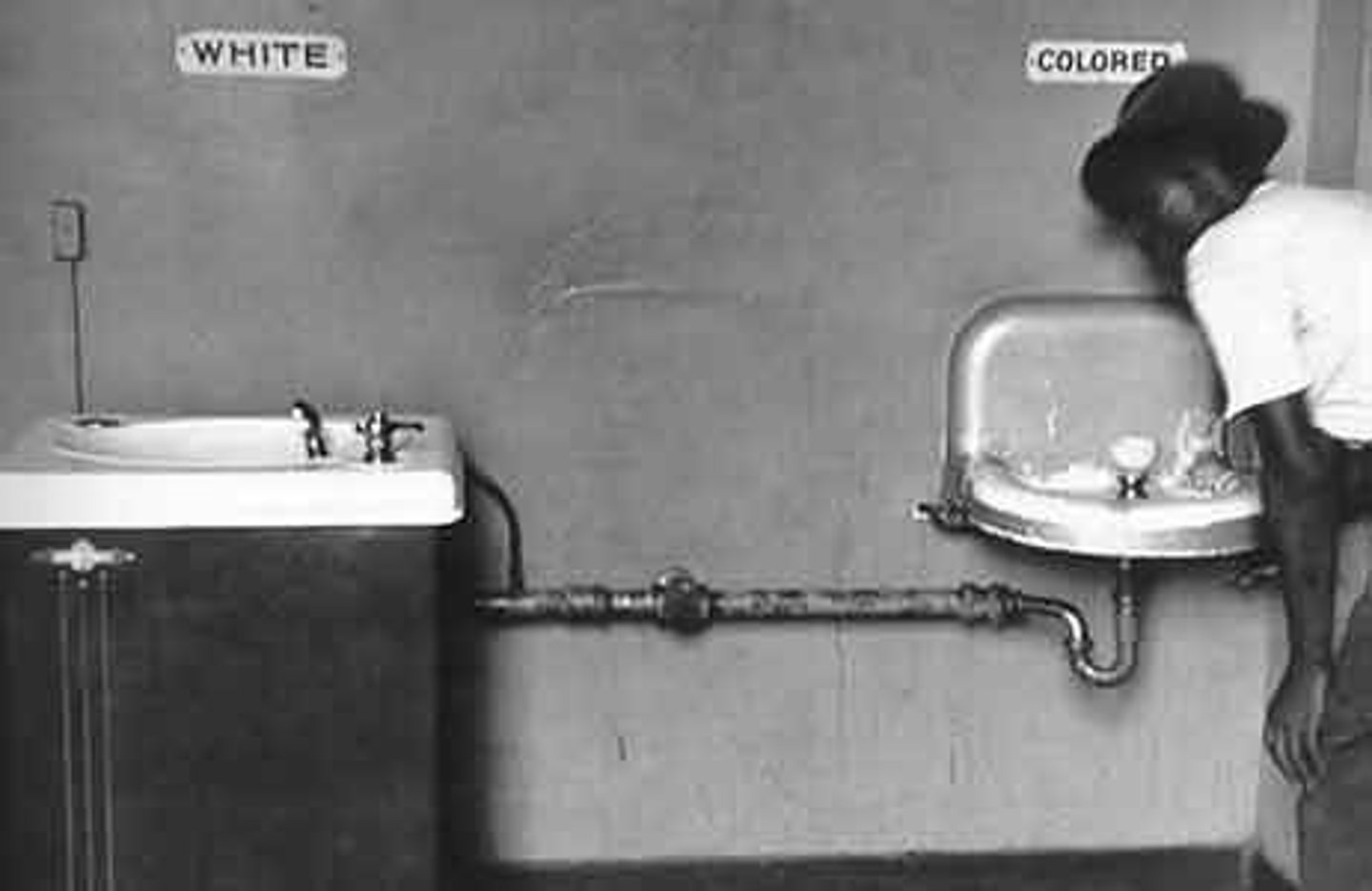

Sexism
beliefs and behaviors that negatively evaluate people based on their gender, or that support unequal status between men and women

Ageism
prejudice, discrimination, or stereotyping of people based on their age

Discrimination
unjustifiable negative behavior toward a group and its members

Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)
a reference book that provides a standardized guide for diagnosing mental health disorders

International Classification of Mental Disorders (ICD)
a global system published by the World Health Organization for classifying mental and physical health conditions, including mental and behavioral disorders

Eclectic approach
an approach to psychotherapy that uses techniques from various forms of therapy that are tailored to a patient's needs

Behavioral perspective
proposes that the causes of mental disorders focus on maladaptive learned associations between or among responses to stimuli

Maladaptive learned associations
abnormal behaviors or cognitive processes that are a result of learning and go against social norms (e.g., post-traumatic stress disorder)

Psychodynamic perspective
proposes that the causes of mental disorders focus on unconscious thoughts and experiences, often developed during childhood
Humanistic perspective
proposes that the causes of mental disorders focus on a lack of social support and being unable to fulfill one's potential
Cognitive perspective
proposes that the causes of mental disorders focus on maladaptive thoughts, beliefs, attitudes, or emotions

Evolutionary perspective
proposes that the causes of mental disorders focus on behaviors and mental processes that reduce the likelihood of survival

Sociocultural perspective
proposes that the causes of mental disorders focus on maladaptive social and cultural relationships and dynamics

Biological perspective
proposes that the causes of mental disorders focus on physiological or genetic issues
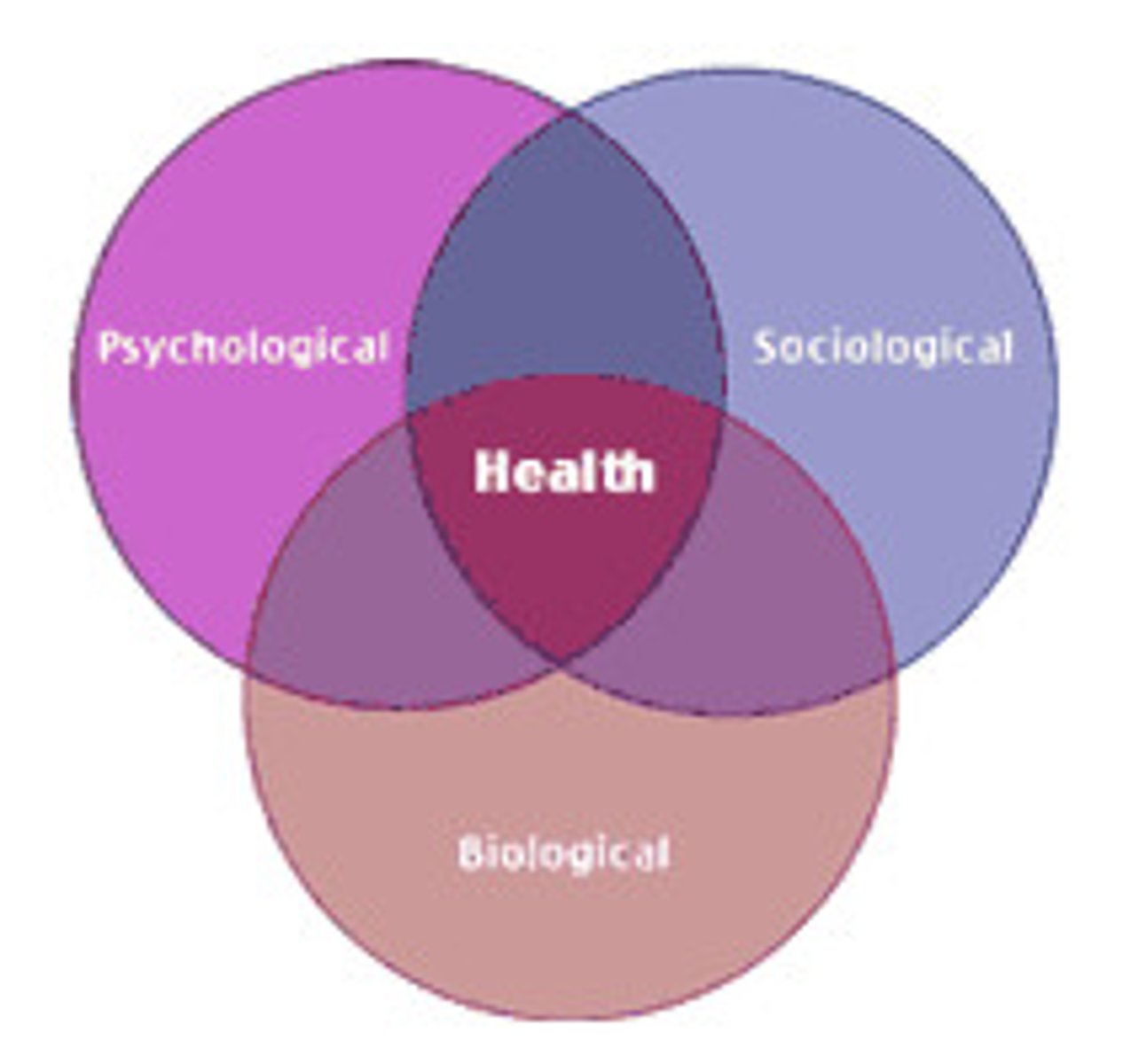
Biopsychosocial model
assumes that any psychological problem potentially involves a combination of biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors
Diathesis-stress model
assumes that psychological disorders develop due to a genetic vulnerability (diathesis) in combination with stressful life experiences (stress)